Boeing is sure that it will overtake Ilona Mask on the road to Mars

Installation of F-1 engines on the S-IC stage of the Saturn-5 launch vehicle, the heaviest rocket in the history of mankind, which put the cargo into orbit. The engines were manufactured by Rocketdyne, while Boeing was engaged in assembling the first stage. March 1, 1965. Photo: NASA Marshall Space Flight Center
Colony on Mars - the issue is almost resolved. Apparently, NASA considers the establishment of a base on Mars even a higher priority than the establishment of a base on the moon. For humanity, the development of another planet in the solar system is an important step in expanding its presence in space. As Ilon Musk said, the expansion of our race’s habitat to two planets is important from a security point. The Martian colony will be a backup of the gene pool of people, for example, in case of a nuclear catastrophe or other disaster on Earth.
But even without taking into account the existential necessity, the conquest of Mars seems inevitable, given the innate desire of humanity to expand into new territories.
The foundation of the Martian colony is a matter of time. An important mission will require substantial cash injections. Its budget is not as big, of course, as the US spending on the production of military fighters, but still considerable. Major players in the aerospace industry are already beginning to prepare the ground for the development of this budget.
')
The first step was made by Ilon Mask and the company SpaceX, which recently presented its plan for the production of hundreds of reusable rockets for transporting nearly a million colonists and hundreds of thousands of tons of cargo to Mars.
Naturally, competitors could not disregard this presentation. NASA’s largest contractor, Boeing Aerospace Corporation, gave its answer. Executive Director Dennis Mullenburg (Dennis Muilenburg), speaking at the conference on innovation in Chicago, confidently stated that it was Boeing that would bring the first settlers to Mars: "I am convinced that the first person to set foot on the surface of Mars will arrive there on a rocket" Boeing, ”he said.
The company opened a special site, " Beyond the Earth ", where it published its own roadmap Path to Mars .
Boeing recalls that from the very beginning of the space age, it was she who “designed, developed, produced and controlled manned and robotic spacecraft and infrastructure”. Ilon Musk was not born yet when the Boeing company participated in the US space program more than 60 years ago.
Recall that in the second half of the 1950s, NASA began to plan a manned lunar expedition, after which it was going to establish a 21-seat underground air force base on the Moon - Lunex Project . At the same time, the plan for creating a military base on the Moon - Project Horizon was considered . It is possible that Boeing participated in the work on these projects, as well as in the well-known Apollo program.
NASA is now seeking to expand the presence of people outside the Earth, including on the surface of Mars. In this regard, Boeing considers it its duty to use the experience of 60 years of participation in the space program to perform new tasks: searching for new living organisms on other planets and satellites, searching for valuable mineral resources, protecting humanity "from unknown threats", and delivering colonists to mars.
Within the framework of the future Martian mission, Boeing’s engineers are ready to participate in all necessary design work. Among them, the company lists the following:
- Development of radiation protection for the safe delivery of people to Mars.
- Testing new technologies to ensure the autonomous operation of astronauts and technology on Mars and in space.
- Development of life-support systems on solar energy and testing them in orbit.
- Conducting research on lunar orbit and on the moon.
Testing of the listed technologies is planned to be carried out during lunar missions , which are considered preparatory.
Boeing Vice President John Elbon previously expressed that the company is considering an interim step in front of the Mars mission - the creation of a station in a circumlunar orbit. The plan provides for the assembly of a station of five modules between 2021 and 2025, which will be delivered by SLS launch vehicles: two residential modules, a transition chamber (airlock), a logistics module, an energy module. If everything goes according to plan, the company expects to send ships to the Martian orbit in the early 2030s, and people on the surface of Mars - in the middle or late 2030s.
For comparison, Ilon Musk wants to send the Red Dragon spacecraft to Mars in 2018, and humans - in 2024.
The Boeing company intends to actively pursue commercial launches into Earth orbit, running around technologies that it later uses when traveling to Mars (for example, for astronauts at the near-moon station, they will establish the same communication delay of 30 minutes as in communications with Mars). Together with NASA, Boeing is developing the Space Launch System heavy rocket. Like the company Ilona Mask, Boeing also has a contract with NASA for the delivery of astronauts to the ISS.
The statements and plans of "Boeing" look more real than the statements of Ilona Mask. Recall, after all, it was Boeing who built the first stage of the S-IC of the Saturn-5 rocket, the largest payload, the most powerful, the heaviest and the largest rocket created at the moment by mankind, which put a payload into orbit.
Boeing’s Executive Director Dennis Mullenburg believes that now space tourism is close to becoming a “viable and prosperous commercial market” over the coming decades. Mullenburg predicts that dozens of space hotels, research laboratories and production workshops for the production of high-precision electronics and other products in microgravity will join the ISS in orbit. It is in this market that the company will run around "Martian" technology. “I think this is a great area of work for us,” he said.
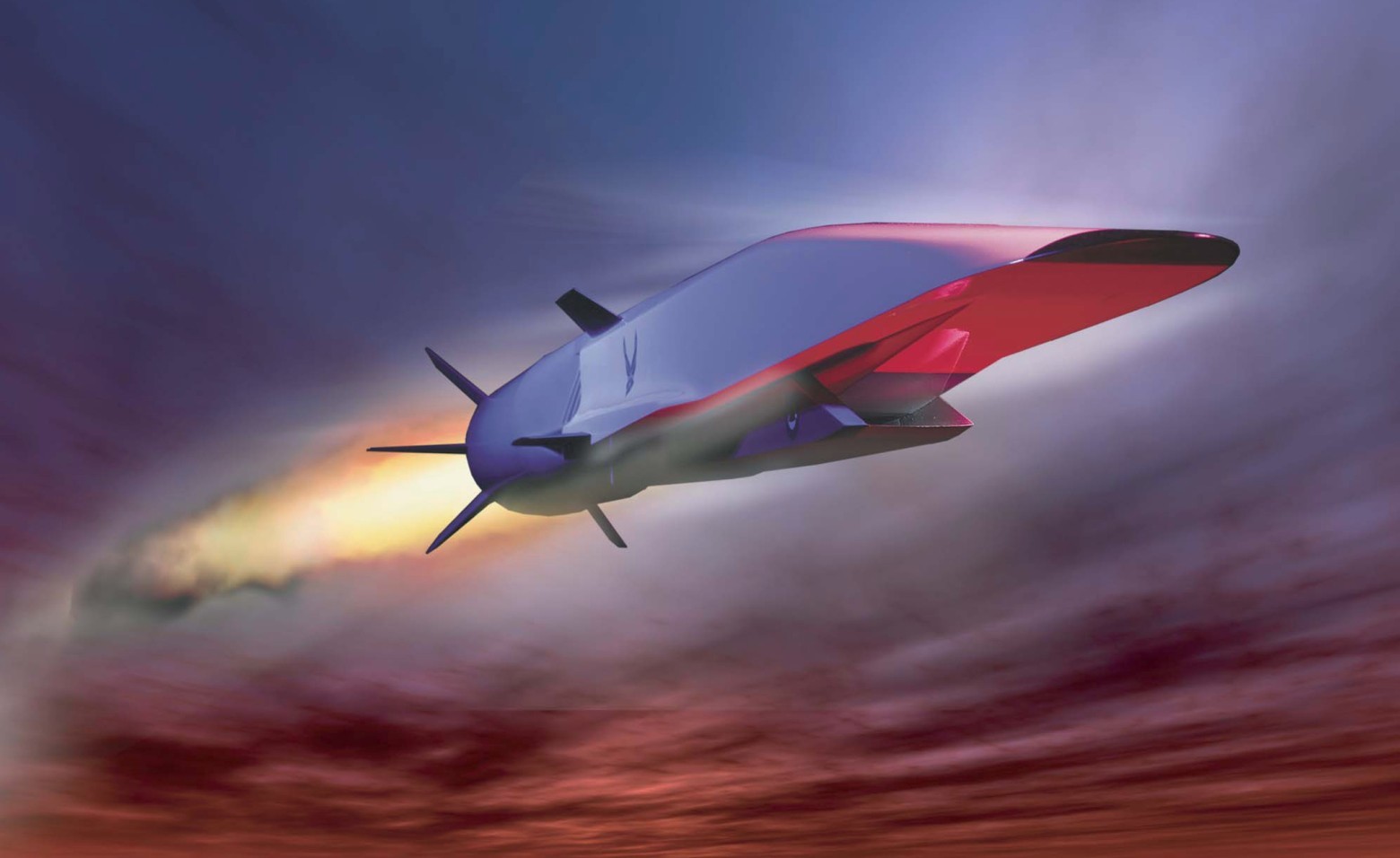
X-51A WaveRider
At the Chicago conference, Mullenburg also noted that he sees the potential for new supersonic airplanes flying at a speed of 3 Mach and more. It should be noted that the experimental hypersonic cruise missile X-51A WaveRider manufactured by Boeing reached a speed of 5.1 Mach on trials in 2013. However, this is hardly relevant to the Mars mission.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/398183/
All Articles