Russian scientists have created a magneto-thrombolytic system that breaks blood clots thousands of times more effective than analogs.
Scientists from ITMO University in collaboration with the St. Petersburg City Mariinsky Hospital developed a unique drug for the treatment of thrombosis. According to the results of experiments, a solution of a nanoparticle-based drug localized on a thrombus using a magnet will be able to cleave the blood clots formed at a rate up to 4000 times greater than the existing domestic and foreign thrombolytics. The associated positive effect is to reduce the dose of the drug by dozens of times and, in this connection, to exclude many side effects, some of which lead to irreversible changes in the body.
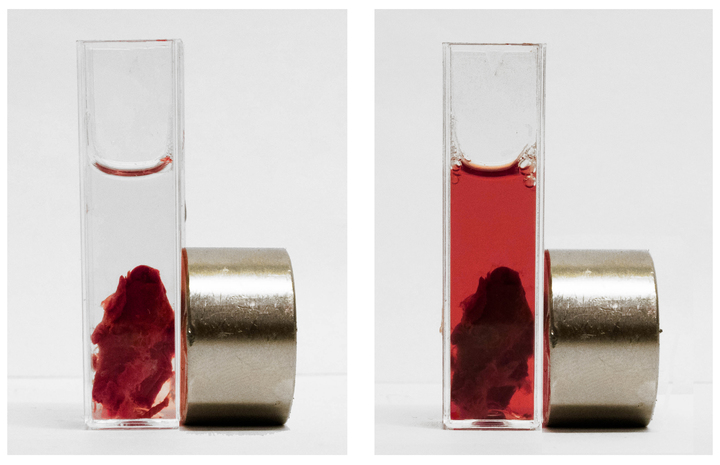
The figure above the cat demonstrates the effect of the developed thrombolytic system on the vascular thrombus extracted during the operation.
Problem
')
Acute critical conditions directly or indirectly associated with vascular occlusion are one of the primary problems in the emergency care process in many countries around the world. In Russia, emergency care for thrombosis is significantly less effective than abroad, which is confirmed by statistics: in 60% of cases with a lethal outcome, heart attacks and strokes caused by thrombolytic conditions were and are the cause of the latter.
One of the primary tasks of emergency assistance in the development of such states is the prompt and effective carrying out of thrombolysis, a procedure that allows a thrombus to be dissolved for a limited period of time.
Even abroad, this procedure can be successfully performed only in 15% of cases, while in Russia the percentage figures, alas, are much lower: only two out of 100 patients brought to the hospital can be effectively helped. The remaining 98% become disabled or end their earthly journey. This disappointing statistic is related to the fact that the time allotted to doctors to dissolve a blood clot is very limited and amounts to 3 ... 4.5 hours. At the end of this time, tissues deprived of blood flow die irretrievably. But even if the patient was “born in a shirt” and ended up in a “happy” 2%, numerous complications inevitably await him, caused by the thrombolysis itself (injected intravenously with a protein that dissolves the clot).
The root of the problem is that thrombolytics do not have directional effects and are instantly distributed throughout the circulatory system. The body's defenses begin blocking the foreign protein, which rapidly reduces its activity. Therefore, the drug is administered in horse doses, in the hope that at least a small fraction of it will reach the goal and manage to get to the thrombus. “Now we are kicking sparrows out of a cannon,” says Ivan Dudanov, MD, professor, corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, head of the regional cardiovascular center of St. Petersburg State Medical University “City Mariinsky Hospital”. - Dissolving a small thrombus, which corked a vessel with a diameter of only 1-2 millimeters, thrombolysis negatively affects the entire network of human blood vessels. So that we could change the current situation, we decided to develop a method for local delivery of the drug, which allows us to repeatedly reduce the dose of the enzyme, provided that the entire therapeutic effect is only on the thrombus. ”
Decision
Scientists have developed a material that allows you to deliver the enzyme for the cleavage of a blood clot directionally and safely for the body. Protein - urokinase, widely used in medicine as thrombolytic agent is enclosed in a magnetite porous base. Moreover, it is possible to make coatings for artificial vessels from such a composite in order to prevent their blockage, as well as stable injection solutions, nano-sized particles of which are easily localized in a thrombus under the action of a magnetic field.
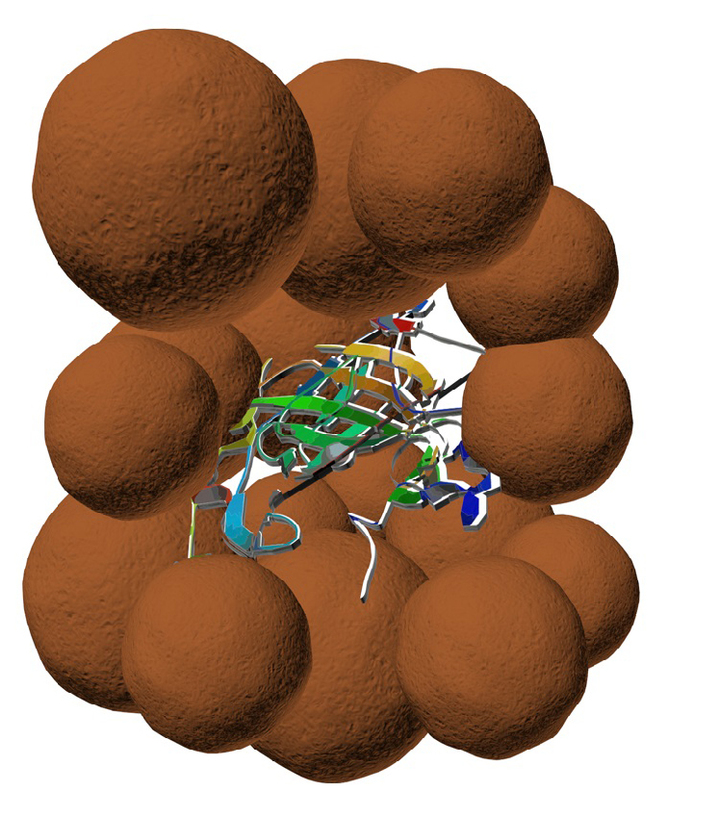
Schematic representation of the nanoparticle thrombolytic agent. Enzyme surrounded by a magnetite cage
It is fundamentally important that the magnetite carcass guarantees the protein inside it reliable protection against various inhibitor substances that are contained in the blood and deactivate free thrombolytics. Andrei Drozdov, project manager and employee of the International Laboratory of Solution Chemistry of Advanced Materials and Technologies, clarifies: “When developing such materials to achieve a prolonged effect, protein is usually placed in a polymer matrix from which it is gradually released, and after a while the drug turns into a pacifier. We experimentally showed that the enzyme in the composite does not lose its therapeutic properties even with repeated use and works for a very long time. A new composite surpasses unprotected enzymes by more than 4000 times in terms of the dissolution rate of a thrombus. ”
The synthesized material consists solely of components that already have permission for intravenous administration and are not dangerous to humans. According to Ivan Dudanov, in the future, drugs developed on the basis of the proposed composite will be highly effective not only for the treatment of thrombosis, but also for its prevention, since the enzyme circulating through the circulatory system in microdoses will clean and gently clean the vessels. In addition, the protein, which is protected by a magnetite skeleton, will be able to cope with its functions for a very long time, until it is eliminated through the liver as an ordinary metabolite.
The development of domestic specialists from ITMO University and the St. Petersburg Mariinsky City Hospital was a logical continuation of the research conducted earlier. In them, scientists managed to develop a technique for capturing various enzymes in a sol-gel matrix based on magnetite and create a prototype of a magnetically controlled bioactive system.
“Within this stage of our project, we showed how the concept we developed works on more specific objects. We prepared thrombolytic colloid and tested its effect on artificial blood clots obtained from human plasma and blood, as well as on human blood clots extracted during surgery. The results obtained may allow us to test a new thrombolytic system on living beings soon. Now we are at the stage of coordination with the Ministry of Education and the science of preclinical research, ”concluded Vladimir Vinogradov, head of the International Laboratory of Solution Chemistry of Advanced Materials and Technologies.
A report on the work done was published in the journal Scientific Reports on June 20, 2016.
Thank you for your time and attention. Be healthy!
That's all, with you there was a simple service for choosing sophisticated Dronk.Ru equipment. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog , there will be many more interesting ...


The figure above the cat demonstrates the effect of the developed thrombolytic system on the vascular thrombus extracted during the operation.
Problem
')
Acute critical conditions directly or indirectly associated with vascular occlusion are one of the primary problems in the emergency care process in many countries around the world. In Russia, emergency care for thrombosis is significantly less effective than abroad, which is confirmed by statistics: in 60% of cases with a lethal outcome, heart attacks and strokes caused by thrombolytic conditions were and are the cause of the latter.
One of the primary tasks of emergency assistance in the development of such states is the prompt and effective carrying out of thrombolysis, a procedure that allows a thrombus to be dissolved for a limited period of time.
Even abroad, this procedure can be successfully performed only in 15% of cases, while in Russia the percentage figures, alas, are much lower: only two out of 100 patients brought to the hospital can be effectively helped. The remaining 98% become disabled or end their earthly journey. This disappointing statistic is related to the fact that the time allotted to doctors to dissolve a blood clot is very limited and amounts to 3 ... 4.5 hours. At the end of this time, tissues deprived of blood flow die irretrievably. But even if the patient was “born in a shirt” and ended up in a “happy” 2%, numerous complications inevitably await him, caused by the thrombolysis itself (injected intravenously with a protein that dissolves the clot).
The root of the problem is that thrombolytics do not have directional effects and are instantly distributed throughout the circulatory system. The body's defenses begin blocking the foreign protein, which rapidly reduces its activity. Therefore, the drug is administered in horse doses, in the hope that at least a small fraction of it will reach the goal and manage to get to the thrombus. “Now we are kicking sparrows out of a cannon,” says Ivan Dudanov, MD, professor, corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, head of the regional cardiovascular center of St. Petersburg State Medical University “City Mariinsky Hospital”. - Dissolving a small thrombus, which corked a vessel with a diameter of only 1-2 millimeters, thrombolysis negatively affects the entire network of human blood vessels. So that we could change the current situation, we decided to develop a method for local delivery of the drug, which allows us to repeatedly reduce the dose of the enzyme, provided that the entire therapeutic effect is only on the thrombus. ”
Decision
Scientists have developed a material that allows you to deliver the enzyme for the cleavage of a blood clot directionally and safely for the body. Protein - urokinase, widely used in medicine as thrombolytic agent is enclosed in a magnetite porous base. Moreover, it is possible to make coatings for artificial vessels from such a composite in order to prevent their blockage, as well as stable injection solutions, nano-sized particles of which are easily localized in a thrombus under the action of a magnetic field.

Schematic representation of the nanoparticle thrombolytic agent. Enzyme surrounded by a magnetite cage
It is fundamentally important that the magnetite carcass guarantees the protein inside it reliable protection against various inhibitor substances that are contained in the blood and deactivate free thrombolytics. Andrei Drozdov, project manager and employee of the International Laboratory of Solution Chemistry of Advanced Materials and Technologies, clarifies: “When developing such materials to achieve a prolonged effect, protein is usually placed in a polymer matrix from which it is gradually released, and after a while the drug turns into a pacifier. We experimentally showed that the enzyme in the composite does not lose its therapeutic properties even with repeated use and works for a very long time. A new composite surpasses unprotected enzymes by more than 4000 times in terms of the dissolution rate of a thrombus. ”
The synthesized material consists solely of components that already have permission for intravenous administration and are not dangerous to humans. According to Ivan Dudanov, in the future, drugs developed on the basis of the proposed composite will be highly effective not only for the treatment of thrombosis, but also for its prevention, since the enzyme circulating through the circulatory system in microdoses will clean and gently clean the vessels. In addition, the protein, which is protected by a magnetite skeleton, will be able to cope with its functions for a very long time, until it is eliminated through the liver as an ordinary metabolite.
The development of domestic specialists from ITMO University and the St. Petersburg Mariinsky City Hospital was a logical continuation of the research conducted earlier. In them, scientists managed to develop a technique for capturing various enzymes in a sol-gel matrix based on magnetite and create a prototype of a magnetically controlled bioactive system.
“Within this stage of our project, we showed how the concept we developed works on more specific objects. We prepared thrombolytic colloid and tested its effect on artificial blood clots obtained from human plasma and blood, as well as on human blood clots extracted during surgery. The results obtained may allow us to test a new thrombolytic system on living beings soon. Now we are at the stage of coordination with the Ministry of Education and the science of preclinical research, ”concluded Vladimir Vinogradov, head of the International Laboratory of Solution Chemistry of Advanced Materials and Technologies.
A report on the work done was published in the journal Scientific Reports on June 20, 2016.
Thank you for your time and attention. Be healthy!
That's all, with you there was a simple service for choosing sophisticated Dronk.Ru equipment. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog , there will be many more interesting ...

 |  |  |
| Why do online stores give money for purchases? | Save up to 8% on every purchase on AliExpres and other online stores in China | Return your money - choose a cashback service for Aliexpress |
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/395527/
All Articles