Morse code on the Martian dunes
NEE NED ZB 6TNN DEIBEDH SIEFI EBEEE SSIEI ESEE SEEE !!
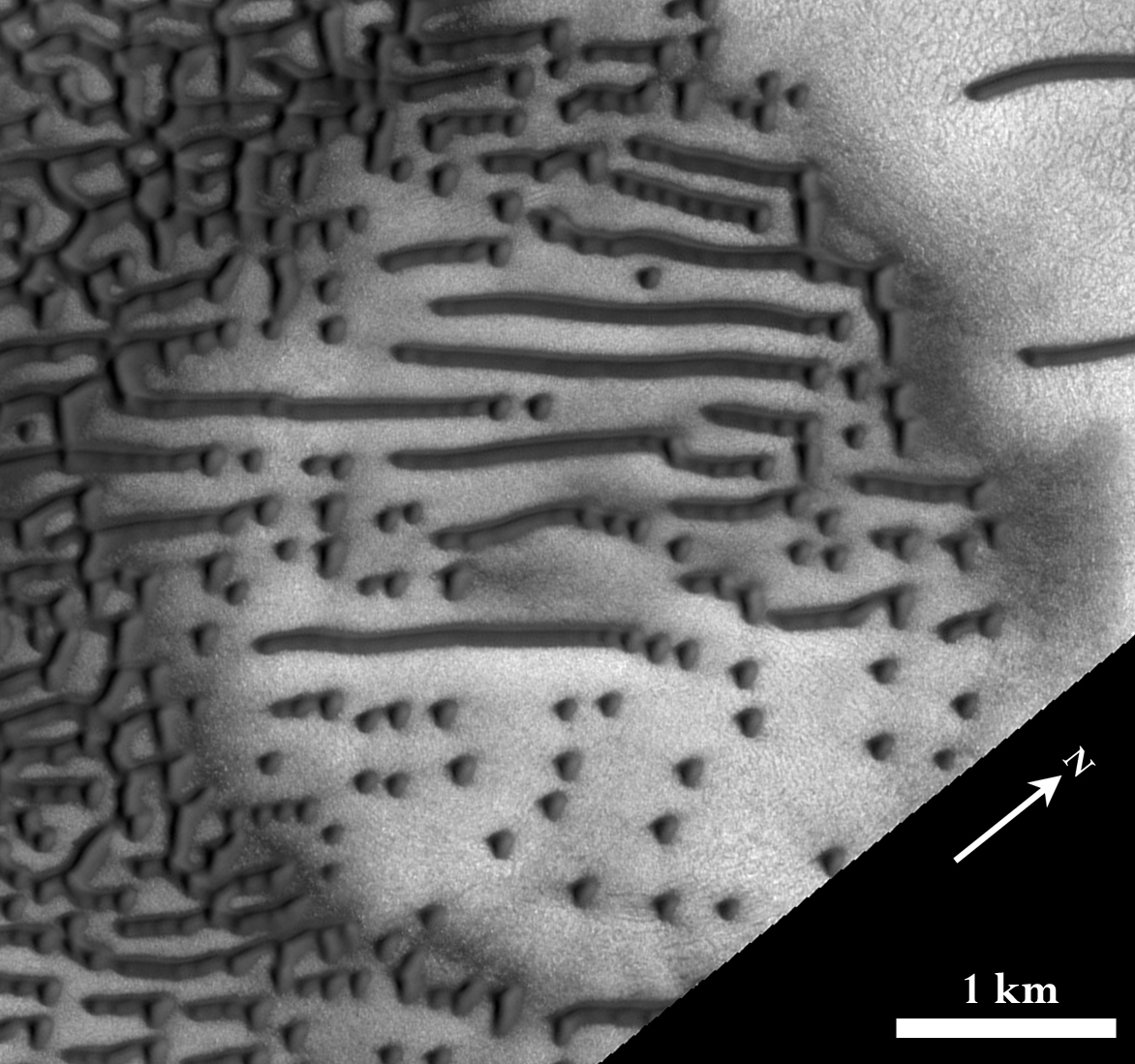
The High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment HiRISE , mounted aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter spacecraft, took a really beautiful photograph of the Martian sand dunes ( photo ESP_044675_2580 ). Some of the dunes look like dots and morse dashes.
NASA experts used a beautiful event to talk about the mechanism for the formation of sand dunes on Mars.
The shape and orientation of sand dunes usually indicate the direction of the wind, but in this image the shape of the dunes is rather complex, so the exact wind direction is not easy to determine. The shape of the dunes is also influenced by local topography, that is, the topographic characteristics of the landscape.
')
Scientists explain that in this case there is a shortage of sand for the formation of dunes due to the fact that the terrain is in a hollow in the shape of a circle - probably, this is an old and already filled crater. Such a topography not only reduces the amount of available sand, but also affects the direction of the winds.
In the Martian Morse "dash" - linear long dunes - formed by bi-directional winds that do not run parallel to the dune. Instead, the cumulative effect of winds in two different directions at certain angles leads to the formation of a dune of such a shape, blowing the sandy material into a linear form.
Small “points” (dunes-dunes) are formed in places where, for some reason, the process of forming a linear dune does not reach completion. At this time, scientists have not yet fully studied this mechanism - and this is one of the reasons why the HiRISE camera takes pictures of this area.
The formation and migration of dunes on Mars is a hot topic for research, because the desert and almost waterless areas of the Red Planet are an excellent natural platform for such "experiments." In many respects, the Martian dunes behave differently, not like the terrestrial ones, which is due to the low density of the atmosphere.
If you are still interested in what is specifically encoded in the “message” in the form of Martian dunes, then, according to NASA’s HiRISE camera pointing specialist, Veronica Bray, the decoding of points and dashes corresponds to the following message :
NEE NED ZB 6TNN DEIBEDH SIEFI EBEEE SSIEI ESEE SEEE !!
(If reptiloids among us want to explain the meaning of the message, this can be done in the comments :)
Black and white photo

Black and white photo overlay

Photo in RGB color model superimposed on the card
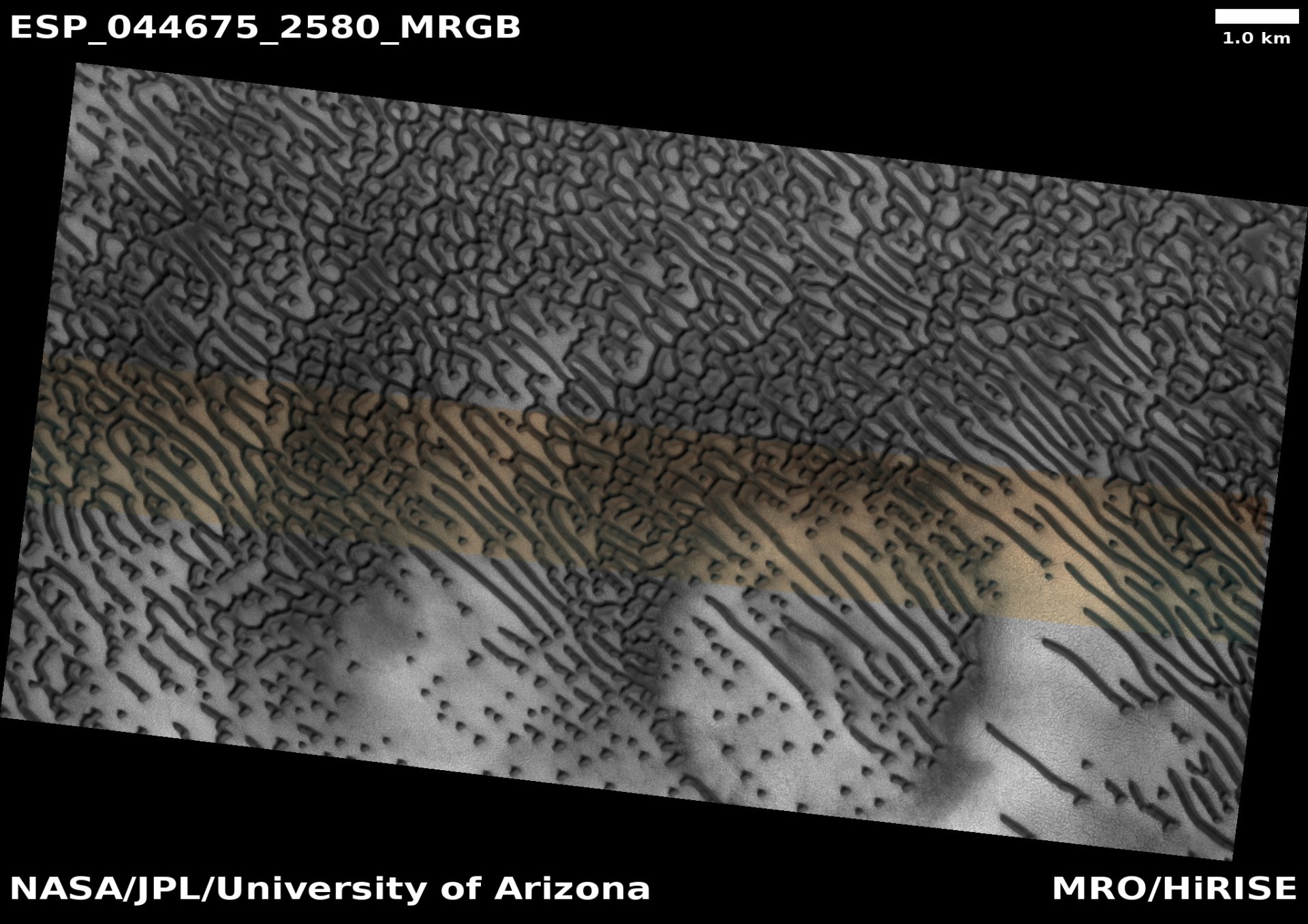
Photo in JP2 format: black and white (1281 MB), color model IRB (725 MB).
A 65 kg HiRISE camera is a 0.5 m aperture reflector. This telescope is the largest telescope sent into deep space. The resolution of the camera reaches 30 cm per pixel at a height of 300 km above the surface of Mars. The width of the swath is up to 6 km. The camera successfully removed the rovers on the surface of Mars, including Opportunity and Curiosity.
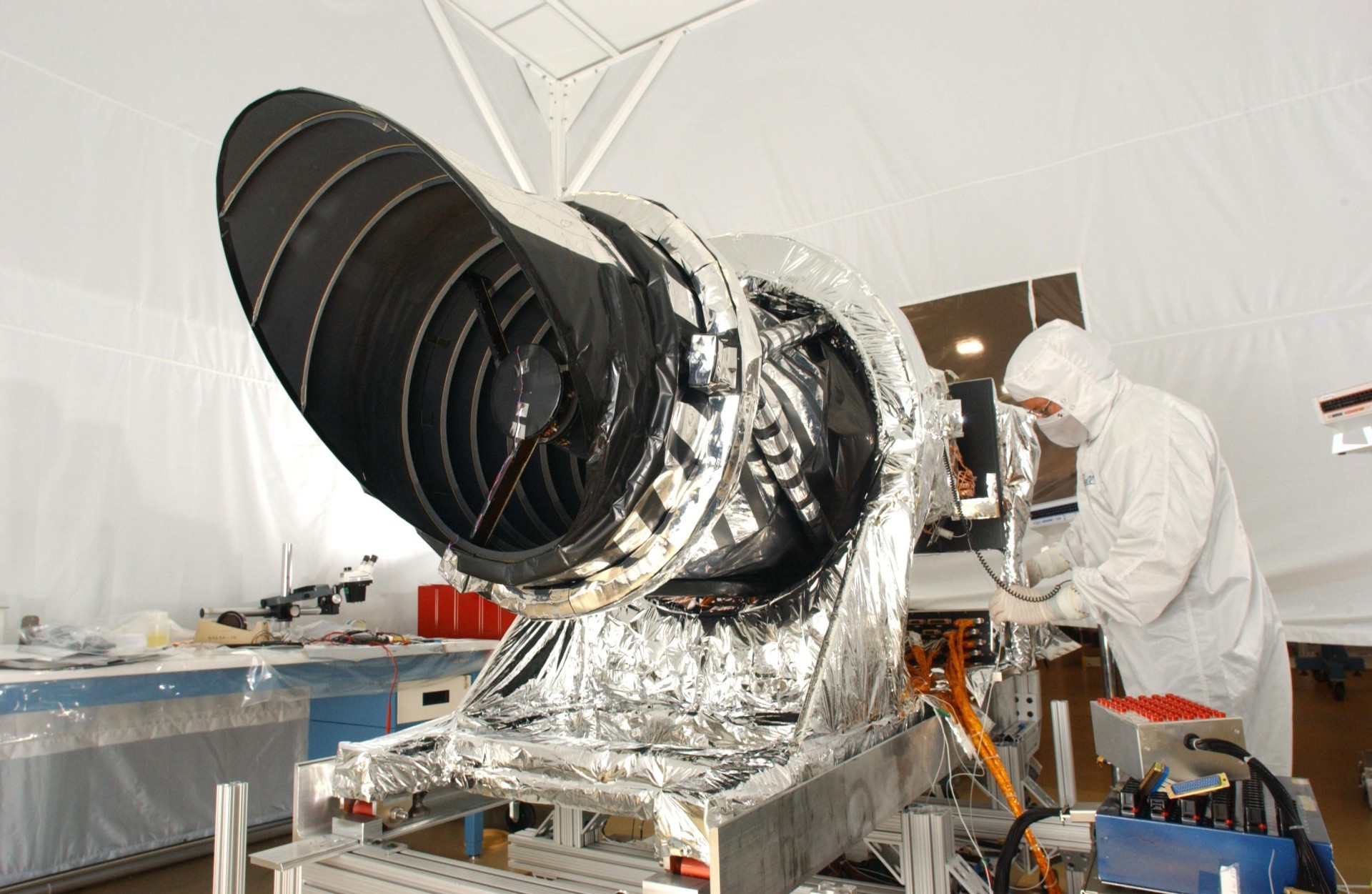

HiRISE camera before installation on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
Photo features
Date Received: February 6, 2016
Local Martian Time: 15:16
Latitude (center of the photo): 77.948 °
Longitude (east): 84,005 °
Distance to object: 365.9 km
The resolution of the original image: 36.6 cm / pixel (with binning 1 x 1), so that objects of approximately 110 cm are recorded
Card resolution: 25 cm / pixel
Map Projection: Polar Stereographic Projection
Emission Angle : 31.7 °
Phase angle : 36.3 °
Sun angle: 58 °, with the sun rising about 32 ° above the horizon
Solar longitude: 105.4 °, northern summer
Context map of Mars, where satellite photography was taken


The second photo from the stereo pair: ESP_045334_2580
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/395855/
All Articles