Google Translate translator connected to the neural network
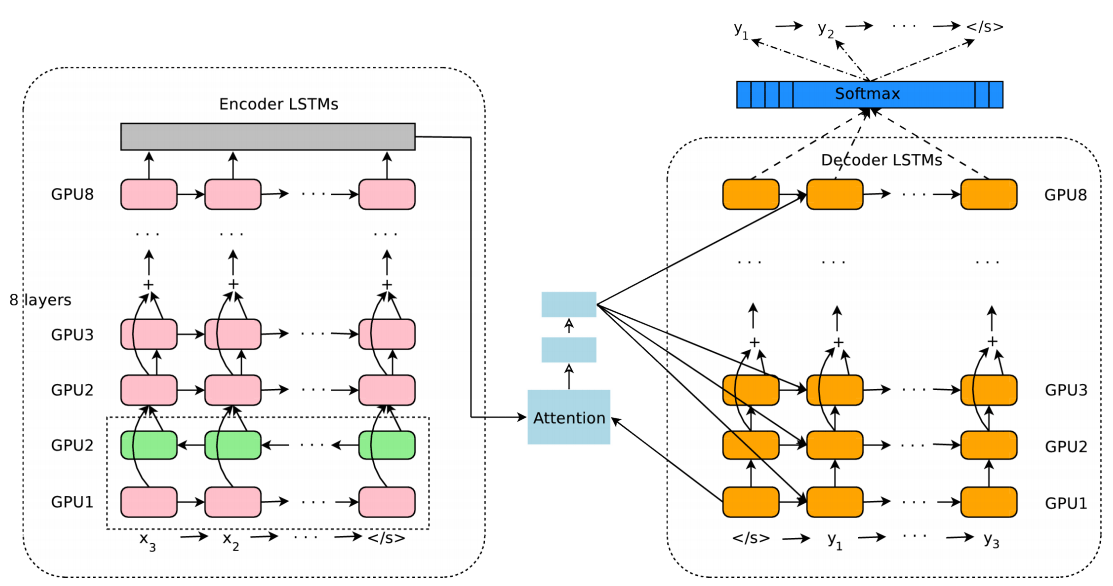
GNMT (Google's Neural Machine Translation) architecture model. Encoder network on the left, decoder on the right, attention module in the middle. The bottom layer of the encoder is two-sided: the pink modules collect information from left to right, and the green ones - in the opposite direction
Google is going to fully translate Google Translate service into deep learning . A detailed description of the neural network algorithm is published on arXiv.org.
According to Google's preliminary estimates, the neural network provides much better translation quality than conventional statistical methods. It has already been tested in English-Chinese in the most complex language pair, and the neural network immediately reduced the number of translation errors by 60%. The result is impressive. Other language pairs will connect to the neural network over the next few months.
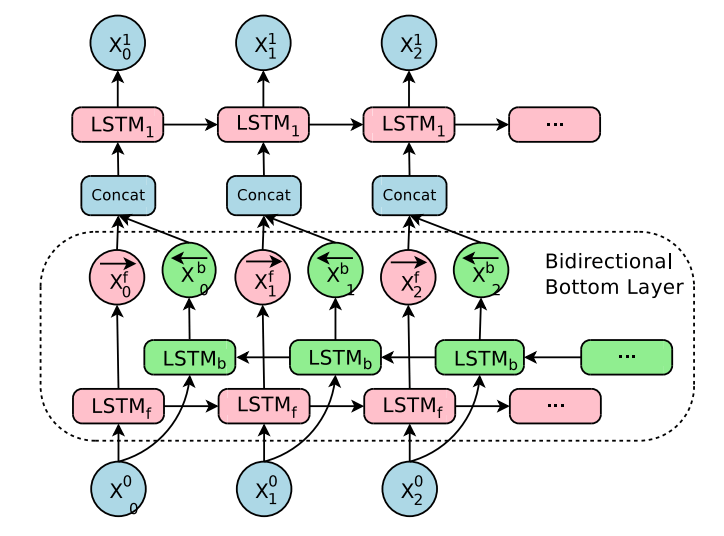
The structure of bidirectional communications in the lower level of the encoder
')
Success in the field of machine translation is another achievement of AI, of which there have been quite a lot lately. The technology of trained neural networks is clearly on the rise and is used in different areas. Particularly clear superiority over other computer technicians is achieved in image recognition and games. In some of the areas, neural networks work even more efficiently than the human brain, for example, they beat a person into separate board games.
Google’s neural network for machine translation is called the Neural Machine Translation System (NMTS). From the very beginning to the end, the translation of the text now fully performs the neural network. Traditionally, AI has been used on Google Translate in limited mode, for some supporting tasks. For example, to compare texts available in several languages, such as official documents of the United Nations or the European Parliament. In this mode, the translation of each word in the texts was compared.
NMTS neural network works on a fundamentally new level. It not only analyzes the existing translation options in the learning process, but also performs intellectual analysis of the sentences, breaking them up into “vocabulary segments”. In a certain representation within the network, these “vocabulary segments” correspond to the meanings of words .
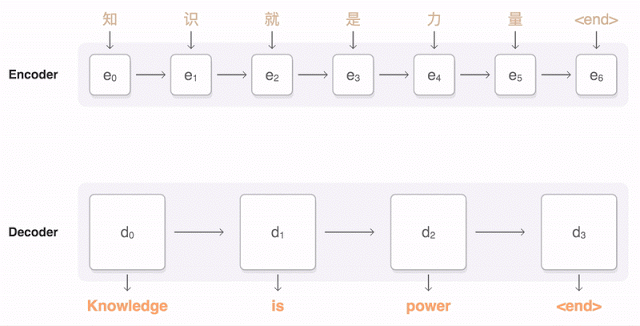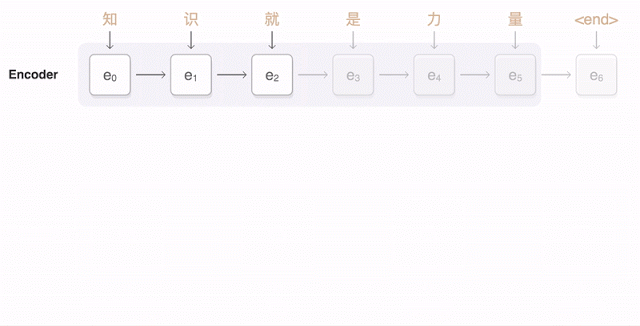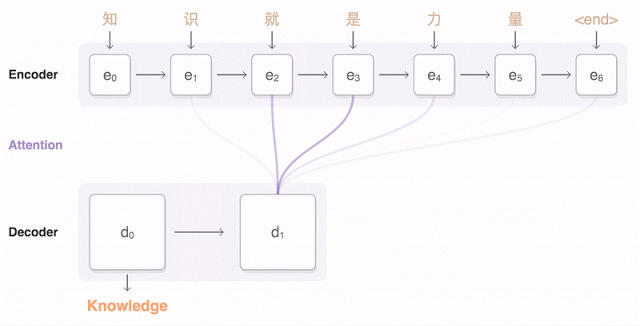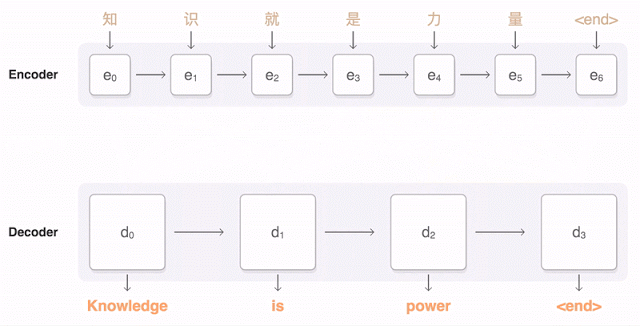
The Google animation shows how the Chinese proposal is broken into parts, and then the neural network selects a suitable translation, given the weight of each fragment in the original text.
In a sense, this approach resembles the work of neural networks in machine vision. The system processes the image pixel by pixel. Then the level of processing gradually increases, reaching such complex features as object borders, geometric patterns, etc. In NMTS, the same neural network that analyzes the source text, then offers its translation.
In this case, Google developers have applied existing developments in this area, as well as several “methodological innovations,” independent experts commented on a scientific paper published on arXiv.org. According to them, the development of Google shows a "stunning" result and clearly demonstrates that neural translation using AI can far surpass the classical methods of machine translation in quality. Google's neural network clearly improves translation quality in many ways.
For optimization, NMTS was run-in on computer equipment specially designed for testing the neural network. It was there that AlphaGo neural network was trained at one time, which then defeated Lee Sedol , one of the world's best go players.
To assess the effectiveness of the system, researchers have picked up a large set of proposals from Wikipedia and news articles on the Internet. These texts fed the NMTS, the old Google Translate machine translation system, and also gave people-translators. In the framework of blind testing, human translators assessed the quality of the translation of each fragment (including the human translation).
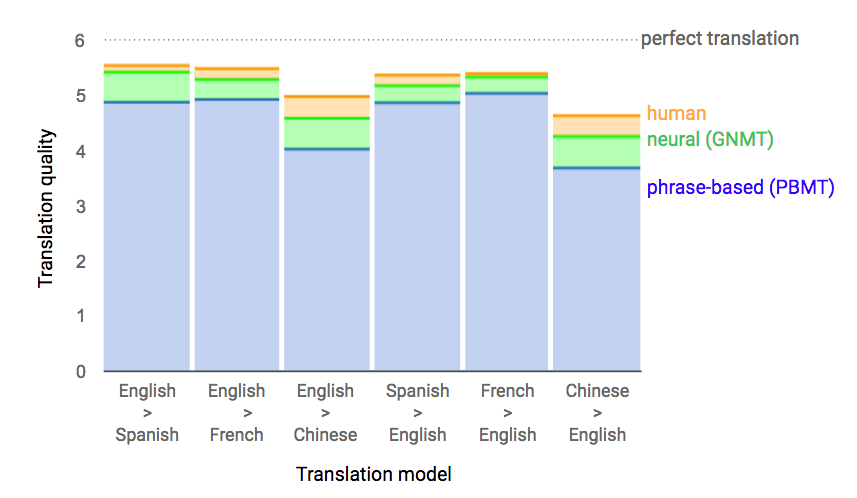
Examples of translation of texts in Chinese, Spanish, French and English with the usual machine translation system (blue), neural network (green) and man (orange)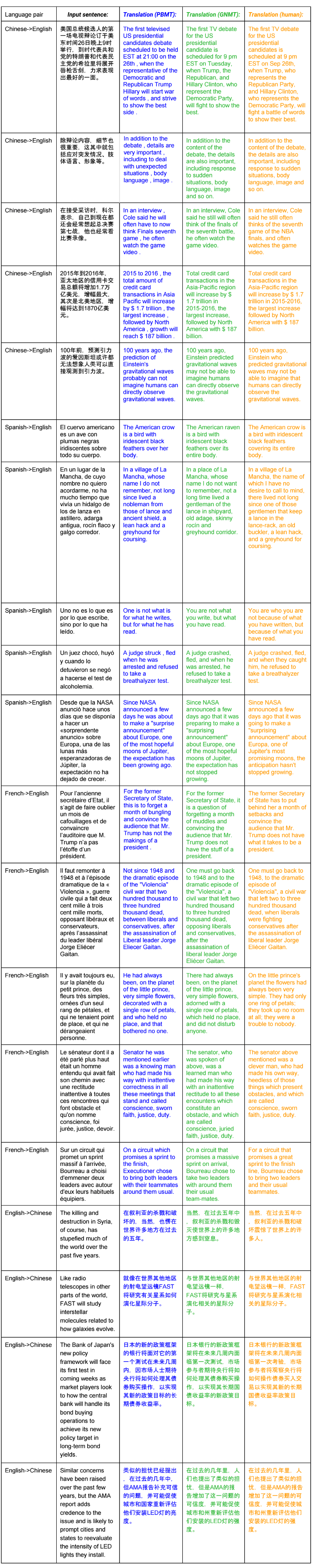

The English-Chinese language pair is known for its high complexity. Despite a significant decrease in the number of errors, the quality of translation in this language pair is still inferior to the quality of translation of other Indo-European languages. In some language pairs, the translation of NMTS is close in quality to the translation by people, but the authors of scientific work warn that it is early to make far-reaching conclusions, because the comparison was made on a limited set of carefully selected simple sentences.
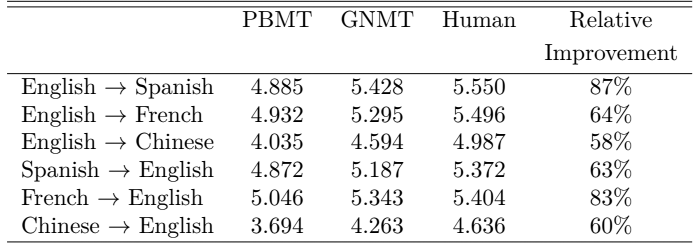
The same results in a more visual form.
According to experts, a computer can approach or bypass a person in terms of the quality of translation only if additional channels of incoming information are connected to the machine translation system. Not only text, but also video, and sound. “In the future, robots will be able to move, manipulate objects, feel pain through pain sensors and express their feelings in the text,” says Jürgen Schmidhuber from the University of Lugano (Switzerland).
The Google Translate system currently processes about 10,000 language pairs for machine translation.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/397959/
All Articles