Ask Ethan # 70: Does the universe have a center?
If it all started with the Big Bang and expanded, does the whole center have any?
I want to stay as close to the edge as I can, without falling off of it. From the edge you can see a lot of things that you will not see from the middle.
- Kurt Vonnegut
Every moment we have more and more questions. Why not answer the largest? Every week I choose one question, and this week the honor went to Eric Vincent, who asks:
Where is the center? For some time now, due to the distribution of matter, I refuse to believe in one big bang that launched the Universe. The article assumes that the Earth is the center of the universe. Is it not as likely as the fact that gravity wins all the time, and that in several places of the Universe there is enough matter to pull everything towards the center, without the need to create an unsubstantiated term (dark energy). Of course, I am not an expert, so I wonder where and why I am wrong.
With the expansion of the Universe, the Big Bang, the dark energy and the idea of the “center”, there are a lot of wrong ideas. Let's see what can be done to clarify the situation!
')
Think of our planet Earth, and the path it makes in space. This video was filmed in 24 hours from the spacecraft Messenger in 2005, which flew around our world on the way to Mercury. Think of Earth, since - just a few generations ago - a huge number of people believed that the Earth rests in space, in the center of the Universe, and does not revolve around the sun.
Since then, we have comprehended a lot of things.

Not only the Earth, but in general, nothing in our solar system is in the center and does not rest. The Earth, together with other planets - and the Sun, of course - revolve around a common center of mass, and not around a certain fixed point. This center of mass flies through space, through the galaxy, in an orbit slightly different from the one you could see in different videos .
Our entire solar system remains in the same plane, with the scattered ellipsoid of the Oort cloud around, and we move around the center of the Milky Way along a giant ellipse.
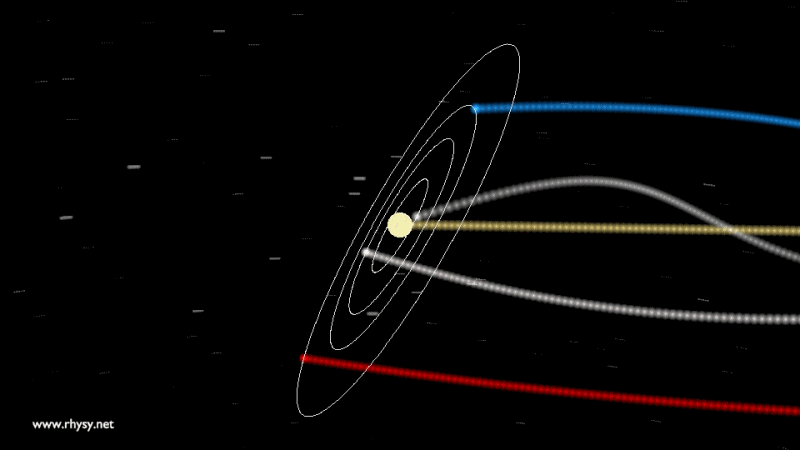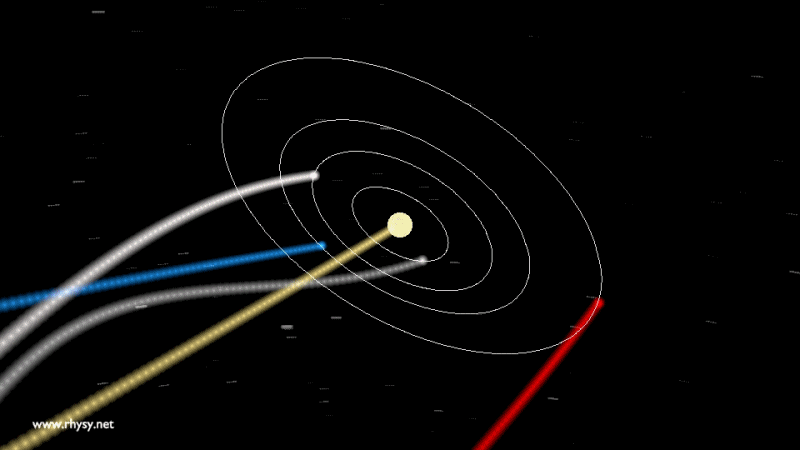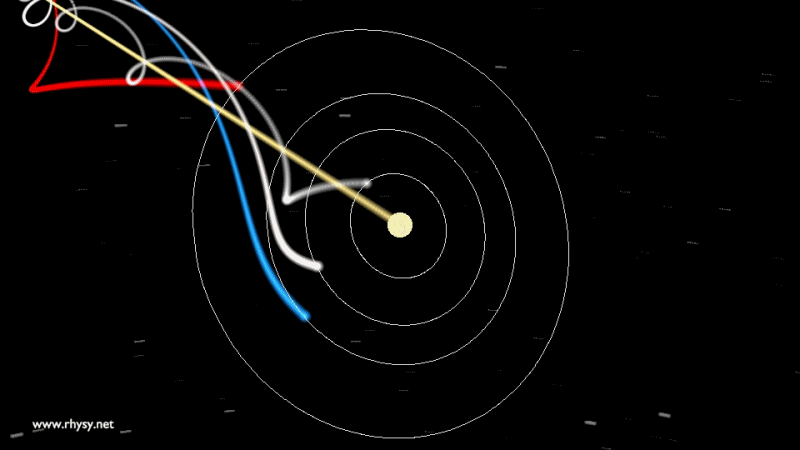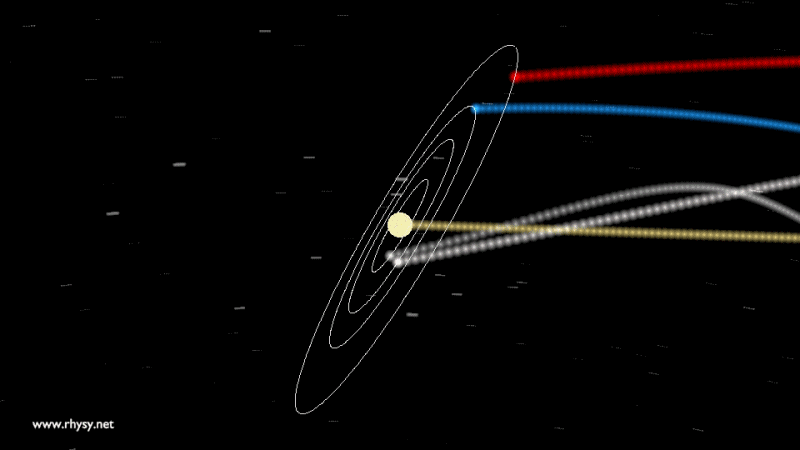
But that is not all! The Milky Way is also not fixed, including its center. Our galaxy rotates and moves through space. We are surrounded by sources of gravity:
- other galaxies, large and small;
- groups and clusters of galaxies;
- intergalactic filaments of gas and dark matter;
- cosmic voids holding back clusters of matter like ours.
In our environs, not only the Milky Way, but all the galaxies, groups and clusters move relative to each other.

More importantly, these movements are not local, but cosmic. On the largest scales, galaxies are not just moving under the influence of gravity, but are subject to cosmic expansion, affecting everything in the universe. And the way it works is contrary to the intuition of most people. When we think of expansion, we imagine an explosion where all the pieces move away from each other. And there are plenty of such phenomena in space - for example, type II supernovae, processing burned nuclear fuel stars into interstellar matter.
youtu.be/eE8QkBlyf5k
Of course, the pieces of the star move away from each other, but because of the explosion, and not because of the expansion of space. And if this picture in any form is connected in your head with the “Big Bang” or “expanding Universe”, then immediately remove it from there.
Think of space itself as a surface of a ball. Not about the three-dimensional "ball in space", but about the two-dimensional surface of the ball. Imagine that coins are glued to it. The ball expands - no matter because of the explosion, or because of the stretching of the surface. Imagine that each coin is a galaxy, or, as in our case, an observer.

From the point of view of any galaxy, all the others are moving away from it. Those that are further away are moving away faster, and those that are closer, are not moving away so quickly.
If you look at it from the point of view of any galaxy, it will be the same. In the context of GR in an expanding universe, not only is there no center, but there is no dedicated observer, there is no privileged galaxy, and there is nothing to “attract” because of gravity.
However, there is a competition that controls the extension.
This is a competition between gravity and expansion, which began after the Big Bang, at the moment when the Universe could first be described as hot, dense, expanding, after which the expansion speed slowed down and the Universe began to cool.
The Big Bang was not an explosion with a certain center, and there was no point that could be described as the place of origin of the observed Universe. As far as we can judge, the space was filled with matter and radiation in a hot state all at once, everywhere - it is this moment that we call the Big Bang.
And the expansion of the universe is governed by its contents, and in different areas there are different amounts of matter. Therefore, oscillations of cosmic microwave radiation existed in the early Universe.

Hot spots (red) and cold (blue) correspond to places in which matter is slightly more or less than on average. Places containing more matter will grow into galaxies, groups, or even clusters, while those containing less matter will not grow. At the same time, the largest rarefied regions will lose all matter and turn into huge cosmic voids.

In the greatest regions with high density, expansion will be locally conquered, and areas will be formed there, thousands of times more massive than the Milky Way. But on a larger scale, expansion will triumph, while it is not matter or radiation that controls it, but dark energy, which is the only way to explain the observed expansion rate in the context of GR.
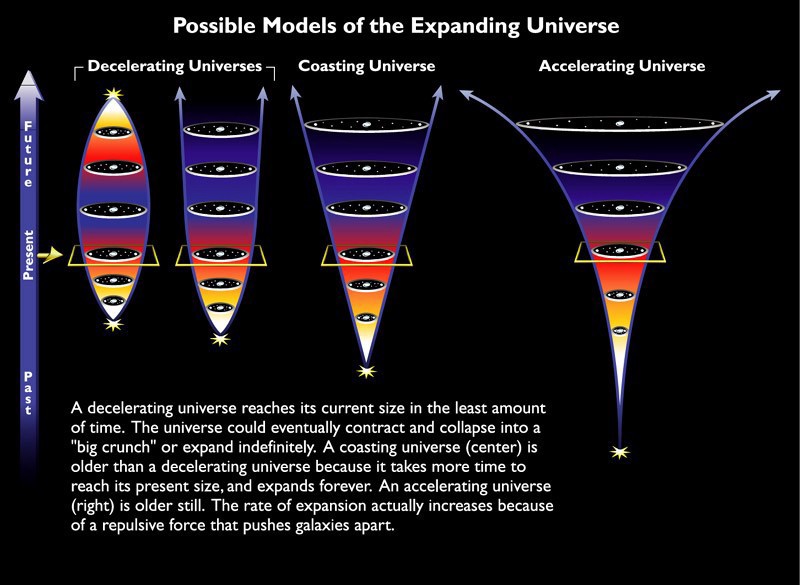
So briefly: the Big Bang happened everywhere in the Universe and at the same time, all areas experience expansion in approximately the same way, heterogeneity in density led to the appearance of galaxies, groups and clusters, as well as cosmic voids, and dark energy revealed itself through the accelerating expansion of the Universe.
Eric is not the only one asking such questions, but I hope that the explanation has been made clear to you and to the rest. Send me your questions and suggestions for the following articles.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/395945/
All Articles