Verticulture: aqua-basil farm for growing basil and tilapia
We grow fresh fish and basil to the table in an urban setting

Aquaponica is a hydroponic-like method of cultivating plants in a liquid. The main difference is aquaponica much closer to a closed ecosystem. Three key types of organisms live in an aqua-phonic installation — aquatic animals (usually fish), plants, and bacteria. Products of vital activity of fish decompose the colony of bacteria, after which the roots of plants absorb the water enriched with nutrients. Purified by bacteria and plants, the water returns to the fish.
')
About a year ago, in Brooklyn (New York, USA), the aquatic farm Verticulture was built on the roof of the Pfizer factory closed in 2008. The farm grows basil jenovese, Thai basil and tilapia fish. The project began in 2014 from the page on Indiegogo . Let's see how everything works on this farm.
Video posted on Indiegogo in 2014
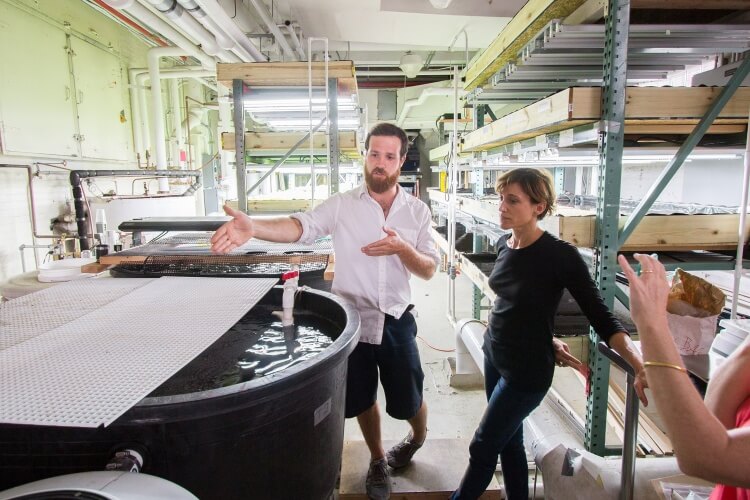
Verticulture is located in a room of only 40 m2. Here, in the factory premises, there are several more “food” startups. The previously closed factory Pfizer even called "the epicenter of grocery startups ."
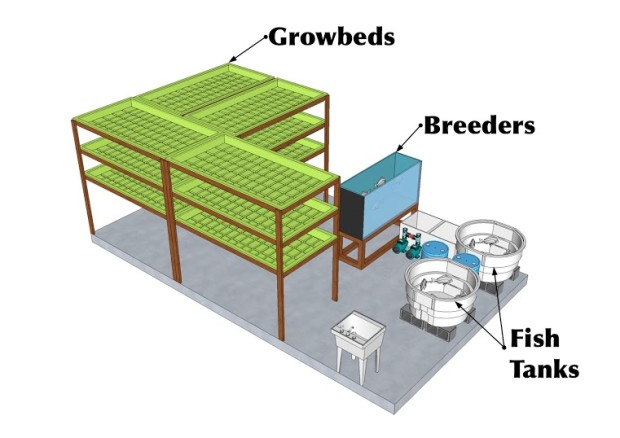
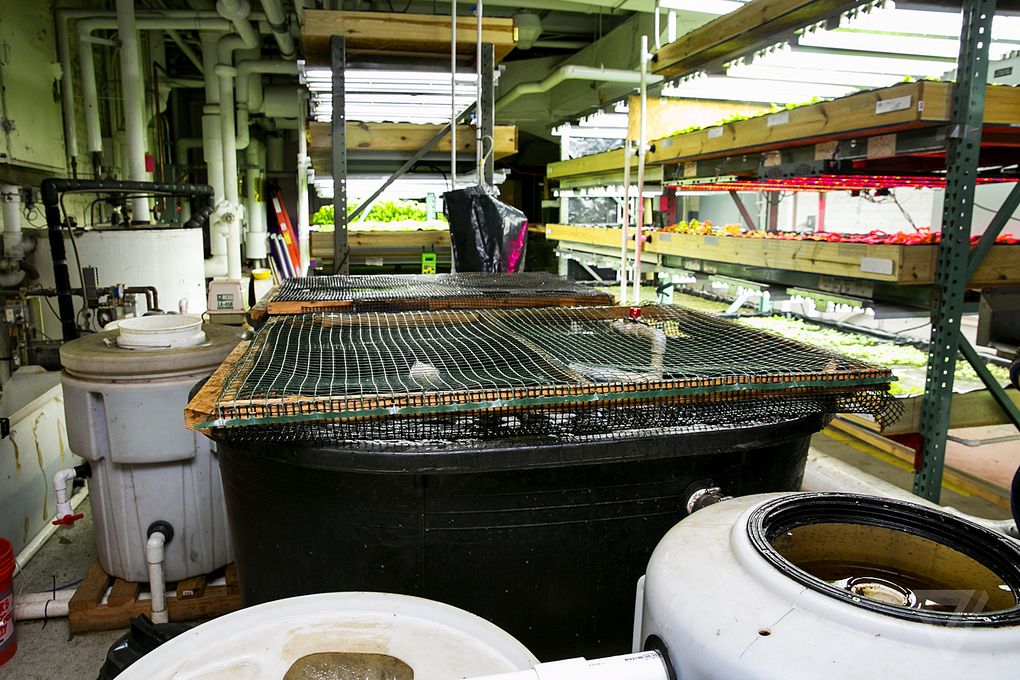
In the premises of the farm space is used most effectively. Boxes of basil are placed above each other in racks up to 3 meters high. Tilapia lives in two tanks. Boxes of basil are communicated using pipes with tanks of fish. Capacities with bacterial culture are located between them, where fish waste is processed into nitrate fertilizer. The roots of plants receive nutrients, and the water is purified from salts, returning to the fish already purified. About 90% of the volume of water entering the system is reused. So far, the lighting system uses fluorescent lamps. The plans include switching to LEDs, they are more profitable than fluorescent lamps: energy is consumed less, and plants grow faster. Constant monitoring of the system is not required - all processes are debugged and run automatically.
In a week, “aqua-farmers” produce about 13-18 kilograms of basil, which is sent to local shops.
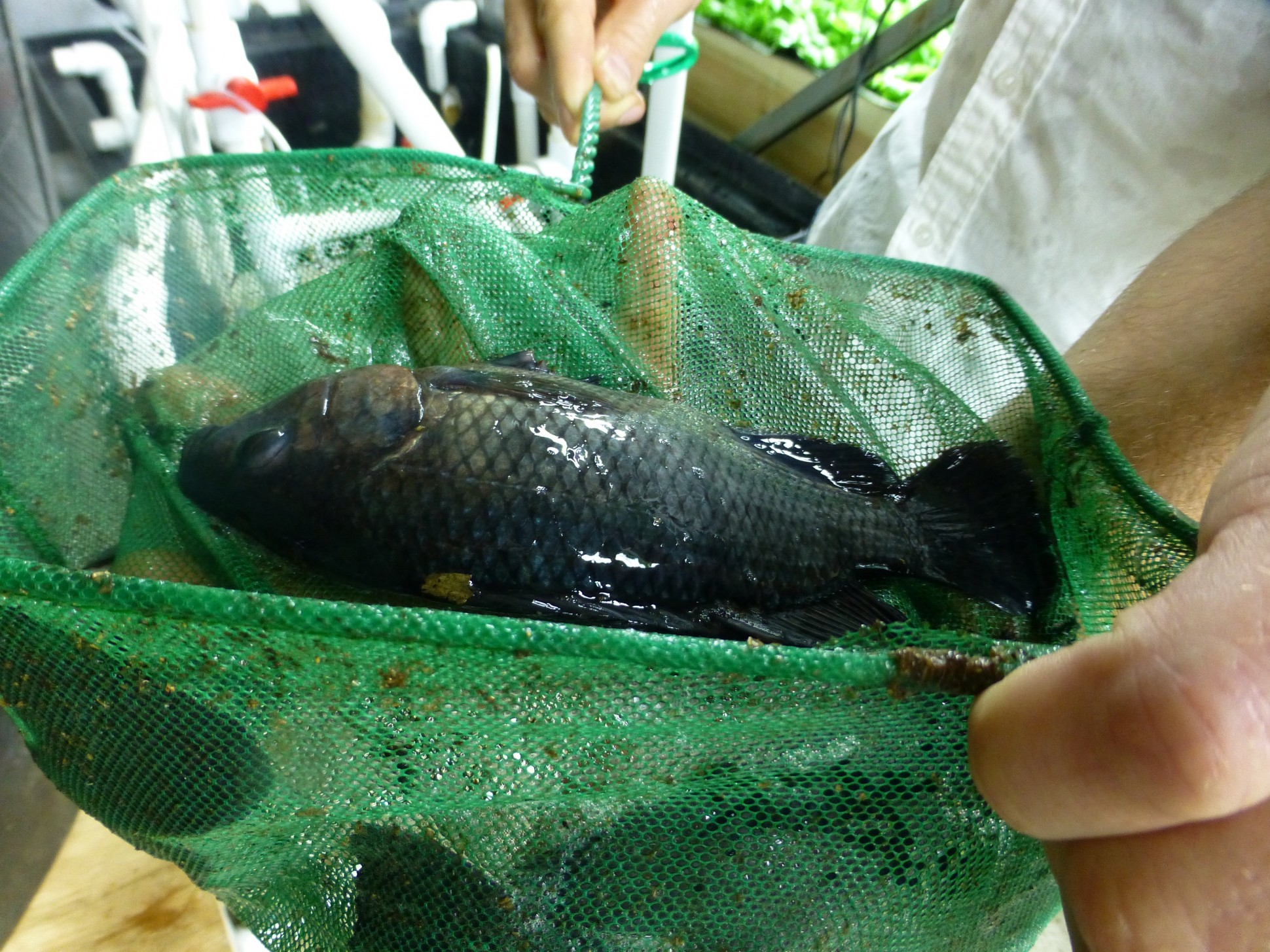
At the same time on the farm lives 150-180 tilapias. Selling fish while only in the plans.
The project has not yet come to profit, so its owners can not yet spend all their time on the farm. Everyone has a main job, and on the farm, team representatives appear at night, on weekends and in their free time. However, 2-3 new customers come to Verticulture every month.
So far, Verticulture is working in test mode, the authors of the idea are working out the technology to create a commercial enterprise - they are planning to build aqua farms in other parts of New York. Now there are experiments on the cultivation of other plants, for example, mint.

The ultimate goal of the project is to make it stable, environmentally friendly and profitable. The authors of the idea hope that they will be able to scale their project by supplying products from aquaponic farms to many major cities around the world. Now the farm is not completely environmentally friendly, since the electricity here is taken from the public grid. In the near future it is planned to correct this shortcoming.

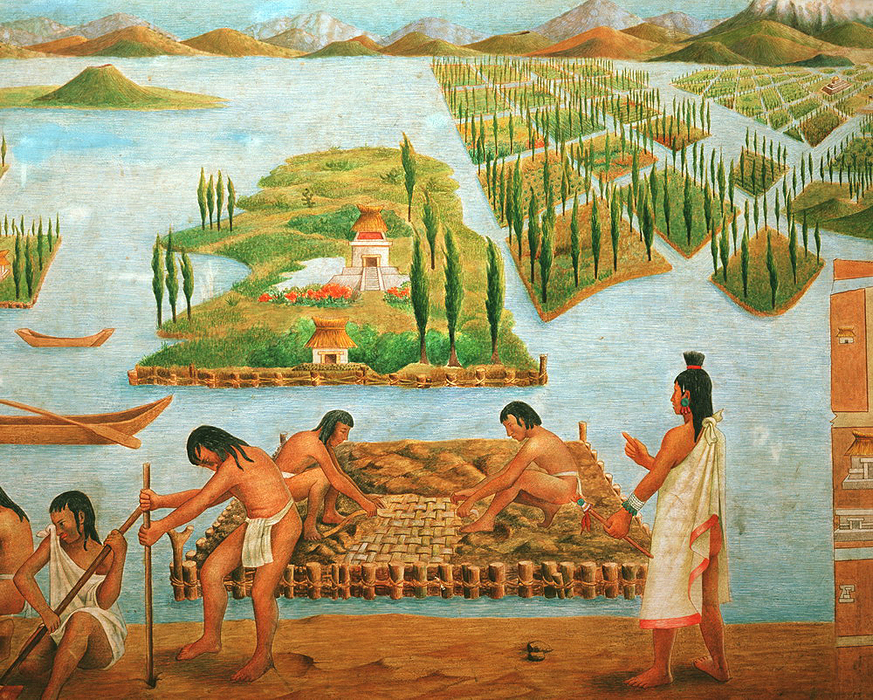
As is often the case, the very idea of aquaponics is not new, the novelty lies mainly in the implementation of an aquaponic farm in urban environments with the help of modern technologies. Even the Aztecs grew plants on mobile or fixed on the shallow waters of the islands. To create a chinamp, workers hammered piles connected by a fence into the soil of the marshy lowlands. Inside a meter-thick layer of earth fell asleep. In the rainy season, the chinamps became islands. Organic matter of aquatic plants and fish waste was used as a fertilizer.

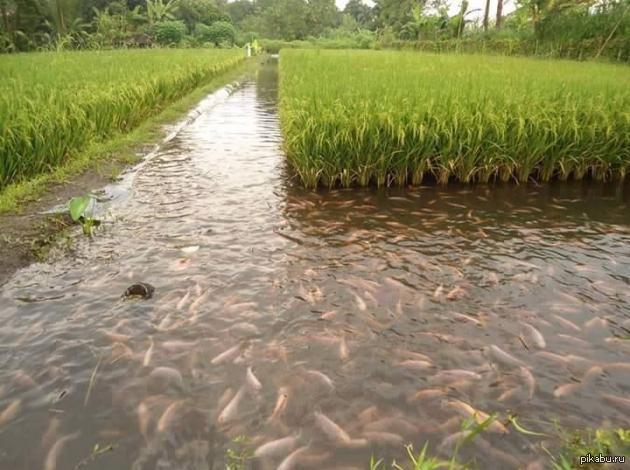
The most common example of aquaponics is rice paddies. Fish is launched into these fields, which fertilizes the fields themselves, giving nutrients to plants, and which the workers then catch. Fish can be different: lake char, marsh eel, carp, golden crucian carp. Such fields still exist today, mainly in South China, Thailand and Indonesia.

China also uses floating aquaponic systems on multicultural fish ponds. The area of such systems exceeds 10,000 m2.
Aquaponic farms are created in Canada, the USA and other countries. Salad and trout are grown here. According to Canadian scientists, the specific microbiological environment, which is formed in aqua-systems, allows to achieve even higher yields than in traditional hydroponics.
The developers of Verticulture do not plan to make large farms, their goal is to create sustainable aqua farms within the city. According to them, the system should be compact and self-sufficient. There should be a minimum amount of waste. Now Verticulture uses 90% less water than on fields where basil is grown.

The creators of Verticulture claim that making such a small system is easy. Fish can be kept in an aquarium or a larger plastic tank. Creating such an aqua-farm is a pleasure inexpensive, but troublesome, especially in an unsuitable climate. The main secret is to choose fish species, bacteria and plants that are well compatible with each other and the size of the system that is optimal for them.

Aquaponica is a hydroponic-like method of cultivating plants in a liquid. The main difference is aquaponica much closer to a closed ecosystem. Three key types of organisms live in an aqua-phonic installation — aquatic animals (usually fish), plants, and bacteria. Products of vital activity of fish decompose the colony of bacteria, after which the roots of plants absorb the water enriched with nutrients. Purified by bacteria and plants, the water returns to the fish.
')
About a year ago, in Brooklyn (New York, USA), the aquatic farm Verticulture was built on the roof of the Pfizer factory closed in 2008. The farm grows basil jenovese, Thai basil and tilapia fish. The project began in 2014 from the page on Indiegogo . Let's see how everything works on this farm.
Video posted on Indiegogo in 2014
Verticulture is located in a room of only 40 m2. Here, in the factory premises, there are several more “food” startups. The previously closed factory Pfizer even called "the epicenter of grocery startups ."
In the premises of the farm space is used most effectively. Boxes of basil are placed above each other in racks up to 3 meters high. Tilapia lives in two tanks. Boxes of basil are communicated using pipes with tanks of fish. Capacities with bacterial culture are located between them, where fish waste is processed into nitrate fertilizer. The roots of plants receive nutrients, and the water is purified from salts, returning to the fish already purified. About 90% of the volume of water entering the system is reused. So far, the lighting system uses fluorescent lamps. The plans include switching to LEDs, they are more profitable than fluorescent lamps: energy is consumed less, and plants grow faster. Constant monitoring of the system is not required - all processes are debugged and run automatically.

In a week, “aqua-farmers” produce about 13-18 kilograms of basil, which is sent to local shops.
At the same time on the farm lives 150-180 tilapias. Selling fish while only in the plans.
The project has not yet come to profit, so its owners can not yet spend all their time on the farm. Everyone has a main job, and on the farm, team representatives appear at night, on weekends and in their free time. However, 2-3 new customers come to Verticulture every month.
So far, Verticulture is working in test mode, the authors of the idea are working out the technology to create a commercial enterprise - they are planning to build aqua farms in other parts of New York. Now there are experiments on the cultivation of other plants, for example, mint.

The ultimate goal of the project is to make it stable, environmentally friendly and profitable. The authors of the idea hope that they will be able to scale their project by supplying products from aquaponic farms to many major cities around the world. Now the farm is not completely environmentally friendly, since the electricity here is taken from the public grid. In the near future it is planned to correct this shortcoming.

As is often the case, the very idea of aquaponics is not new, the novelty lies mainly in the implementation of an aquaponic farm in urban environments with the help of modern technologies. Even the Aztecs grew plants on mobile or fixed on the shallow waters of the islands. To create a chinamp, workers hammered piles connected by a fence into the soil of the marshy lowlands. Inside a meter-thick layer of earth fell asleep. In the rainy season, the chinamps became islands. Organic matter of aquatic plants and fish waste was used as a fertilizer.

The most common example of aquaponics is rice paddies. Fish is launched into these fields, which fertilizes the fields themselves, giving nutrients to plants, and which the workers then catch. Fish can be different: lake char, marsh eel, carp, golden crucian carp. Such fields still exist today, mainly in South China, Thailand and Indonesia.

China also uses floating aquaponic systems on multicultural fish ponds. The area of such systems exceeds 10,000 m2.
Aquaponic farms are created in Canada, the USA and other countries. Salad and trout are grown here. According to Canadian scientists, the specific microbiological environment, which is formed in aqua-systems, allows to achieve even higher yields than in traditional hydroponics.
The developers of Verticulture do not plan to make large farms, their goal is to create sustainable aqua farms within the city. According to them, the system should be compact and self-sufficient. There should be a minimum amount of waste. Now Verticulture uses 90% less water than on fields where basil is grown.

The creators of Verticulture claim that making such a small system is easy. Fish can be kept in an aquarium or a larger plastic tank. Creating such an aqua-farm is a pleasure inexpensive, but troublesome, especially in an unsuitable climate. The main secret is to choose fish species, bacteria and plants that are well compatible with each other and the size of the system that is optimal for them.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/395909/
All Articles