Chicago "getting smarter" before our eyes
Chicago - the city of winds at the intersection of cash flows, the second after the New York economic center of the United States today is seriously claiming to at least equal the level of development and integration of smart digital technologies with leading intellectual centers of Asia and Europe in the foreseeable future. The ambitious plans of the city administration in implementing the Array of Things program, designed to turn Chicago into the epicenter of the Midwest Internet of Things until the end of 2017, will be covered in this publication.

Among the leaders of the marathon, who had previously managed to respond to the dynamically developing trend of the present - the concept of a smart city today is particularly noticeable Asian and European projects. Barcelona and Amsterdam were the first to set the pace, almost immediately after them the baton was picked up in South Korea, Japan, Singapore and India. In Asian countries, where the need for smart technologies is due to ultra-high population density, programs for the intellectualization of urban infrastructure have received government support. It is not strange, but the United States, which for decades has been accumulating the most advanced intellectual potential of the planet, turned out to be in the role of catching up. Only in September 2015, the Obama administration has found in the budget of the country $ 160 million for the development of the national program “Smart Cities”. After the distribution, Chicago got $ 3.1, which largely contributed to the implementation of the plans of the Chicago municipality, which promised the city in March 2015 the rebirth and status of the “epicenter of the Internet of things” of the Midwest.
Stand alone devices - part of our tomorrow
')
Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things are the quintessence of the cities of the future, the most incredible concepts of which are lively discussed and developed by futurists and engineers from all over the world. Refrigerators, self-ordering and sending them to the delivery service, self-driving cars, reducing the percentage of accidents to the absolute minimum, centrally managed real-time municipal service services - all these and many other possibilities will be united in the framework of a single concept of the smart city of the future.
The concept of industry 4.0, which in 2011 was formulated by German scientists, predicts the imminent and inevitable fourth industrial revolution, involving the mass connection of industrial equipment to the network in order to fully automate production. On the other hand, the Internet of Things will use the automation and optimization of processes in the daily life of citizens, using a remote control module connected via Wi-Fi integrated into any devices - from a toaster, air conditioner, front door and watering system to a car, street lamp and benches. Then, with the alarm bell, the whole house will come to life, in which things around us in our living space will interact with each other in real time almost without our participation.
Imagine the integration of technology at this level in our everyday life is still difficult. But, as statistics show, the amount of data transmitted over the network for the past few years has doubled annually. On the other hand, if the total amount of all digital information for 2006 was estimated at 0.16 zettabyte, then, in accordance with forecasts of leading analytical companies, by 2020 the total annual traffic volume will be described by a figure of 44 zettabyte.
A curious outlook was provided by Cisco, which is actively promoting the future digital technology in the Asian market. According to analysts of the company, 99.4% of physical objects potentially considered as a link in the global Internet of things have not yet been included. At the same time, in 2008-2009 the number of devices connected to the network exceeded the population of the globe. Thus, according to the figurative statement of Cisco experts, by the end of the past decade, it would be logical to call the Internet of people the Internet of things.
Low start
The presence of advanced technology is becoming more pronounced on the streets of many US cities. For example, in New York, Internet monitoring of fire-hazardous buildings is already conducted, and up to 7,500 access points to high-speed (1 Gb / s) free Internet will be installed on the streets. In Boston parks and squares, you can sit on a bench with solar panels, recharge the gadget, and at the same time, you can check the level of air pollution according to the built-in analyzer. Chicago, being the second after New York economically center of the country and the first most important trading hub, has played a lead in launching the WindyGrid digital analytics platform before anyone else in 2012.
WindyGrid has a wide variety of useful information from all over Chicago: starting with the movement of buses and the statistics of calls to the 911 service, to information about buildings in the city that have a certain historical value. In addition to collecting and analyzing incoming data, the service tracks suspicious street activity through HD cameras built into street lights.
The processed information is recorded in the relevant thematic subsections on the Plenario website in open form with reference to the city map and is available for viewing on the city portal of Chicago.

marchello74 / iStock
One of the innovations that, according to the municipality of Chicago, will help take control of the problem of rodent control, is the installation of solar-powered sensors on garbage bins. According to the reports of sanitary services, the data obtained in a short time allowed reducing the number of rodents in critical areas by 20%.
In 2013, UI LABS launched the Chicago Smart Infrastructure Development Program - City Digital , which focuses on four key areas of life support: “transport”, “energy management”, “water and sanitation”, and “infrastructure”. For the last two in the same year, pilot projects started, on which it is worthwhile to dwell a little more.
One of the projects is devoted to the study of the possibility of using the useful ability of green space to reduce the level of wastewater. Sensors installed in the drainage system send information to the cloud for further analysis. Based on the data obtained, a map was drawn up with specific recommendations for landscaping. The second project is devoted to the development of a navigation platform for urban infrastructure below the ground. Using the sonar devices and the data obtained with the help of these specialists, they created a virtual map of underground water, gas, electricity and telecommunications, as well as the underground. The possibility of rapid assessment of the entire urban underground communication infrastructure, the health and efficiency of its individual sections made it possible to optimize the monitoring process and significantly reduce the cost of identifying and subsequent elimination of detectable defects. The next pilot projects to optimize the “transport network” and “energy management” are next in line from October 2016.
Array of things
The creation of a global “fitness tracker” on the territory of Chicago, which allows collecting and analyzing in real time detailed information about the weather, noise level, traffic, air, water, city communications and other data, was taken over by Argonne National Laboratory , which suggested using for this purpose analytical platform Argonne Waggle Platform .
To collect some useful information, it was decided to use special devices - nodes in the form of compact cylinders with a height of 35 cm. The node is completed with a set of sensors and every 15 seconds sends an information packet to the central server with information about pressure, noise, light, humidity and air temperature, CO2, NO2, SO2 and ozone concentrations. The data is analyzed by the Argonne Waggle Platform and broadcast on the screens of the citizens' smartphones using the application. In addition to the dry statistics, the service provides the user with more detailed useful recommendations based on the data obtained.
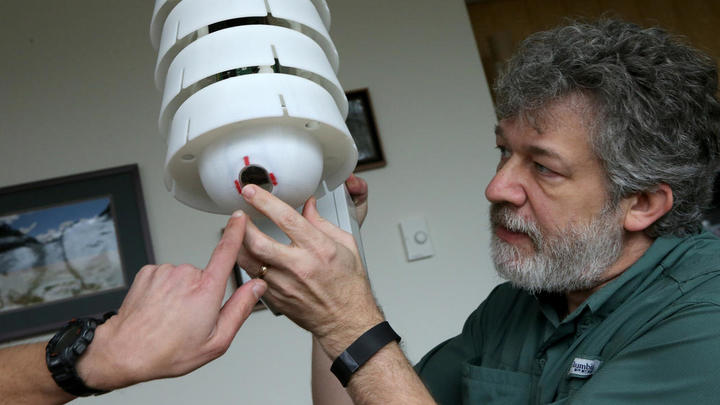

Senior Scientific Developer at the Argonne National Laboratory Charlie Catlett shows a camera hidden in a touch box in the shape of a beehive Antonio Perez / Chicago Tribune
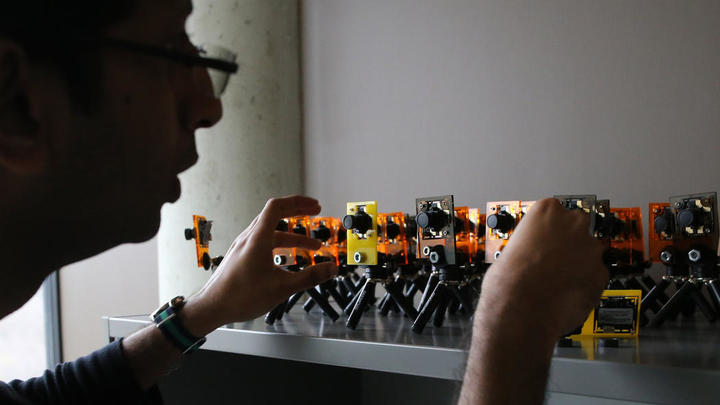

Argonne National Laboratory Array of Things Project by Antonio Perez / Chicago Tribune

Pete Beckman shows the image of the sky, which is transmitted from the test sensor Antonio Perez / Chicago Tribunee
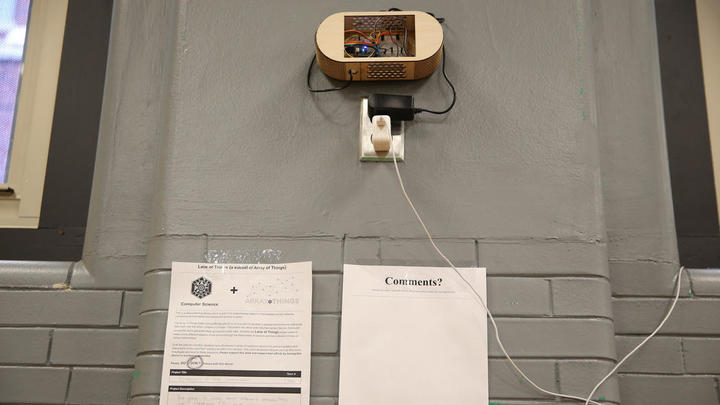

Lane Tech students installed their own sensor in the school cafeteria that measures humidity, temperature, and hydrogen, carbon, and methane levels. Antonio Perez / Chicago Tribune
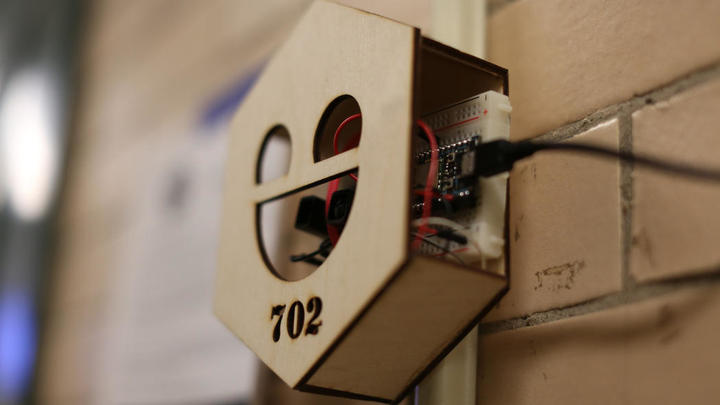
Computer sensor created by students of Lane Tech High School Antonio Perez / Chicago Tribune
The next step will be to study the relationship between the conditions created within the city infrastructure and the trends in the spread and progression of a number of diseases, such as bronchial asthma. Problems related to the regulation of urban traffic and monitoring the level of water elevation in the region’s water bodies will also be in the zone of special attention.
Equipping the nodes with infrared cameras will allow you to track the ice on the sidewalks, which will enable the city services to quickly, dosed out and locally eliminate the effects of the elements using salts and reagents. This approach, according to experts and representatives of the municipality, will not only save a lot of money in the city budget, but also reduce the amount of harmful substances polluting the Chicago River and Lake Michigan.
Several nodes within the pilot project were installed on the building of the University of Chicago in 2013. In the first quarter of 2016, 50 devices were already installed, by the beginning of 2017 it is planned to increase this figure to 200, and by the end of 2017 to bring their number to 500.
As we have already noted, in 2015, the amount of $ 3.1 million was allocated from the national program for the development of smart city Chicago, which allowed to partially cover the costs associated with new and existing pilot projects. Argonne National Laboratory has already spent about $ 1 million on the development and field testing of the Argonne Waggle Platform analytical platform. And another $ 150,000 has been invested in a pilot project. The Chicago municipality has borne the costs associated with the development, production, installation, commissioning and power supply of the nodes. The cost of the initial set is estimated at $ 500, the cost of the promising set with pre-installed cameras and an expanded set of sensors is estimated at $ 2,000.

tupungato / iStock

Timothy_Wang / iStock
Total freedom of access
The first tangible results in the form of additional revenues to the city budget and a qualitative improvement in the work of the infrastructure are expected to be fixed this year. The main hopes, however, are placed on the integration of AoT services. At the same time, today access to the developments that are already operating for the benefit of the city and the citizens is completely free. Organizations and initiative groups, enthusiastic engineers and residents of Chicago at any time can offer to supplement the already existing infrastructure with their innovative projects and additions aimed at improving the quality of life.
One of the priority areas of development, which focuses on special attention - ecology. This is quite understandable: the need for constant “monitoring the quality of life” at all levels is extremely important not only for the residents of the city, but also for the numerous tourists who regularly replenish the city budget. Moreover, the attractiveness of Chicago as a beach resort is growing from year to year. In 2016, the city of winds was recognized as the best beach city in the United States, ahead of Los Angeles, Miami, San Francisco and Honolulu.

“The budget of any city, even such as Chicago, is not infinite, and there is no reason not to share the results of the development with everyone for free. On the other hand, we intend to use the open resources of other smart cities, because, ultimately, we all work for a future in which the interests of everyone become equally important, ” said Chicago Information Services head Brenna Berman.
Privacy
One of the main conditions on which the authors of the Array of Things project themselves insist is a special emphasis on the inadmissibility of using the data obtained to the detriment of the private life of city residents. To this end, the collection of any type of data is coordinated with the city’s Department of Security and Privacy.
According to the authors of the project and the developers of systems that are integrated into City Digital, AoT does not concern and in the future will not touch the confidential information of Chicago residents, since all sensors that “extract” useful information for subsequent analysis collect it within the city infrastructure, without affecting what is happening in private apartments. In addition, the current registered “raw” information is not stored anywhere and is not sent anywhere: only the final measurement results are sent to the head server.
It is noteworthy that, guided by considerations of privacy, the developers of pilot projects at this stage refused to use Wi-Fi and Bluetooth wireless communication channels to communicate with smartphones. At the same time, to guarantee that in the future, guided by considerations of rationality and comfort, the municipality will not lift such a restriction, today nobody can.
The inviolability of personal space is a major concern for not only Chicago residents, but also for any other city that wishes to assign itself the status of “smart”. The question is really not idle, because in the zone of practically free or almost free access, in addition to the private IoT network, there can be many objects of urban infrastructure. An over-targeted advertisement will become common, which is literally everywhere and creating the illusion of personal contact, and in fact sensitively and instantly reacting to a change in your mood by means of a tracking camera. Add to this the possibilities of modern facial recognition technologies and get at your disposal a “personal free advertising agent” who will accompany you when you move always and along any routes. And this is just one of the examples, of which there can be many.
Inevitably, associations with the computer game Watch Dogs , released in 2014, arise. The main character - a hacker, lives and operates in Chicago, according to the creators, totally connected to the network. Hacking urban networks allows a hacker to eavesdrop on conversations, gain access to comprehensive information about residents, and tinker at the urban infrastructure level. The slogans of the game “Everything is interconnected. Communication is power ”and“ Hacking is our weapon ”, which are surprisingly consonant with the fears of citizens.
Of course, the picture we have drawn, on the current development of the Internet of things, is nothing more than imagination. But there are other challenges that may be much closer and much more pressing and painful. The reverse, not so comfortable and promising side of the Internet of things within the concept of a smart city, we will devote a separate material.
Thank you for your attention and the time spent with us.
T & P
That's all, with you there was a simple service for choosing sophisticated Dronk.Ru equipment. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog , there will be many more interesting ...


Among the leaders of the marathon, who had previously managed to respond to the dynamically developing trend of the present - the concept of a smart city today is particularly noticeable Asian and European projects. Barcelona and Amsterdam were the first to set the pace, almost immediately after them the baton was picked up in South Korea, Japan, Singapore and India. In Asian countries, where the need for smart technologies is due to ultra-high population density, programs for the intellectualization of urban infrastructure have received government support. It is not strange, but the United States, which for decades has been accumulating the most advanced intellectual potential of the planet, turned out to be in the role of catching up. Only in September 2015, the Obama administration has found in the budget of the country $ 160 million for the development of the national program “Smart Cities”. After the distribution, Chicago got $ 3.1, which largely contributed to the implementation of the plans of the Chicago municipality, which promised the city in March 2015 the rebirth and status of the “epicenter of the Internet of things” of the Midwest.
Stand alone devices - part of our tomorrow
')
Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things are the quintessence of the cities of the future, the most incredible concepts of which are lively discussed and developed by futurists and engineers from all over the world. Refrigerators, self-ordering and sending them to the delivery service, self-driving cars, reducing the percentage of accidents to the absolute minimum, centrally managed real-time municipal service services - all these and many other possibilities will be united in the framework of a single concept of the smart city of the future.
The concept of industry 4.0, which in 2011 was formulated by German scientists, predicts the imminent and inevitable fourth industrial revolution, involving the mass connection of industrial equipment to the network in order to fully automate production. On the other hand, the Internet of Things will use the automation and optimization of processes in the daily life of citizens, using a remote control module connected via Wi-Fi integrated into any devices - from a toaster, air conditioner, front door and watering system to a car, street lamp and benches. Then, with the alarm bell, the whole house will come to life, in which things around us in our living space will interact with each other in real time almost without our participation.
Imagine the integration of technology at this level in our everyday life is still difficult. But, as statistics show, the amount of data transmitted over the network for the past few years has doubled annually. On the other hand, if the total amount of all digital information for 2006 was estimated at 0.16 zettabyte, then, in accordance with forecasts of leading analytical companies, by 2020 the total annual traffic volume will be described by a figure of 44 zettabyte.
A curious outlook was provided by Cisco, which is actively promoting the future digital technology in the Asian market. According to analysts of the company, 99.4% of physical objects potentially considered as a link in the global Internet of things have not yet been included. At the same time, in 2008-2009 the number of devices connected to the network exceeded the population of the globe. Thus, according to the figurative statement of Cisco experts, by the end of the past decade, it would be logical to call the Internet of people the Internet of things.
Low start
The presence of advanced technology is becoming more pronounced on the streets of many US cities. For example, in New York, Internet monitoring of fire-hazardous buildings is already conducted, and up to 7,500 access points to high-speed (1 Gb / s) free Internet will be installed on the streets. In Boston parks and squares, you can sit on a bench with solar panels, recharge the gadget, and at the same time, you can check the level of air pollution according to the built-in analyzer. Chicago, being the second after New York economically center of the country and the first most important trading hub, has played a lead in launching the WindyGrid digital analytics platform before anyone else in 2012.
WindyGrid has a wide variety of useful information from all over Chicago: starting with the movement of buses and the statistics of calls to the 911 service, to information about buildings in the city that have a certain historical value. In addition to collecting and analyzing incoming data, the service tracks suspicious street activity through HD cameras built into street lights.
The processed information is recorded in the relevant thematic subsections on the Plenario website in open form with reference to the city map and is available for viewing on the city portal of Chicago.

marchello74 / iStock
One of the innovations that, according to the municipality of Chicago, will help take control of the problem of rodent control, is the installation of solar-powered sensors on garbage bins. According to the reports of sanitary services, the data obtained in a short time allowed reducing the number of rodents in critical areas by 20%.
In 2013, UI LABS launched the Chicago Smart Infrastructure Development Program - City Digital , which focuses on four key areas of life support: “transport”, “energy management”, “water and sanitation”, and “infrastructure”. For the last two in the same year, pilot projects started, on which it is worthwhile to dwell a little more.
One of the projects is devoted to the study of the possibility of using the useful ability of green space to reduce the level of wastewater. Sensors installed in the drainage system send information to the cloud for further analysis. Based on the data obtained, a map was drawn up with specific recommendations for landscaping. The second project is devoted to the development of a navigation platform for urban infrastructure below the ground. Using the sonar devices and the data obtained with the help of these specialists, they created a virtual map of underground water, gas, electricity and telecommunications, as well as the underground. The possibility of rapid assessment of the entire urban underground communication infrastructure, the health and efficiency of its individual sections made it possible to optimize the monitoring process and significantly reduce the cost of identifying and subsequent elimination of detectable defects. The next pilot projects to optimize the “transport network” and “energy management” are next in line from October 2016.
Array of things
The creation of a global “fitness tracker” on the territory of Chicago, which allows collecting and analyzing in real time detailed information about the weather, noise level, traffic, air, water, city communications and other data, was taken over by Argonne National Laboratory , which suggested using for this purpose analytical platform Argonne Waggle Platform .
To collect some useful information, it was decided to use special devices - nodes in the form of compact cylinders with a height of 35 cm. The node is completed with a set of sensors and every 15 seconds sends an information packet to the central server with information about pressure, noise, light, humidity and air temperature, CO2, NO2, SO2 and ozone concentrations. The data is analyzed by the Argonne Waggle Platform and broadcast on the screens of the citizens' smartphones using the application. In addition to the dry statistics, the service provides the user with more detailed useful recommendations based on the data obtained.

Senior Scientific Developer at the Argonne National Laboratory Charlie Catlett shows a camera hidden in a touch box in the shape of a beehive Antonio Perez / Chicago Tribune

Argonne National Laboratory Array of Things Project by Antonio Perez / Chicago Tribune

Pete Beckman shows the image of the sky, which is transmitted from the test sensor Antonio Perez / Chicago Tribunee

Lane Tech students installed their own sensor in the school cafeteria that measures humidity, temperature, and hydrogen, carbon, and methane levels. Antonio Perez / Chicago Tribune

Computer sensor created by students of Lane Tech High School Antonio Perez / Chicago Tribune
The next step will be to study the relationship between the conditions created within the city infrastructure and the trends in the spread and progression of a number of diseases, such as bronchial asthma. Problems related to the regulation of urban traffic and monitoring the level of water elevation in the region’s water bodies will also be in the zone of special attention.
Equipping the nodes with infrared cameras will allow you to track the ice on the sidewalks, which will enable the city services to quickly, dosed out and locally eliminate the effects of the elements using salts and reagents. This approach, according to experts and representatives of the municipality, will not only save a lot of money in the city budget, but also reduce the amount of harmful substances polluting the Chicago River and Lake Michigan.
Several nodes within the pilot project were installed on the building of the University of Chicago in 2013. In the first quarter of 2016, 50 devices were already installed, by the beginning of 2017 it is planned to increase this figure to 200, and by the end of 2017 to bring their number to 500.
As we have already noted, in 2015, the amount of $ 3.1 million was allocated from the national program for the development of smart city Chicago, which allowed to partially cover the costs associated with new and existing pilot projects. Argonne National Laboratory has already spent about $ 1 million on the development and field testing of the Argonne Waggle Platform analytical platform. And another $ 150,000 has been invested in a pilot project. The Chicago municipality has borne the costs associated with the development, production, installation, commissioning and power supply of the nodes. The cost of the initial set is estimated at $ 500, the cost of the promising set with pre-installed cameras and an expanded set of sensors is estimated at $ 2,000.

tupungato / iStock

Timothy_Wang / iStock
Total freedom of access
The first tangible results in the form of additional revenues to the city budget and a qualitative improvement in the work of the infrastructure are expected to be fixed this year. The main hopes, however, are placed on the integration of AoT services. At the same time, today access to the developments that are already operating for the benefit of the city and the citizens is completely free. Organizations and initiative groups, enthusiastic engineers and residents of Chicago at any time can offer to supplement the already existing infrastructure with their innovative projects and additions aimed at improving the quality of life.
One of the priority areas of development, which focuses on special attention - ecology. This is quite understandable: the need for constant “monitoring the quality of life” at all levels is extremely important not only for the residents of the city, but also for the numerous tourists who regularly replenish the city budget. Moreover, the attractiveness of Chicago as a beach resort is growing from year to year. In 2016, the city of winds was recognized as the best beach city in the United States, ahead of Los Angeles, Miami, San Francisco and Honolulu.

“The budget of any city, even such as Chicago, is not infinite, and there is no reason not to share the results of the development with everyone for free. On the other hand, we intend to use the open resources of other smart cities, because, ultimately, we all work for a future in which the interests of everyone become equally important, ” said Chicago Information Services head Brenna Berman.
Privacy
One of the main conditions on which the authors of the Array of Things project themselves insist is a special emphasis on the inadmissibility of using the data obtained to the detriment of the private life of city residents. To this end, the collection of any type of data is coordinated with the city’s Department of Security and Privacy.
According to the authors of the project and the developers of systems that are integrated into City Digital, AoT does not concern and in the future will not touch the confidential information of Chicago residents, since all sensors that “extract” useful information for subsequent analysis collect it within the city infrastructure, without affecting what is happening in private apartments. In addition, the current registered “raw” information is not stored anywhere and is not sent anywhere: only the final measurement results are sent to the head server.
It is noteworthy that, guided by considerations of privacy, the developers of pilot projects at this stage refused to use Wi-Fi and Bluetooth wireless communication channels to communicate with smartphones. At the same time, to guarantee that in the future, guided by considerations of rationality and comfort, the municipality will not lift such a restriction, today nobody can.
The inviolability of personal space is a major concern for not only Chicago residents, but also for any other city that wishes to assign itself the status of “smart”. The question is really not idle, because in the zone of practically free or almost free access, in addition to the private IoT network, there can be many objects of urban infrastructure. An over-targeted advertisement will become common, which is literally everywhere and creating the illusion of personal contact, and in fact sensitively and instantly reacting to a change in your mood by means of a tracking camera. Add to this the possibilities of modern facial recognition technologies and get at your disposal a “personal free advertising agent” who will accompany you when you move always and along any routes. And this is just one of the examples, of which there can be many.
Inevitably, associations with the computer game Watch Dogs , released in 2014, arise. The main character - a hacker, lives and operates in Chicago, according to the creators, totally connected to the network. Hacking urban networks allows a hacker to eavesdrop on conversations, gain access to comprehensive information about residents, and tinker at the urban infrastructure level. The slogans of the game “Everything is interconnected. Communication is power ”and“ Hacking is our weapon ”, which are surprisingly consonant with the fears of citizens.
Of course, the picture we have drawn, on the current development of the Internet of things, is nothing more than imagination. But there are other challenges that may be much closer and much more pressing and painful. The reverse, not so comfortable and promising side of the Internet of things within the concept of a smart city, we will devote a separate material.
Thank you for your attention and the time spent with us.
T & P
That's all, with you there was a simple service for choosing sophisticated Dronk.Ru equipment. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog , there will be many more interesting ...

 |  |  |
| Why do online stores give money for purchases? | Review of Xiaomi Mi Air Purifier 2 or how to clean the air of the metropolis? | Return your money - choose a cashback service for Aliexpress |
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/395013/
All Articles