Construction of the communication line Kamchatka - Sakhalin - Magadan. Cable Innovator Excursion - Ship Layer
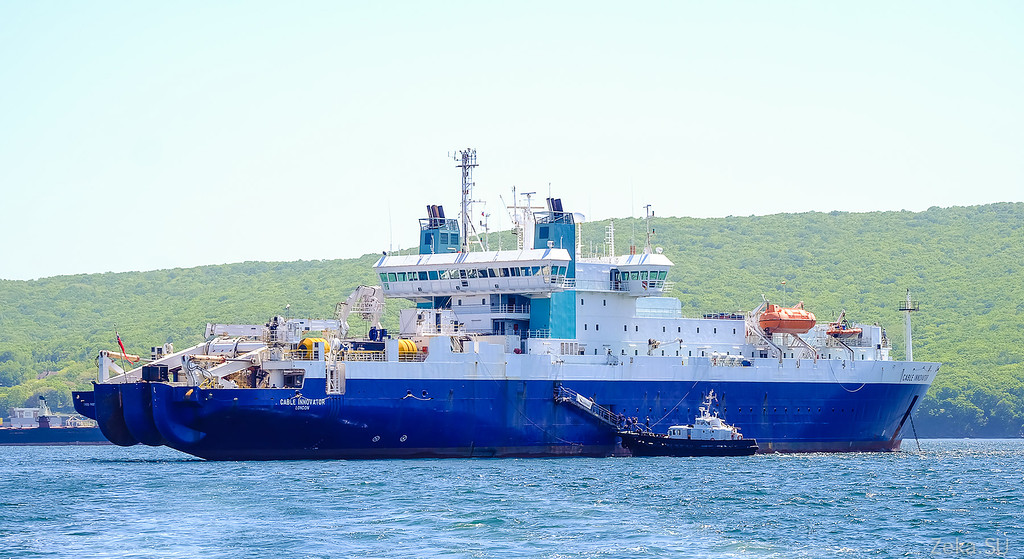
Probably, many people know that the company Rostelecom has been conducting a global construction of a communications highway in the Far East for the second year. Since 2014, the construction of the underwater fiber-optic communication line (POLS) Kamchatka - Sakhalin - Magadan. Last year, in the month of June, this project moved to the most difficult part of this project - to lay the submarine cable. This work is carried out by the ship-cable-laying company Global Marine Enable Innovator .
Last year, this boat already came to our port , but, unfortunately, it did not take excursions. And this year, apparently under the impression of the successes of last year, Rostelecom invited several media representatives on board to show this miracle of technology, which is the most difficult work in this project.

Initially it was planned that during the summer of 2015 all the works on the project would be carried out and both branches of the AOLS would be laid in Magadan and Kamchatka.
')
But the Sea of Okhotsk turned out to be inhospitable and did not accept the entire cable. Weather conditions and bottom relief did not allow both branches to be laid in one season. And now, at the end of May, able Innovator arrived in our city to take on board part of the team and specialists from the customer companies Rostelecom and Huawei.
So, able Innovator is the world's largest cable laying machine for optics, built in 1995 at the Kvaerner Masa shipyard in Finland. It is a diesel-electric (diesel engines, but the drive for electric screws). Equipped with a bunch of stabilization systems and thrusters in order to position the ship in any conditions with an accuracy of one meter (as the participants of the works complained to me, because of the additional propulsion units installed on the ship along the sides, they prohibit fishing from the side so that the line is not tightened in the mechanisms; oh, sadness, sadness, grief).

In the photo you can see that it is equipped with two cuttings, fore and aft. In the stern cabin there are staff members who are responsible for the process of laying, in the bow, everything is the same as in all other ships: the captain, the navigator.

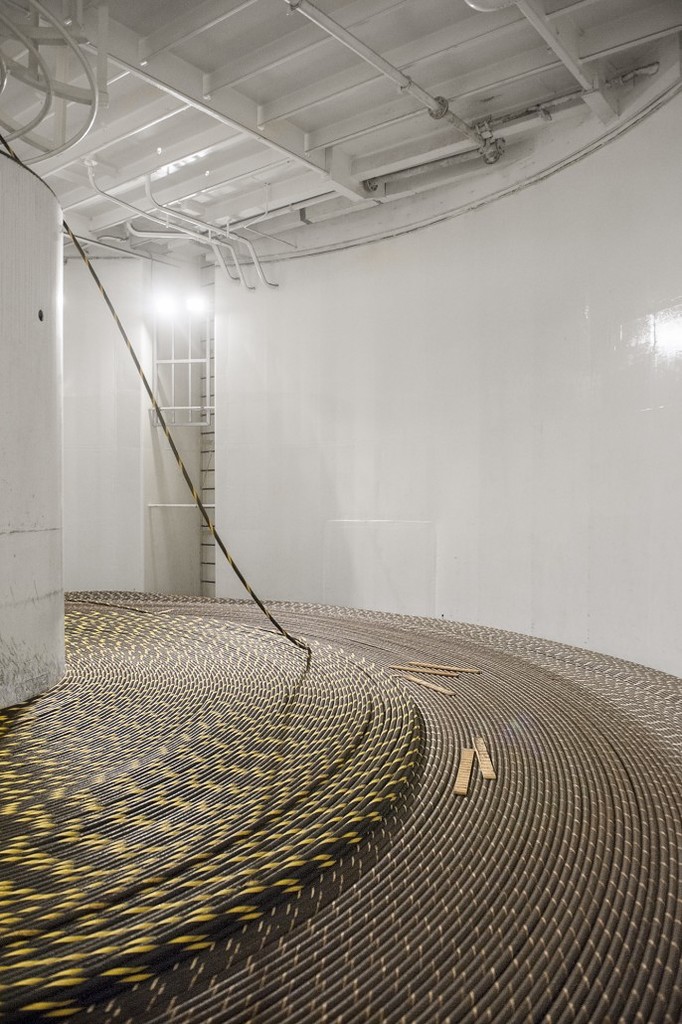
There are 3 holds for the cable tank, their capacity is enough to lay the cable on the floor of the globe.

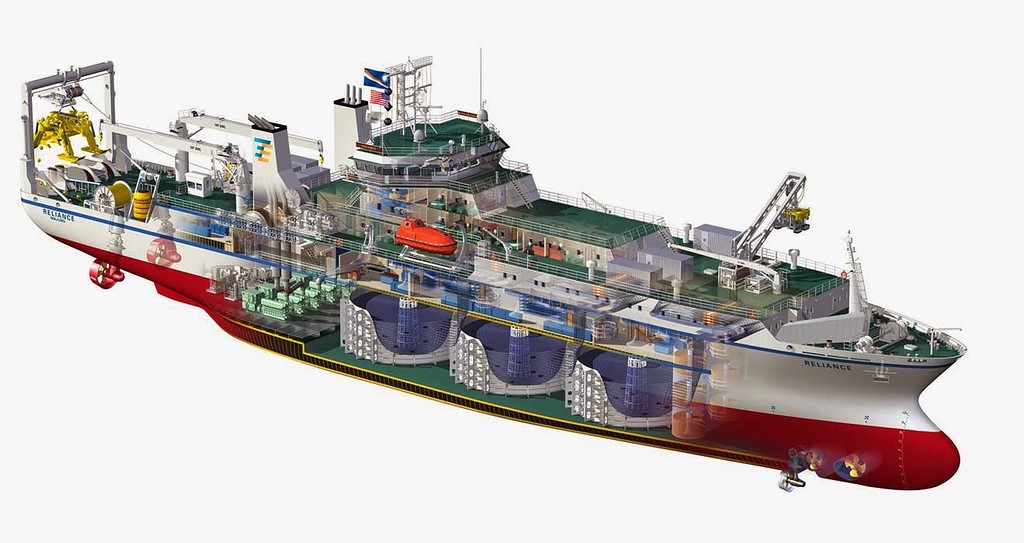
Scheme of the device of a similar ship:

For laying under water, 2 devices are used - Plow and Robot. The plow is lowered from the stern and dragged behind the ship. He plows the trench at the bottom of the sea and lays a cable into it. Plow is the main tool. But the robot is already used in emergency cases, when there are rocks on the bottom of the sea, when the cable breaks and you need to find its end, and for the repair of submarine cables.
I will divide the tour into 3 parts:
Part 1 - felling, captain's bridge;
Part 2 - Cable Deck;
Part 3 - Underwater tools Plow and Robot.
On Habré already wrote similar materials, and therefore you can not read anything new for yourself.
In order for you to understand a little how to lay the cable in general, I will tell you a little theory.
Works are divided into several stages:
1. Research and design
At this stage, the bottom of the sea is investigated, or ready-made materials from previous studies are taken. Depending on the relief of the bottom, the route is built. Naturally, current communications at the bottom are taken into account. But the benefit is that the Sea of Okhotsk is not rich in underwater pipelines and underwater optical highways, well, except that the secret communication cables of the Pacific Fleet to which enemy submarines listen .
2. Cable manufacture and loading
The cable is made immediately solid coil, so that under ideal conditions, it can be laid from beginning to end, and loaded onto the ship. At the production stage, erbium amplifiers EDFA (Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier), a fiber-optic amplifier on an erbium-doped optical fiber, are immediately incorporated into the cable.
Due to the fact that Russia does not have such civilian ships, the manufacture of the cable and its installation were entrusted to Huawei.
By the way, due to the fact that the work was not completed in one season, the cable was unloaded in Singapore, and able Innovator worked on other orders.
3. Gasket
It's simple. At the bottom, from the ship, they lower the plow and turn the small one forward. He digs a trench, a cable is buried in it.

The only difference with the picture is that there is a couple of kilometers under the ship.
For safety, one more Neptunia tug boat participated in laying the cable from Magadan to Sakhalin. It was on a safety net and cleared the bottom of the trash from the trawl along the way. Here it is:

This year Neptunia did not go with them.
Here is another informative video:
4. If everything went well and the cable reached from coast to coast, then it is connected to the coast station. And from the station already, in the old manner, with wires pulling the Internet to the consumer.
In Magadan at Rostelkom everything went well. The cable was stretched, tested for six months and now they sell fast Internet to everyone.
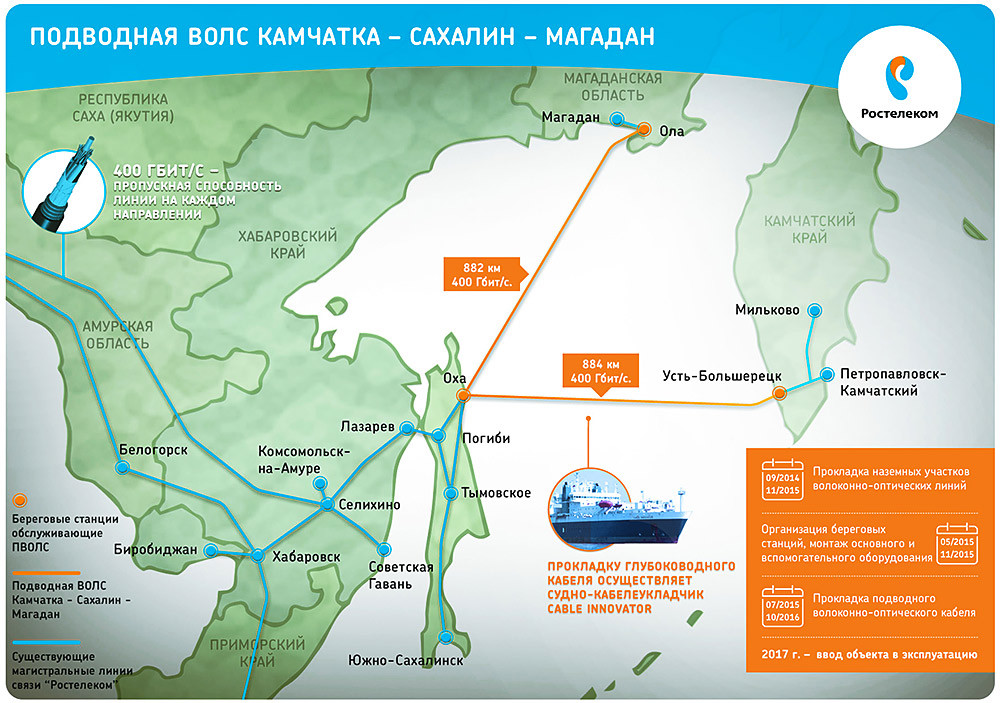
According to the latest information, from June 7, 2016, the cable was connected to the coast station in Ust-Bolsheretsk and cable laying to Sakhalin should end on July 22. So, the chance that next year the normal Internet will appear in Kamchatka is very high.
All right, it was all lyrics, and now we will go on a tour of the ship.
The ship stood near the island of Russian, I even thought that you can approach him on a kayak, but, alas, the weather did not allow.
We were brought on board a small boat:

Hospitable ladder opened its arms to the guests and members of the team:

Then the labyrinths of corridors and stairs began:

Everyone was invited to the mess-room and the Captain with the Russian assistant told us about what we would see:

Naturally, the conversation on all ships begins safety. Where to run in the event of a siren. For these purposes, everyone was recorded and counted on their heads, so that in the event of something not losing anyone:

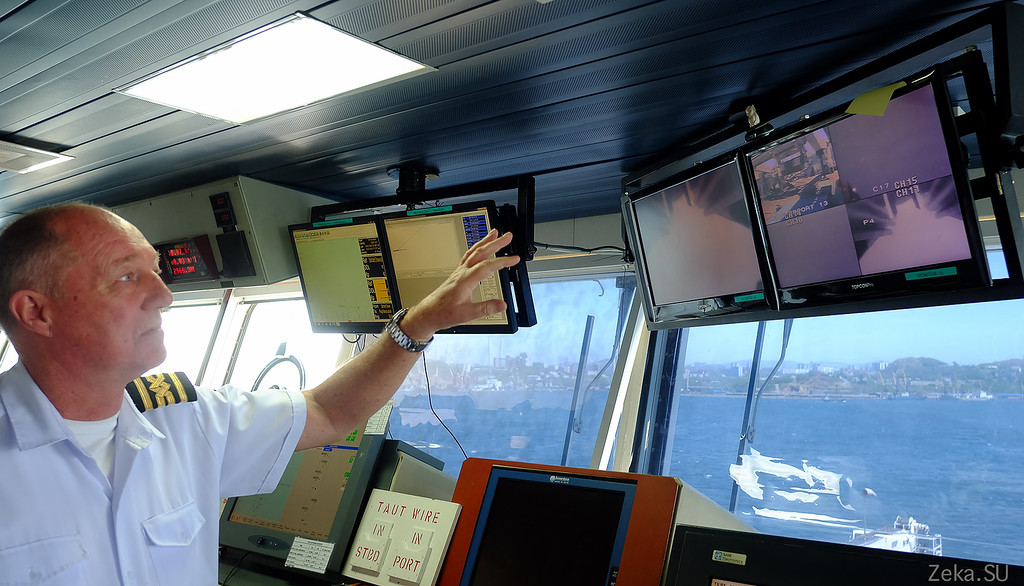
I do not understand anything in the captain bridges, so if anyone knows better, correct me:

Front deck view:

The same, but from the other side:

View from the bridge to the bridge over the Eastern Bosphorus:

Talkies to communicate with the team, and so I understand, telex:

Actually we are on excursions. Rostelecom and media representatives:


One of the control panels. These colored buttons turn on the lights:

Compass:

So I understand, this is the navigator's workplace. Behind him is a box with maps:

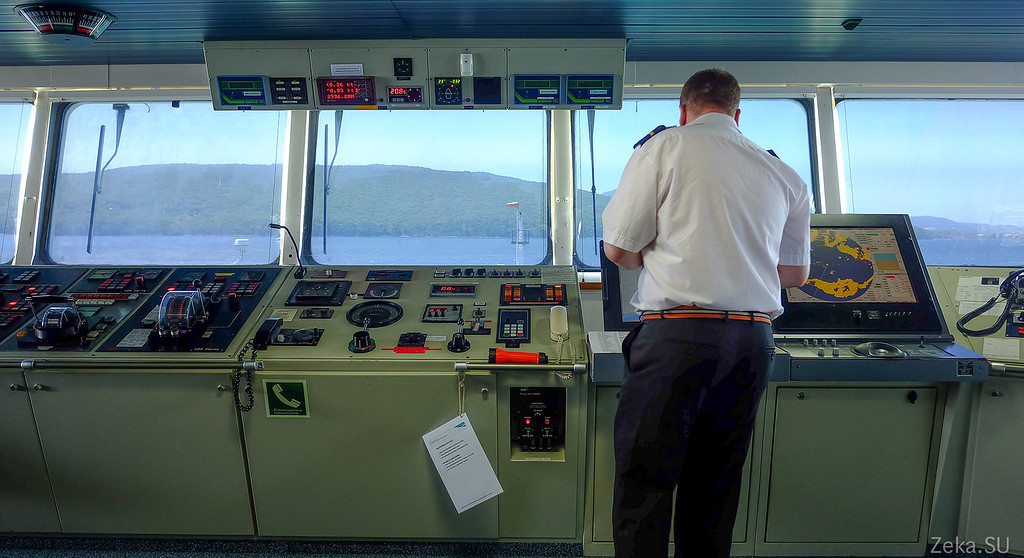
World and Russian navigation, and the actual place of work of the skipper. All these “full speed ahead”, “stop machine”:

Captain, assistant and Alexey Sapunov, director of the Far East region of Rostelecom:
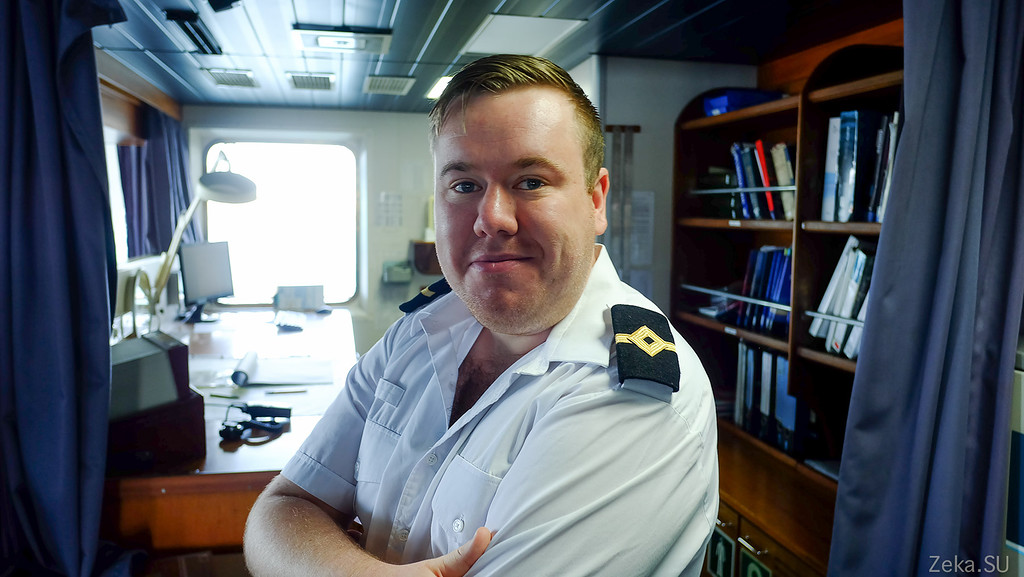


But this is the aft control room. There are more sensitive and delicate ship management tools. With the help of these joysticks and the stabilization system, you can move ships literally one meter to the right and left:
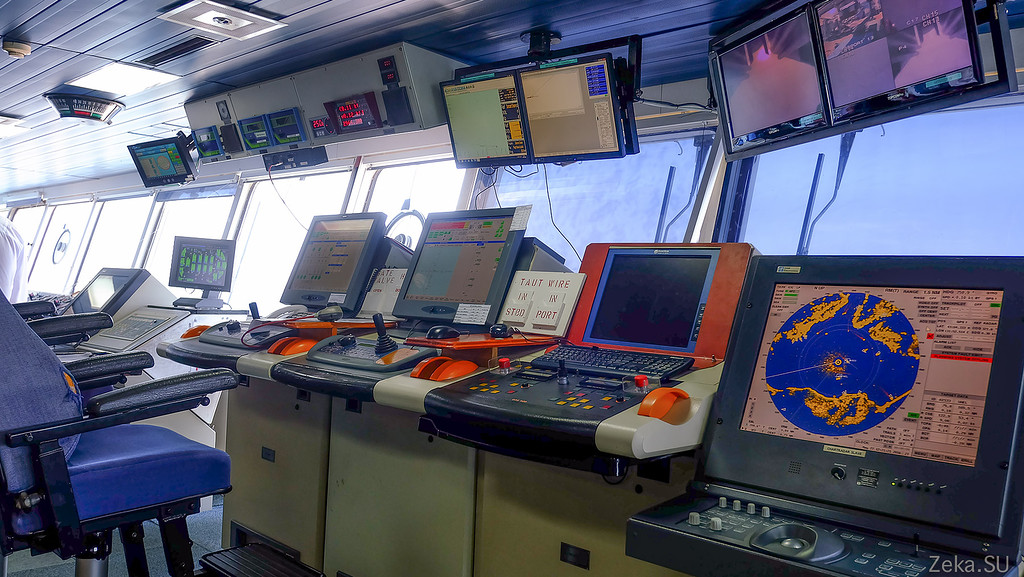


This is also broadcast from cameras installed on the underwater vehicle. At the moment it is swimming under water in the Bosphorus East:

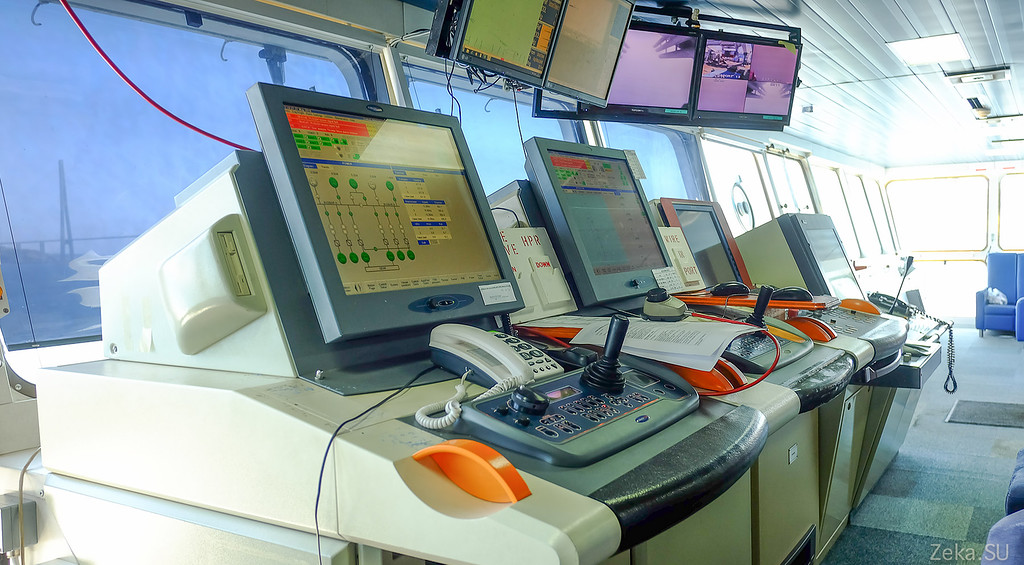
An underwater vehicle at a depth of a pair of meters plows the expanses of the Sea of Japan:

On the sly he photographed a secret map of the seabed of the Sea of Okhotsk with a diagram of the cable. I hope they do not beat me much for this:

Ship Safety Plan:

On the balcony is cozy. Sofa, flowers grow, on the other hand, similarly:

Crew Jobs:


View from the bridge to Vladivostok and the internal raid in the Eastern Bosphorus:

And this is a view of the stern of the vessel. A crane is visible which controls the cable feed and the plow (located below it on the left). In the containers there are additional equipment and ... "offices" of those who manage all this. In one of the containers there is a control room for the underwater robot. This is done so that it is easy to change the functionality of the vessel, depending on customer requirements. Do not need some equipment - unloaded the container in the port and all the rules:

In general, thanks to Captain Christopher Niva for the tour and go further:

On the nose, nothing extra:

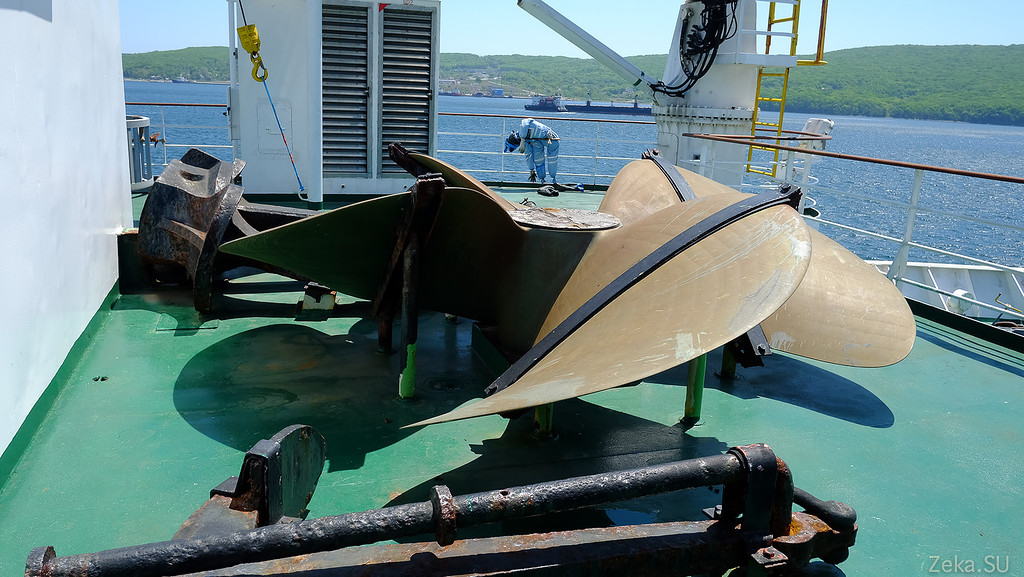
Spare screw and anchors on the upper deck:

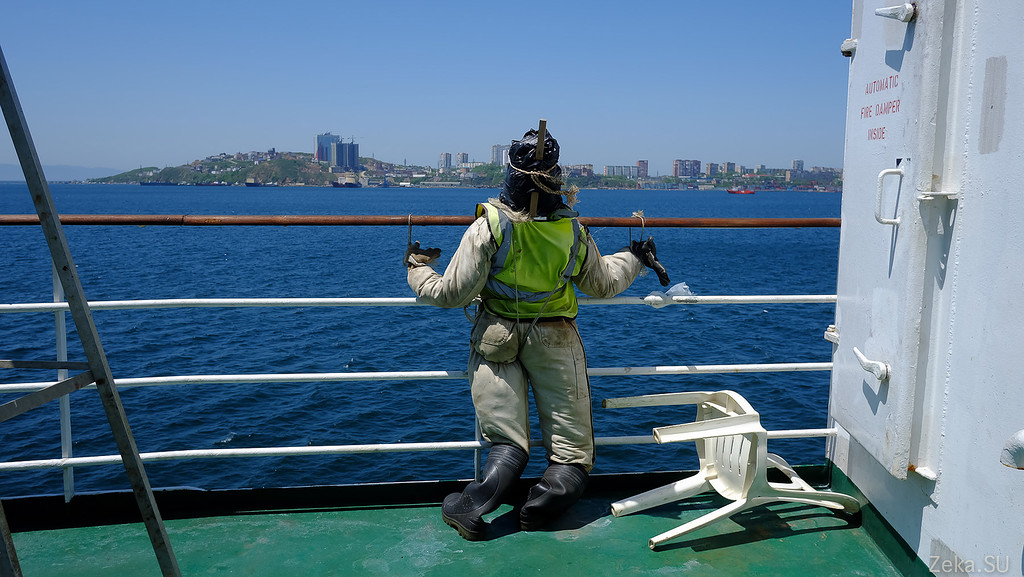
It also smelled fiercely of Asian food from the ventilation system and there was an incomprehensible person:

On the other side was his friend, but without shoes:
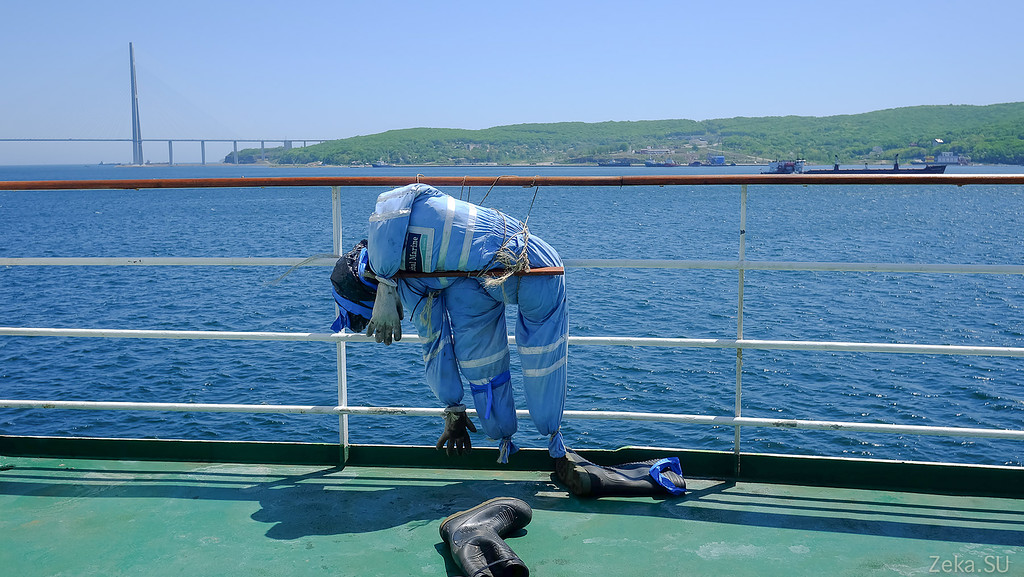

We then argued for a long time who these people were and why they were so punished? Our version was to scare away seabirds so that the deck would not be soiled. It turned out that we were only half right. These gentlemen really work as stuffed animals. Only not from the birds, but from their more intelligent two-legged competitors. It turns out that if you stand on the roadstead in the port, incomprehensible people can get on board from a small boat, and stuffed from afar resemble security officers.
On this deck, they carry out all the work related to cable processing, feeding it to the stern and repairing it. In addition, on this deck are storage facilities - tanks for cable and storage for optical amplifiers.
And now about this all in order.
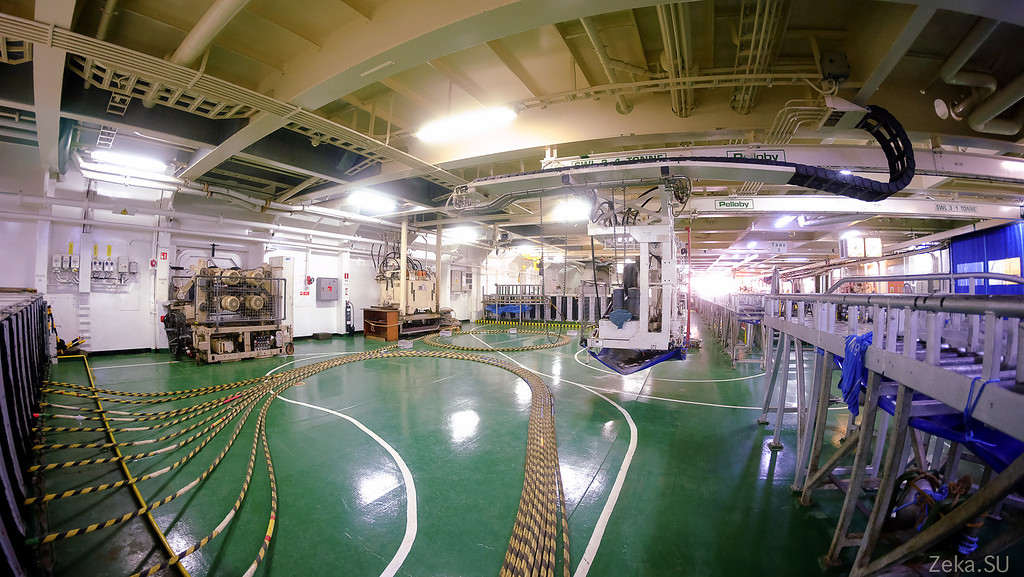
The deck itself resembles a factory floor in miniature: conveyors, hoists, warehouses with products:
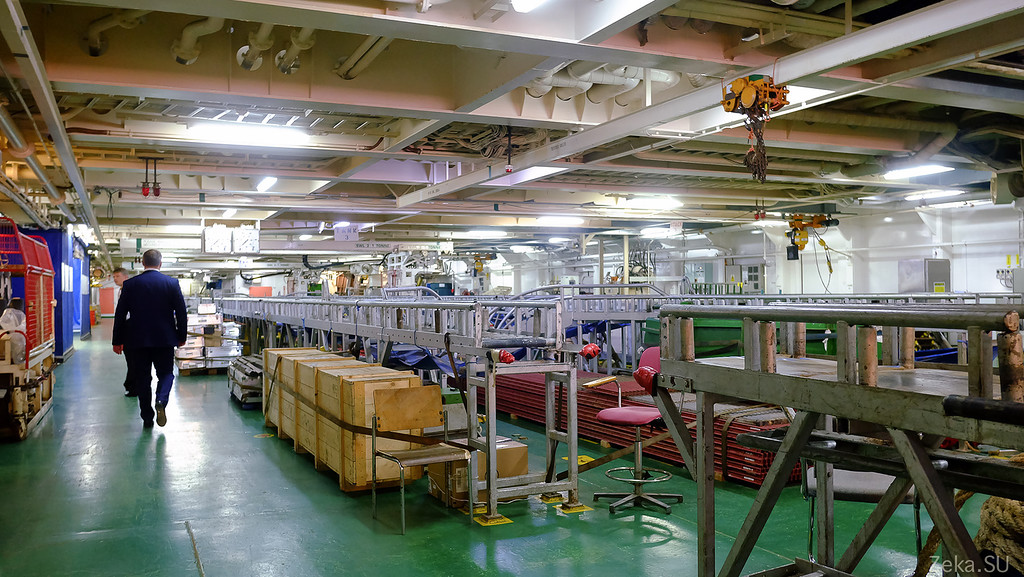

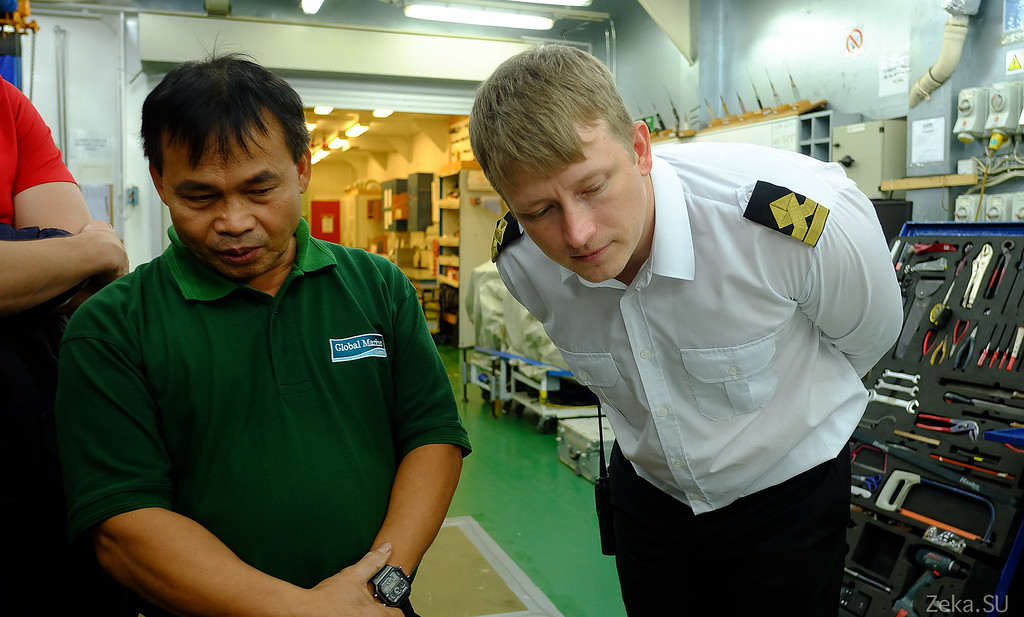
We will not be entertained by the captain, but by the head of the cable deck:

To begin to tell you about the submarine cable.
In my hands in the underwater optical cable in the cut. It consists of several protective shells, plastic, carrying steel or aluminum wires and in the middle are optical fibers:
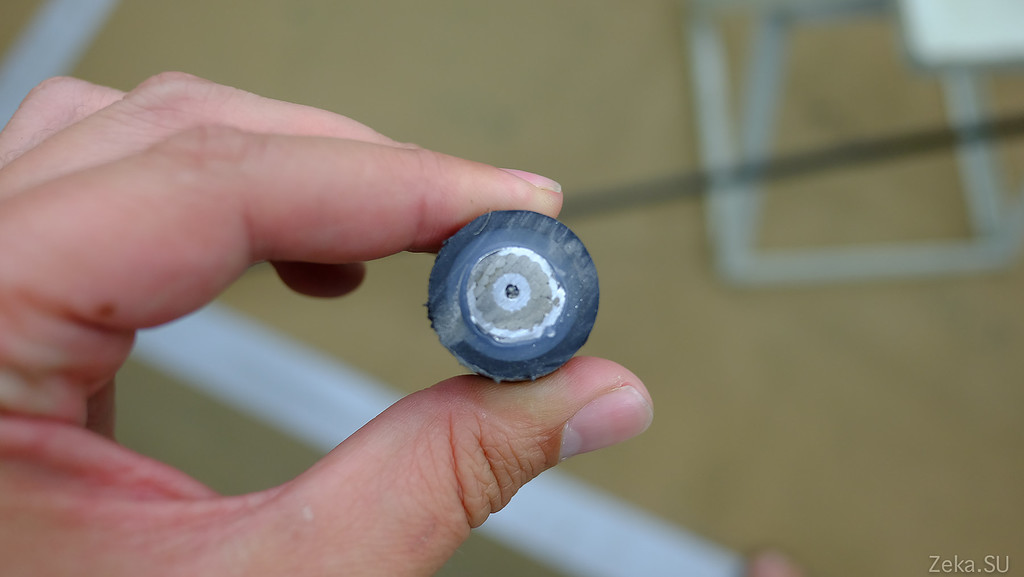

I think so clearer:
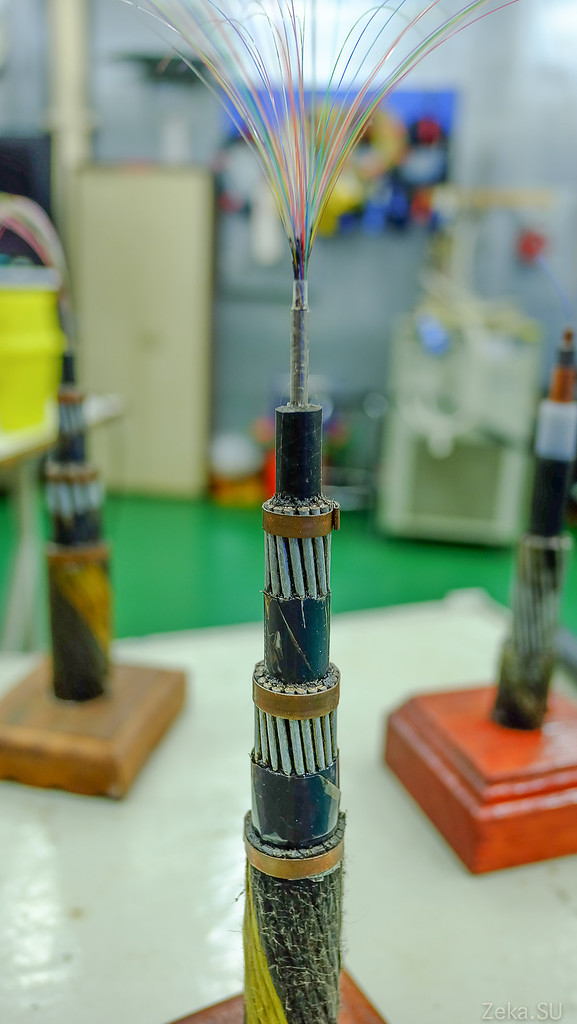

To be brief and concise, it works like this: the optical fibers are inside an aluminum, copper, plastic tube, sometimes filled with grease. The tube is wrapped with an insulating material or filled with polyethylene. All of this is wrapped in steel reinforcing threads that are wrapped with a waterproof sheath, such as polyethylene. Sometimes several layers of supporting cables are used. As in the above photo.
Rostelecom is laying almost the same cable, with the only difference: it has only 4 wires of optical fiber laid. But this should be enough for the coming years, because the sealing equipment allows transmitting up to 8Tbit / s through this cable. What should be enough for these regions with interest for the next thirty years. Naturally, there will be much less traffic, as there are few consumers in these areas and they do not need to feed the maximum flow.
In the welding room there is a whole exhibition of cables that you had to work with:

Judging by the appearance, the leftmost cable is designed for laying in the most dangerous places of the globe. Where not only sharks and crocodiles can gnaw him, but elephants and hippos can stomp on them:

So, we are with you in the welding shop where the cable connection works are carried out. Immediately pay attention to the door with a sign "Do not enter! Dangerously". There is an X-ray room. But we will come back to this later.
The welding shop is necessary for the repair of the submarine cable in case of a break, for connecting the cable from the shore to the submarine cable being mounted, well, or in the case for building it up. In our case, as the chief master of the site said: “We in Kamchatka will connect the cable to the shore end quickly, you have only 4 threads to weld”.

This is a coupler. In it the welded fibers keep within and the ends of a cable are connected. True, we were assured that this sample is old, there are already clutches of the new model, more durable.
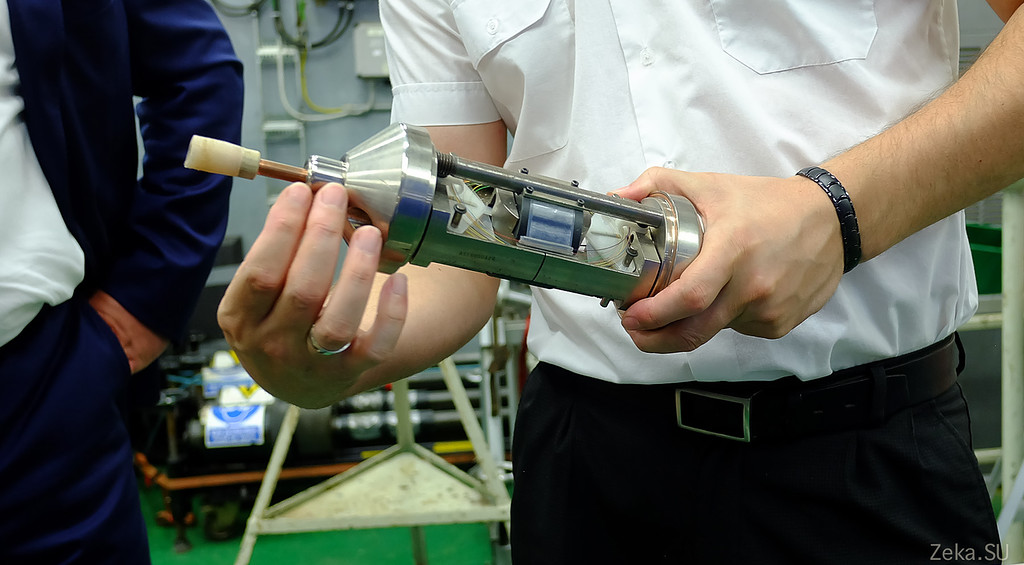

In this way we insert the clutch into the cable break and fasten:
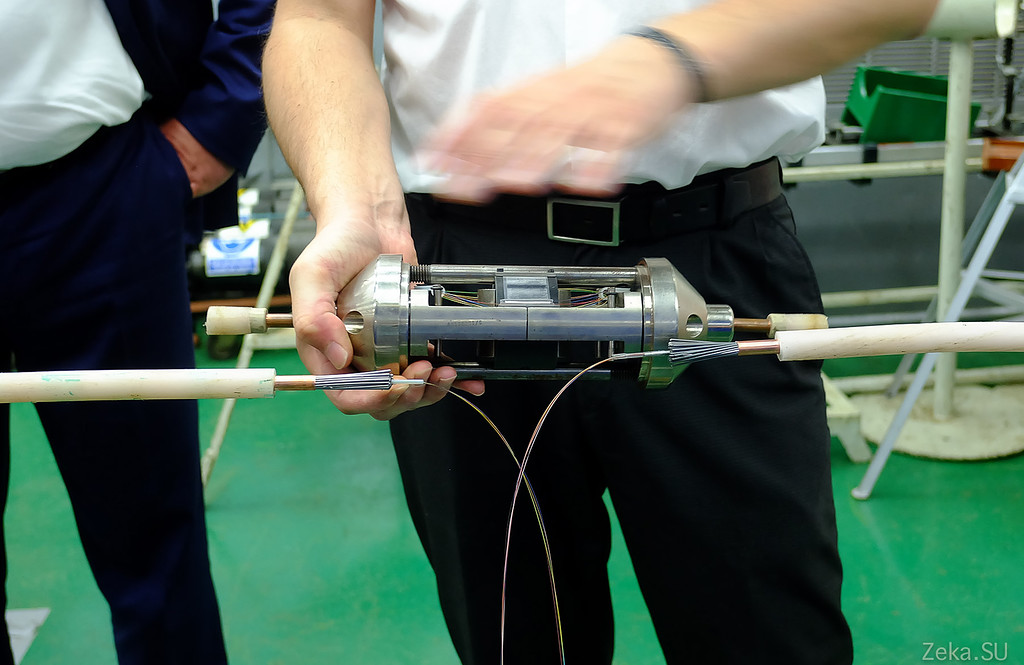
Heavy gizmo:
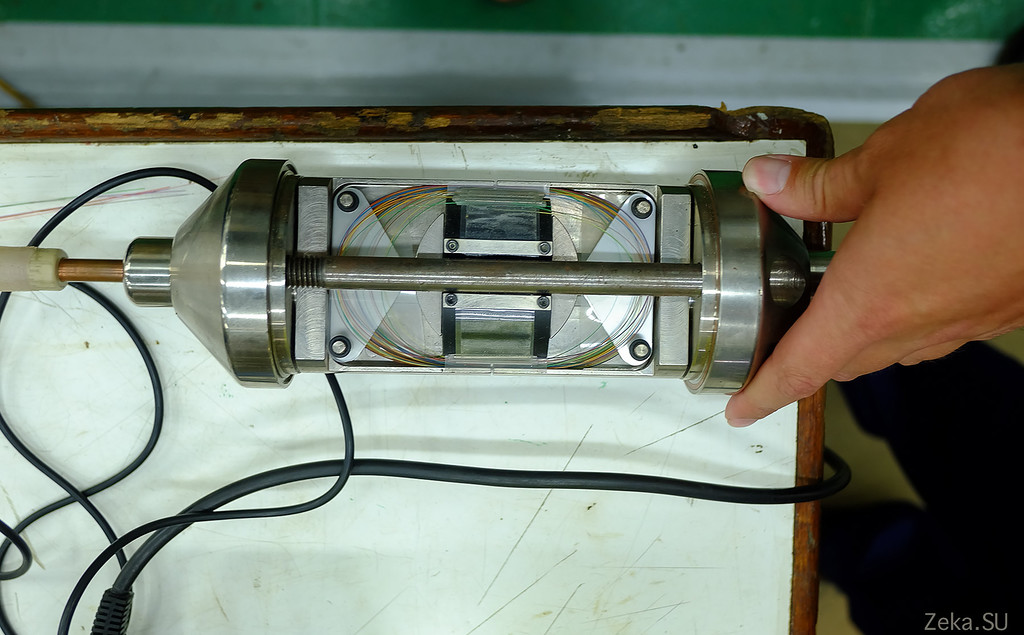

Next stage. Waterproofing. Clutch carefully poured plastic:
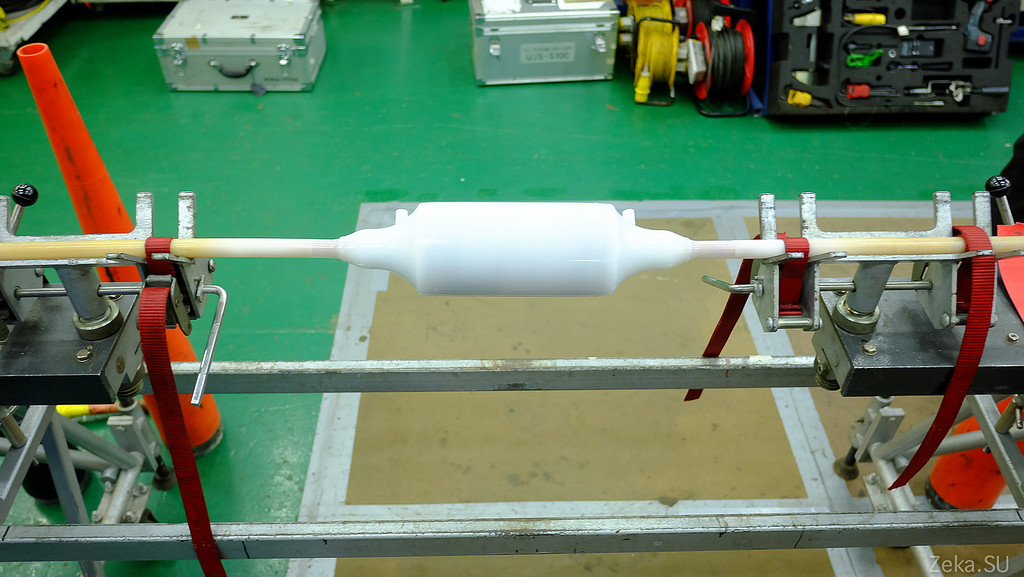
To prevent the clutch from bursting at the junction with the cable, it is terminated with such “rubber” things:
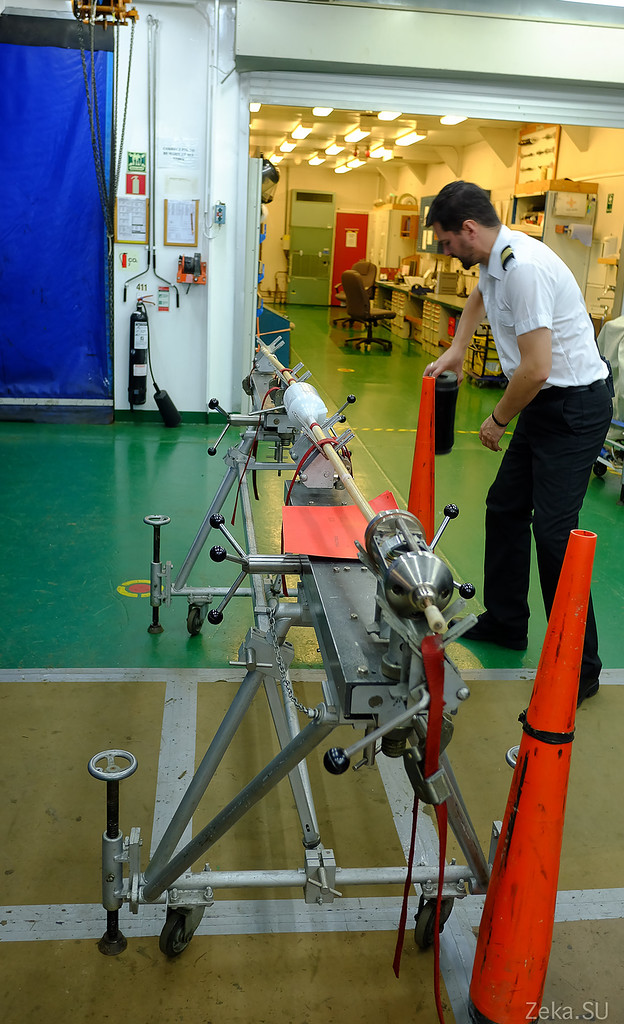

The result is an airtight, heavy and durable “gut” that you can safely carry anything. In one such on a shoulder you will not drag. I understand why they need winches and hoists here:
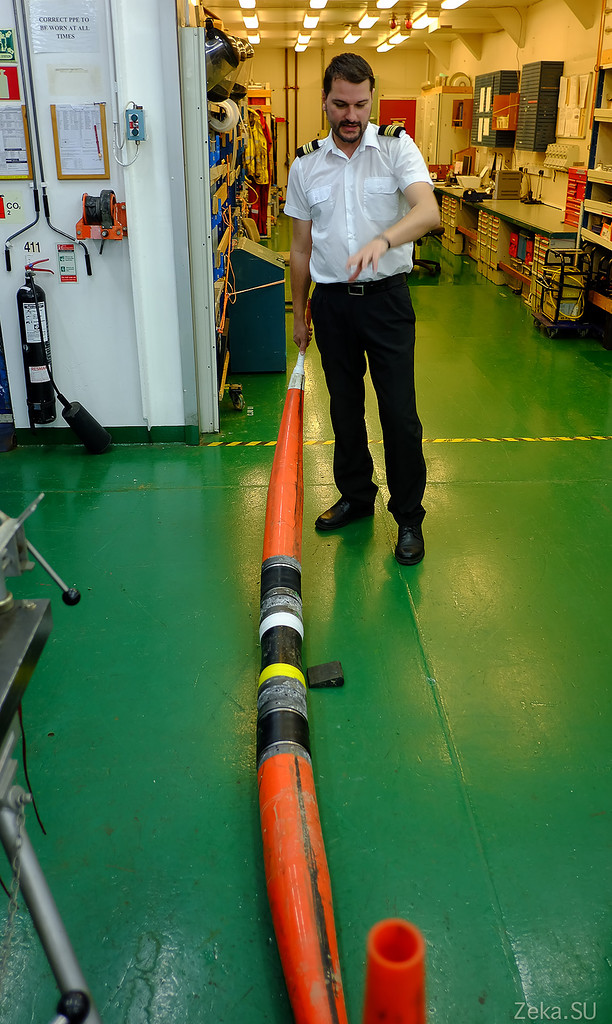

The tightness of the package is checked on x-rays. Remember that cabinet, which is dangerous to enter?
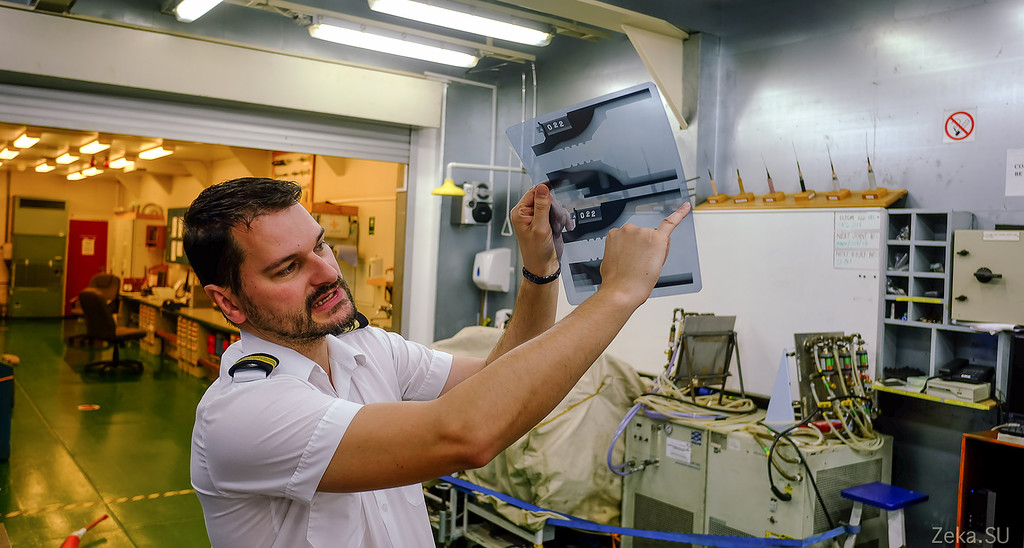

And now about the main thing! The most important thing is to weld the optical fibers well. That's actually the whole set of the young welder.
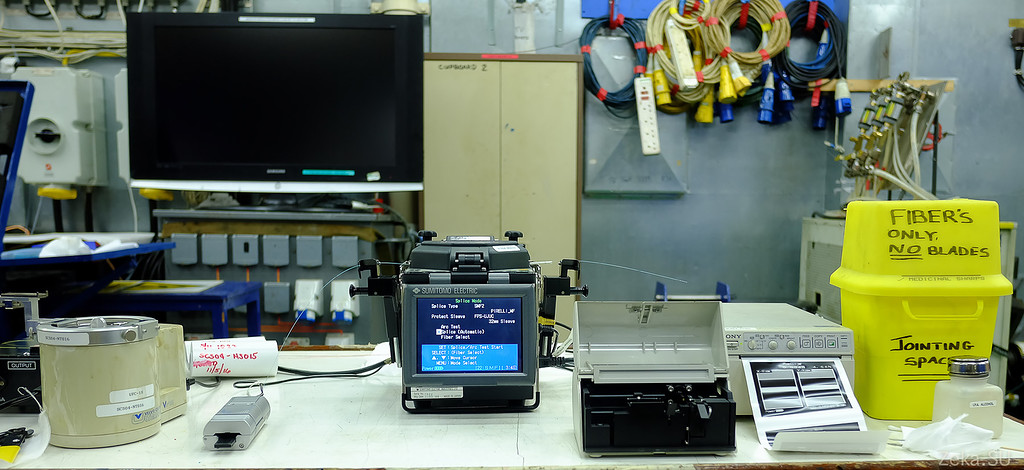

First, the cable is cleaned and the end is neatly cleaved to make it even:

Then the two ends are inserted into the welding machine:
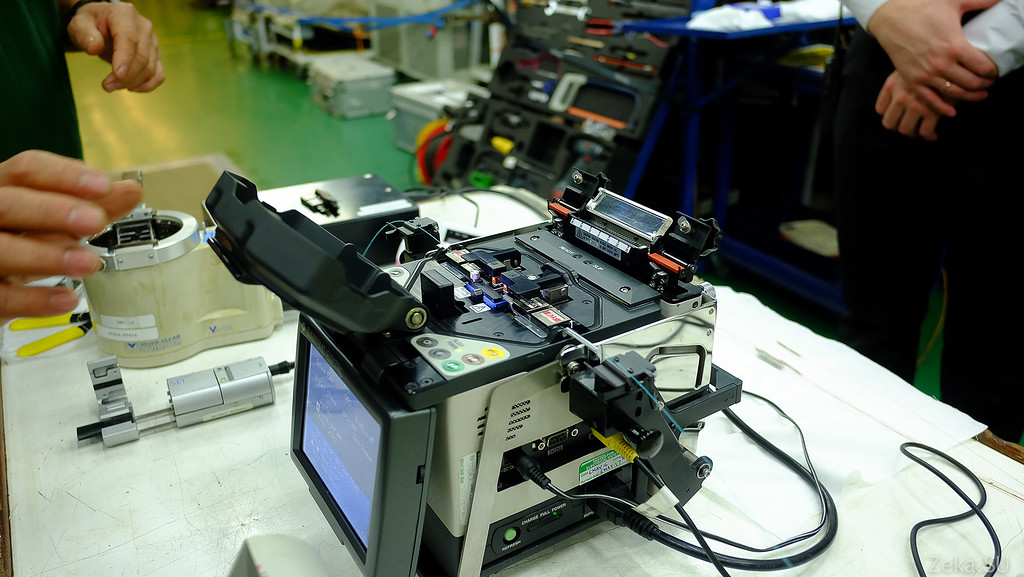
Press the button and watch:

Then repeat this for each core. Just after these operations, all the welded threads of the cable are placed into the sleeve and a “protective gut” is assembled around it:

This concludes the inspection of the workshop and proceeds to the cable storage facilities.
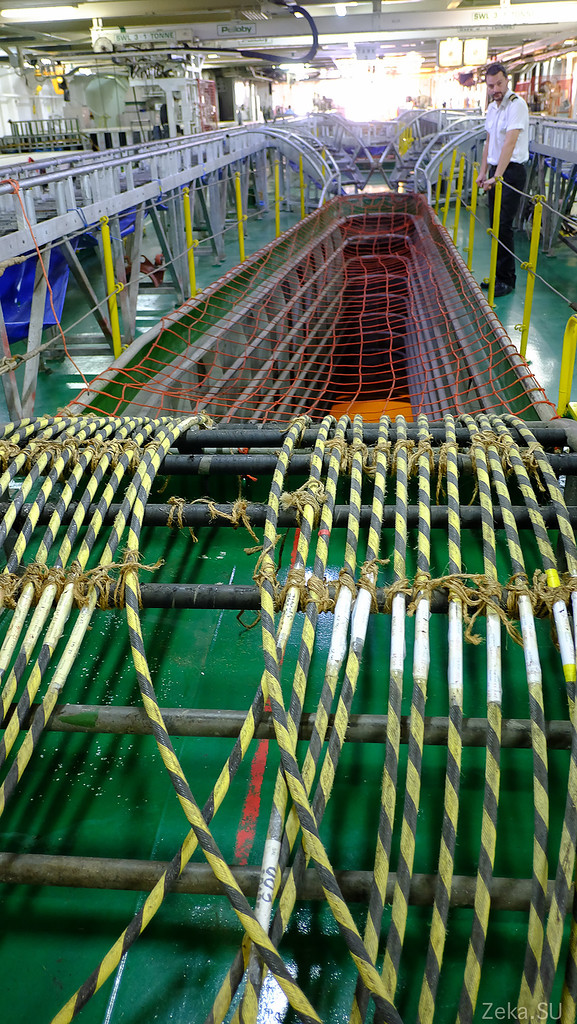
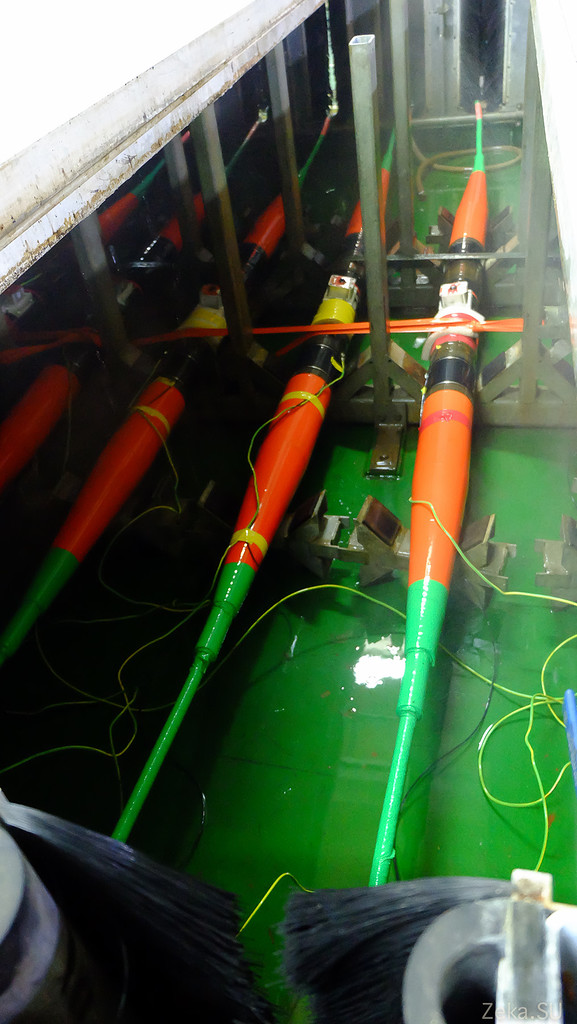
All 900 km of cable are laid in one of three cable tanks:

As you can see, here in the tank there is only 3.5 meters of cable in height:

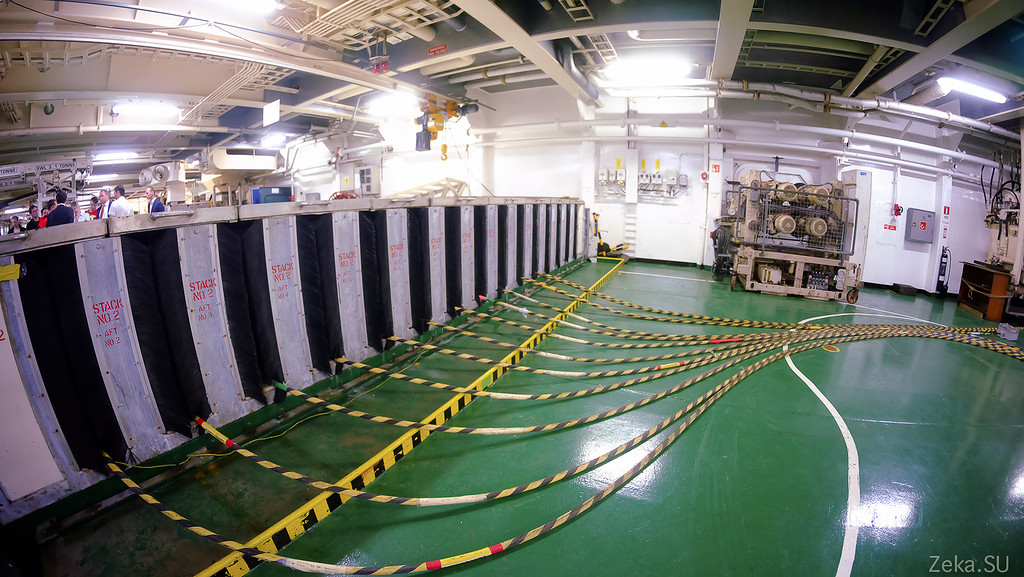
An optical amplifier is installed on the cable, every 80 km. Here they are in a special storage:

A special microclimate is maintained in the storage. Apparently due to the characteristics of the equipment:

Amplifiers are most often made on the basis of doping fiber with a rare-earth element — erbium.
How it works?
An additional high power laser beam, but different from the frequency of the laser transmitting information, is introduced into the fiber and causes the erbium atoms in the amplifier to go into an excited unstable state. When a photon of laser radiation with useful information weakened by a long fiber road, is received by this atom, it receives energy from this excited atom, and is re-emitted with a new force and flies further, more precisely, it is reemitted in the form of 2 quanta and more useful photons become.
For those who write the above incomprehensible, I explain on the fingers.
Tennis balls are thrown into the pipe, on which information is recorded and they fly through the pipe from point A to point B. The pipe is long, and when experiencing air resistance they slow down and may not reach its end. Nearby, along a parallel pipe, the air is pumped at high speed, and it causes the wheel blades to turn quickly like a water mill, or a paddle steamer, located somewhere in the middle of the pipe. Having flown to this wheel, tennis balls get this wheel on the ass, like a tennis racket and with new forces fly further ... another 80km.
Who cares - read a normal and useful article on this topic , well, or Wikipedia .
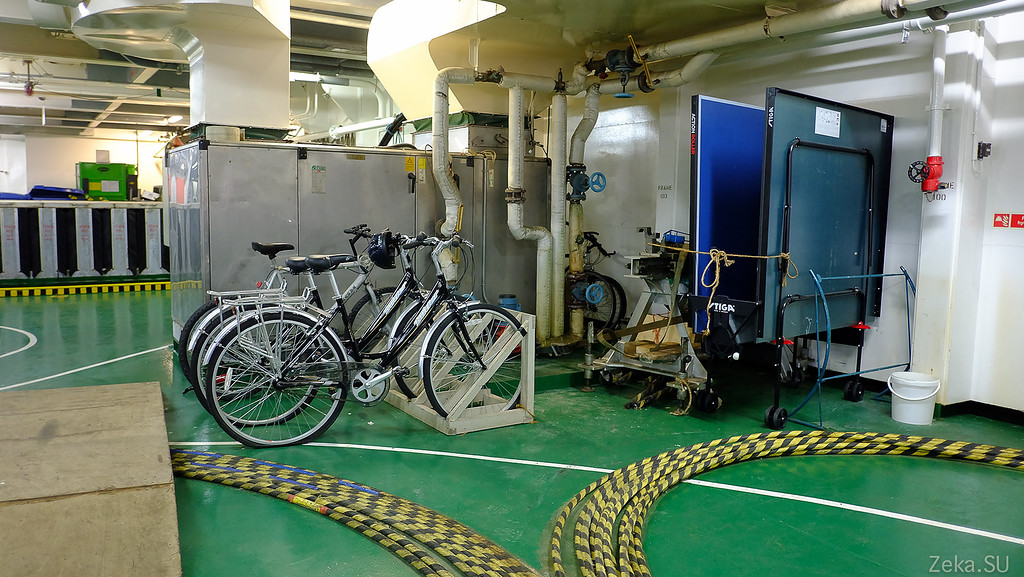
Here are some additional equipment for working with cable. Tennis table and bicycles. The crew revealed the secret of bicycles.
A pier was under repair in Singapore, and there it was too far to go around the port area. I had to buy bicycles. But the secret of the tennis table refused to open. Mysterious English agents:

Self-propelled truck for transportation of amplifiers and ready-made coupling couplings:

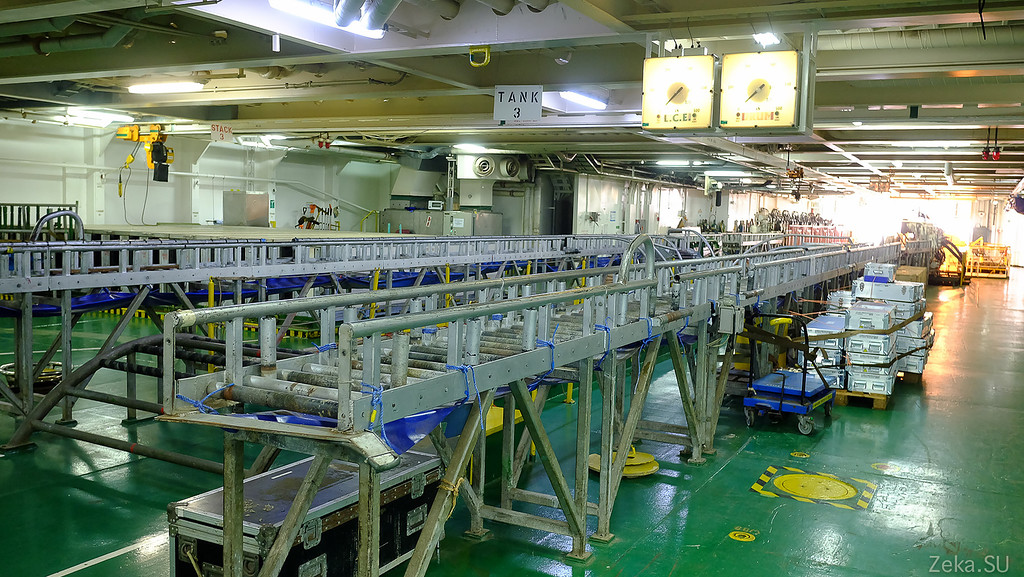
Conveyor with guides for pulling the cable from the hold to the stern of the vessel:

And this is already a winch, in order to pull out or feed the cable into the sea, it is hard to pull the cable from the depth of a couple of kilometers with your hands;
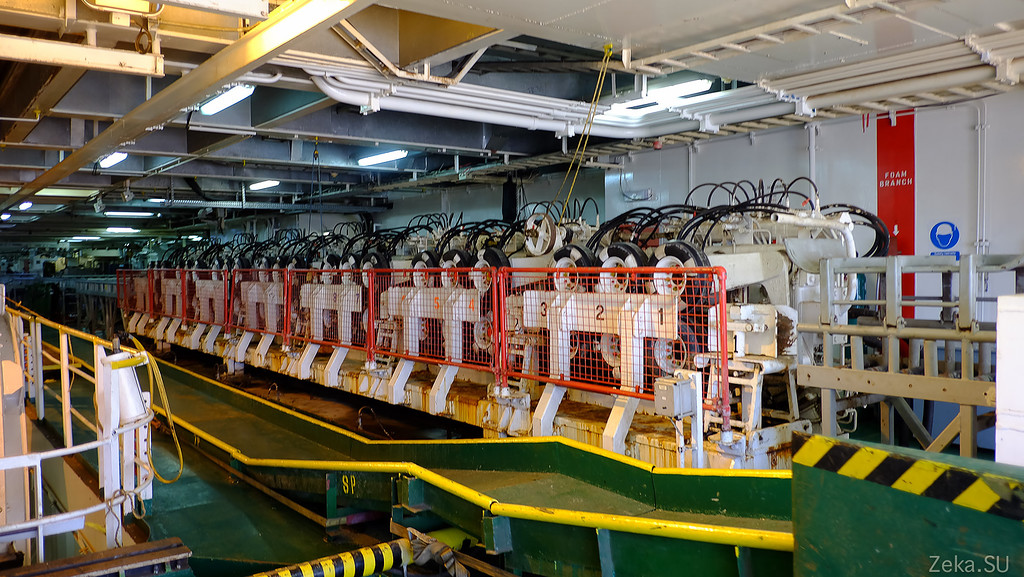

So it looks like in the work:
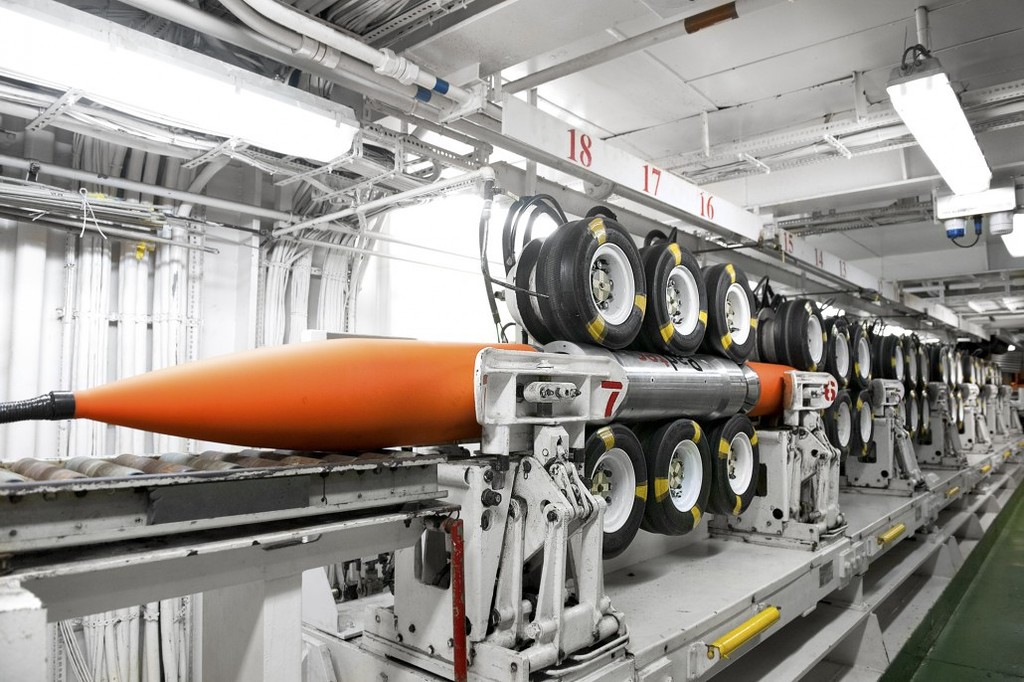

Another part of the feeder:
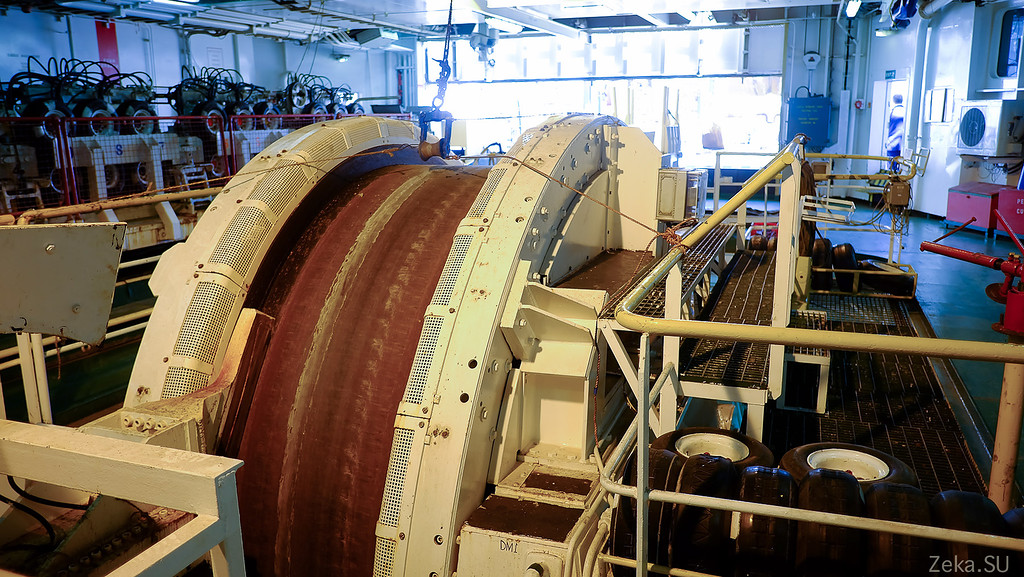
And this, as I understand it, is just spare couplings, amplifiers in case of an unexpected cable break. You understand, it is better to take everything in advance. There are no stores in the Sea of Okhotsk:

. In general, let's thank this person for an excellent excursion and go on. On the stern, where we look deep-water equipment:

All cable laying work is carried out from the stern of the vessel:

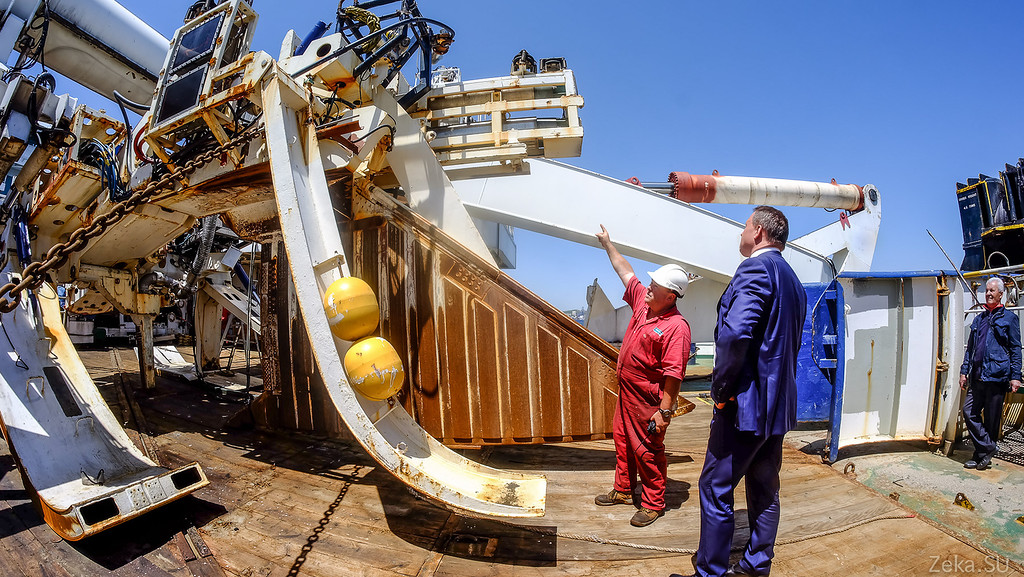
As you can see, there are two cargo cranes here. A crane for lowering the plow, it leans back like on our military search vessels , by the way, is completely new. The team had to replace it recently for repair in Singapore. The second similar crane is located on the left side and is designed to work with an underwater robot.
Crane for the underwater vehicle:
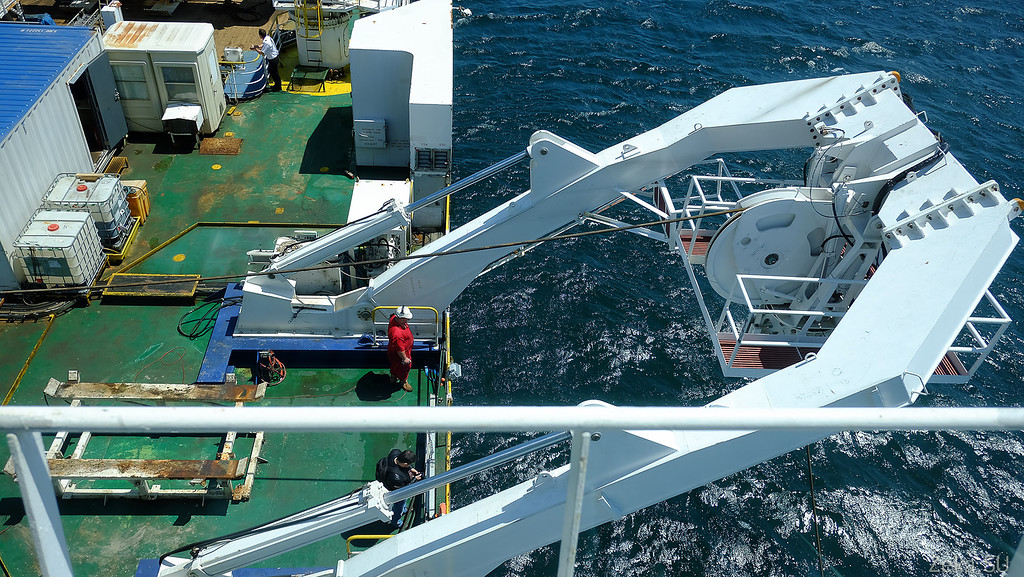

General view of the deck. Workplaces for the operators of management of this equipment and warehouses of consumables are organized in containers:

Head of the deck farm and Rostelecom representatives:

This is a plow. It is lowered into the water, to a depth of 2.5 km and on these skis it drags on a rope along the bottom behind the ship:
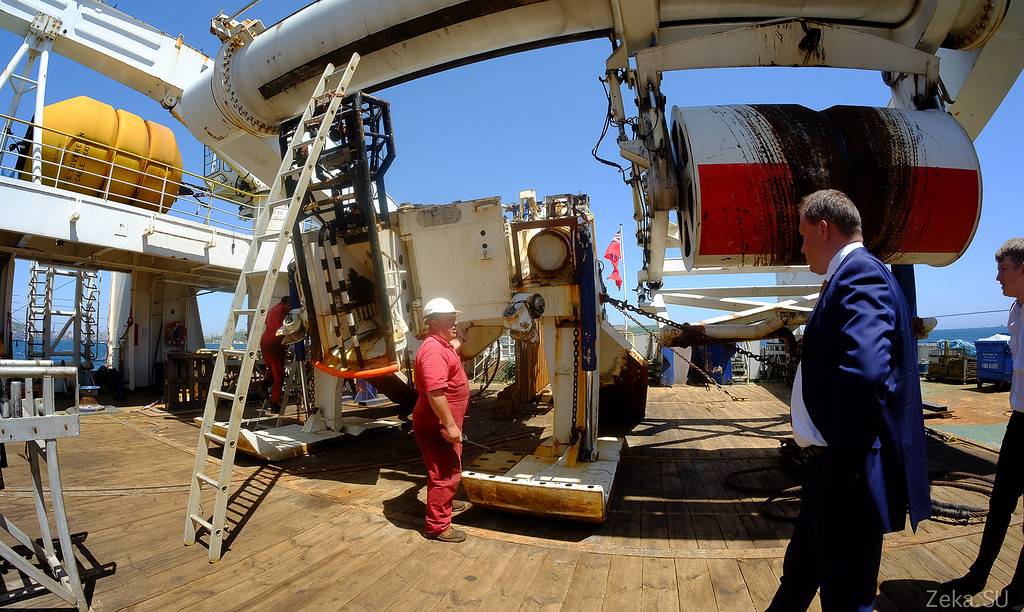

It has cameras and several moving parts to regulate the depth of plowing:
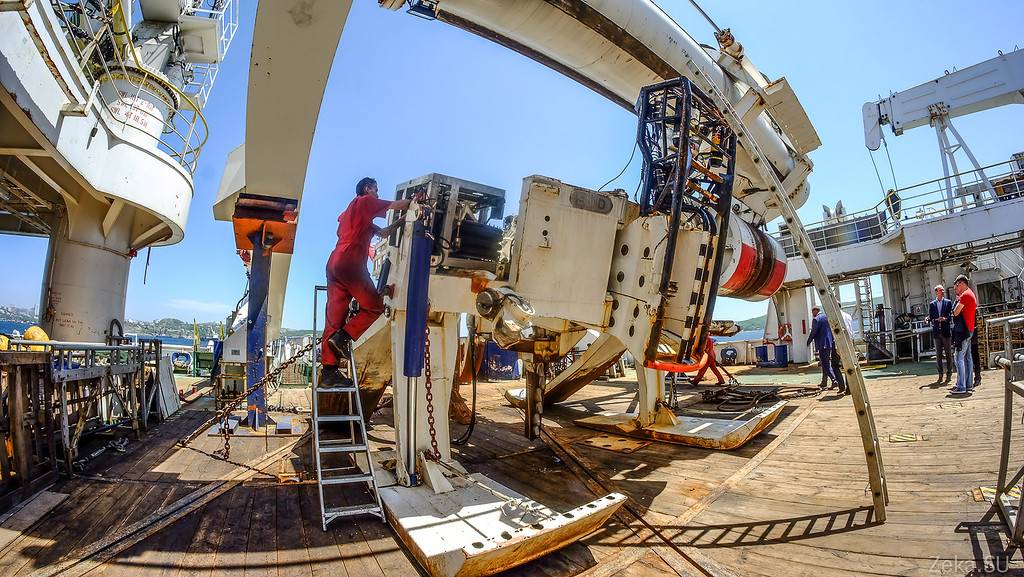

With this tooth, he plows the bottom to a depth of 1-1.5 meters and the cable is laid in a trench:
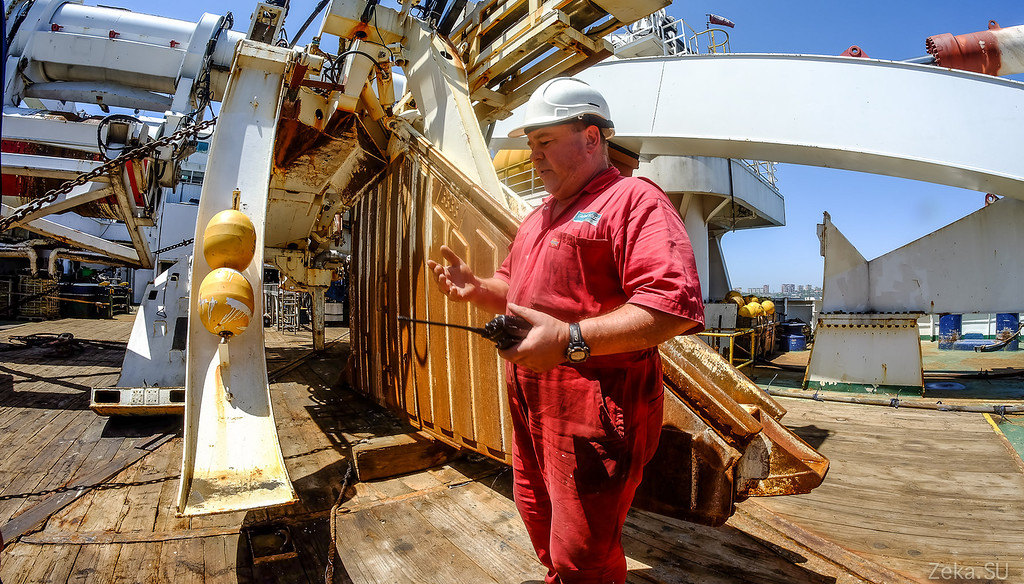

The dude told that in the Sea of Okhotsk, when laying a cable to Magadan, it was difficult. That plow sank in huge sediments of silt, then ran across rocks and even broke a couple of times. I had to get, cook, repair. In general, have suffered enough. Add to this still cold weather:
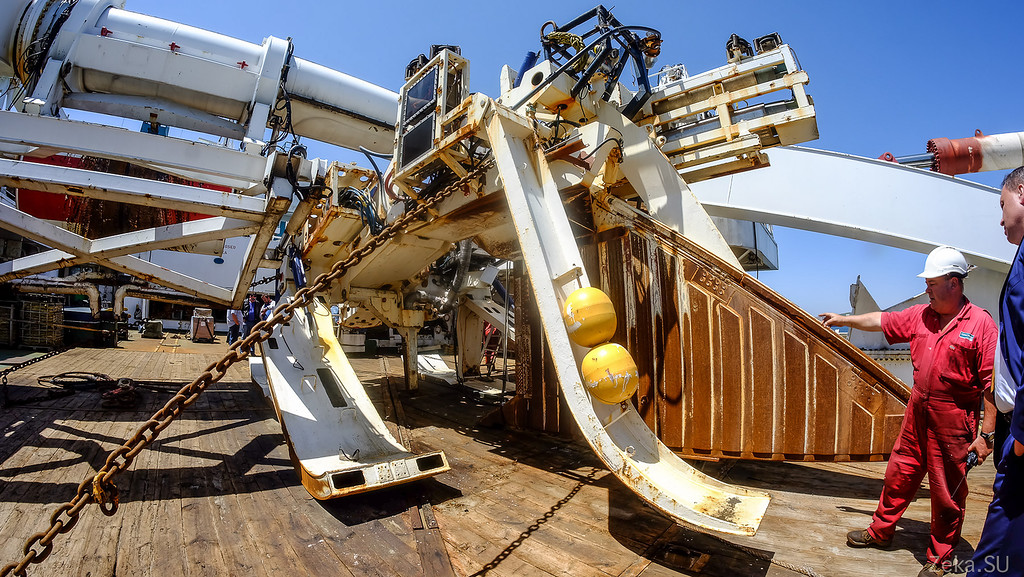

Awesome design. Compare with human growth:

Actually, through this hole below, they place the cable in the trench:
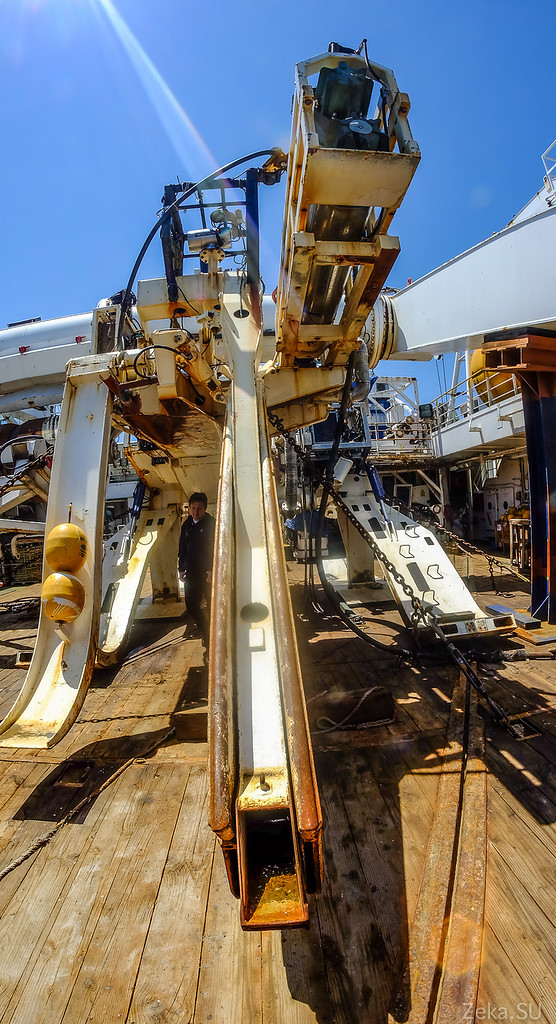

It looks like a plow that went into the depths of the ocean:

The photo shows a crane, cable conveyor and plow cable in coils:

We now turn to the robot.
Underwater controlled vehicle. It is used for fine work with the cable. For laying on the stone bottom and searching for cable breaks:
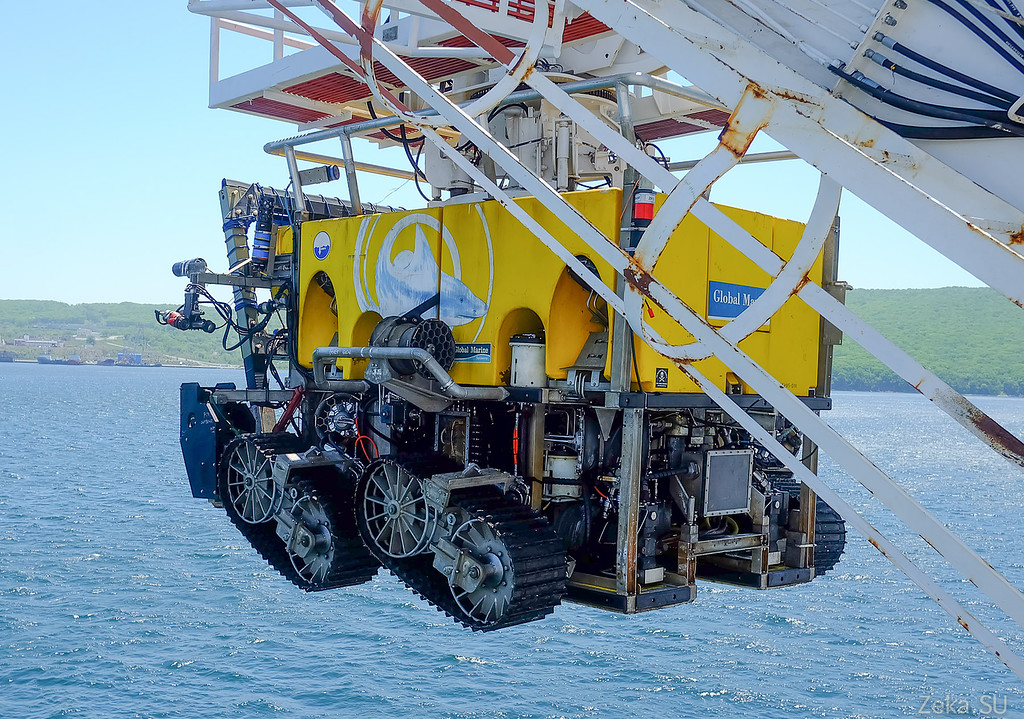

The robot is equipped with cameras, he can swim under water and ride along the bottom. Hydromonitors are on board to erode the soil, or vice versa, to cover the cable with soil:
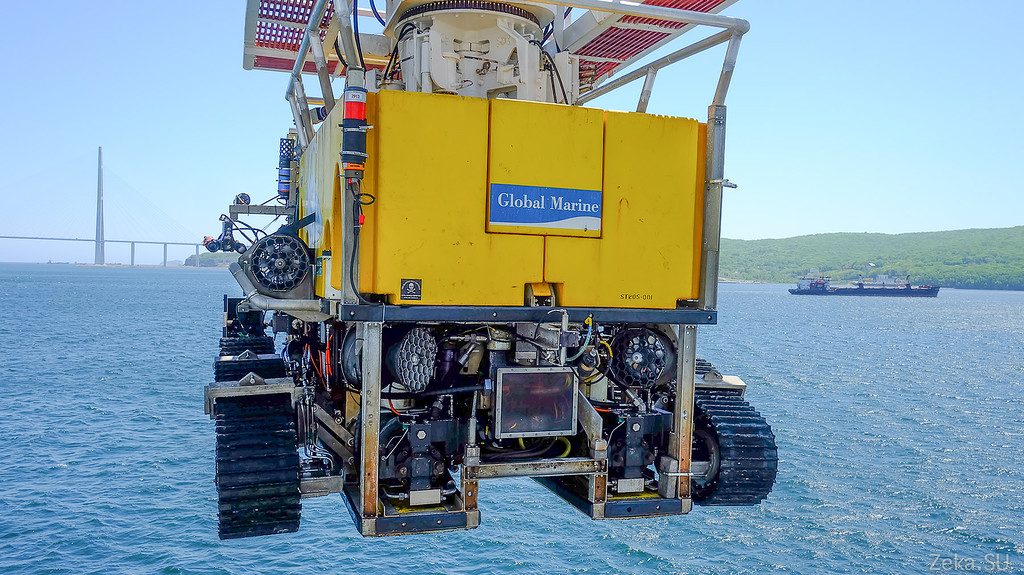

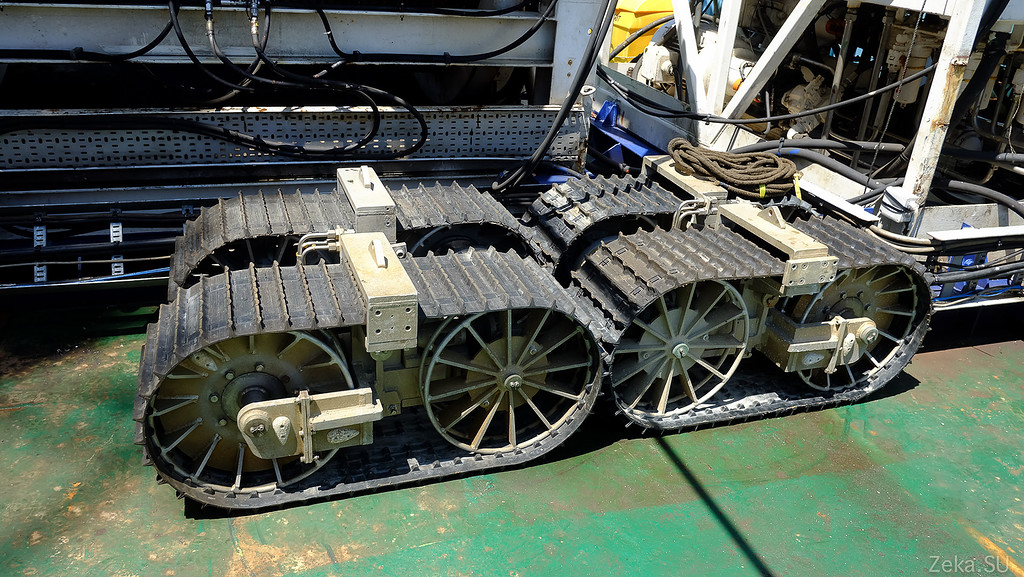
Deck for maintenance of the robot, on the background of spare tracks are lying:
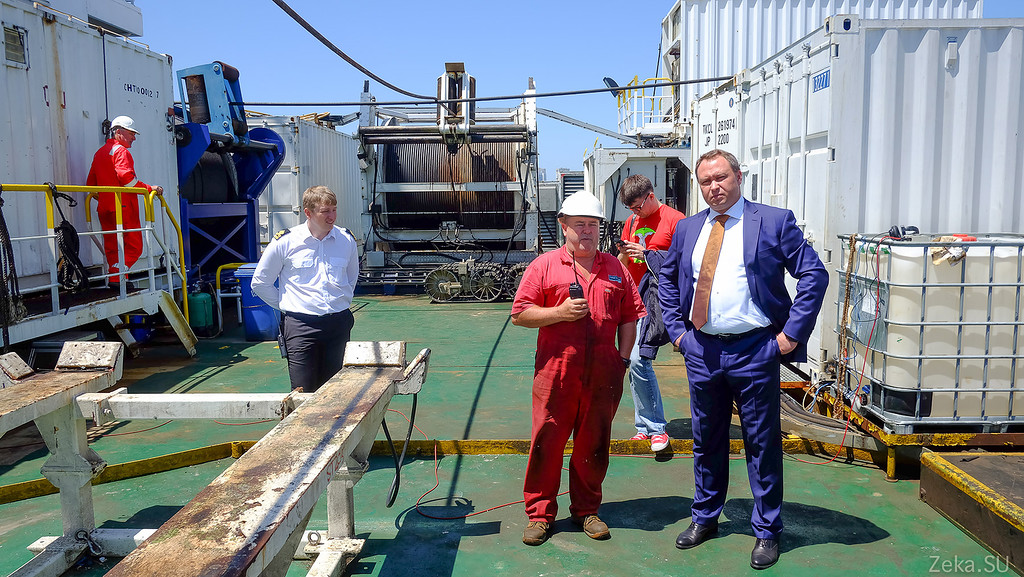

Agree - handsome. In our country there are definitely no such:
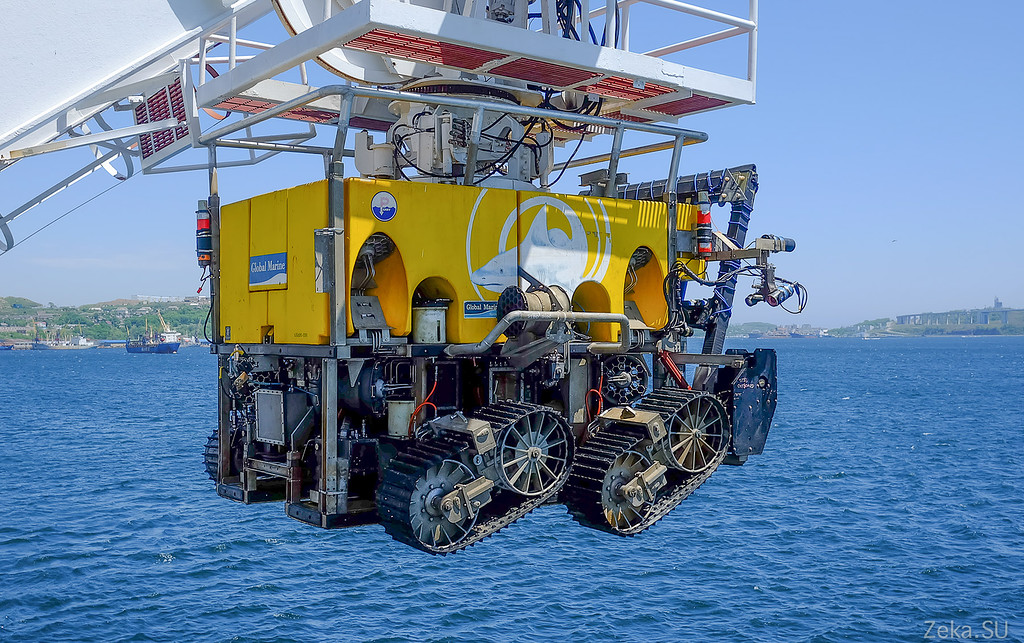
Laying the cable with a robot is much slower and more expensive. For example, consumables:
- Want to see how he can swim with us?
- Of course we want!

And here we were immediately kicked out of the deck:

And he was sent down to conquer the depths of the Eastern Bosphorus:

Crane operator:

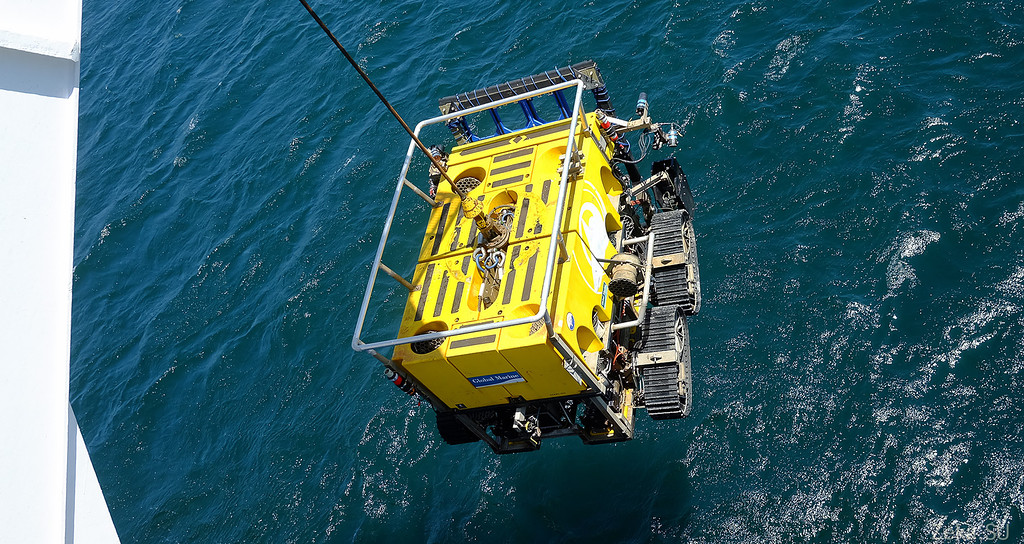
Find a robot?

In one of the containers the control room for the underwater unit was built. The robot is controlled by 2 driver-operators:
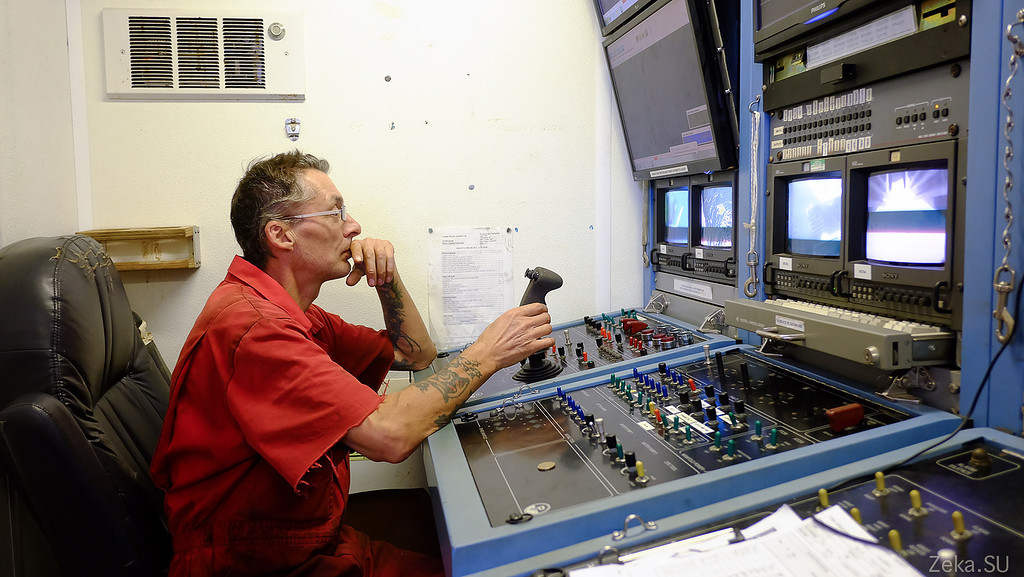

It has several cameras installed, both navigation and, for example, a camera that controls the state of the suspension so that it does not fall off:
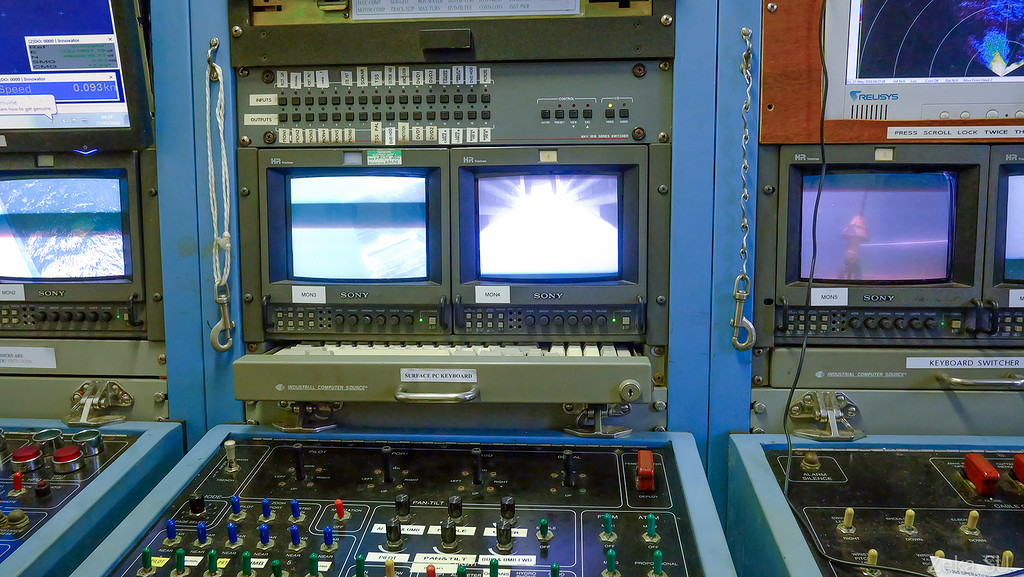

There is also a sonar, and cameras that are just installed at the work site with the cable to watch the work of the manipulators and hydro-monitors:
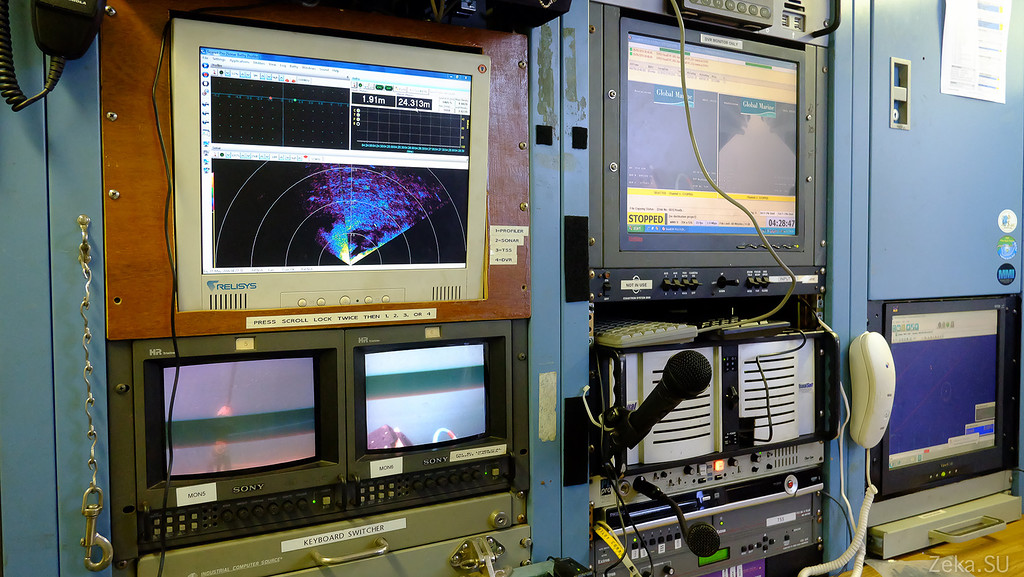

They did not sink to the bottom, they float at a depth of 2 meters:

Telemetry:
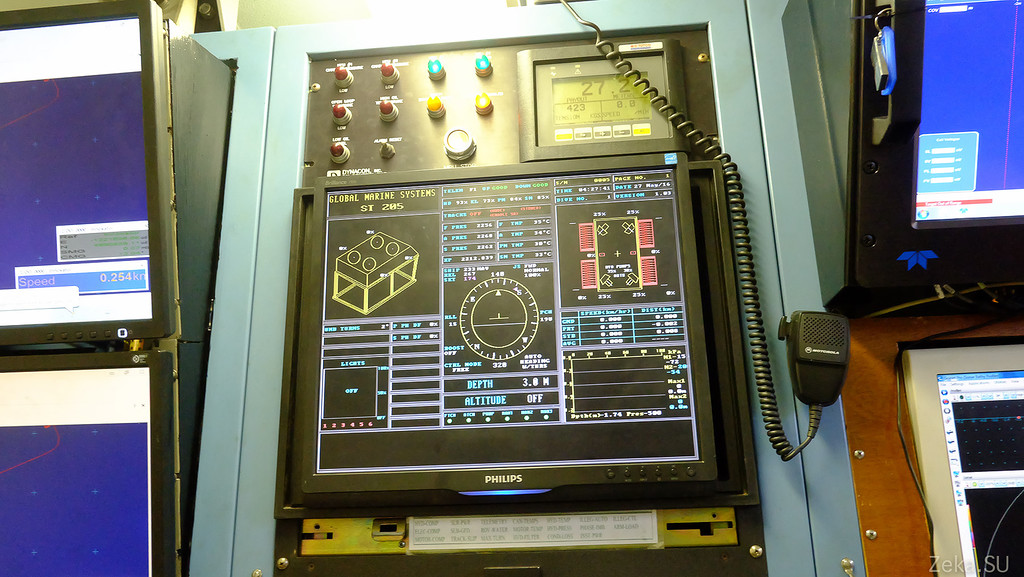

Control panel:
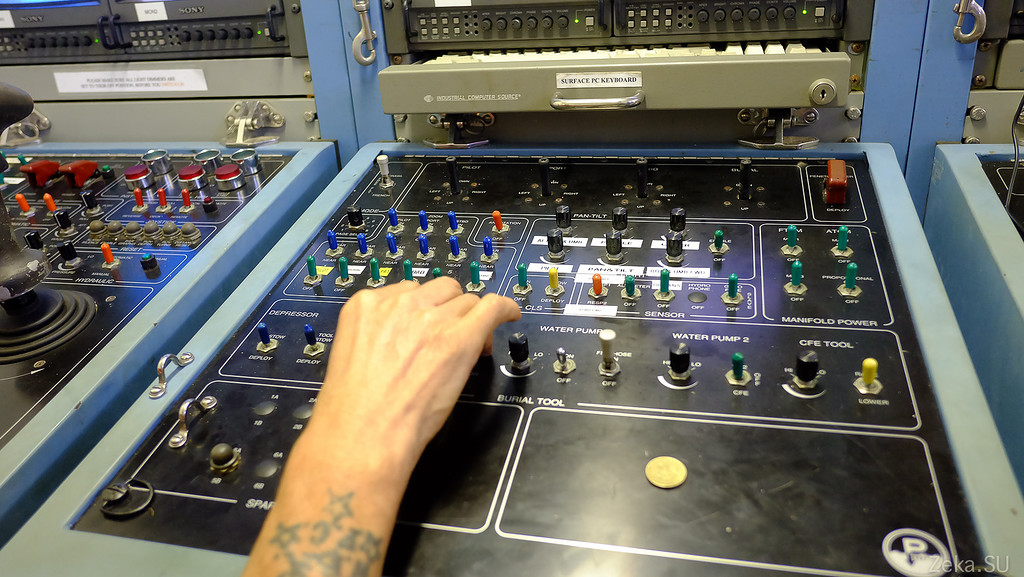

And here is the second driver. Hiding around the corner:

At this point , we will thank this wonderful man for a smart excursion:
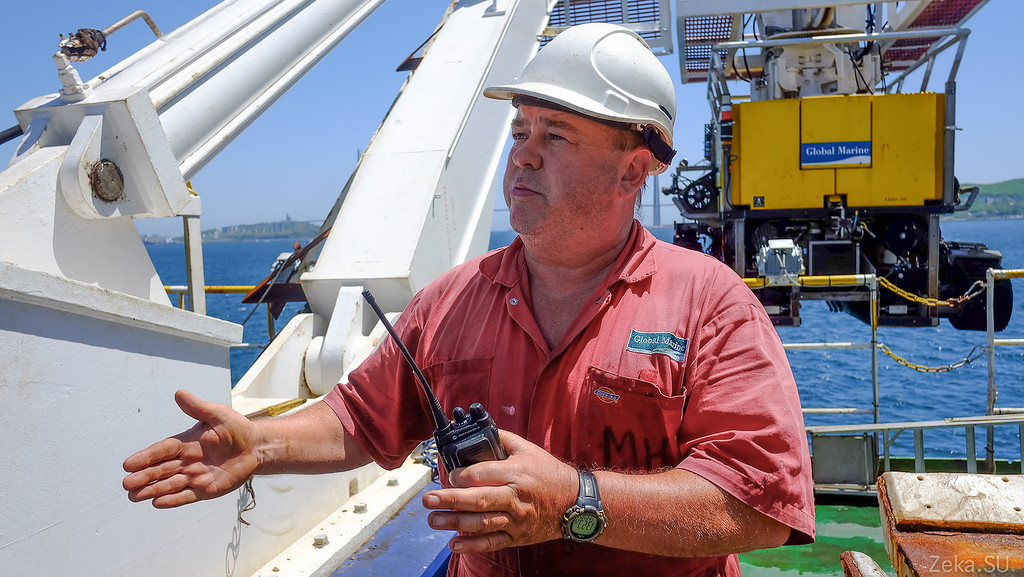

In general, on this positive note, I, perhaps, will end my excursion aboard the cable layer.
Of course, it’s a pity that in such a big country there are no vessels of this class, but the country itself has no task for laying ocean cables. For forcing rivers and bays, more than just simple technical means. Such work probably can do the military, but the military perform only work aimed at ensuring the country's security. And here is another.
Thanks to the company Rostelecom, which invited me to this beautiful boat.
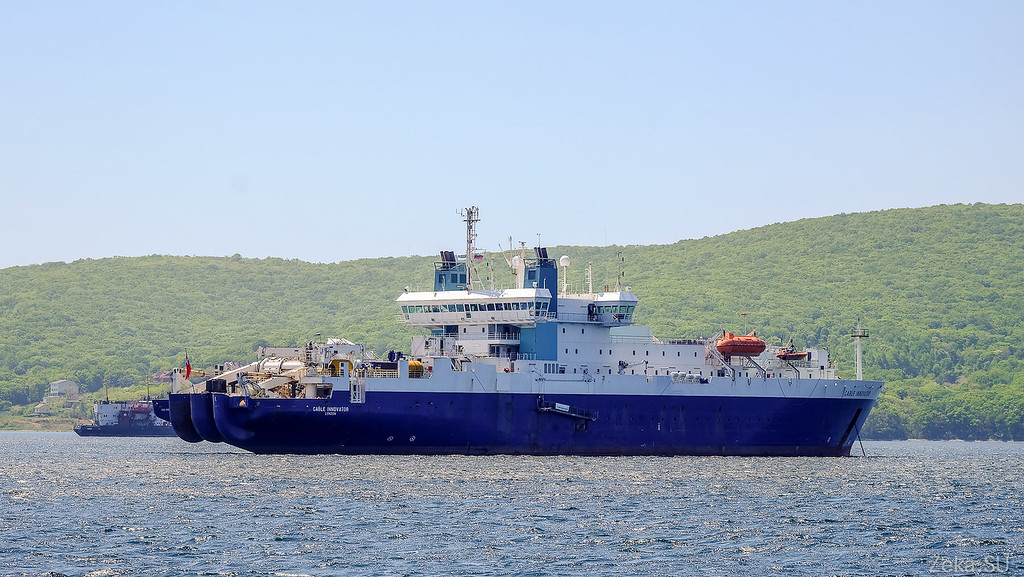
Last year, this boat already came to our port , but, unfortunately, it did not take excursions. And this year, apparently under the impression of the successes of last year, Rostelecom invited several media representatives on board to show this miracle of technology, which is the most difficult work in this project.

Initially it was planned that during the summer of 2015 all the works on the project would be carried out and both branches of the AOLS would be laid in Magadan and Kamchatka.
')

But the Sea of Okhotsk turned out to be inhospitable and did not accept the entire cable. Weather conditions and bottom relief did not allow both branches to be laid in one season. And now, at the end of May, able Innovator arrived in our city to take on board part of the team and specialists from the customer companies Rostelecom and Huawei.
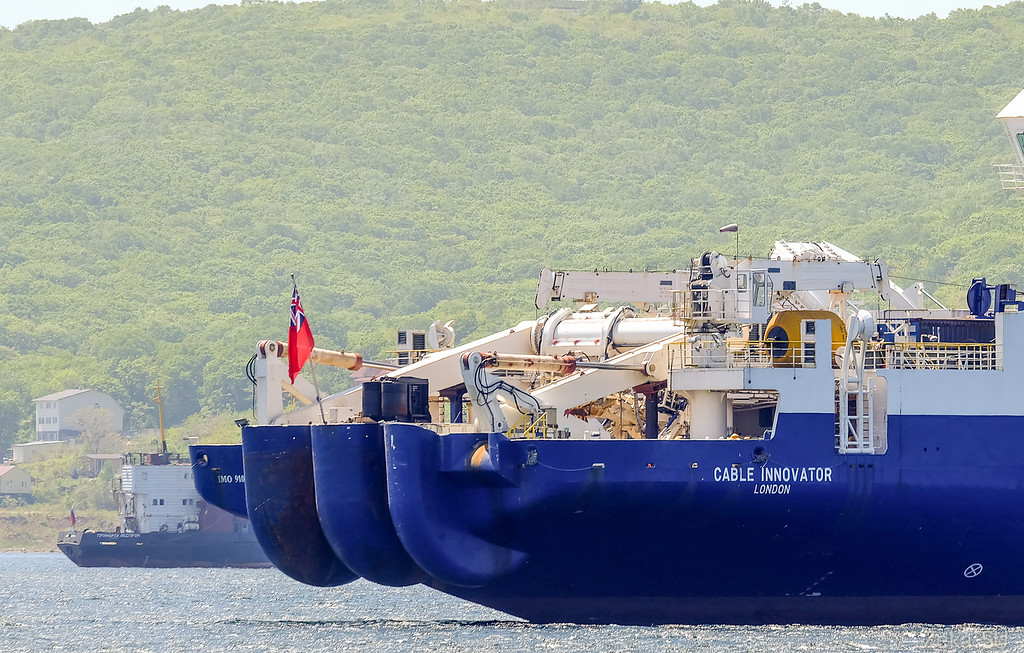
So, able Innovator is the world's largest cable laying machine for optics, built in 1995 at the Kvaerner Masa shipyard in Finland. It is a diesel-electric (diesel engines, but the drive for electric screws). Equipped with a bunch of stabilization systems and thrusters in order to position the ship in any conditions with an accuracy of one meter (as the participants of the works complained to me, because of the additional propulsion units installed on the ship along the sides, they prohibit fishing from the side so that the line is not tightened in the mechanisms; oh, sadness, sadness, grief).

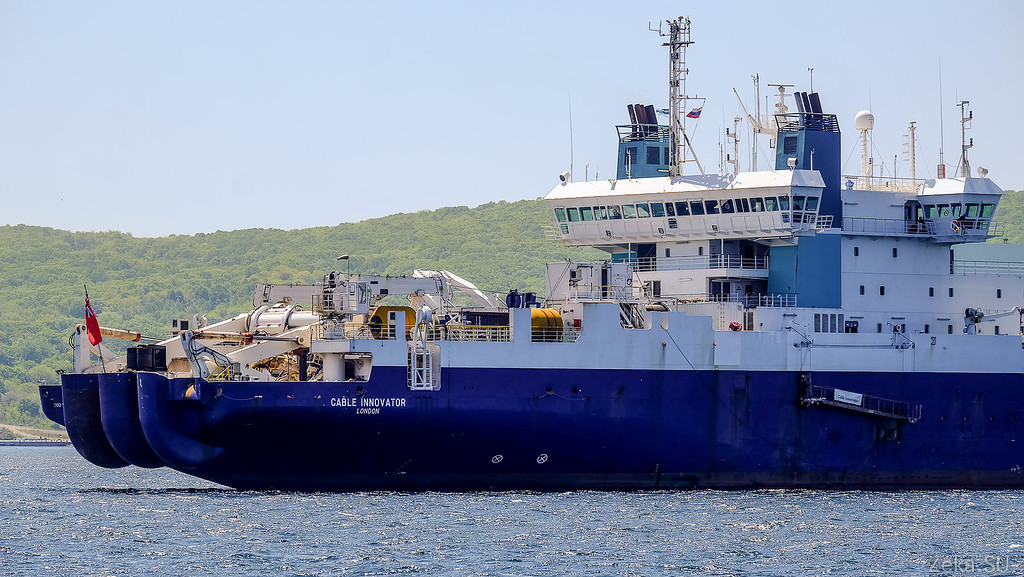
In the photo you can see that it is equipped with two cuttings, fore and aft. In the stern cabin there are staff members who are responsible for the process of laying, in the bow, everything is the same as in all other ships: the captain, the navigator.

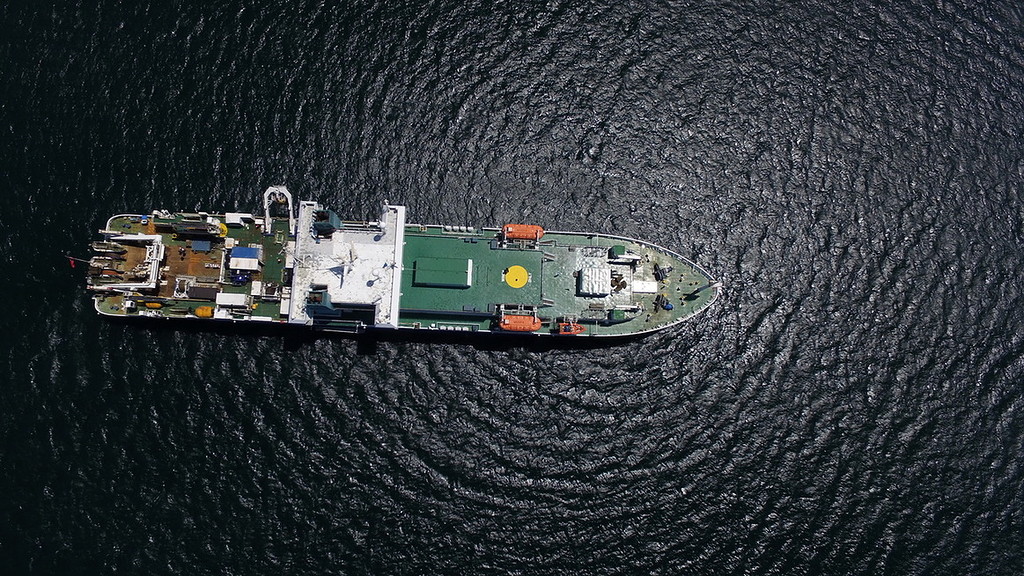
There are 3 holds for the cable tank, their capacity is enough to lay the cable on the floor of the globe.

Scheme of the device of a similar ship:

For laying under water, 2 devices are used - Plow and Robot. The plow is lowered from the stern and dragged behind the ship. He plows the trench at the bottom of the sea and lays a cable into it. Plow is the main tool. But the robot is already used in emergency cases, when there are rocks on the bottom of the sea, when the cable breaks and you need to find its end, and for the repair of submarine cables.
I will divide the tour into 3 parts:
Part 1 - felling, captain's bridge;
Part 2 - Cable Deck;
Part 3 - Underwater tools Plow and Robot.
Submarine cable laying technology
On Habré already wrote similar materials, and therefore you can not read anything new for yourself.
In order for you to understand a little how to lay the cable in general, I will tell you a little theory.
Works are divided into several stages:
1. Research and design
At this stage, the bottom of the sea is investigated, or ready-made materials from previous studies are taken. Depending on the relief of the bottom, the route is built. Naturally, current communications at the bottom are taken into account. But the benefit is that the Sea of Okhotsk is not rich in underwater pipelines and underwater optical highways, well, except that the secret communication cables of the Pacific Fleet to which enemy submarines listen .
2. Cable manufacture and loading
The cable is made immediately solid coil, so that under ideal conditions, it can be laid from beginning to end, and loaded onto the ship. At the production stage, erbium amplifiers EDFA (Erbium Doped Fiber Amplifier), a fiber-optic amplifier on an erbium-doped optical fiber, are immediately incorporated into the cable.
Due to the fact that Russia does not have such civilian ships, the manufacture of the cable and its installation were entrusted to Huawei.
By the way, due to the fact that the work was not completed in one season, the cable was unloaded in Singapore, and able Innovator worked on other orders.
3. Gasket
It's simple. At the bottom, from the ship, they lower the plow and turn the small one forward. He digs a trench, a cable is buried in it.

The only difference with the picture is that there is a couple of kilometers under the ship.
For safety, one more Neptunia tug boat participated in laying the cable from Magadan to Sakhalin. It was on a safety net and cleared the bottom of the trash from the trawl along the way. Here it is:

This year Neptunia did not go with them.
Here is another informative video:
4. If everything went well and the cable reached from coast to coast, then it is connected to the coast station. And from the station already, in the old manner, with wires pulling the Internet to the consumer.
In Magadan at Rostelkom everything went well. The cable was stretched, tested for six months and now they sell fast Internet to everyone.
According to the latest information, from June 7, 2016, the cable was connected to the coast station in Ust-Bolsheretsk and cable laying to Sakhalin should end on July 22. So, the chance that next year the normal Internet will appear in Kamchatka is very high.
All right, it was all lyrics, and now we will go on a tour of the ship.
The ship stood near the island of Russian, I even thought that you can approach him on a kayak, but, alas, the weather did not allow.
We were brought on board a small boat:

Hospitable ladder opened its arms to the guests and members of the team:

Then the labyrinths of corridors and stairs began:

Everyone was invited to the mess-room and the Captain with the Russian assistant told us about what we would see:

Naturally, the conversation on all ships begins safety. Where to run in the event of a siren. For these purposes, everyone was recorded and counted on their heads, so that in the event of something not losing anyone:

Captain's bridge
I do not understand anything in the captain bridges, so if anyone knows better, correct me:

Front deck view:

The same, but from the other side:

View from the bridge to the bridge over the Eastern Bosphorus:

Talkies to communicate with the team, and so I understand, telex:

Actually we are on excursions. Rostelecom and media representatives:


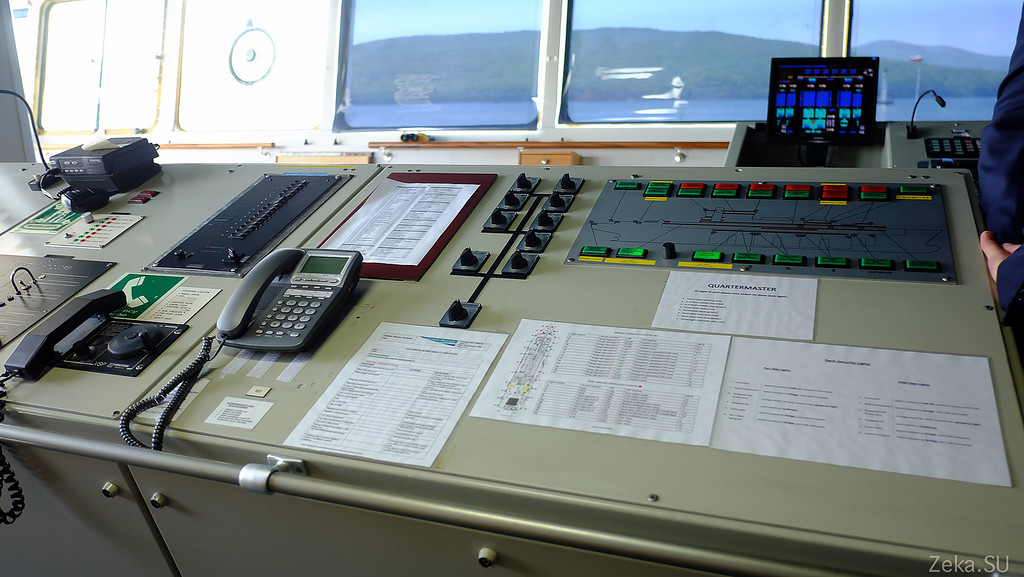
One of the control panels. These colored buttons turn on the lights:

Compass:

So I understand, this is the navigator's workplace. Behind him is a box with maps:

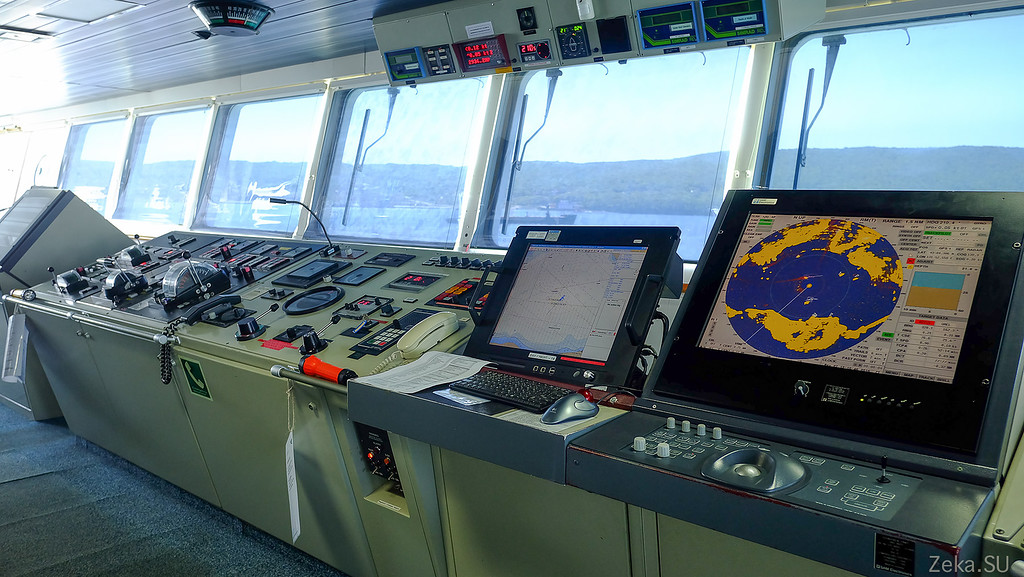
World and Russian navigation, and the actual place of work of the skipper. All these “full speed ahead”, “stop machine”:

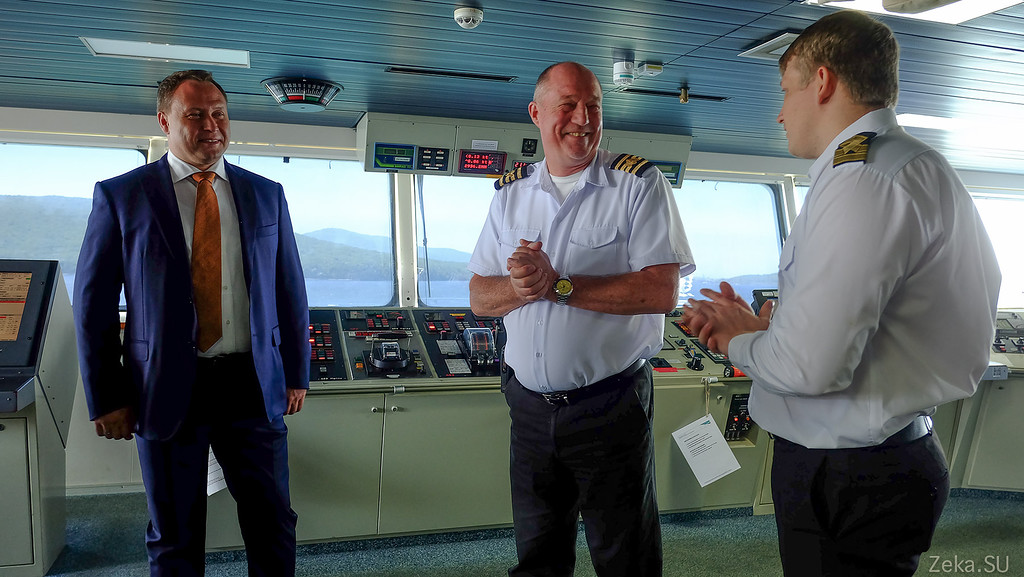
Captain, assistant and Alexey Sapunov, director of the Far East region of Rostelecom:


But this is the aft control room. There are more sensitive and delicate ship management tools. With the help of these joysticks and the stabilization system, you can move ships literally one meter to the right and left:


This is also broadcast from cameras installed on the underwater vehicle. At the moment it is swimming under water in the Bosphorus East:

An underwater vehicle at a depth of a pair of meters plows the expanses of the Sea of Japan:

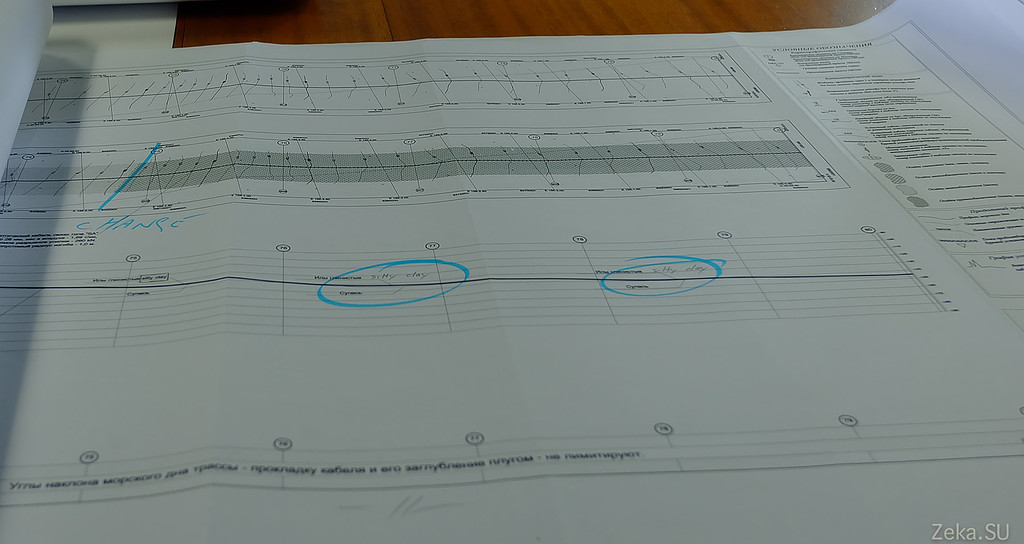
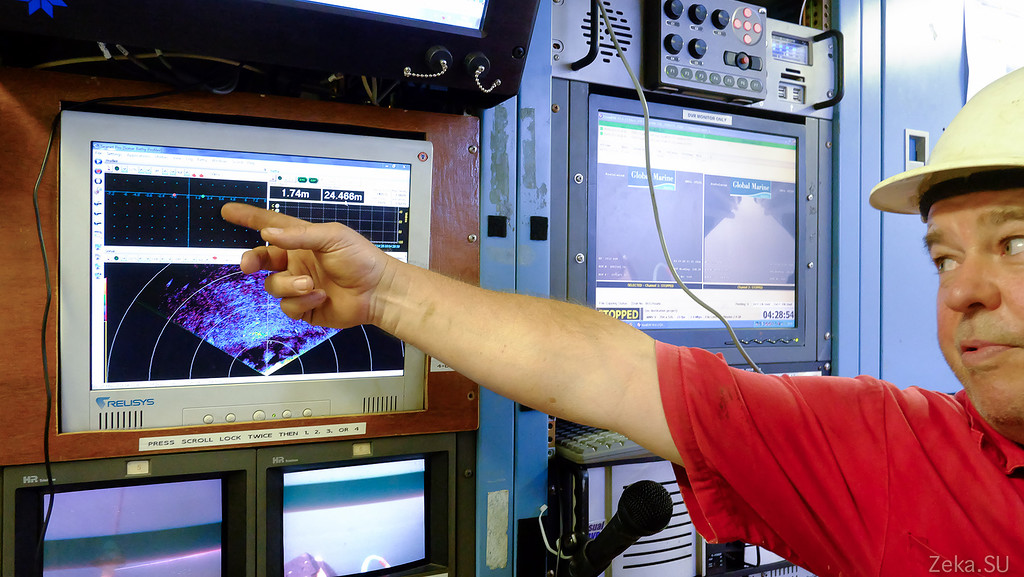
On the sly he photographed a secret map of the seabed of the Sea of Okhotsk with a diagram of the cable. I hope they do not beat me much for this:

Ship Safety Plan:

On the balcony is cozy. Sofa, flowers grow, on the other hand, similarly:

Crew Jobs:


View from the bridge to Vladivostok and the internal raid in the Eastern Bosphorus:

And this is a view of the stern of the vessel. A crane is visible which controls the cable feed and the plow (located below it on the left). In the containers there are additional equipment and ... "offices" of those who manage all this. In one of the containers there is a control room for the underwater robot. This is done so that it is easy to change the functionality of the vessel, depending on customer requirements. Do not need some equipment - unloaded the container in the port and all the rules:

In general, thanks to Captain Christopher Niva for the tour and go further:

On the nose, nothing extra:

Spare screw and anchors on the upper deck:

It also smelled fiercely of Asian food from the ventilation system and there was an incomprehensible person:

On the other side was his friend, but without shoes:

We then argued for a long time who these people were and why they were so punished? Our version was to scare away seabirds so that the deck would not be soiled. It turned out that we were only half right. These gentlemen really work as stuffed animals. Only not from the birds, but from their more intelligent two-legged competitors. It turns out that if you stand on the roadstead in the port, incomprehensible people can get on board from a small boat, and stuffed from afar resemble security officers.
Cable deck
On this deck, they carry out all the work related to cable processing, feeding it to the stern and repairing it. In addition, on this deck are storage facilities - tanks for cable and storage for optical amplifiers.
And now about this all in order.
The deck itself resembles a factory floor in miniature: conveyors, hoists, warehouses with products:

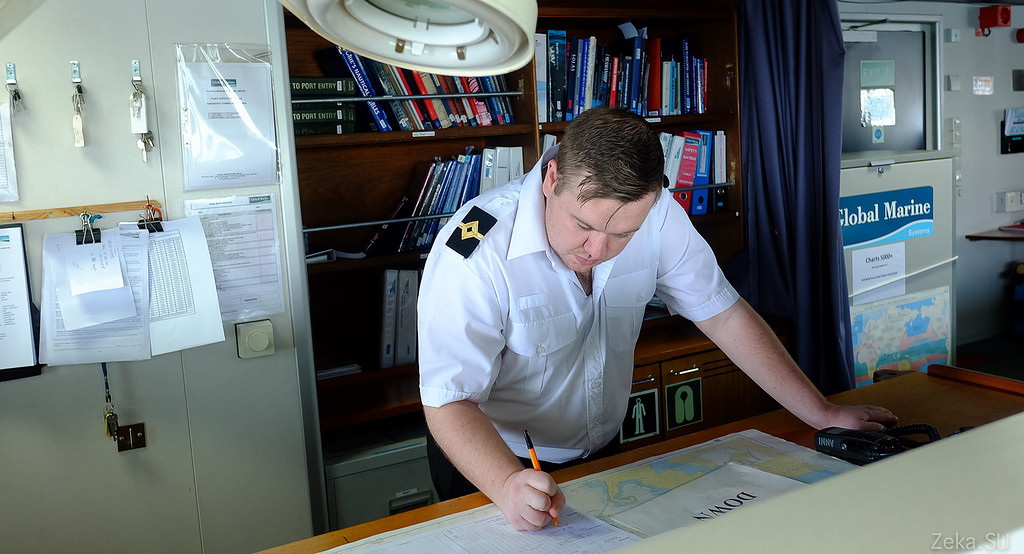
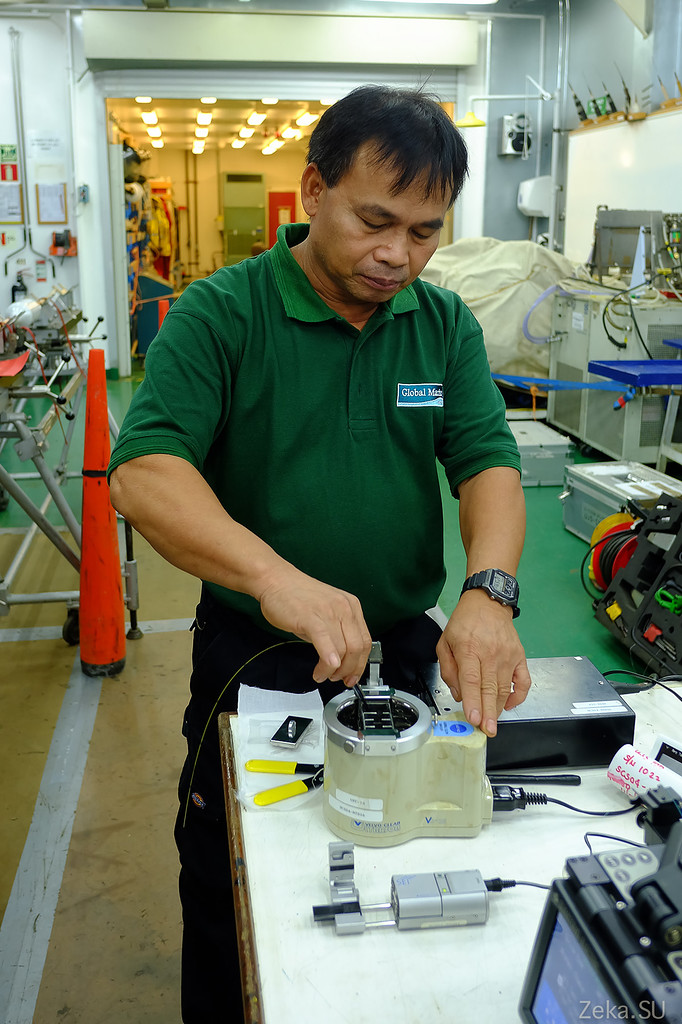
We will not be entertained by the captain, but by the head of the cable deck:

To begin to tell you about the submarine cable.
In my hands in the underwater optical cable in the cut. It consists of several protective shells, plastic, carrying steel or aluminum wires and in the middle are optical fibers:

I think so clearer:

To be brief and concise, it works like this: the optical fibers are inside an aluminum, copper, plastic tube, sometimes filled with grease. The tube is wrapped with an insulating material or filled with polyethylene. All of this is wrapped in steel reinforcing threads that are wrapped with a waterproof sheath, such as polyethylene. Sometimes several layers of supporting cables are used. As in the above photo.
Rostelecom is laying almost the same cable, with the only difference: it has only 4 wires of optical fiber laid. But this should be enough for the coming years, because the sealing equipment allows transmitting up to 8Tbit / s through this cable. What should be enough for these regions with interest for the next thirty years. Naturally, there will be much less traffic, as there are few consumers in these areas and they do not need to feed the maximum flow.
In the welding room there is a whole exhibition of cables that you had to work with:

Judging by the appearance, the leftmost cable is designed for laying in the most dangerous places of the globe. Where not only sharks and crocodiles can gnaw him, but elephants and hippos can stomp on them:

So, we are with you in the welding shop where the cable connection works are carried out. Immediately pay attention to the door with a sign "Do not enter! Dangerously". There is an X-ray room. But we will come back to this later.
The welding shop is necessary for the repair of the submarine cable in case of a break, for connecting the cable from the shore to the submarine cable being mounted, well, or in the case for building it up. In our case, as the chief master of the site said: “We in Kamchatka will connect the cable to the shore end quickly, you have only 4 threads to weld”.

This is a coupler. In it the welded fibers keep within and the ends of a cable are connected. True, we were assured that this sample is old, there are already clutches of the new model, more durable.

In this way we insert the clutch into the cable break and fasten:

Heavy gizmo:

Next stage. Waterproofing. Clutch carefully poured plastic:

To prevent the clutch from bursting at the junction with the cable, it is terminated with such “rubber” things:

The result is an airtight, heavy and durable “gut” that you can safely carry anything. In one such on a shoulder you will not drag. I understand why they need winches and hoists here:

The tightness of the package is checked on x-rays. Remember that cabinet, which is dangerous to enter?

And now about the main thing! The most important thing is to weld the optical fibers well. That's actually the whole set of the young welder.

First, the cable is cleaned and the end is neatly cleaved to make it even:

Then the two ends are inserted into the welding machine:

Press the button and watch:

Then repeat this for each core. Just after these operations, all the welded threads of the cable are placed into the sleeve and a “protective gut” is assembled around it:

This concludes the inspection of the workshop and proceeds to the cable storage facilities.
All 900 km of cable are laid in one of three cable tanks:

As you can see, here in the tank there is only 3.5 meters of cable in height:

An optical amplifier is installed on the cable, every 80 km. Here they are in a special storage:

A special microclimate is maintained in the storage. Apparently due to the characteristics of the equipment:

Amplifiers are most often made on the basis of doping fiber with a rare-earth element — erbium.
How it works?
An additional high power laser beam, but different from the frequency of the laser transmitting information, is introduced into the fiber and causes the erbium atoms in the amplifier to go into an excited unstable state. When a photon of laser radiation with useful information weakened by a long fiber road, is received by this atom, it receives energy from this excited atom, and is re-emitted with a new force and flies further, more precisely, it is reemitted in the form of 2 quanta and more useful photons become.
For those who write the above incomprehensible, I explain on the fingers.
Tennis balls are thrown into the pipe, on which information is recorded and they fly through the pipe from point A to point B. The pipe is long, and when experiencing air resistance they slow down and may not reach its end. Nearby, along a parallel pipe, the air is pumped at high speed, and it causes the wheel blades to turn quickly like a water mill, or a paddle steamer, located somewhere in the middle of the pipe. Having flown to this wheel, tennis balls get this wheel on the ass, like a tennis racket and with new forces fly further ... another 80km.
Who cares - read a normal and useful article on this topic , well, or Wikipedia .
Here are some additional equipment for working with cable. Tennis table and bicycles. The crew revealed the secret of bicycles.
A pier was under repair in Singapore, and there it was too far to go around the port area. I had to buy bicycles. But the secret of the tennis table refused to open. Mysterious English agents:

Self-propelled truck for transportation of amplifiers and ready-made coupling couplings:

Conveyor with guides for pulling the cable from the hold to the stern of the vessel:

And this is already a winch, in order to pull out or feed the cable into the sea, it is hard to pull the cable from the depth of a couple of kilometers with your hands;

So it looks like in the work:

Another part of the feeder:

And this, as I understand it, is just spare couplings, amplifiers in case of an unexpected cable break. You understand, it is better to take everything in advance. There are no stores in the Sea of Okhotsk:

. In general, let's thank this person for an excellent excursion and go on. On the stern, where we look deep-water equipment:

Deepwater Equipment
All cable laying work is carried out from the stern of the vessel:

As you can see, there are two cargo cranes here. A crane for lowering the plow, it leans back like on our military search vessels , by the way, is completely new. The team had to replace it recently for repair in Singapore. The second similar crane is located on the left side and is designed to work with an underwater robot.
Crane for the underwater vehicle:

General view of the deck. Workplaces for the operators of management of this equipment and warehouses of consumables are organized in containers:

Head of the deck farm and Rostelecom representatives:

This is a plow. It is lowered into the water, to a depth of 2.5 km and on these skis it drags on a rope along the bottom behind the ship:

It has cameras and several moving parts to regulate the depth of plowing:

With this tooth, he plows the bottom to a depth of 1-1.5 meters and the cable is laid in a trench:

The dude told that in the Sea of Okhotsk, when laying a cable to Magadan, it was difficult. That plow sank in huge sediments of silt, then ran across rocks and even broke a couple of times. I had to get, cook, repair. In general, have suffered enough. Add to this still cold weather:

Awesome design. Compare with human growth:

Actually, through this hole below, they place the cable in the trench:

It looks like a plow that went into the depths of the ocean:

The photo shows a crane, cable conveyor and plow cable in coils:

We now turn to the robot.
Underwater controlled vehicle. It is used for fine work with the cable. For laying on the stone bottom and searching for cable breaks:

The robot is equipped with cameras, he can swim under water and ride along the bottom. Hydromonitors are on board to erode the soil, or vice versa, to cover the cable with soil:

Deck for maintenance of the robot, on the background of spare tracks are lying:

Agree - handsome. In our country there are definitely no such:

Laying the cable with a robot is much slower and more expensive. For example, consumables:

- Want to see how he can swim with us?
- Of course we want!

And here we were immediately kicked out of the deck:

And he was sent down to conquer the depths of the Eastern Bosphorus:

Crane operator:

Find a robot?

In one of the containers the control room for the underwater unit was built. The robot is controlled by 2 driver-operators:

It has several cameras installed, both navigation and, for example, a camera that controls the state of the suspension so that it does not fall off:

There is also a sonar, and cameras that are just installed at the work site with the cable to watch the work of the manipulators and hydro-monitors:

They did not sink to the bottom, they float at a depth of 2 meters:

Telemetry:

Control panel:

And here is the second driver. Hiding around the corner:

At this point , we will thank this wonderful man for a smart excursion:

In general, on this positive note, I, perhaps, will end my excursion aboard the cable layer.
Of course, it’s a pity that in such a big country there are no vessels of this class, but the country itself has no task for laying ocean cables. For forcing rivers and bays, more than just simple technical means. Such work probably can do the military, but the military perform only work aimed at ensuring the country's security. And here is another.
Thanks to the company Rostelecom, which invited me to this beautiful boat.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/396463/
All Articles