Cool Nikon D5500a takes stunning photos of the cosmos
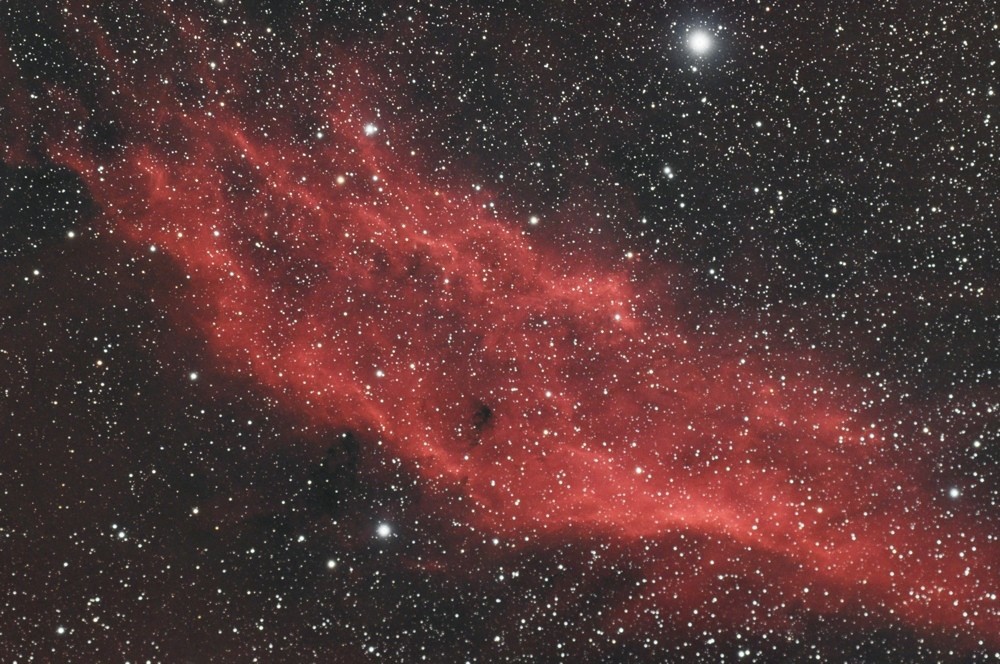

California Nebula (NGC1499), shot by amateur photographer Filippo Bradashia on a cooled D5500a camera with an AIRY ED100 apochromatic refractor
Italian astrophotography equipment manufacturer PrimaLuceLab has released an interesting modification of the Nikon D5500a camera specifically for astrophotography. The modification is adapted for long exposures and uses a custom-made cooling system for the CCD sensor. The most serious astrophotographers have always cooled their sensors, and now, astrophotography of fantastic beauty has become easier and more accessible.
The camera superbly shoots stars, nebulae, the moon and the planets of the solar system. Together with the refractor, it can be used without a computer.

')
Sensor cooling is performed by two Peltier elements - thermoelectric transducers, the principle of action of which is based on the Peltier effect - the occurrence of a temperature difference during the flow of electric current. The temperature difference arises due to the absorption of heat during the passage of electric current at the point of contact of two dissimilar semiconductors with different levels of electron energy in the conduction band. When current flows through the contact of such materials, the electron must acquire energy in order to move to a higher-energy conduction band of another semiconductor. When this energy is absorbed, the point of contact of the semiconductors is cooled.
The Peltier elements for Nikon D5500a Cooled use semiconductors, which, under voltage, create a temperature difference of up to 27 ° C (49 ° F). That is, the CCD sensor will be 27 degrees colder than the surrounding air. The minimum sensor temperature is -27 ° C.

Sensor cooling is critically important when shooting with a long shutter speed, because the cold sensor has much less noticeable background noise, which is created directly by electrons on an analog CCD chip consisting of photosensitive photodiodes.
It is also important that the cooling system maintains a constant predetermined matrix temperature throughout the entire shooting, so dark noise master frames (dark frames) need not be recorded after each shot of the object. They can be recorded at any time.
This is what a dark frame at 6400 ISO looks like with the cooling system turned on (left) at a sensor temperature of -2 ° C, and with the cooling system turned off (right) at a sensor temperature of 20 ° C. As they say, the difference is obvious.

The specialized Nikon D5500a Cooled model is also equipped with a special system that prevents the formation of water condensate on the surface of the cooled sensor. The Anti-Dewing system heats only the front filter above the sensor, but not the CCD itself. The presence of a relatively warm surface in the path of air does not allow moisture to condense.
The external touchscreen with a diagonal of 3.2 "displays the current temperature of the sensor, the target temperature and the time after which it will be reached. It also shows the relative power of the cooling system (from 1 to 5), the speed of rotation of the cooler (without vibration, probably on magnetic bearings) and the intensity of the Anti-Dewing system on the front filter.
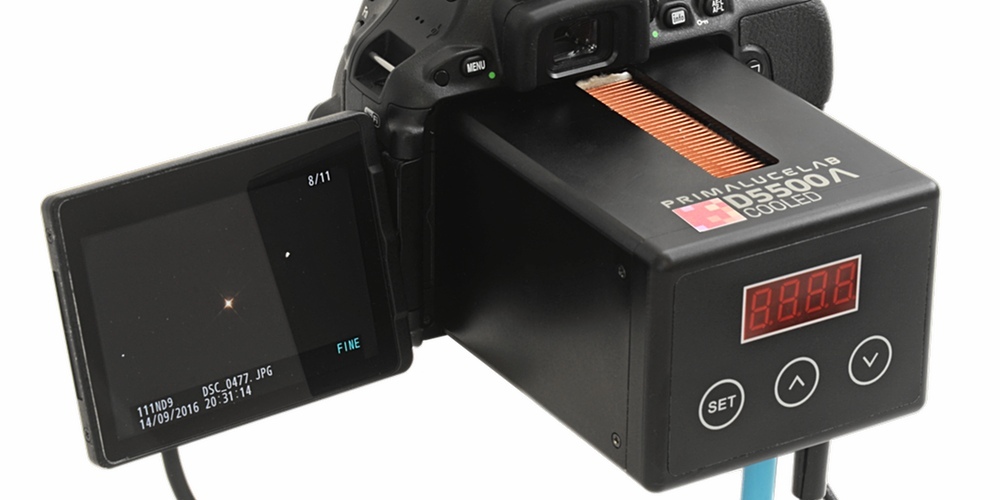

The control buttons on the back of the cooling unit allow you to set its operation parameters and select the cooling power.
For astrophotography, some other improvements have been made to the camera. For example, the infrared cut-off filter from the camera is removed. This filter is inserted into ordinary cameras so that they do not distort the white balance under normal daylight. The natural white balance is of no use to us, but the infrared range is just very necessary.
Instead of the IR cut-off filter, a filter is installed that transmits waves with a longer wavelength than the visible red color (0.64-0.77 μm), that is, in the IR range. The filter is specifically designed to capture the light behind the H-alpha spectral line (656.28 nm), which corresponds to the transition of a hydrogen electron from the third to the second energy level. This spectral line is important for astronomers, because the transition of an electron in hydrogen from the third to the second level occurs everywhere in the Universe. Including in this spectrum, many emission nebulae glow - beautiful clouds of ionized gas.

Four visible spectral emission lines of hydrogen in the Balmer series . Far red line - H-alpha
The following graph shows which range is recorded by the D5550 with the original filter, and which is recorded by the modderskaya version for astrophotography. The graph shows the spectral line H-alpha.

Probably, the trick with the special recording of light behind the H-alpha spectral line was borrowed from another astro camera D810a - the first specialized full-length Nikon camera for astronomers. The Japanese company released the model independently for $ 3,799, but the Italian modders refined the cheaper Nikon D5500a ($ 2,420). In many functions, it is not inferior to the factory D810a. However, the size of the sensor is slightly smaller: 23.5 × 15.6 mm instead of full frame 36 × 24 mm. She also knows how to make shots with a maximum shutter speed of 900 seconds (15 minutes) and make an interval shooting, recording sequences of frames with different shutter speeds. The maximum number of frames in a sequential shooting is 50. For example, you can program the camera to shoot 20 frames with a shutter speed of 300 s and then 10 frames with a shutter speed of 900 s.
If required, the Nikon D5500a can shoot all night offline. In the morning you will wake up and check whether the SpaceX rocket has flown in the frame . In case of long battery life, both the camera and the cooling system can be powered from a single 12V 3A power supply, that is, from a standard network adapter, like a laptop.
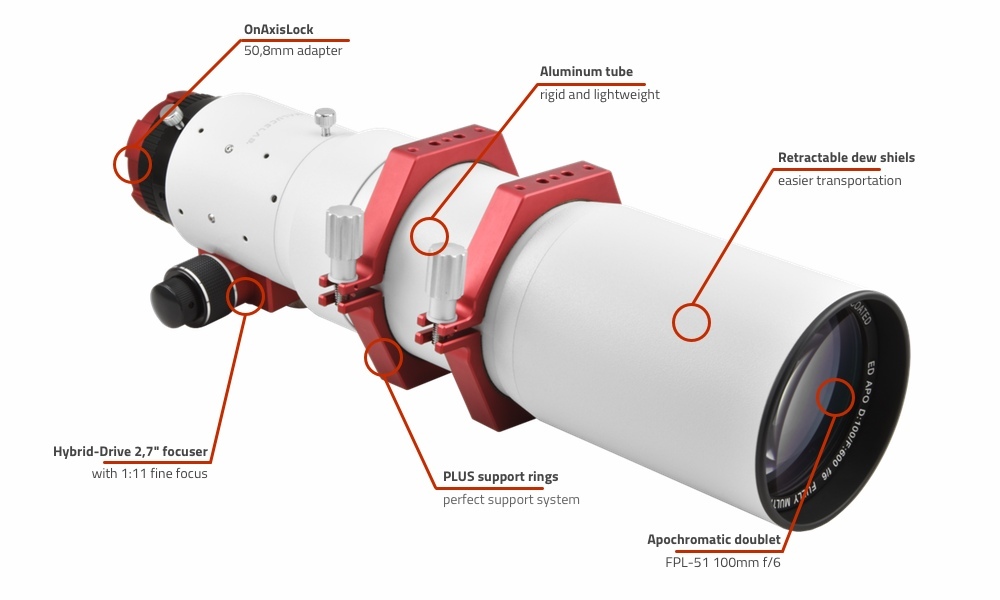
For photographing distant stars for the camera are available different refractors. For example, AIRY ED100.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/398393/
All Articles