China opened the heavenly eye. Today began the world's largest radio telescope
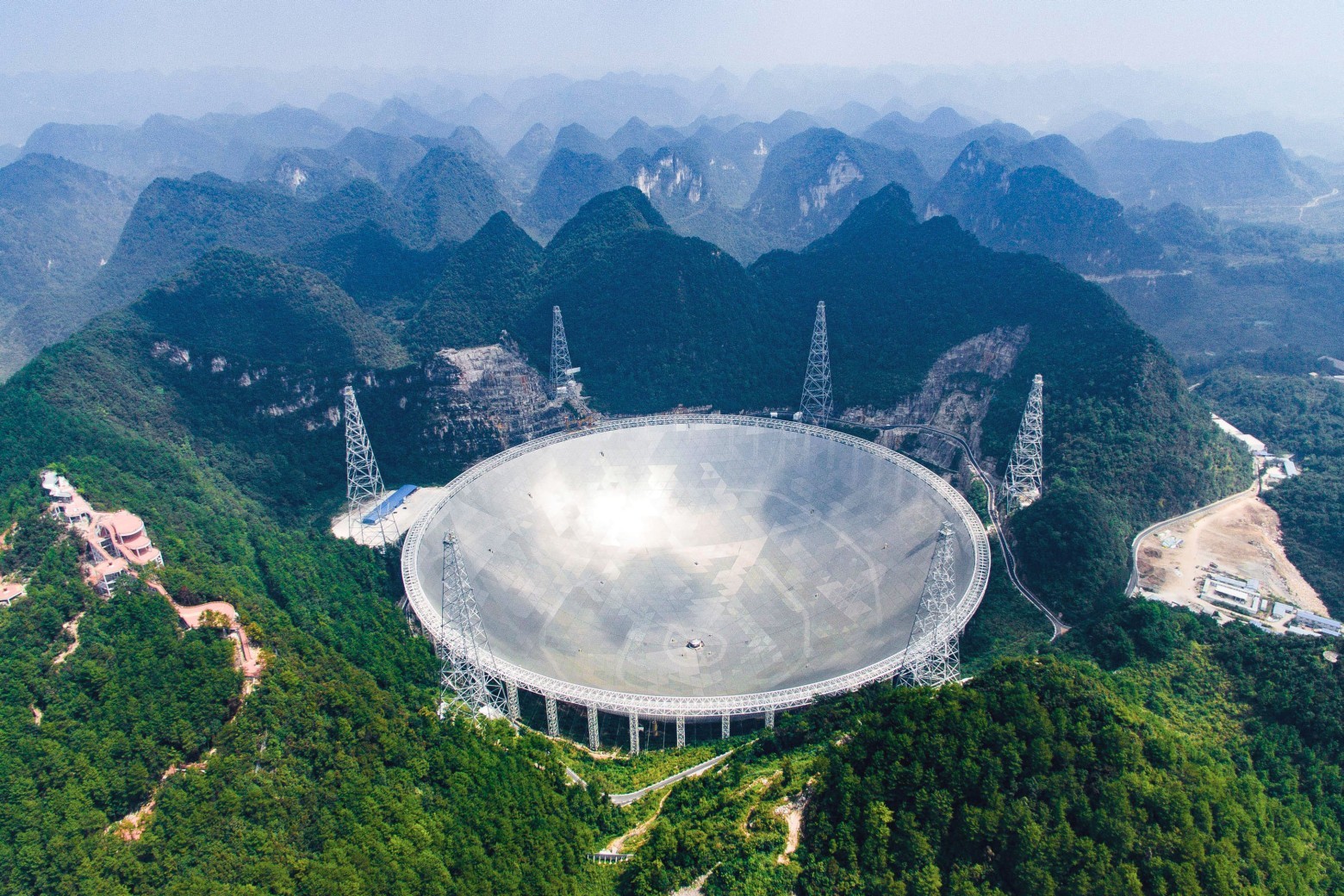

Aerial view of the FAST telescope in the remote area of Pingan County, Qiannan-Bui-Miai Autonomous Region, Guizhou Province, South-West China. Photo: Liu Xu / Xinhua
On September 25, 2016, the world's largest radio telescope Spherical radio telescope with a five -hundred-meter aperture (Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope, FAST) sent a reflector towards space and received a signal from distant galaxies . Today was the opening ceremony of the FAST. Before that, it was launched several times in test mode. In one of the test launches, he caught the signal from the pulsar at a distance of 1,351 light years from Earth.
According to experts , this gigantic scientific tool demonstrates China’s ambitions in space exploration and the desire to achieve international recognition of advanced Chinese science. Building a telescope with the unofficial name 天 天, that is, the Heavenly Eye, took five years and cost $ 180 million.
The FAST radio telescope with a diameter of 500 meters exceeds the size of the 305-meter observatory of the Arecibo radio telescope in Puerto Rico, which was considered the largest in the world over the past 53 years. It should be noted here that the Russian radio telescope RATAN-600 has a diameter of 576 meters, but its aperture is not filled. Thus, it is Arecibo and FAST that are the world's largest aperture filled radio telescopes.
')
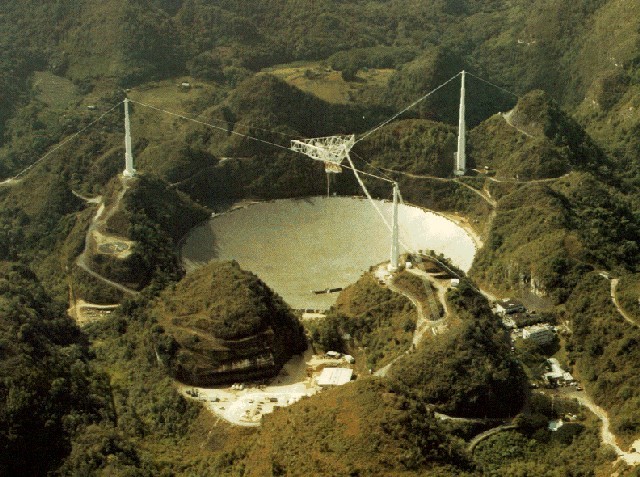

Radio telescope in Arecibo
According to the Chinese media, FAST has twice as much sensitivity as the Observatory in Arecibo, as well as a 5-10 times higher speed for studying the sky.
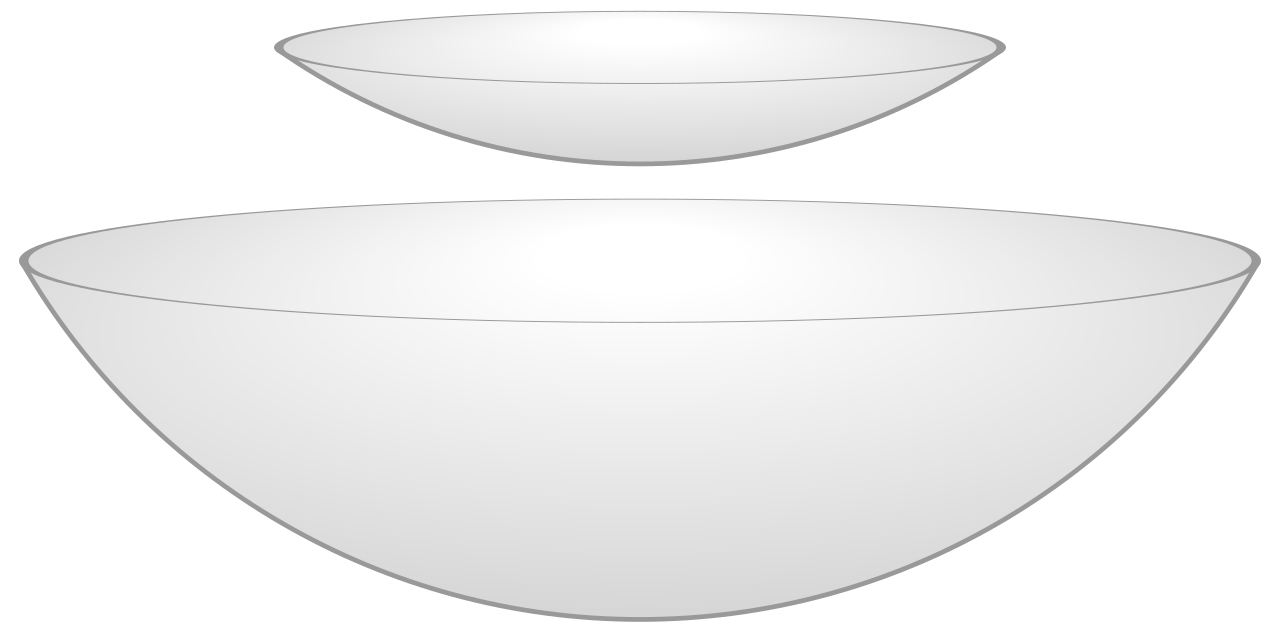
Comparing Arecibo and FAST Plates
The design of the FAST radio telescope consists of one reflector, in which 4450 triangular reflecting panels with a side of 11 meters are interconnected in the shape of a geodesic dome.
The position of each panel can be adjusted with high accuracy - this is the purpose of the grid of steel ropes with hydraulic drives. Thus, the radio telescope focuses on a certain direction. FAST can focus on any area within ± 40 ° of zenith. At the same time, a reflector section with a diameter of only 300 meters from a total 500-meter plate is activated. That is, it turns out that there are two factual errors in the name of the FAST telescope: after all, the telescope aperture is less than 500 meters, and the telescope is not spherical.

The construction of the telescope took five years. Over the years, engineers and builders had to live in one of the mountain gorges far from civilization, where at first there was not even electricity. It was this abandoned place chosen from 400 variants: a natural valley in the mountains at an altitude of about 1000 m above sea level was ideally suited in size and was a natural defense against radio frequency interference ( photo of the telescope cup from a satellite ). For the sake of a scientific project, the authorities ordered the resettlement of 65 villagers in this valley and resettled 9110 residents from eight villages in the vicinity. In August of this year, it was reported that those who had been resettled would be lodged in new houses or would be paid large compensations from the aid fund for the poor and would be given bank loans.
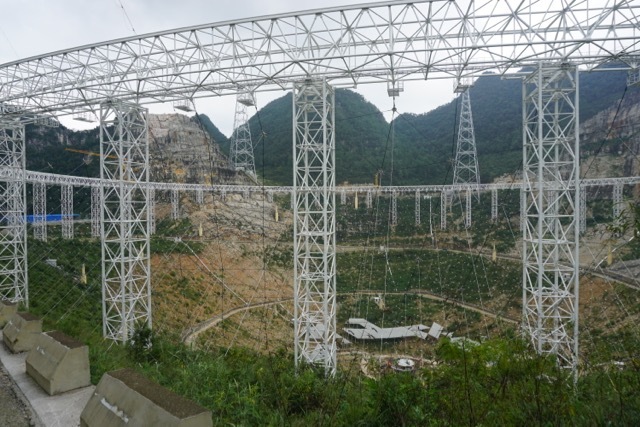

FAST radio telescope in September 2015, a year before launch
Within a radius of five kilometers around FAST, there will not be a single source of interference, such as a microwave, which has given rest to Australian astronomers for 17 years . According to the construction conditions, a full radio silence must be observed within a radius of 5 km.
Despite the need for complete radio silence, the authorities decided to build tourist facilities in the vicinity of the radio telescope, including a viewing platform on a nearby mountain. Chinese and foreign tourists can come and see this miracle with their own eyes. In this decision, there is a reason: for example, about 90,000 tourists and 200 scientists come to Arecibo annually.
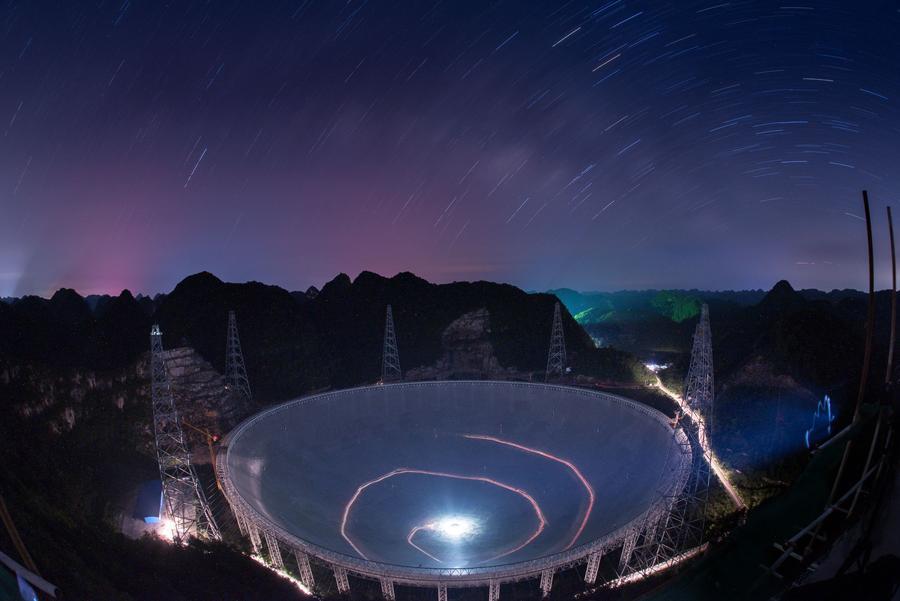

Radio Telescope FAST in September 2016
Hundreds of astronomy scientists and enthusiasts from across the country gathered at the FAST launching ceremony in Pintan province. The President of China congratulated scientists, engineers and builders who completed the most complex technical project.
Among the main objectives of the FAST telescope are the search for gravitational waves, radio emission from stars and galaxies, and the detection of signals from extraterrestrial civilizations. “The ultimate goal of FAST is to discover the laws of the development of the universe,” said Qian Lei, junior researcher at the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in an interview with local television. “Theoretically, if there is a developed civilization in space, then the radio signal from it will be similar to the signal that we can receive from a pulsar.”
Chinese astronomers will receive priority to work on FAST in the first two or three years of its existence, and then they promise to open the object for scientists from around the world.
Perhaps this will happen before, because now there are not enough specialists for the project in China. To use FAST at full capacity, hundreds of researchers are needed, and the FAST research team cannot even find 50 astronomers in China .
China's ambitions
China spends billions of dollars on giant space projects. Even American research teams, not to mention European and Russian science, which receives very modest sums from the state, can envy such budgets.
In September of this year, China launched into orbit its second space laboratory, Tyangun-2 (Heavenly Palace - 2) measuring 10.4 meters in diameter (3.34 meters in diameter), which is generally similar in size and function to Soviet orbital stations of the second generation "Salyut-6" and "Salyut-7".
In mid-October, China plans to send two astronauts to the station. In mid-April 2017, it is planned to launch the Tianzhou-1 cargo spacecraft, which will deliver fuel and other materials to the station.
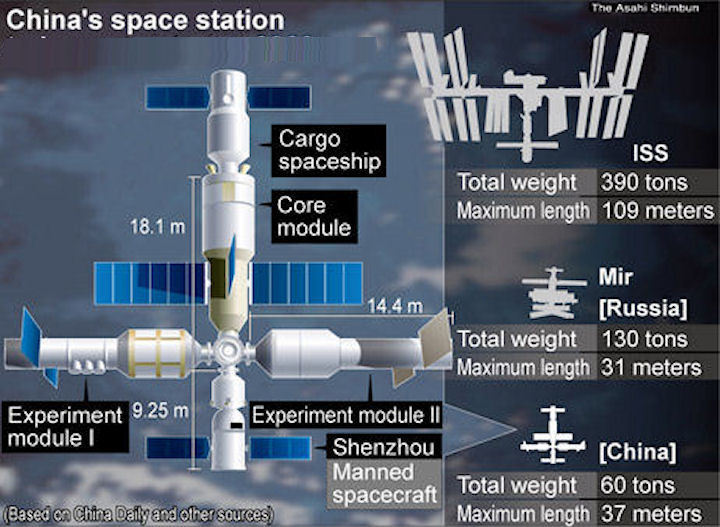
Plan for the future of the Chinese space station in comparison with other third-generation space stations
In the coming years, China plans to build a third-generation space station in orbit. The program is designed for several stages until 2020-2022.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/397753/
All Articles