Scientists from the Netherlands confirmed: the second information layer in DNA exists
The sequence of alternation of bases, defined in the DNA molecule, located in every cell of our body makes us the way we are. At the same time, a number of scientists have been studying the possibility and likelihood of the existence of an “alternative” hidden language, which also encodes vital information of the genome, in a different way and at a different level for quite a long time. This coded information should serve as a guide to action, using which the cells of our body are able to recognize and process the main array of information in a strictly defined sequence.
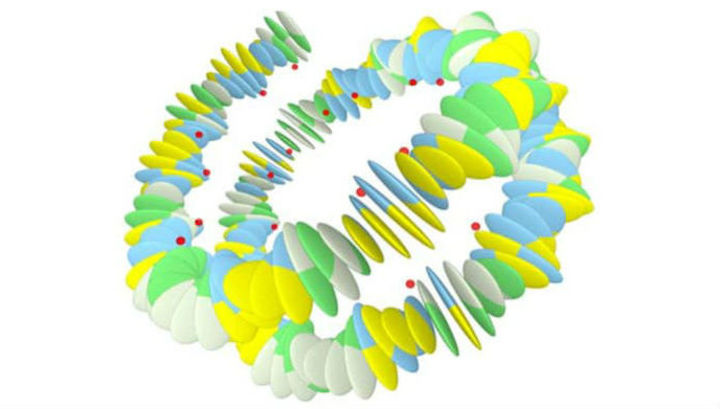
June 7, 2016 on the pages of the scientific publication journals.plos.org published the work of a group of scientists from the Netherlands who were able to prove the existence in our DNA of the second hidden information layer.
How DNA encodes the structure of proteins
')
As is known, DNA bases are those building blocks of the universe that determine the very possibility of the existence and reproduction of all life on our planet. The DNA molecule consists of four types of nitrogen-containing nucleotide bases, denoted by the letters "A", "T", "C" and "G".
Each of our cells contains about 30 thousand different genes, while for some bacteria only 500 genes are enough. The genes contain codes according to which proteins are synthesized and the order in which the amino acids are located in them is determined. No matter where the cells are located in the human body, they always contain the same set of genes. However, depending on the type of cells — skin, nerve, or muscle cells — they use different genes to synthesize new proteins.
Long strands of DNA in the chromosomes of the cell are tightly compressed. The compact arrangement of DNA in chromosomes is due to special proteins, around which DNA strands are wound. But proteins are present in the cell, which, in order to facilitate the synthesis of new proteins according to the code contained in the DNA, if necessary, translate the DNA from a compact form into an unfolded one. Under the influence of these proteins, chromosome cells that are being prepared for division unfold and occupy 10,000 times more space from now on.
The “A”, “T”, “C” and “G” nucleotides that make up the long DNA molecules are arranged in a specific order to ensure the coding of proteins during their synthesis, which originates from 20 different types of amino acids. At the same time, DNA plays the role of a matrix - each protein has its own gene, according to the sample of which amino acids are synthesized, forming the desired protein. Thus, the genetic code is embodied in proteins, and the sequence of nucleotides in the gene determines the sequence of amino acids in the protein. The simplest analogy is Morse code, where dots, dashes and their combination correspond to certain letters of the alphabet. The sequence of nucleotides that are read three at a time corresponds to the amino acid sequence in the protein. In this case, a set of three nucleotides that are read at a time encodes one amino acid. For example, the AUG nucleotide set encodes the acid acidomethionine.
There are 64 combinations of nucleotides, but only 20 different types of amino acids are synthesized. This means that some ternary nucleotide sequences are not used for the synthesis of amino acids, but to indicate the interruption of the synthesis procedure. There are no completely meaningless sets of ternary nucleotides - each of them performs a specific function. There are several sets of nucleotides that encode the same amino acids. The largest gene consists of two million nucleotides placed on each of its threads, and the smallest consists of one thousand.
The process of reading genetic information (“transcription”) begins with the discovery and deployment of a small part of the DNA double helix at the end of the chromosome. The genetic codes of this region of the chromosome are then copied to the RNA molecule that grows as the copying process progresses, and the protein copying mechanism moves along the DNA strand. The process of transferring a genetic code ends when the so-called terminal group of amino acids is synthesized at the end of RNA - its presence signals the end of the protein chain of the given code.
The sequence of alternation of these bases in the molecules determines the information that allows the cells of our body to produce a strictly defined amount of the necessary proteins and support other vital functions. But, despite the fact that all cells of our body contain the same set of genes, the cells themselves develop in different ways and the simplest confirmation of this is the existence of cells of various types of tissues that make up various organs. And all this again and again makes scientists look for an additional key to the "redundant", that is, until the end of the decrypted information.
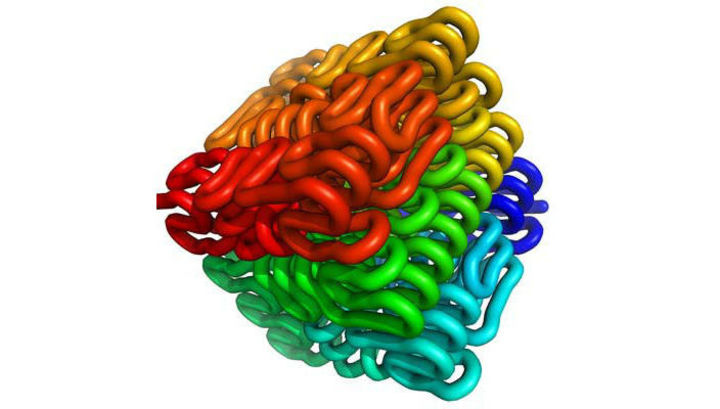
DNA molecules are extremely compactly packed. On the other hand, it is known that, in its disentangled form, a chain of molecules contained in one cell, on average, is 2 meters. According to a hypothesis that has not changed since the 1980s, the mechanical properties of the DNA molecule determine how it will be “folded” inside the cell. The latest research by Dutch scientists has confirmed: a change in the shape of the molecule leads to a change in the "convolution" of the DNA helix. It is this fact that made it possible to speak about the presence in DNA of the second coding mechanism, playing no less important in the processes of supporting the reproduction of proteins than the basic genetic code.
The research team from the Leiden Institute of Physics (Leiden Institute of Physics) under the leadership of Helmut Schissel (Helmut Schiessel), developed a computer model, the purpose of which was to test the hypothesis described above and search for ways to prove its reliability. The logical basis for the model in question was similar baker yeast cells and yeast of the genus Schizosaccharomycetes, which contain a DNA molecule with the same base sequence, but with different mechanical properties.
As demonstrated by the mathematical analysis of the model, the DNA molecules of the yeast are really twisted (configured) and acquire a compact size under the influence of different mechanical influences by different algorithms.
Another confirmation of the existence of a secondary code
The main genetic code contained in DNA was partially deciphered as early as the 60s of the last century. From that moment on, the scientific community was absolutely certain that only the information on proteins, which are produced by the body's cells as a response to external events and stimuli, is recorded in the DNA. Despite the fact that over time this concept was somewhat extended, the basic principles of "monolingual" coding in DNA remained unchanged.
However, research in this direction continued. In 2013, a group of scientists from the University of Washington (University of Washington, UW) was the first to declare the existence of a hidden secondary code that directly determines the reading sequence of the main genetic instructions contained in DNA. The results of studies confirming the hypothesis were published on the pages of Science .
The scientists concluded that the information in the genetic code is recorded in two different languages. The first describes and regulates the structure and amount of proteins produced by cells, the second determines the sequence of execution of instructions that control the reading of genes. The constructions of the second language, as the scientists noted in their publication, were written over the constructions of the first, which was the main reason that, being “in the most visible place,” he had been hidden from the attention of the scientific community for so long.
Investigating genetic sequences, scientists then concluded that some types of codons (up to 15% of their total number), called duons, can have two meanings, one of which is associated with the description of the structure of proteins, the other with the principles of gene control. Moreover, these two values are very closely related to each other, because the instructions of gene control in some cases allow stabilizing certain areas of the most complex proteins at the time of their production. And it is the duons that form the basis of the structures of the second language, with the help of which the second layer of information is recorded in the DNA.
“For more than 40 years, we believed that all changes in the genetic code of DNA molecules affect only the production of proteins in cells,” says Dr. John Stamatoyanopoulos, a professor of medicine and genomics at Washington University, “Now we know that, reading the genetic information, we missed almost half of it, which, in turn, distorted the overall picture of our knowledge. Armed with new knowledge about the availability of additional information, soon we will be able to fully read everything that is written in DNA, in the most powerful information storage device created by nature itself. ”
Value of work
Knowledge of the fact that DNA molecules simultaneously contain two types of information will enable scientists to more fully recognize the changes in proteins that will occur as a result of mutagenic processes affecting the structure of DNA. An accurate and complete picture of changes in the structure of proteins will allow scientists to accurately and unambiguously determine which diseases are the causes and which result from such changes and develop new methods of treating diseases based on changes in that part of the DNA information that controls only the functions of genes.
On the other hand, for the first time, scientists were able to confirm that genetic mutations, which, as suggested earlier, could only affect the structure of the basic code of a genetic sequence, can also affect the mechanical structure of DNA, which, in turn, will lead to changes in the reading sequence instructions for the production of proteins, change the type and quantity of the latter.
Publication on the website of the Leiden Institute of Physics
Detailed description of the work in the journal PLOS One
That's all, with you there was a simple service for choosing sophisticated Dronk.Ru equipment. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog , there will be many more interesting ...


June 7, 2016 on the pages of the scientific publication journals.plos.org published the work of a group of scientists from the Netherlands who were able to prove the existence in our DNA of the second hidden information layer.
How DNA encodes the structure of proteins
')
As is known, DNA bases are those building blocks of the universe that determine the very possibility of the existence and reproduction of all life on our planet. The DNA molecule consists of four types of nitrogen-containing nucleotide bases, denoted by the letters "A", "T", "C" and "G".
Each of our cells contains about 30 thousand different genes, while for some bacteria only 500 genes are enough. The genes contain codes according to which proteins are synthesized and the order in which the amino acids are located in them is determined. No matter where the cells are located in the human body, they always contain the same set of genes. However, depending on the type of cells — skin, nerve, or muscle cells — they use different genes to synthesize new proteins.
Long strands of DNA in the chromosomes of the cell are tightly compressed. The compact arrangement of DNA in chromosomes is due to special proteins, around which DNA strands are wound. But proteins are present in the cell, which, in order to facilitate the synthesis of new proteins according to the code contained in the DNA, if necessary, translate the DNA from a compact form into an unfolded one. Under the influence of these proteins, chromosome cells that are being prepared for division unfold and occupy 10,000 times more space from now on.
The “A”, “T”, “C” and “G” nucleotides that make up the long DNA molecules are arranged in a specific order to ensure the coding of proteins during their synthesis, which originates from 20 different types of amino acids. At the same time, DNA plays the role of a matrix - each protein has its own gene, according to the sample of which amino acids are synthesized, forming the desired protein. Thus, the genetic code is embodied in proteins, and the sequence of nucleotides in the gene determines the sequence of amino acids in the protein. The simplest analogy is Morse code, where dots, dashes and their combination correspond to certain letters of the alphabet. The sequence of nucleotides that are read three at a time corresponds to the amino acid sequence in the protein. In this case, a set of three nucleotides that are read at a time encodes one amino acid. For example, the AUG nucleotide set encodes the acid acidomethionine.
There are 64 combinations of nucleotides, but only 20 different types of amino acids are synthesized. This means that some ternary nucleotide sequences are not used for the synthesis of amino acids, but to indicate the interruption of the synthesis procedure. There are no completely meaningless sets of ternary nucleotides - each of them performs a specific function. There are several sets of nucleotides that encode the same amino acids. The largest gene consists of two million nucleotides placed on each of its threads, and the smallest consists of one thousand.
The process of reading genetic information (“transcription”) begins with the discovery and deployment of a small part of the DNA double helix at the end of the chromosome. The genetic codes of this region of the chromosome are then copied to the RNA molecule that grows as the copying process progresses, and the protein copying mechanism moves along the DNA strand. The process of transferring a genetic code ends when the so-called terminal group of amino acids is synthesized at the end of RNA - its presence signals the end of the protein chain of the given code.
The sequence of alternation of these bases in the molecules determines the information that allows the cells of our body to produce a strictly defined amount of the necessary proteins and support other vital functions. But, despite the fact that all cells of our body contain the same set of genes, the cells themselves develop in different ways and the simplest confirmation of this is the existence of cells of various types of tissues that make up various organs. And all this again and again makes scientists look for an additional key to the "redundant", that is, until the end of the decrypted information.

DNA molecules are extremely compactly packed. On the other hand, it is known that, in its disentangled form, a chain of molecules contained in one cell, on average, is 2 meters. According to a hypothesis that has not changed since the 1980s, the mechanical properties of the DNA molecule determine how it will be “folded” inside the cell. The latest research by Dutch scientists has confirmed: a change in the shape of the molecule leads to a change in the "convolution" of the DNA helix. It is this fact that made it possible to speak about the presence in DNA of the second coding mechanism, playing no less important in the processes of supporting the reproduction of proteins than the basic genetic code.
The research team from the Leiden Institute of Physics (Leiden Institute of Physics) under the leadership of Helmut Schissel (Helmut Schiessel), developed a computer model, the purpose of which was to test the hypothesis described above and search for ways to prove its reliability. The logical basis for the model in question was similar baker yeast cells and yeast of the genus Schizosaccharomycetes, which contain a DNA molecule with the same base sequence, but with different mechanical properties.
As demonstrated by the mathematical analysis of the model, the DNA molecules of the yeast are really twisted (configured) and acquire a compact size under the influence of different mechanical influences by different algorithms.
Another confirmation of the existence of a secondary code
The main genetic code contained in DNA was partially deciphered as early as the 60s of the last century. From that moment on, the scientific community was absolutely certain that only the information on proteins, which are produced by the body's cells as a response to external events and stimuli, is recorded in the DNA. Despite the fact that over time this concept was somewhat extended, the basic principles of "monolingual" coding in DNA remained unchanged.
However, research in this direction continued. In 2013, a group of scientists from the University of Washington (University of Washington, UW) was the first to declare the existence of a hidden secondary code that directly determines the reading sequence of the main genetic instructions contained in DNA. The results of studies confirming the hypothesis were published on the pages of Science .
The scientists concluded that the information in the genetic code is recorded in two different languages. The first describes and regulates the structure and amount of proteins produced by cells, the second determines the sequence of execution of instructions that control the reading of genes. The constructions of the second language, as the scientists noted in their publication, were written over the constructions of the first, which was the main reason that, being “in the most visible place,” he had been hidden from the attention of the scientific community for so long.
Investigating genetic sequences, scientists then concluded that some types of codons (up to 15% of their total number), called duons, can have two meanings, one of which is associated with the description of the structure of proteins, the other with the principles of gene control. Moreover, these two values are very closely related to each other, because the instructions of gene control in some cases allow stabilizing certain areas of the most complex proteins at the time of their production. And it is the duons that form the basis of the structures of the second language, with the help of which the second layer of information is recorded in the DNA.
“For more than 40 years, we believed that all changes in the genetic code of DNA molecules affect only the production of proteins in cells,” says Dr. John Stamatoyanopoulos, a professor of medicine and genomics at Washington University, “Now we know that, reading the genetic information, we missed almost half of it, which, in turn, distorted the overall picture of our knowledge. Armed with new knowledge about the availability of additional information, soon we will be able to fully read everything that is written in DNA, in the most powerful information storage device created by nature itself. ”
Value of work
Knowledge of the fact that DNA molecules simultaneously contain two types of information will enable scientists to more fully recognize the changes in proteins that will occur as a result of mutagenic processes affecting the structure of DNA. An accurate and complete picture of changes in the structure of proteins will allow scientists to accurately and unambiguously determine which diseases are the causes and which result from such changes and develop new methods of treating diseases based on changes in that part of the DNA information that controls only the functions of genes.
On the other hand, for the first time, scientists were able to confirm that genetic mutations, which, as suggested earlier, could only affect the structure of the basic code of a genetic sequence, can also affect the mechanical structure of DNA, which, in turn, will lead to changes in the reading sequence instructions for the production of proteins, change the type and quantity of the latter.
Publication on the website of the Leiden Institute of Physics
Detailed description of the work in the journal PLOS One
That's all, with you there was a simple service for choosing sophisticated Dronk.Ru equipment. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog , there will be many more interesting ...

 |  |  |
| Why do online stores give money for purchases? | Review of Xiaomi Mi Air Purifier 2 or how to clean the air of the metropolis? | Return your money - choose a cashback service for Aliexpress |
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/395077/
All Articles