ProDOS 2.4 for Apple II: the first in 23 years OS update for Apple II
We all know that in most cases, PC software needs to be updated. Often, developers add new functions, some elements of their software protection, correct errors of the previous version of the software platform. Unfortunately, not always updates to the installed software come out with the necessary frequency.
For example, the operating system update for the Apple II computer was the first since 1993. This update was released not by Apple Corporation, but by a third-party developer. John Brooks [John Brooks] introduced an update called ProDOS 2.4. The announcement of the OS version is timed to the thirtieth anniversary of the Apple IIGS. This is one of the most popular modifications of the Apple II.
If you do not have the original Apple system (and it remained in working condition with a very limited number of users), then you can try out the new product in a browser emulator created by the developers of Internet Archive. The release included Bitsy Bye, a bootloader that allows you to search for files on several floppy disks (or USB drives formatted in a special way). Bitsy Bye is an example of an almost perfectly optimized program. It works with just 1 kilobyte of RAM.
The update also has a 400 byte bootloader. In addition, the update contains a whole collection of useful utilities, including the MiniBas tiny BASIC interpreter, utilities for working with disk images and programs, software for working with archives. All this takes a very small amount, fit on a single 5.25-inch floppy disk (140 KB of memory). A ProDOS 2.4 image is available here .
Among other useful utilities included in the update, its author notes the following:
- New MiniBas from Usotsuki. This is a small program that can be used instead of Basic.System:
1.1. Only 1 block is required instead of 21 blocks for Basic.System;
1.2. Downloads and executes executables for Bitsy Bye;
1.3. It supports two types of commands:
1.3.1. & "Filename" - to work with Binary or Basic;
1.3.2. & - to return to ProDOS. - ADT Pro and FastDsk - utilities that allow you to transfer information from floppy disks to modern computers;
- Verify - utility for viewing and editing disk blocks;
- Manage ProDOS and DOS 3.3 - file and disk management for any Apple II system;
- Shrinkit is a utility for accessing Access Apple II Shrinkit archives.
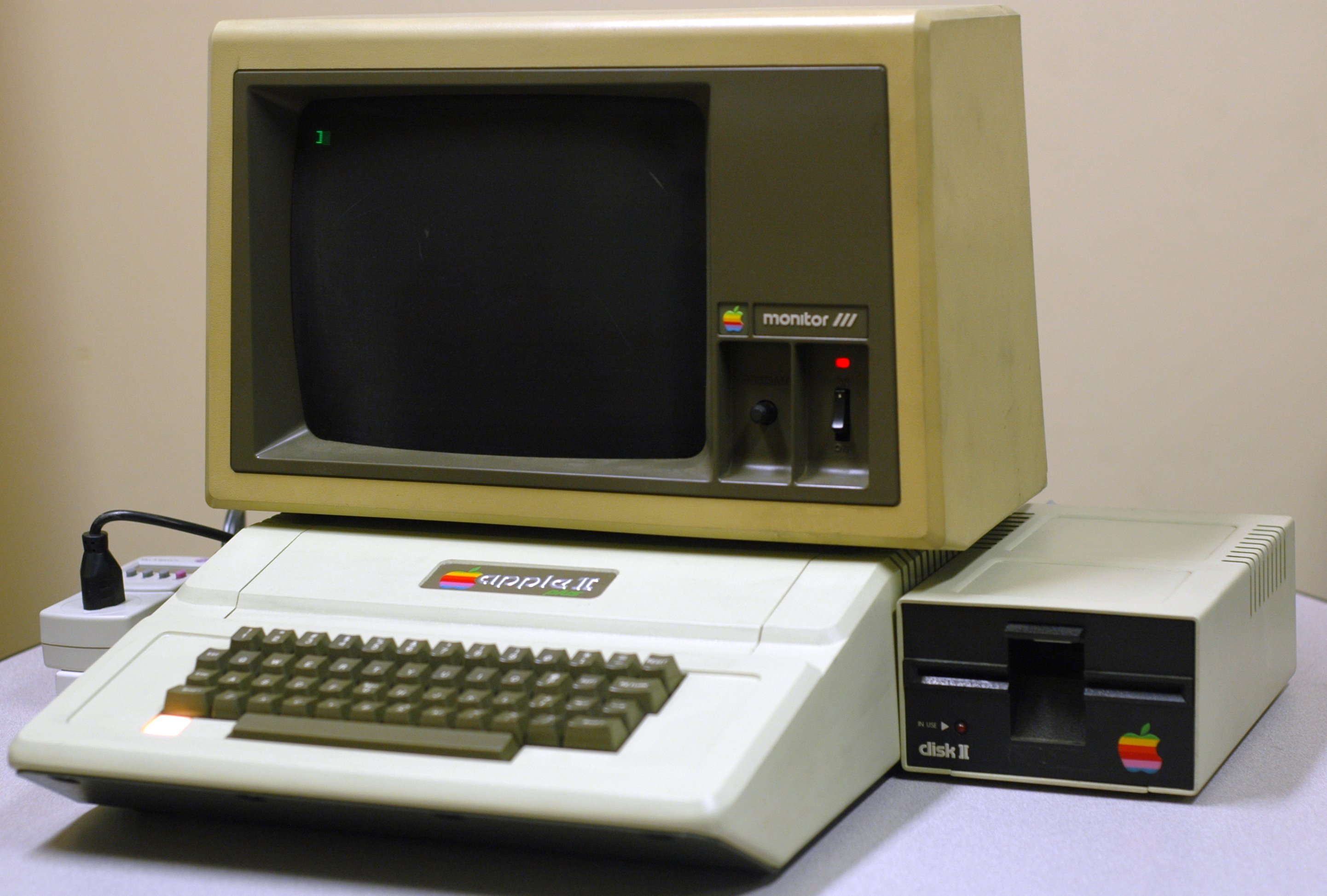

Apple II (Apple spelling is still used) [] is the first serial computer manufactured by Apple Computer. The system was first introduced in 1977 at the West Coast Computer Fair. The computer has become one of the most successful personal systems of the time. There were several modifications of the Apple II, and one of them was produced until the 90s of the last century. It is estimated that the total number of systems of this type produced reaches 5-6 million.
The system was positioned by the company as a public computer, on which both a programmer and a student can work. Up to this point, most personal computers were used mainly by professional users (electronics enthusiasts, scientists, engineers). According to some experts, Apple II was one of the factors that led to the revolution in the field of personal computers.
The first Apple II computers (Apple] [), launched on June 5, 1977, were equipped with a MOS Technology 6502 processor at 1 MHz, 4 KB of RAM (expandable up to 48 KB), 4 KB of ROM containing a monitor and an Integer BASIC interpreter (aka Basic for integer operations), an interface for connecting a cassette recorder.
Notable was the fact that the video controller could operate in various modes, including the following:
- Test mode, 24 lines of 40 characters each, monochrome;
- Color graphics mode, resolution 280 * 192 pixels, 6 colors;
- Color graphics mode, 40 * 48 color elements with 16 colors.
In order to connect a monitor or TV, a composite video output with support for standard NTSC was used. The sound was also, it was reproduced by a speaker that was controlled through a register in memory.
The Apple II board has 8 expansion slots. One of them allowed to connect an additional RAM module. Others were used to provide I / O (external device controllers, serial and parallel ports).
As for software, Apple II used mainly Apple DOS, ProDOS, UCSD P-System, CP / M operating systems (with CP / M card). On the Apple IIGS version, the GS / OS system was mainly used. The vast majority of software for this model of personal computer was written in the Apple DOS environment. This is how most commercial software was created.
There are several Apple II emulators, the browser emulator from the Internet Archive is far from being the only one. Emulators are available for different platforms, including mobile phones. Most - free projects. Apple II enthusiasts have previously launched The Lost Classics Project to convince Apple II copyright owners to make such programs freely available.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/397549/
All Articles