How it's made: the stages of creating a modern smartphone
For many, the phones that we see in stores or on storefront pages are a combination of certain parameters for a certain price. Sometimes it is flavored with a brand halo, sometimes with advertising, and sometimes with that very pleasant and seductive function for which you can spend much more than the planned budget. Anyway, this is a finished product. We propose to look behind and show the whole way of the device - from the idea and the printed circuit board to the storefront. Ready? Go!

From the outset, it is worth making a remark that the description below covers the most popular and common situations for the Russian market, but leaves room for exceptions.
Surely, many already know the principles of cooperation between OEM and ODM, which dominate the market in various variations.
Both of them slightly modified from their relatively encyclopedic values, and now the devices can be very conditionally divided into three categories:
All options have their advantages and disadvantages, all of them are able to please users and a bestseller for a great price as Honor 4C Pro , and the flagship Galaxy S7 or iPhone level, and a pleasant entry-level phone that is perfect for the role of the second or even the very first for a child .
Of course, the timing of the development of devices from these categories also vary. If in the first one there are mainly flagship solutions (but other price categories are possible) with a period from the beginning to the counter, sometimes reaching 9-12 months, then in the second there can be flagships and medium-level devices. The scattering of development terms is also large here: from 4-5 months to a year. In the latter category, play the very devices that offer excellent value for money in the initial and middle price segment. Work on them is faster due to the presence of a “base” on which the product is built.
Due to the fact that a decent layer of work on flagships and most mid-level devices takes place in beautiful and secret laboratories, the most relevant will be to consider the cycle of an inexpensive device, where the development process is more dynamic.
Demand creates supply. It is this idea that is fundamental to all devices, from flagships to budget decisions. It is necessary both to offer a good price for the buyer, coupled with the wide capabilities of the device, and to be able to do it in time, because competitors are not asleep.
Based on the parameters such as the desired networks (3G or LTE), the screen and its resolution, wireless modules, the Android version (it is unlikely in 2016 it makes sense to talk about the button phone), as well as the battery and the time when the partner will be ready to start production, the product born on paper.
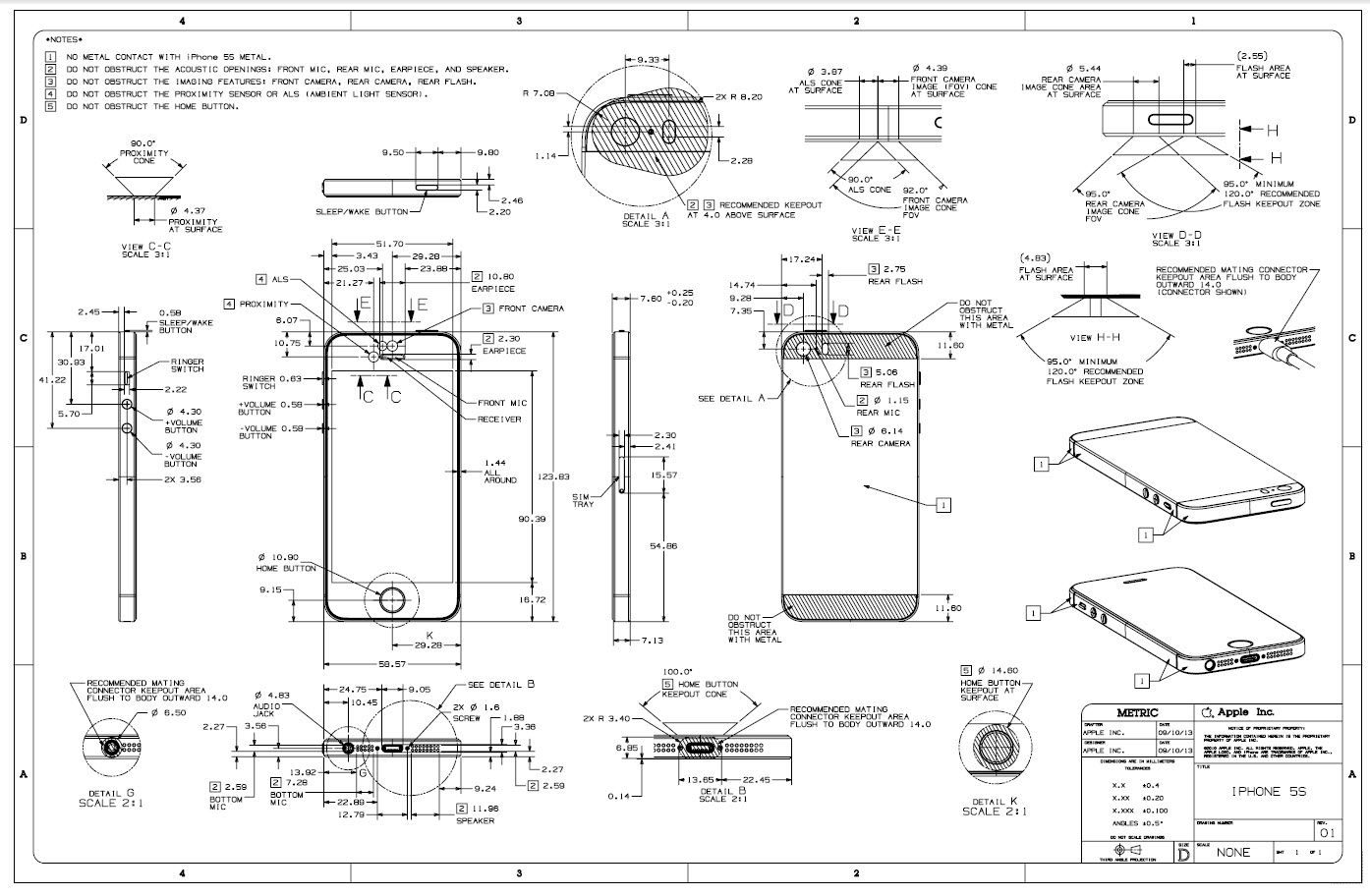
In some places, the system fails, and chimeras come into the world with too much price compared to competitors or a completely new technology on board, which remains undervalued by the market. Anyway, priorities and strengths are laid down initially in accordance with market expectations for a certain period.
First samples are being prepared and, as a rule, far from the final appearance and materials; work begins on software and hardware. The device will have to endure tests for strength, falling, simulation of long use, consisting of repeated presses and real torture for all its nodes. Each such iteration is accompanied by conclusions, corrections and, of course, a new series of bullying.

In parallel with this, other real devices begin to pass tests where they are planned for sale, to take into account the regional characteristics of networks, buildings and the position of satellites in the sky (yes, this is not a joke). The purpose of all this is to collect data for corrections in the design for the second and third revision of devices as part of working on it to achieve optimal results.
Work on the software includes both general stability and regional features. It’s no secret that Russia is one of the most difficult regions for manufacturers: for example, interface translation in 99% of cases is longer compared to English, users are not ready to put up with errors in software, which in Europe simply wouldn’t attach importance, and numbers can start with both 8 and 7 and be equivalent - in a word, there are peculiarities, and there are many of them. Not least are the results of the camera or cameras, work with wireless accessories.
All this, coupled with the settings for operators and a number of seemingly small things, can be a decisive factor when choosing a device in the store and its commercial success.
Based on the tests of the first stage, the device already acquires its final forms: the work with navigation and the network passes without complaints, the software becomes more stable, the camera shoots better - half the way to work on the software is completed.
At this moment, another important milestone begins for any device - the passage of tests for obtaining notifications and certificates in the territory of the Russian Federation. The essence of the test comes down to the fact that the phone must comply with the SAR standards, as well as be safe for the user, together with the battery, and by itself, the charger also passes the tests. And you should not be skeptical about the words about the tests - in the Russian Federation they are quite serious and harsh, so you can not worry about the safety for the owner of any device with a certificate of conformity.
In parallel with this, the device is sent for a review to Google (we're talking about an Android smartphone) for CTS / GTS tests. This is an automated and multi-level testing, its goal is to identify errors that would prevent the end user from comfortably using Google services. There will not be missed and fatal errors and incorrect settings of access rights for applications inside the software, as well as identify problems in terms of stability. Errors revealed at this stage are not recommendations, but a blocking factor, and without their correction to the device, the way is further ordered.
The only exception is where all this is taken into account in full and immediately it is the representatives of the Nexus line, whose software is done by Google.

As you might guess, the errors identified in this step are not recommendations, but a blocking factor, without which the device is ordered further.
So, the strength tests are passed, certificates are received by Google gives "good", the components of the device are fixed, production is preparing for a trial run, and the software is almost perfect. As a rule, at this moment work with the media, the first teasers, begins with the third iteration of the devices. Around this stage, leaks usually occur.

There comes the turn of painstaking work on the instructions, packaging design and its contents, as well as update tests for ordinary users and the preparation of service.
Of course, there is no limit to perfection, but at this stage there are no significant problems in the firmware, or they should be solved by the moment of the start of sales and are minimized to the point of finalization.
A trial run and analysis of its results is another milestone, because in fact, the output is a device that is completely equivalent to what will begin to be sold in just a few weeks. Thus, the start date of the mass launch is determined, and the remaining controversial points continue to be solved in the software - users will receive them with the first update, which often coincides with the start of sales.
 The first batch was produced, which passed all the checks and is ready for shipment and customs clearance. At the same time, an advertising campaign is in full swing, the first announcements and reviews in the media appear, and the pre-order form and samples in the open display become available to those who want to buy.
The first batch was produced, which passed all the checks and is ready for shipment and customs clearance. At the same time, an advertising campaign is in full swing, the first announcements and reviews in the media appear, and the pre-order form and samples in the open display become available to those who want to buy.
After passing the customs through the logistics chain, the very same boxes with the cherished apparatuses fall into the store's warehouse and its real showcases. But this does not mean that the work is completed and the project documentation is solemnly burned, and the work of the team resembles the picture below.
On the contrary, the stage begins to collect feedback on the software and the product itself, which affects the composition of the firmware updates, the following production, and even the following devices.
As you can see, the Russian market is one of the most difficult and for a number of security requirements, and for the level of software development, which makes it possible to choose from a variety of devices with comprehensively high quality standards regardless of the price segment

From the outset, it is worth making a remark that the description below covers the most popular and common situations for the Russian market, but leaves room for exceptions.
Surely, many already know the principles of cooperation between OEM and ODM, which dominate the market in various variations.
ODM ( English original design manufacturer) - a manufacturer of a product that is created according to its own original project , and not under a license.
')
An ODM contract is a type of cooperation between two companies, in which one company orders another for the development and production of a certain product (for example, equipment or software , etc.), and then launches it for sale under its own brand .
Thus, an ODM contract differs from an OEM contract in that in the first case the customer places an order not only for manufacturing, but also for product development, and in the second, only for manufacturing, and he himself designs and designs.
Both of them slightly modified from their relatively encyclopedic values, and now the devices can be very conditionally divided into three categories:
- fully closed loop, from the PCB to the plant within the parent company or, in extreme cases, related industries to maintain a large volume;
- Classic OEM, when production refers to a third-party organization for the parent company;
- Classic ODM with modifications by the parent company, when the reference design is taken as a basis, and work begins on its basis.
All options have their advantages and disadvantages, all of them are able to please users and a bestseller for a great price as Honor 4C Pro , and the flagship Galaxy S7 or iPhone level, and a pleasant entry-level phone that is perfect for the role of the second or even the very first for a child .
Of course, the timing of the development of devices from these categories also vary. If in the first one there are mainly flagship solutions (but other price categories are possible) with a period from the beginning to the counter, sometimes reaching 9-12 months, then in the second there can be flagships and medium-level devices. The scattering of development terms is also large here: from 4-5 months to a year. In the latter category, play the very devices that offer excellent value for money in the initial and middle price segment. Work on them is faster due to the presence of a “base” on which the product is built.
Due to the fact that a decent layer of work on flagships and most mid-level devices takes place in beautiful and secret laboratories, the most relevant will be to consider the cycle of an inexpensive device, where the development process is more dynamic.
Stage 0
Demand creates supply. It is this idea that is fundamental to all devices, from flagships to budget decisions. It is necessary both to offer a good price for the buyer, coupled with the wide capabilities of the device, and to be able to do it in time, because competitors are not asleep.
Based on the parameters such as the desired networks (3G or LTE), the screen and its resolution, wireless modules, the Android version (it is unlikely in 2016 it makes sense to talk about the button phone), as well as the battery and the time when the partner will be ready to start production, the product born on paper.

In some places, the system fails, and chimeras come into the world with too much price compared to competitors or a completely new technology on board, which remains undervalued by the market. Anyway, priorities and strengths are laid down initially in accordance with market expectations for a certain period.
Stage 1
First samples are being prepared and, as a rule, far from the final appearance and materials; work begins on software and hardware. The device will have to endure tests for strength, falling, simulation of long use, consisting of repeated presses and real torture for all its nodes. Each such iteration is accompanied by conclusions, corrections and, of course, a new series of bullying.

In parallel with this, other real devices begin to pass tests where they are planned for sale, to take into account the regional characteristics of networks, buildings and the position of satellites in the sky (yes, this is not a joke). The purpose of all this is to collect data for corrections in the design for the second and third revision of devices as part of working on it to achieve optimal results.
Work on the software includes both general stability and regional features. It’s no secret that Russia is one of the most difficult regions for manufacturers: for example, interface translation in 99% of cases is longer compared to English, users are not ready to put up with errors in software, which in Europe simply wouldn’t attach importance, and numbers can start with both 8 and 7 and be equivalent - in a word, there are peculiarities, and there are many of them. Not least are the results of the camera or cameras, work with wireless accessories.

All this, coupled with the settings for operators and a number of seemingly small things, can be a decisive factor when choosing a device in the store and its commercial success.
Stage 2
Based on the tests of the first stage, the device already acquires its final forms: the work with navigation and the network passes without complaints, the software becomes more stable, the camera shoots better - half the way to work on the software is completed.
At this moment, another important milestone begins for any device - the passage of tests for obtaining notifications and certificates in the territory of the Russian Federation. The essence of the test comes down to the fact that the phone must comply with the SAR standards, as well as be safe for the user, together with the battery, and by itself, the charger also passes the tests. And you should not be skeptical about the words about the tests - in the Russian Federation they are quite serious and harsh, so you can not worry about the safety for the owner of any device with a certificate of conformity.
In parallel with this, the device is sent for a review to Google (we're talking about an Android smartphone) for CTS / GTS tests. This is an automated and multi-level testing, its goal is to identify errors that would prevent the end user from comfortably using Google services. There will not be missed and fatal errors and incorrect settings of access rights for applications inside the software, as well as identify problems in terms of stability. Errors revealed at this stage are not recommendations, but a blocking factor, and without their correction to the device, the way is further ordered.
The only exception is where all this is taken into account in full and immediately it is the representatives of the Nexus line, whose software is done by Google.

As you might guess, the errors identified in this step are not recommendations, but a blocking factor, without which the device is ordered further.
Stage 3
So, the strength tests are passed, certificates are received by Google gives "good", the components of the device are fixed, production is preparing for a trial run, and the software is almost perfect. As a rule, at this moment work with the media, the first teasers, begins with the third iteration of the devices. Around this stage, leaks usually occur.

There comes the turn of painstaking work on the instructions, packaging design and its contents, as well as update tests for ordinary users and the preparation of service.
Of course, there is no limit to perfection, but at this stage there are no significant problems in the firmware, or they should be solved by the moment of the start of sales and are minimized to the point of finalization.
Stage 4
A trial run and analysis of its results is another milestone, because in fact, the output is a device that is completely equivalent to what will begin to be sold in just a few weeks. Thus, the start date of the mass launch is determined, and the remaining controversial points continue to be solved in the software - users will receive them with the first update, which often coincides with the start of sales.
The final
 The first batch was produced, which passed all the checks and is ready for shipment and customs clearance. At the same time, an advertising campaign is in full swing, the first announcements and reviews in the media appear, and the pre-order form and samples in the open display become available to those who want to buy.
The first batch was produced, which passed all the checks and is ready for shipment and customs clearance. At the same time, an advertising campaign is in full swing, the first announcements and reviews in the media appear, and the pre-order form and samples in the open display become available to those who want to buy.After passing the customs through the logistics chain, the very same boxes with the cherished apparatuses fall into the store's warehouse and its real showcases. But this does not mean that the work is completed and the project documentation is solemnly burned, and the work of the team resembles the picture below.
On the contrary, the stage begins to collect feedback on the software and the product itself, which affects the composition of the firmware updates, the following production, and even the following devices.
As you can see, the Russian market is one of the most difficult and for a number of security requirements, and for the level of software development, which makes it possible to choose from a variety of devices with comprehensively high quality standards regardless of the price segment

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/395667/
All Articles