How the Cardberry loyalty card aggregator works
In my wallet a lot of space is occupied by discount cards. These are at least three cards from stores of children's goods, a couple of cards from electronics stores, cosmetics, cards for pharmacies and grocery stores. The Cardberry project was conceived as a way to get rid of a large amount of plastic, replacing it with a single, commensurate device.
And now you can buy this card. I tested it on myself and found out if it is easy to use and whether it is accepted in stores. Then I realized that this would not be enough, and looked into the office to Cardberry, to communicate with the founders and developers.
Leave questions in the comments - I invited the founders to Geektimes to answer them.

Relief wallets began with the transition from coins to paper money, and then - to plastic cards . Cardberry's concept is to free the wallet from a large number of plastic cards that we carry with us all the time - this is primarily about loyalty cards, but in the future we will work with bank cards.
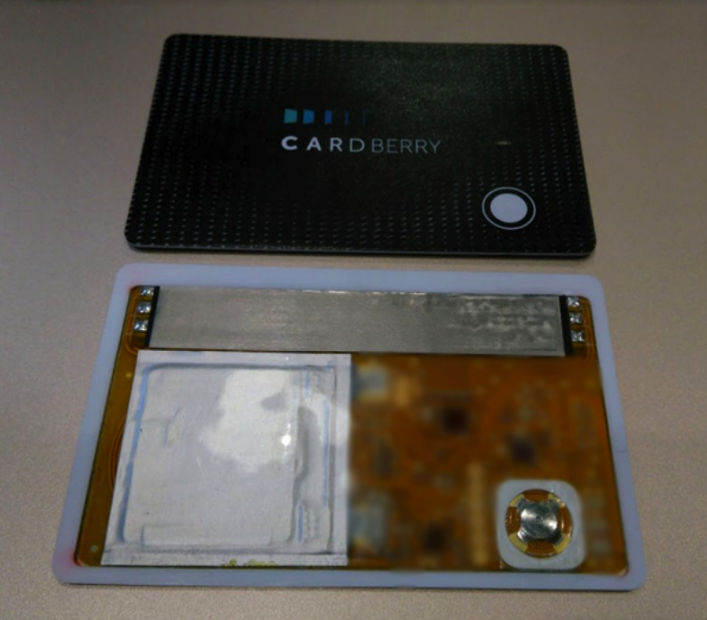
The company's history began with the idea of creating a universal plastic card in November 2013. Then the founders began to analyze the technologies used. Cards were divided into three types - with a magnetic stripe, with a bar code and with a number, as well as combined. The main and most important element of the Cardberry card is the magnetic stripe. If a barcode from any discount card can be photographed and shown on the phone screen in a store, and is highly likely to be able to be counted, then a magnetic stripe cannot be obtained without the card itself. Therefore, the greatest problem was precisely the emulation of the magnetic strip.
The magnetic stripe on the map is, in fact, a tape with positively and negatively magnetized areas. When the card is pulled through the reader, a magnetic field is created on the read head. The developers had the task to recreate the sequence of the changing magnetic field on the head of the card reader. Among the first prototypes of the card was a device with USB, with serial coils ColiCraft, with longitudinal winding. Data from these cards was read correctly in 30-60% of cases. More details about the first prototypes were written by the developers themselves at Habrahabr .
For the first time, it was possible to buy something in the store using Cardberry on March 14, 2014, but this technology was not suitable for further use for several reasons. Including because the signal transmission was not a point, and information from one track could be read on all three. Due to the mutual influence of magnetic fields, the second track was inoperable. The prototype at the same time worked from three finger-type batteries, which from the point of view of the concept was a huge minus.
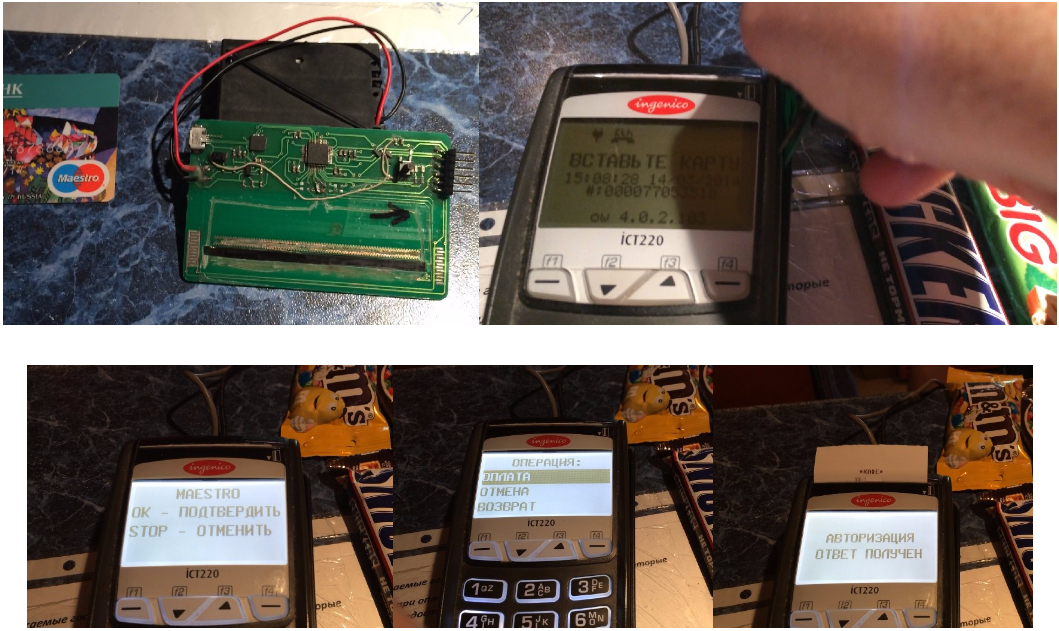

Prototype
Emulation of a magnetic strip without the magnetic strip itself proved to be a difficult task. The existing technology of this type was not found, so Cardberry developed its own module that can recreate the first and second of the three tracks of the magnetic strip. A coil with an ultrathin core with high magnetic permeability was made, a way was found to remove the magnetic field pickups on neighboring tracks - the Cardberry card became three-track. But it was not enough to design it - it was also necessary to find factories that can produce such a module together with other components of the device.
The next call concerned the issue of entering data on the card. All work goes through the appropriate application, but how to record the data from the loyalty card on Cardberry for use in the store? This question seemed simple, until the developers found out that the readers, firstly, are expensive if they work with more than one track, and, secondly, they work unstable with different models of smartphones. In addition to designing my own module for emulating a magnetic strip, I had to make my own reader with a charger.
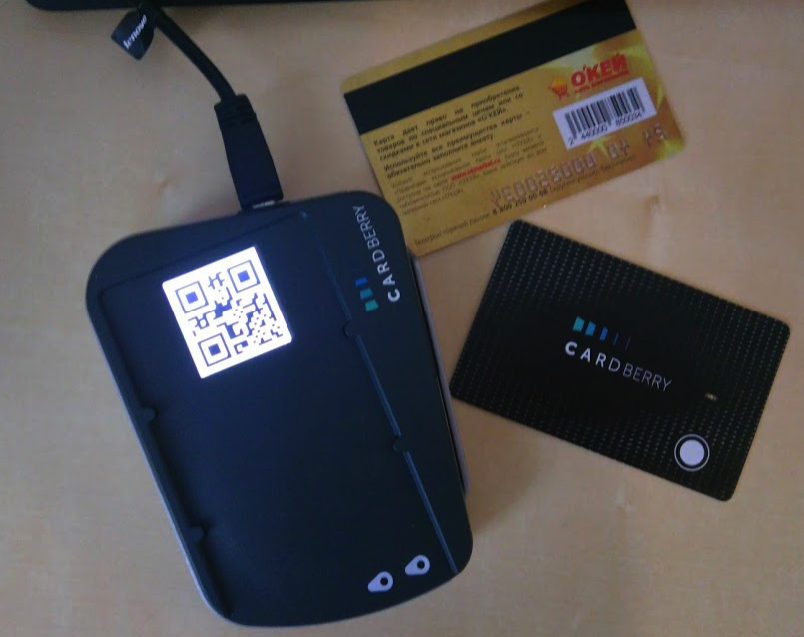
The reader is also a charger. Charging method - contactless. The receivers existing in the market turned out to be too thick, therefore a receiving coil with a 0.1 mm flexible plate was developed. A screen is being used to transfer data from a magnetic strip - the corresponding QR code is generated on it. Now there is a new device that is free from the display - it transmits data to the smartphone directly via Bluetooth.

Production
In order for the card to be easily rolled into the reader and placed in the users' wallets, its thickness should not exceed 0.87-0.89 millimeters. In this gadget, this should fit the battery, which does not have to be put every day to charge. At first it turned out to find batteries with a capacity of 60 - 80 mAh with a thickness of 0.55 mm to 0.67 mm, but in this case the device was too thick. We stopped at a lithium-polymer battery with a capacity of 20 mAh, whose thickness is 0.5 millimeter.
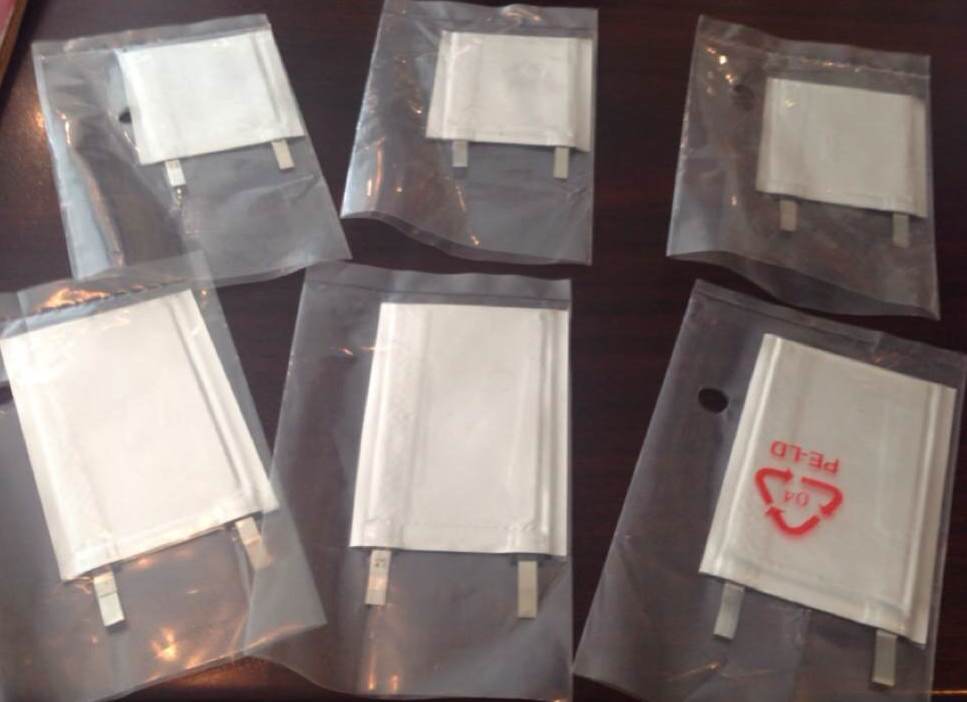

One of the first batteries that tried to use the card

Here and further, the schemes on the map are conceived, since publishing them will prevent the device from being patented.
The card must communicate with the phone, so it needs a fast receiver. All work with the application and the card should be carried out directly at the store's checkout, so an increase in time can add only inconvenience to the user. For this, a miniature Bluetooth module was used.
The LED module allows you to emulate a bar code. In the store for this you need to send a scanner beam to the device.

The first prototypes were made on the basis of thick printed circuit boards. For the card, a flexible board with a thickness of 0.1 millimeter was needed. The problem is that in Russia such boards are not made to order by commercial companies. In order to set up production, one of the company's employees, Alexander, lived for about a year and a half in the Chinese city of Shenzhen.

Due to large-scale investments, the city of Shenzhen has become a major industrial and financial center in a short period of time. This is one of the reasons for the choice - it was convenient to negotiate with various factories here.
Alexander spoke about the difficulties and intricacies of the relationship with Chinese partners. First of all, he debunked the myth of the workaholism of the Chinese: "We collect a sample with two girls and one English-speaking manager. Time is ten minutes to six, work remains for half an hour. Exactly at six the bell rings, the girls relax their hands, the components fall on the table, and they get up and leave. The manager already had to linger and help finish the job. "
The second important problem is that the Chinese do not know how to say no. They take on any work, say that they are able to do it efficiently and quickly, but in the end, after receiving the money, they can do something similar to the necessary component and say "This is all that we could." It took a long time to correspond with the factories in order to return at least part of the money. “Then we decided to go differently: we paid a little money for the sample, and only after that we made a large order,” adds Alexander.
When it was possible to make and break in the production of components, one more important question remained: the frame. The technology of creating smart cards did not fit, because the sintering of layers under pressure and at high temperature is technically impossible in the case of such a gadget. As a result, we stopped at a transparent PVC case, which was then applied to the drawing.
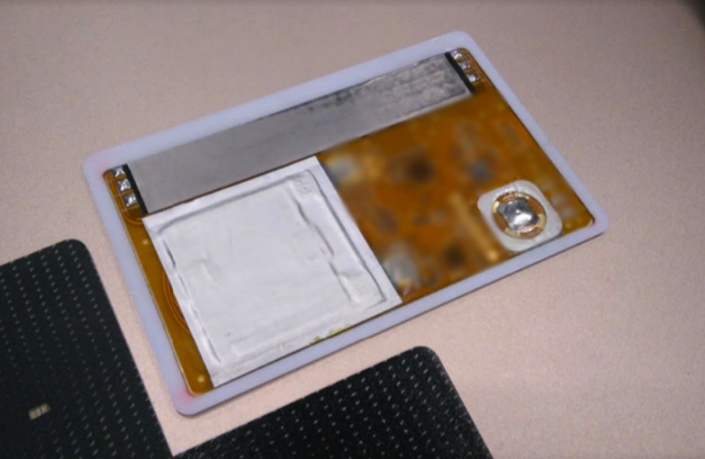
It looks like the map before painting. One can see a square battery, a module that emulates a magnetic strip, a bluetooth module, a button.
Left - collected in China map. On the right is a map, the assembly and painting of which took place in Russia, in the Moscow region town of Pushkino in its own shop.

After receiving the collected cards, you must flash them. To do this, use a snap.
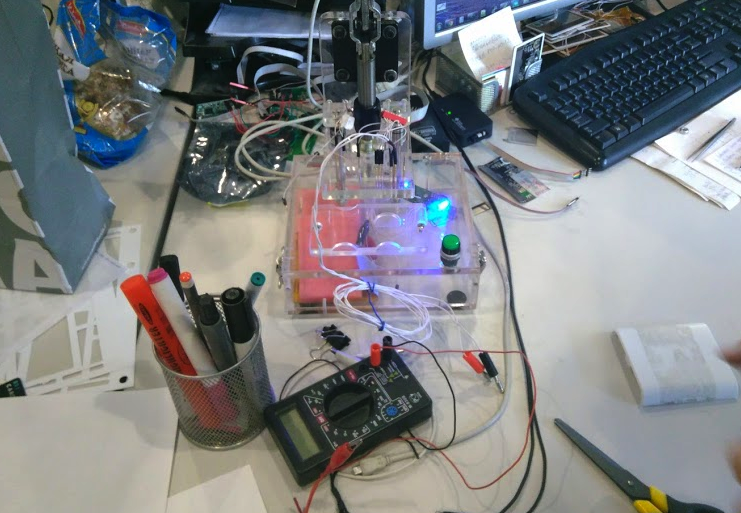
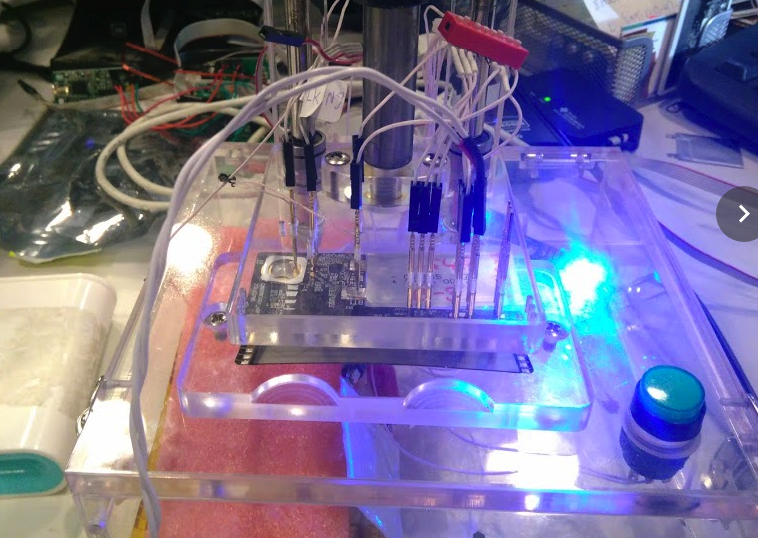
At this booth the cards are being tested. A certain percentage is rejected. Which is a commercial secret, unfortunately.

Outcome and outlook
The product comes in a nice little cardboard box. The Cardberry package consists of a card, a reader for recharging the card and entering data from a magnetic strip of loyalty cards into the application, and from the Android and iOS application itself, which allows you to manage and share your cards with friends. You only need to carry a card and a smartphone with you - the device's battery should last for many days.


To get started, you need to download the application and enter data from loyalty cards. In the process you are photographing the map from two sides, put bar codes in the application. If the card is equipped with a magnetic stripe, then you pass it through the reader, which forms a QR code - and you scan it with a smartphone.

In the store, you press the button on the map, open the application on your smartphone and select the desired loyalty card. Then - give Cardberry at the checkout.
Reader and the card itself will soon undergo changes. To get rid of the extra component - namely, the display on the reader - the data after rolling the card will be transmitted via Bluetooth to the smartphone. Charging will be a contact - for this purpose, a module is used, resembling a chip on a bank card, but not being one.
This is what the next generation reader looks like:
The fee for the reader is on the left for the first generation, on the right for the second.
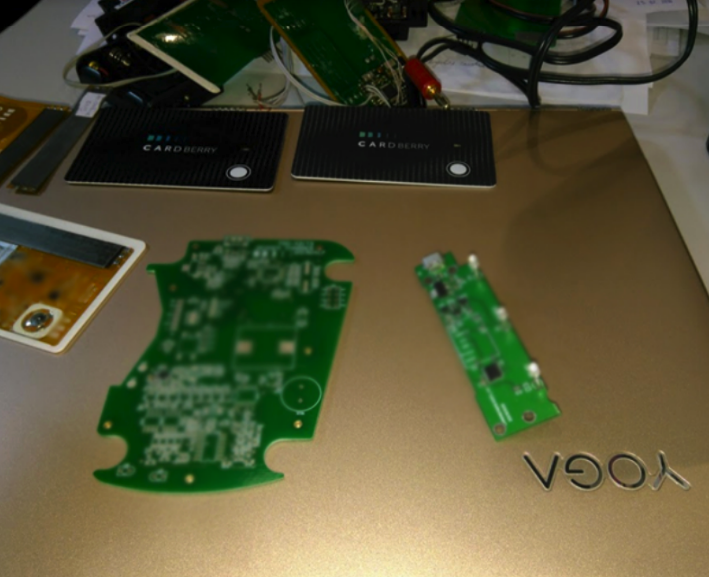

The next generation card features a smaller battery and the presence of charging contacts.
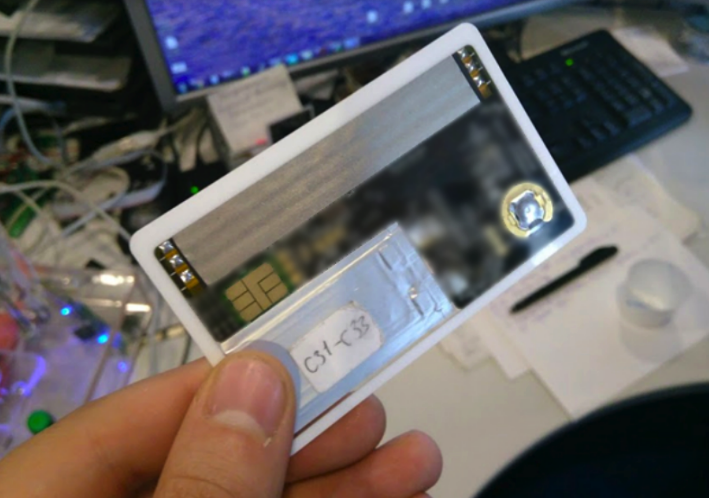

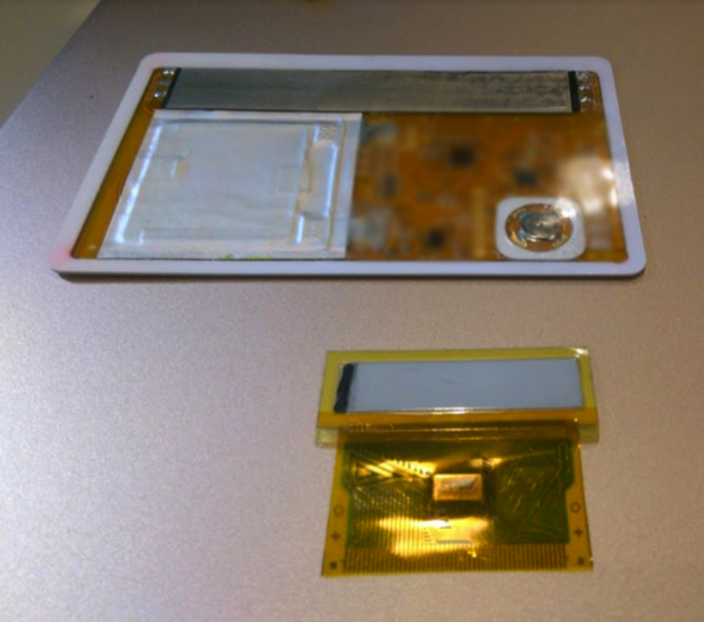
The map may receive a display in the future. This is one of the options: a display showing the first three characters of the name of the card or its number, a Bluetooth signal, a battery and other data.
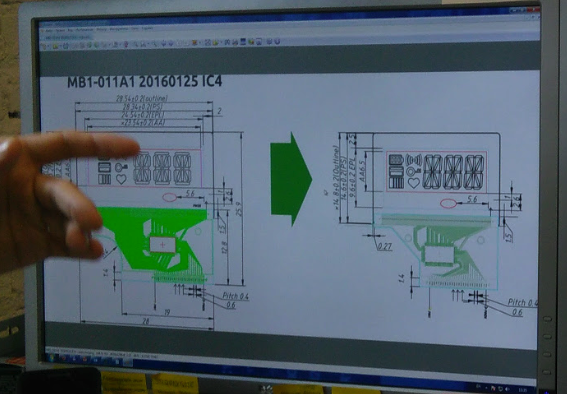
Immediately did not use the display, because the finished modules were too cumbersome. If this idea is developed, in any case it will be necessary to design your own version. The display on the background of the map shows how much one of the existing modules would occupy space.

Sales
From the very beginning, the company positioned the device as a gadget for girls who have a lot of loyalty cards. Later in the process of working with experts, the strategy was changed. Now most of the buyers are men, as Marina Druzhenets, the founder of the project, says. And they come thanks to the fact that they are talking about the map in various IT publications and at industry events, including competitions - Telecom Idea, Generation S.
I wonder how the prices for this device have changed over time, and how it affected sales. One hundred dollars two years ago is not such big money as one hundred dollars today. However, people left pre-orders. For the New Year 2015-2016, the card was sold for 5500, and now for 8500. At the same time, the number of sales has not changed, from which it was concluded that people interested in such a gadget buy a card for which the price in a certain plug is not an important factor.
Cardberry has already switched to self-sufficiency, but now there is a minimal budget for marketing. Articles in IT publications and public speaking allow people to learn about the project.
In terms of monetization, the company has a number of developments. First, joint projects with banks are possible. Such projects would allow the use of a co-branded Cardberry as a bank card out of the box. Secondly, retailers may be interested in Cardberry. They will receive information about cardholders, will be able to issue free discount cards instead of spending money on the production of physical cards, as well as the ability to send information about promotions and discounts based on geolocation to the client and communicate with the client in real time through the application.
To date, over a thousand Cardberry sets have been sold. The company actively leads sales in the corporate segment - the cards are branded as a corporate gift.
Analogs and competitors
The main global trends in consumer loyalty at the moment:
- Mobile technology. The percentage of smartphones continues to grow, and the prices of such devices - to fall.
- Smart cards. The card chip stores data on transactions, detailed information about the level of the program participant, rules for charging bonuses, data on discounts and promotions.
- NFC and RFID. Chips of wireless communication in maps and smartphones.
- Geolocation targeting. GPS and GLONASS allows you to determine the location of the client so that the seller can convey the most relevant offers.
- Big data. Analysis of large amounts of data allows you to identify patterns in customer behavior, so that, again, convey to him the most relevant suggestions.
People do not enjoy the benefits of loyalty programs in full. In Russia, on average, there are 12-14 discount cards per person, of which 70% are not used, and every three cards out of five are lost or deteriorated. It’s inconvenient to carry them with you, so with great pleasure 30% of consumers are ready to switch to digital loyalty programs - for example, receiving cards through an application without their physical option.
Retailers are interested in retaining old customers, as attracting a new one is seven times more expensive, and the average check of a loyal customer is 67% more than a new customer’s check. An effective loyalty program generates up to 20% of additional store profits.
To solve these problems, and in the wake of existing trends, the development of applications and devices has begun, allowing users to be included in loyalty programs.
In the Russian market, the only competitors are map aggregators in the form of mobile applications. Such applications allow you to store a barcode or card number, but not a magnetic strip. From the screen of the phone, not all scanners can read the barcode, in addition, problems arise due to the beam of the reader gleaming from the screen.
In several models of Samsung smartphones used technology Loop. It allows you to reproduce a magnetic strip by a magnetic field, but this possibility is limited to one track, with interference to unused coils (tracks) of the magnetic head. The Korean company uses technology for its payment system. Since only one track is emulated, Samsung went for a trick: a non-chip card with a magnetic stripe and PayPass is translated into a digit for writing to a smartphone, but only its copy with a single track.
The first idea in the world to bring all the cards into one was proposed by a startup Stratos in 2012. But the card can still only be "reserved" - it did not come out in the series. Later Coin cards were issued - about 300 thousand units in the USA, but in May 2016 sales were stopped, and the technology was bought by FitBit. Three more startups - Plastc, Swype, Brilliant card - have not yet released the finished product to the market.
In early 2016, LG introduced the LG Pay card aggregator. As in the case of Cardberry, the system is distinguished from Apple Pay, Google Wallet and Samsung Pay by the presence of a physical device - the White Card. The card may appear until the end of 2016.
Results
Cardberry card is a convenient assistant for the aggregation of loyalty cards. The main difficulties are in the human factor: older sellers may not accept such a device. In some stores, you may encounter the fact that employees are not ready to accept the card due to the lack of an agreement with the developers.
Not all scanners recognize the LED barcode. In this case, you have to show the barcode from your smartphone, but even then the old scanners may not cope with the task.
The main question that arose among many people at the presentations of the device is whether it is possible to add bank cards. At the moment the question is being worked out, but due to the lack of certain security measures, it is not recommended to do this. In the future, co-branding with banks is planned, or the opportunity to add data from any bank cards that are not equipped with a chip without restriction.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/397401/
All Articles