How Seagate tests its hard drives
Tom's Hardware journalist visited Seagate Research Center in Longmont, Colorado, and saw how Seagate developed and tested hard drives.

Training
Every year, Seagate spends two billion dollars on research and development, providing the company's drives with high reliability with an average annual failure rate (AFR) of just 1.2%. As shown in the image below, the disc development process is divided into eight stages:

')
Production stages: 1 - concept, 2 - design, 3 - testing, 4 - launch on sale
Despite the fact that the main work of the center in Longmont lies in the “Design” phase, it begins a little earlier - in the “Concept” phase. Here experts determine the requirements for the product, prepare documentation and testing methodology. To confirm the possibility of making a disc, a prototype is created at the design stage. After completing the formation of the structure, the specialists perform technical and economic calculations that make it possible to understand whether to proceed with the development of engineering design.
Endurance tests
At the design stage, engineers are tasked with optimizing the functionality, production plan and price, without reducing the level of quality and reliability. Seagate re-evaluates the calculated values until it is certain that the reliability of the disc corresponds to the planned level. When the first level of reliability and performance is achieved, Seagate produces a larger batch of disks and raises the bar for performance. Then the cycle repeats again.
At the end of this phase, the drive will pass more than 500 tests, many of which last for weeks.
Test laboratories

It is time to get acquainted with two cameras for atmospheric testing. They are multifunctional modules capable of raising the temperature to 100 ˚C and lowering it to -50 ˚C.
The second type of testing is performed in high-volume temperature test chambers, and the third - in hot rooms, where the temperature of the room is controlled, not the disk.
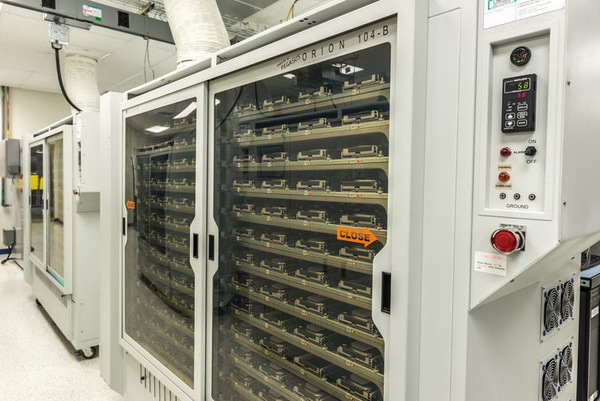
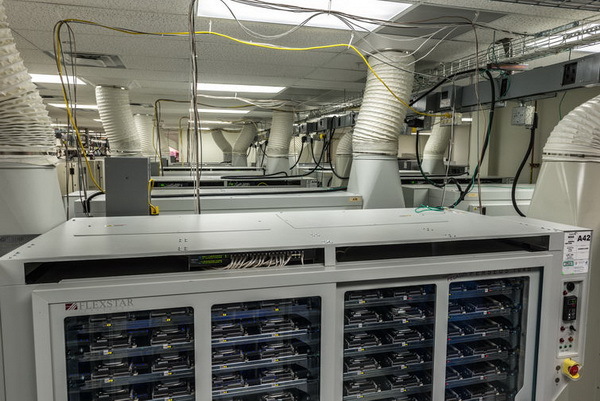


The racks in the photo above perform both scripts on SAS and SATA drives, as well as head movement tests.
With all this it is necessary to remember that the modeling of external influences on the disks is no less important than the performance tests.

Vibration tests
In the course of testing, vibration loads are also carried out. The vibration table transmits oscillations to the disk in three dimensions, and a workstation nearby controls the whole process:
ops.bestofmedia.com/us/ooyala_frame.html#ZybzNweTq3oghlnbi_M_LxsRJG3G5Ezo
Vibration Test:
ops.bestofmedia.com/us/ooyala_frame.html#9udzNweTp5_Yky8Fr16U-7PBMtiUcJV3
Microvibrations:
You are mistaken in assuming that a disk mounted in a rack or in a PC case does not experience parasitic rotational loads. Microvibrations occur even in these cases. And if the drives for high-performance systems have built-in accelerometers on the printed circuit board, consumer-grade models do not have such compensating systems, therefore performance occurs when vibrations occur.
Drop tests
The concept of a shock test is simple: you lift the disc, throw it down and study the damage, and use more special mechanisms for more accurate results. Of course, very precise mechanisms are required for more accurate results:
Video: ops.bestofmedia.com/us/ooyala_frame.html#cwNjRweTr-o_Ydb_6d0Hy8lYd6kaTX0m
Other tests
The Electromagnetic Interference Laboratory (EMI) is working to ensure that products meet all the norms and standards of electronic products. All attention is paid to three parameters:
1) electromagnetic energy produced by the disk during operation;
2) the sensitivity of the disk to electromagnetic interference;
3) disc opposition to electrostatic discharge.
Radiation is measured using an EMI detector. The receiver antenna rotates to detect electromagnetic radiation with different polarities.
The device in the photo below is a stun gun. Experts investigate its effects on the mechanics and performance of the disk.
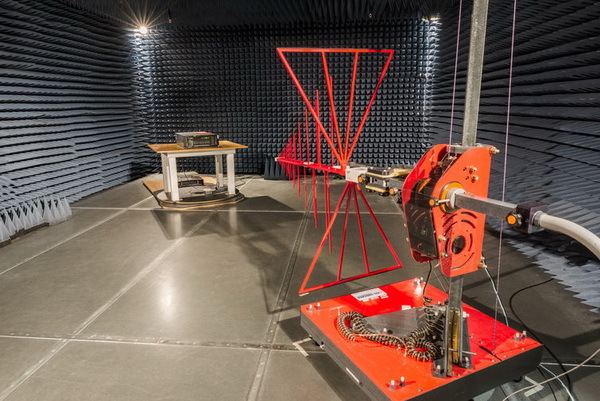
An important parameter for many storage systems is acoustics. For digital video recorders and embedded solutions, the level of acoustic noise is critical.
Analysis
In Longmont, there is a full-fledged production laboratory that allows you to create prototypes of any Seagate disks in a fully automated way:
Video: ops.bestofmedia.com/us/ooyala_frame.html#FueDRweTo-njhSPQvYBqKr2HrcV21eqa
Assembly
An important element in the production process of truly reliable discs is the cleanliness of the surrounding surfaces. Dirt on magnetic plates or heads can affect the reliability of the disc.
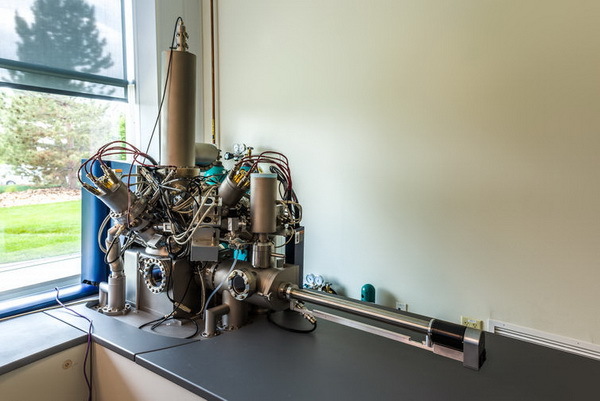
The search for pollutants begins in a mass spectrometer on secondary ions.
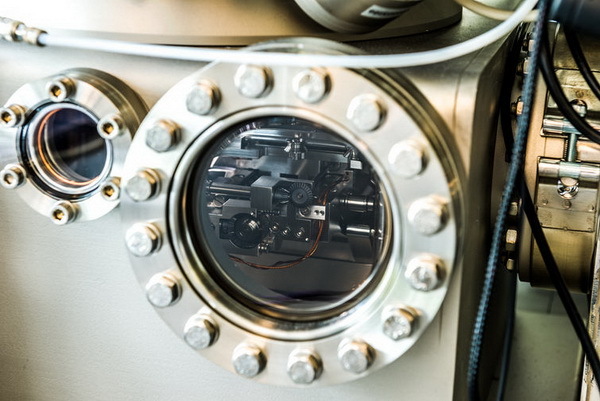

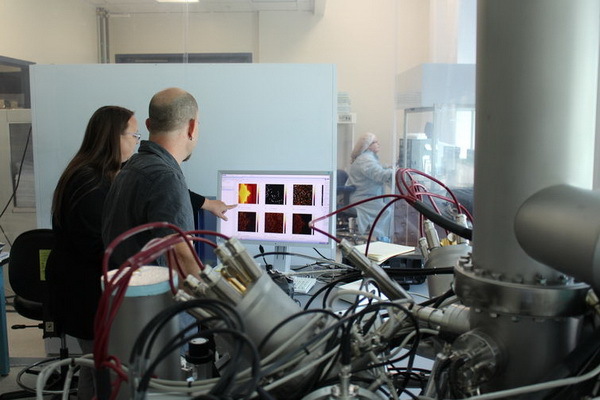
With the help of scanning electron microscopes (SEM), samples are studied, filtered in a particle metrology laboratory and then subjected to a dehydration procedure. At another SEM, shown below, the studied white dots were identified as inclusions of corrosion with a size of only a few dozen molecules.

In the laboratory of metallography, work on cross-cutting of various samples is being carried on without interruption.
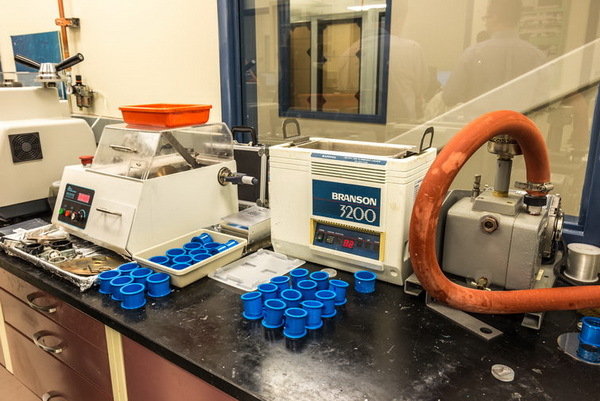

Most often this happens to find out what happens to materials, especially on surfaces.
Video: ops.bestofmedia.com/us/ooyala_frame.html#p0ZjRweToa2__rkfjriiVksJ18k5vI9x
To make better
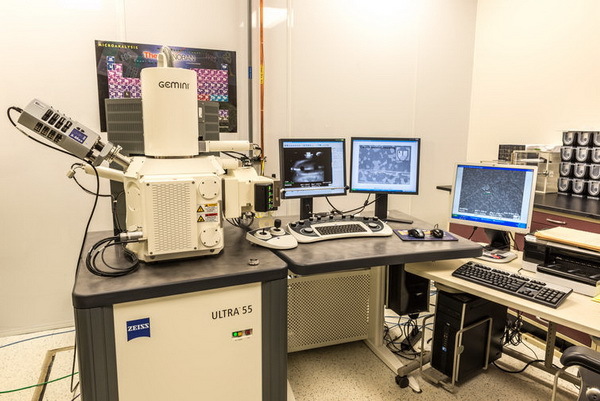
In the photo - one of the five test systems Gemini. Each of them has 6288 slots for calibrating, installing, downloading and testing firmware. From the beginning of the design process (PDP) through to the very end, Gemini runs a lot of scripts on all developed drives. Gemini facilitate the study of various firmware for a variety of scenarios and a large number of tests.

But it’s still one thing to look at the numbers, and quite another to see with your own eyes how the tests go, which takes thousands of hours and helps to increase the reliability of the product.

You can find the full text of the article here: www.thg.ru/storage/kak_seagate_delaet_hdd/index.html

Training
Every year, Seagate spends two billion dollars on research and development, providing the company's drives with high reliability with an average annual failure rate (AFR) of just 1.2%. As shown in the image below, the disc development process is divided into eight stages:

')
Production stages: 1 - concept, 2 - design, 3 - testing, 4 - launch on sale
Despite the fact that the main work of the center in Longmont lies in the “Design” phase, it begins a little earlier - in the “Concept” phase. Here experts determine the requirements for the product, prepare documentation and testing methodology. To confirm the possibility of making a disc, a prototype is created at the design stage. After completing the formation of the structure, the specialists perform technical and economic calculations that make it possible to understand whether to proceed with the development of engineering design.
Endurance tests
At the design stage, engineers are tasked with optimizing the functionality, production plan and price, without reducing the level of quality and reliability. Seagate re-evaluates the calculated values until it is certain that the reliability of the disc corresponds to the planned level. When the first level of reliability and performance is achieved, Seagate produces a larger batch of disks and raises the bar for performance. Then the cycle repeats again.
At the end of this phase, the drive will pass more than 500 tests, many of which last for weeks.
Test laboratories

It is time to get acquainted with two cameras for atmospheric testing. They are multifunctional modules capable of raising the temperature to 100 ˚C and lowering it to -50 ˚C.
The second type of testing is performed in high-volume temperature test chambers, and the third - in hot rooms, where the temperature of the room is controlled, not the disk.


The racks in the photo above perform both scripts on SAS and SATA drives, as well as head movement tests.
With all this it is necessary to remember that the modeling of external influences on the disks is no less important than the performance tests.

Vibration tests
In the course of testing, vibration loads are also carried out. The vibration table transmits oscillations to the disk in three dimensions, and a workstation nearby controls the whole process:
ops.bestofmedia.com/us/ooyala_frame.html#ZybzNweTq3oghlnbi_M_LxsRJG3G5Ezo
Vibration Test:
ops.bestofmedia.com/us/ooyala_frame.html#9udzNweTp5_Yky8Fr16U-7PBMtiUcJV3
Microvibrations:
You are mistaken in assuming that a disk mounted in a rack or in a PC case does not experience parasitic rotational loads. Microvibrations occur even in these cases. And if the drives for high-performance systems have built-in accelerometers on the printed circuit board, consumer-grade models do not have such compensating systems, therefore performance occurs when vibrations occur.
Drop tests
The concept of a shock test is simple: you lift the disc, throw it down and study the damage, and use more special mechanisms for more accurate results. Of course, very precise mechanisms are required for more accurate results:
Video: ops.bestofmedia.com/us/ooyala_frame.html#cwNjRweTr-o_Ydb_6d0Hy8lYd6kaTX0m
Other tests
The Electromagnetic Interference Laboratory (EMI) is working to ensure that products meet all the norms and standards of electronic products. All attention is paid to three parameters:
1) electromagnetic energy produced by the disk during operation;
2) the sensitivity of the disk to electromagnetic interference;
3) disc opposition to electrostatic discharge.
Radiation is measured using an EMI detector. The receiver antenna rotates to detect electromagnetic radiation with different polarities.
The device in the photo below is a stun gun. Experts investigate its effects on the mechanics and performance of the disk.

An important parameter for many storage systems is acoustics. For digital video recorders and embedded solutions, the level of acoustic noise is critical.
Analysis
In Longmont, there is a full-fledged production laboratory that allows you to create prototypes of any Seagate disks in a fully automated way:
Video: ops.bestofmedia.com/us/ooyala_frame.html#FueDRweTo-njhSPQvYBqKr2HrcV21eqa
Assembly
An important element in the production process of truly reliable discs is the cleanliness of the surrounding surfaces. Dirt on magnetic plates or heads can affect the reliability of the disc.

The search for pollutants begins in a mass spectrometer on secondary ions.


With the help of scanning electron microscopes (SEM), samples are studied, filtered in a particle metrology laboratory and then subjected to a dehydration procedure. At another SEM, shown below, the studied white dots were identified as inclusions of corrosion with a size of only a few dozen molecules.

In the laboratory of metallography, work on cross-cutting of various samples is being carried on without interruption.

Most often this happens to find out what happens to materials, especially on surfaces.
Video: ops.bestofmedia.com/us/ooyala_frame.html#p0ZjRweToa2__rkfjriiVksJ18k5vI9x
To make better
In the photo - one of the five test systems Gemini. Each of them has 6288 slots for calibrating, installing, downloading and testing firmware. From the beginning of the design process (PDP) through to the very end, Gemini runs a lot of scripts on all developed drives. Gemini facilitate the study of various firmware for a variety of scenarios and a large number of tests.

But it’s still one thing to look at the numbers, and quite another to see with your own eyes how the tests go, which takes thousands of hours and helps to increase the reliability of the product.

You can find the full text of the article here: www.thg.ru/storage/kak_seagate_delaet_hdd/index.html
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/395911/
All Articles