The evolution of mobile autofocus: from contrast to Dual Pixel
Hi, Giktayms! When shooting on a smartphone (and not only) it is very important that the photos are clear and clear. For this, the snapshot object must be in focus before you click on the “Take a Photo” button. Recently, many smartphone manufacturers are working to improve the autofocus technology, and today we will look at the pros and cons of each, and how they differ. As usual, all the details under the cut.

When choosing a camera phone, many people pay attention to the number of megapixels - they say, who has more of them, is even better. However, it is often more important and more useful to look at other factors that have no less serious influence on the quality of photos. Among them - the type of autofocus camera smartphone. Apple, Samsung, LG and other manufacturers are now actively involved in this area, and many have really managed to make significant progress.
Using the camera's automatic focusing system, the lens is adjusted so as to focus directly on the subject, thereby ensuring the difference between a clear picture and a missed opportunity.
')
Simplified principle of the camera is that the rays of light are reflected from the photographed objects and then fall on the sensor, which converts the flow of photons into a stream of electrons. After that, the current is converted into a set of bits, the data is processed and recorded in the camera's memory. CMOS sensors, which convert charge into voltage directly in a pixel, provide direct access to the content of an arbitrary pixel, are now particularly popular with smartphone manufacturers.
In theory, everything works like this: the lens focuses the light on the sensor, the sensor then creates a digital photo.
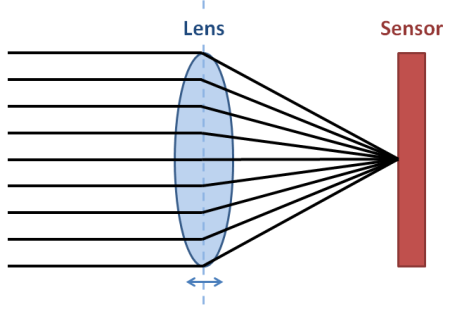
In reality, everything is not so simple. The angle of the incoming best light depends on the distance at which the object is photographed. The diagram below shows the lenses that focus the rays of light on a blue object: the green and red objects are out of focus and will be blurred in the final image. If we want to focus on a green or red object, we need to change the distance between the lenses and the sensor.

At the dawn of the camera industry, most devices had a fixed focus. In modern smartphones, it is possible to adjust the distance between the lenses and the sensor. Therefore, you get high-quality detailed images. Now for the implementation of autofocus in smartphones, three methods are mainly used: contrast, phase and laser.
Contrast autofocus refers to the passive type of autofocus. Until now, this solution is used in most smartphones - largely because it is one of the simplest. Using the sensor, the amount of light on the object is measured, after which it also moves the lens depending on the contrast. If the contrast is maximum, then the subject is in focus.

In general, contrast autofocus is quite good at its task and has a big fat plus - it is quite simple and does not require any complicated “hardware” for its work.
But he has several drawbacks. In particular, contrast autofocus is slower than the others - it usually takes about a second to focus on an object. During this time, you can take a picture, or the moment will be missed if you wanted to shoot, for example, a quickly moving object. This is due to the fact that the lion's share of time is occupied by the process of “shifting the focus point / lens of the lens - contrast assessment - shift - contrast assessment”. In addition, the contrast autofocus is not the possibility of tracking focus, and in poor lighting conditions it is unlikely to impress you. Therefore, this type of autofocus today is used mainly in budget smartphones such as the Lenovo A536 , ASUS Zenfone Go and others.
One of the pioneers here was the Samsung company, which borrowed technology from digital SLR cameras and equipped its Galaxy S5 with phase autofocus. The point is, in this case special sensors are used - they catch the transmitted light flux from different points of the image using lenses and mirrors. Inside the sensor, light is divided into two parts, each of which falls on a supersensitive sensor. The distance between the streams of light is measured by the sensor, after which he himself determines how much the lens needs to be shifted for precise focusing. For example, the Samsung Galaxy S5 takes only 0.3 seconds to focus on an object.
Visually, the principle of the phase autofocus is presented below.

The first and main advantage of phase autofocus is that it is much faster than contrast, it’s just a must have for shooting moving objects. In addition, the camera can assess the movement of an object using sensors, hence we get the possibility of tracking autofocus.
But there are also disadvantages. Phase autofocus, as well as contrast, also does not do very well with its tasks in low light conditions. It also needs a more powerful hardware, so it is usually available in high-end smartphones. Among them, Huawei Honor 7 , Sony Xperia M5 and Samsung Galaxy Note 5 , which, by the way, can be found in M.Video.
Some manufacturers went further and decided to use laser autofocus in smartphones (more on this later), while others were actively engaged in improving phase autofocus technology. For example, Apple in its iPhone 6s and iPhone 6s Plus uses the so-called “focal pixels” - the point is that the technology uses part of the pixels as a phase sensor, and shooting on Apple’s smartphones is really fast. In fact, this is the same phase autofocus, here we must pay tribute to marketers.
But Dual Pixel technology, which Samsung uses in its Galaxy S7 and Galaxy S7 Edge smartphones, is really different from phase focusing in other smartphones' cameras. Although it is a kind of phase autofocus, it still has some differences and subtleties. In smartphones, phase autofocus is somewhat limited - in order to assign a focal sensor to each pixel, you need to strongly reduce it, from here we get noise and photo blurring. Usually, about 10% of light-sensitive points are equipped with sensors, some manufacturers, however, do not go beyond 5%.
In Dual Pixel, each pixel is equipped with a separate sensor due to the increase in pixel sizes. The processor processes the readings of each pixel, but it does it so quickly that autofocus still takes tenths of a second. Samsung says that Dual Pixel technology is similar to focusing with the human eye, but this is again a marketing ploy.

Nevertheless, we must recognize the innovativeness of this approach to phase autofocus in modern smartphones. Now it is a real exclusive for the Galaxy S7 and Galaxy S7 Edge .
Like phase, laser autofocus refers to the active type of autofocus. This direction has long been engaged in the company LG, which first implemented a laser autofocus in its smartphone G3. The technology is based on the principle of a laser rangefinder: a laser emitter illuminates an object, and a sensor measures the distance to it and the time of arrival of the reflected laser beam.
One of the main advantages of this autofocus is time. As they say in LG, the whole process of autofocusing with a laser takes 0.276 seconds. Significantly faster contrast autofocus and a little bit faster than the phase.

The obvious advantage of laser autofocus is that it is incredibly fast and works well in low light conditions. But it only works at a certain distance - the best effect is achieved if the distance from the smartphone to the object is less than 0.6 meters. And after five meters - hello, contrasting autofocus.
Laser autofocus is mainly equipped with LG smartphones - for example, LG G4 . But there are exceptions: the same One Plus 2 or Asus Zenfone 2 Laser . However, the latter is clear from the name, and the price is attractive for such a set of possibilities.
At some point, the manufacturers realized that they needed to do something outlandish, outside of phase or laser autofocus. This is how dual cameras came into being: not one but two lenses are used at once to get clear pictures. While one camera with a fixed focus receives a snapshot of distant objects, the other focuses on objects that are nearby.
An important advantage of a dual camera is the ability to quickly take a picture, and then focus on it later, just like in a Lytro camera. But if we talk about a more accurate focus, here the dual camera clearly loses the phase focus.

So far, not many smartphones on the market are available with dual cameras - these are HTC devices (for example, One M9 + ), Honor 6 Plus, and others. Rumor has it that Apple, in its new iPhone, will decide to use a dual camera.
Infrared autofocus technology, which Lenovo showed at the MWC last year, works essentially as a laser autofocus, but in speed it is about twice as fast as the contrast. You can test it on the example of Lenovo Vibe Shot .
Since everyone chooses a smartphone for their needs, it is difficult to advise something that suits everyone at once. Someone in awe of the autofocus from Huawei that was customizable after the shooting, others consider the Dual Pixel to be optimal. If we take in general, at the moment the phase autofocus is the right decision for most of the flagships, and the manufacturers prove this to us all the time.

When choosing a camera phone, many people pay attention to the number of megapixels - they say, who has more of them, is even better. However, it is often more important and more useful to look at other factors that have no less serious influence on the quality of photos. Among them - the type of autofocus camera smartphone. Apple, Samsung, LG and other manufacturers are now actively involved in this area, and many have really managed to make significant progress.
What is autofocus, and why do we need it?
Using the camera's automatic focusing system, the lens is adjusted so as to focus directly on the subject, thereby ensuring the difference between a clear picture and a missed opportunity.
')
Simplified principle of the camera is that the rays of light are reflected from the photographed objects and then fall on the sensor, which converts the flow of photons into a stream of electrons. After that, the current is converted into a set of bits, the data is processed and recorded in the camera's memory. CMOS sensors, which convert charge into voltage directly in a pixel, provide direct access to the content of an arbitrary pixel, are now particularly popular with smartphone manufacturers.
In theory, everything works like this: the lens focuses the light on the sensor, the sensor then creates a digital photo.

In reality, everything is not so simple. The angle of the incoming best light depends on the distance at which the object is photographed. The diagram below shows the lenses that focus the rays of light on a blue object: the green and red objects are out of focus and will be blurred in the final image. If we want to focus on a green or red object, we need to change the distance between the lenses and the sensor.

At the dawn of the camera industry, most devices had a fixed focus. In modern smartphones, it is possible to adjust the distance between the lenses and the sensor. Therefore, you get high-quality detailed images. Now for the implementation of autofocus in smartphones, three methods are mainly used: contrast, phase and laser.
Contrast autofocus
Contrast autofocus refers to the passive type of autofocus. Until now, this solution is used in most smartphones - largely because it is one of the simplest. Using the sensor, the amount of light on the object is measured, after which it also moves the lens depending on the contrast. If the contrast is maximum, then the subject is in focus.

In general, contrast autofocus is quite good at its task and has a big fat plus - it is quite simple and does not require any complicated “hardware” for its work.
But he has several drawbacks. In particular, contrast autofocus is slower than the others - it usually takes about a second to focus on an object. During this time, you can take a picture, or the moment will be missed if you wanted to shoot, for example, a quickly moving object. This is due to the fact that the lion's share of time is occupied by the process of “shifting the focus point / lens of the lens - contrast assessment - shift - contrast assessment”. In addition, the contrast autofocus is not the possibility of tracking focus, and in poor lighting conditions it is unlikely to impress you. Therefore, this type of autofocus today is used mainly in budget smartphones such as the Lenovo A536 , ASUS Zenfone Go and others.
Phase autofocus: a fast and advanced alternative
One of the pioneers here was the Samsung company, which borrowed technology from digital SLR cameras and equipped its Galaxy S5 with phase autofocus. The point is, in this case special sensors are used - they catch the transmitted light flux from different points of the image using lenses and mirrors. Inside the sensor, light is divided into two parts, each of which falls on a supersensitive sensor. The distance between the streams of light is measured by the sensor, after which he himself determines how much the lens needs to be shifted for precise focusing. For example, the Samsung Galaxy S5 takes only 0.3 seconds to focus on an object.
Visually, the principle of the phase autofocus is presented below.

The first and main advantage of phase autofocus is that it is much faster than contrast, it’s just a must have for shooting moving objects. In addition, the camera can assess the movement of an object using sensors, hence we get the possibility of tracking autofocus.
But there are also disadvantages. Phase autofocus, as well as contrast, also does not do very well with its tasks in low light conditions. It also needs a more powerful hardware, so it is usually available in high-end smartphones. Among them, Huawei Honor 7 , Sony Xperia M5 and Samsung Galaxy Note 5 , which, by the way, can be found in M.Video.
Some manufacturers went further and decided to use laser autofocus in smartphones (more on this later), while others were actively engaged in improving phase autofocus technology. For example, Apple in its iPhone 6s and iPhone 6s Plus uses the so-called “focal pixels” - the point is that the technology uses part of the pixels as a phase sensor, and shooting on Apple’s smartphones is really fast. In fact, this is the same phase autofocus, here we must pay tribute to marketers.
But Dual Pixel technology, which Samsung uses in its Galaxy S7 and Galaxy S7 Edge smartphones, is really different from phase focusing in other smartphones' cameras. Although it is a kind of phase autofocus, it still has some differences and subtleties. In smartphones, phase autofocus is somewhat limited - in order to assign a focal sensor to each pixel, you need to strongly reduce it, from here we get noise and photo blurring. Usually, about 10% of light-sensitive points are equipped with sensors, some manufacturers, however, do not go beyond 5%.
In Dual Pixel, each pixel is equipped with a separate sensor due to the increase in pixel sizes. The processor processes the readings of each pixel, but it does it so quickly that autofocus still takes tenths of a second. Samsung says that Dual Pixel technology is similar to focusing with the human eye, but this is again a marketing ploy.

Nevertheless, we must recognize the innovativeness of this approach to phase autofocus in modern smartphones. Now it is a real exclusive for the Galaxy S7 and Galaxy S7 Edge .
Laser autofocus: the most active
Like phase, laser autofocus refers to the active type of autofocus. This direction has long been engaged in the company LG, which first implemented a laser autofocus in its smartphone G3. The technology is based on the principle of a laser rangefinder: a laser emitter illuminates an object, and a sensor measures the distance to it and the time of arrival of the reflected laser beam.
One of the main advantages of this autofocus is time. As they say in LG, the whole process of autofocusing with a laser takes 0.276 seconds. Significantly faster contrast autofocus and a little bit faster than the phase.

The obvious advantage of laser autofocus is that it is incredibly fast and works well in low light conditions. But it only works at a certain distance - the best effect is achieved if the distance from the smartphone to the object is less than 0.6 meters. And after five meters - hello, contrasting autofocus.
Laser autofocus is mainly equipped with LG smartphones - for example, LG G4 . But there are exceptions: the same One Plus 2 or Asus Zenfone 2 Laser . However, the latter is clear from the name, and the price is attractive for such a set of possibilities.
Dual camera: bold, but not clear to everyone
At some point, the manufacturers realized that they needed to do something outlandish, outside of phase or laser autofocus. This is how dual cameras came into being: not one but two lenses are used at once to get clear pictures. While one camera with a fixed focus receives a snapshot of distant objects, the other focuses on objects that are nearby.
An important advantage of a dual camera is the ability to quickly take a picture, and then focus on it later, just like in a Lytro camera. But if we talk about a more accurate focus, here the dual camera clearly loses the phase focus.

So far, not many smartphones on the market are available with dual cameras - these are HTC devices (for example, One M9 + ), Honor 6 Plus, and others. Rumor has it that Apple, in its new iPhone, will decide to use a dual camera.
Infrared autofocus technology, which Lenovo showed at the MWC last year, works essentially as a laser autofocus, but in speed it is about twice as fast as the contrast. You can test it on the example of Lenovo Vibe Shot .
What to choose?
Since everyone chooses a smartphone for their needs, it is difficult to advise something that suits everyone at once. Someone in awe of the autofocus from Huawei that was customizable after the shooting, others consider the Dual Pixel to be optimal. If we take in general, at the moment the phase autofocus is the right decision for most of the flagships, and the manufacturers prove this to us all the time.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/395039/
All Articles