DeepMind has created a computer that learns to use its memory.

DeepMind has developed a new type of AI that can learn to use its own memory. The project was named Differential Neural Computer (DNC).
What consequences can a project have, the purpose of which is to “teach” a computer to use its own memory? The main thing - the weak form of AI is becoming more effective than ever. For example, such a system can help a person to move in a completely unfamiliar city without the slightest inconvenience.
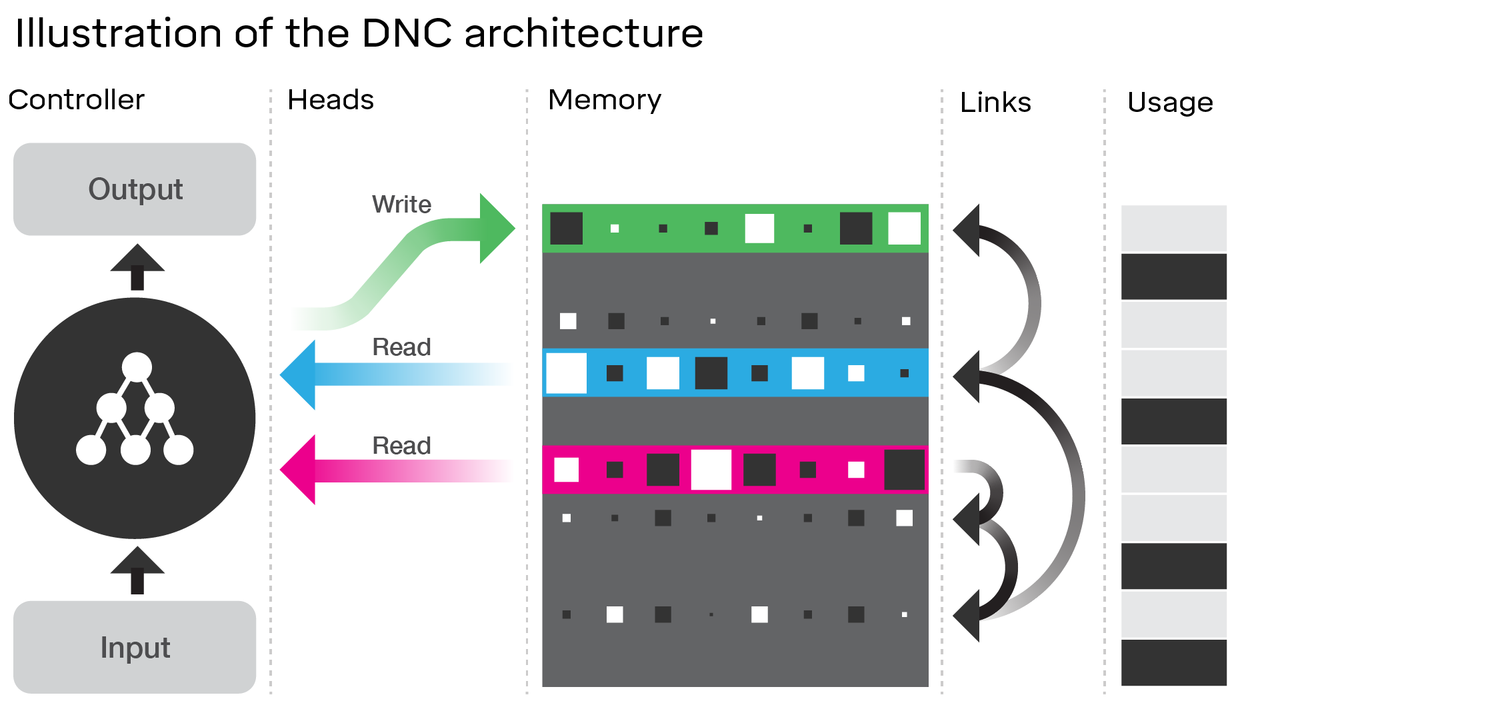
DNC architecture illustration. The neural network controller receives information from outside using memory data through specific read / write operations. In order to help the controller work with memory, the DNC stores temporary references to the tracking of recorded data, and also records the current usage levels for each memory location.
')
The main achievement of DeepMind employees is that they were able to teach their AI to perform each subsequent task, without forgetting how the previous ones were performed. In a typical situation, the system can use the same memory area to record information on the performance of various tasks. After completing the first task, the machine starts to perform the second. And the data on the implementation of the first to replace the data on the implementation of the second.
DNC plays tag
DeepMind DNC doesn't do that. Employees of the company provide the neural network with a memory location in external media, and train the system how to use it. The learning process is in the nature of trial and error. On their website, the project representatives stated the following: “When the DNC generates a response, we compare it with the desired correct answer. Over time, the system learns to give answers closer and closer to the right. "
The heart of the DNC is the neural network, which is called the controller. The creators of the system hold here an analogy with the processor in the computer. The controller is responsible for receiving data, writing them to memory and reading from memory. In addition, the controller analyzes the data and generates an answer in response to a question asked by the system.
The controller performs several types of operations in memory. Every moment he decides to write something in memory or not. If the decision is "yes", then the controller can choose two options for recording - in the unused sector or in the sector where there is already information that the controller has previously searched for. This provides the ability to update information recorded in a fixed sector. If all sectors in memory are used, the controller may decide to free up memory, just as on a regular hard disk you can overwrite a sector that is no longer necessary.
As in the case of recording, the controller can read data from a number of sectors. The system can search for the necessary information in each sector, or immediately read the data that is stored in the sector related to the requested data.
All this allows the system to effectively address the issue of memory usage, data storage and retrieval.
After the neural network received the London Underground map, the computer immediately began to give difficult answers to complex questions about moving around the metro. These answers were based on the principle of deduction. Here is an example of one of the questions that the DNC can answer correctly immediately after loading the metro map into the system’s memory: “When we enter the subway car and pass one stop along the Central Line, then along the Koltsevaya Line there are four more stops, and along the Jubili Line two stops, what stop will we take? ” For digital assistants like Siri, such a question is overwhelming - they simply cannot find the right answer, despite all the computing power of Apple data centers. But the AI from DeepMind is quite able to give the correct answer.

Source: Photofusion / Getty
Moreover, this system can give advice on the shortening of the way between different stops. She gives the correct answer in 9 cases out of 10.
According to the developers, their system can give the correct answer because the principle of its work is similar to the fundamental principles of human thinking. Of course, the DeepMind system is still far from the real machine analog of human intelligence, but the current version works fine. The human brain is still more skillfully disposed of stored data, including the process of posting new information.
DeepMind specialists hope that in the future they will be able to create a system that, without introducing specialized programs into its memory, will be able to use the information available to it to solve certain problems. In this case, you can already talk about a complete self-learning system that can use the available data to solve complex problems.
So far it is unclear when Alphabet will be able to use the advantages of the new system in its commercial products and services. So far, the division team has been conducting in-depth research and says nothing about when the commercial use of the developed system will begin.
Experts believe that the company is far advanced in the research of AI, Herbert Jaeger from the Bremen Jacobs University , said that the DeepMind team "overcame one of the most important stages of the evolutionary development of modern neural systems." This scientist is confident that in fact the company has created something more significant than described by its representatives in an article in the journal Nature .
Like all other DeepMind projects, this one is based on deep learning. Virtually the same technology that helped the AlphaGo system win in 4 games of go out of 5 world champion Lee Sedol.
Now DeepMind, in conjunction with the Future of Humanity Institute, is doing another interesting job. A combined team of specialists creates a “red button” for a strong AI form. This is a tool that will turn off artificial intelligence in the event that it gets out of control.
The problem of creating such an instrument is well illustrated in the statement of Nick Bostrom, director of the Institute for the Future of Humanity: “If an intellectual explosion threatens us with extinction, then we need to understand whether we can control the detonation process. Today, it would be more reasonable to speed up work on solving the problem of control, rather than suspend the conduct of research in the field of artificial intelligence. But so far, six people are involved in solving the problem of control, while dozens, if not hundreds of thousands, are working on creating artificial intelligence. ”
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/398357/
All Articles