Fintech replaces banks: China is ahead, West is catching up
 The development of technology in the most drastic way changes the nature of the interaction of people with banks. Fewer less willing to go and solve problems with live clerks in real offices. Digital tools and interaction tools are becoming increasingly popular - ATMs, online chat rooms, mobile applications and Internet banking. Until recently, the “figure” was only an addition to traditional banking services. But very soon, new technologies will completely change the financial landscape.
The development of technology in the most drastic way changes the nature of the interaction of people with banks. Fewer less willing to go and solve problems with live clerks in real offices. Digital tools and interaction tools are becoming increasingly popular - ATMs, online chat rooms, mobile applications and Internet banking. Until recently, the “figure” was only an addition to traditional banking services. But very soon, new technologies will completely change the financial landscape.We, Wirex , work in the field of instant money transfers without banking intermediation. Our service is part of the fintech ecosystem, which in the very near future will seriously compete with traditional banks, so we would like to tell you about the development and prospects of fintech and its benefits for end users of financial services.
In recent years, investments in fintech have been growing exponentially: if in 2010 it was about 1.8 billion US dollars, by 2015 they grew to 19 billion. At the same time, 70% of investments go to increasing the comfort of customers in the consumer sector.
The volume of investments leads the segment of payments. It is here that the banks are experiencing the most powerful pressure from the new players. The Internet has formed an e-commerce ecosystem with its own payment systems, such as PayPal and Alipay . He also created a platform for a new generation of credit systems - systems of equal rights (P2P, peer-to-peer) lending.
')
The widespread penetration of mobile Internet and the spread of smartphones has led to changes in the rules of the game in the consumer sector and the SMB segment. In Europe and America, mobile payment systems for small and medium business and microbusiness have emerged and are developing, for example, Square and iZettle . Apple Pay and Android Pay entered the consumer market in 2014 and 2015.
Technology will change not only the service model. The banking system does not get off with the reduction of physical branches and the release of advanced mobile applications. The very concept and content of financial products will change. Most likely, our generation is the latest generation of debit and credit card holders. They will be replaced by debit and credit systems that are available on all mobile devices.
East vs West
Today, despite solid investments and loud statements about the imminent death of the banking system, the share of digital financial instruments accounts for no more than 1% of revenues in the consumer sector. Of course, on the side of fintech, the advantages of the newest technologies, the ability to provide a completely different level of comfort, however, the assets of existing financial organizations include the reach of a huge audience and scope. The Western market - both American and European - has not yet reached a turning point, banks are still “stronger” than Fintech. But the moment of truth is near.
According to Citigroup forecasts, the share of fintech in the consumer sector will increase by 2020 from 1 to 10%, and by 2023, to 17%. The figures are approximate, as global financial systems are in the early stages of transformation. The main question is whether the existing financial institutions in Europe and America can accept the changes, introduce modern technologies and ... survive? To remain competitive, banks need to change quickly. It is not enough to talk about the blockchain and conduct fashionable hackathons, you need to take real steps until fintech companies have captured a significant market share.
Perhaps this fact will surprise you, but China is far ahead of Western countries in terms of the development of Fintech and has passed that turning point long ago. Here, the scale and advantages of advanced technologies are completely on the side of fintech.
At one time, local Internet giants were not afraid to enter the financial services market and acquired a significant share of the e-commerce and payments market in favor of third parties. Trite ahead of clumsy banks, offered convenient, reliable, fast and cheap alternatives to traditional bank payments.
Today, Chinese fintech companies are the largest in the world. Alipay and Tenpay have more clients than leading banks. And their rears are securely covered by prosperous parent corporations from e-commerce and the financial sector, whose capabilities exceed the capabilities of Western venture capital.
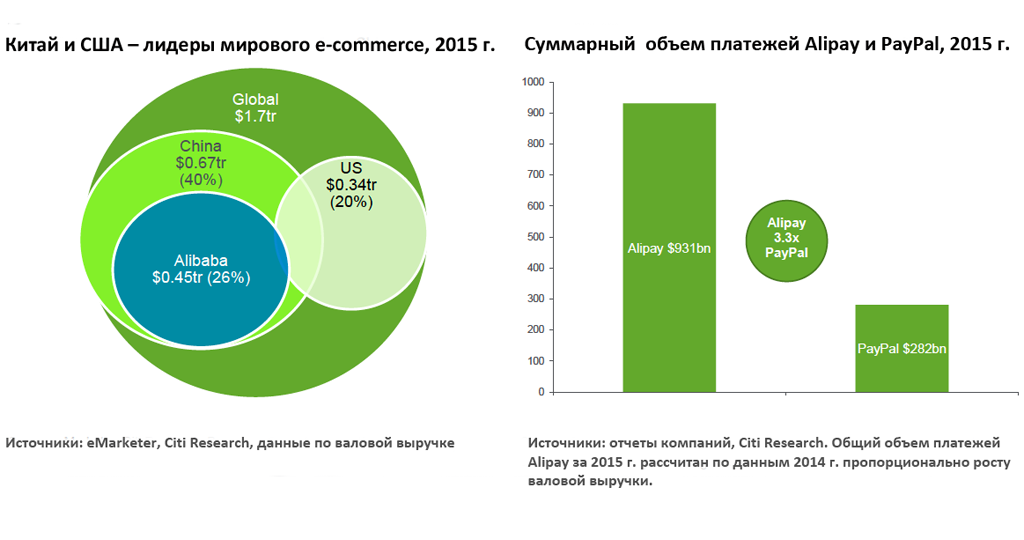
The Chinese technology giants Baidu , Alibaba and Tencent (hereinafter - BAT ) invested in the development of financial services much more actively than their colleagues - Google, Apple, Facebook and Amazon (hereinafter - GAFA ). Now Alibaba and Tencent’s share in the national payments market in favor of third parties is 33% and 10%, respectively. The proportion of the entire “big four” GAFA in non-cash payments in the United States, according to some estimates, does not exceed 2%.
Chinese fintech owes its success to several factors:
- High internet and mobile penetration .
A necessary condition for the availability and relevance of modern payment technologies. - Early entry to the market .
Alibaba and Tencent created Alipay and Tenpay payment systems more than 10 years ago to support their own e-commerce and online gaming businesses. In the West, the first of the GAFA four was Google, invested in payment systems only in 2011, seven years after the launch of Alipay. - Huge national e-commerce sector .
In 2015, the global gross earnings of e-commerce amounted to 1.7 trillion US dollars. According to eMarketer, by 2018, revenue will increase to 3 trillion. The share of Chinese e-commerce accounts for 672 billion dollars, or 40% of world volumes. By 2018, Chinese e-commerce will grow to 1.6 trillion dollars, and this is more than half of the global market. Alibaba's revenue in 2015 reached nearly 500 billion, which is two times more than Amazon. Alipay has become the largest payment platform, with a total payment volume three times higher than PayPal. - Serious user base .
China is ahead of developed markets in terms of using social networks as payment systems. Tencent has created the country's largest P2P system based on the WeChat social network. WeChat has 550 million users today. - Relative underdevelopment of the banking system .
- Flexible legislation .
- The strategic importance of financial instruments for Chinese Internet giants .
As we have said, initially FINTECH-tools were created to support the core business of corporations. And now fintech systems are actively capturing offline. Thus, over the past two years, Alipay has connected 130,000 offline companies: restaurants, supermarkets, taxi services and medical institutions.
And although in Western countries the level of development of the Internet and mobile networks was not inferior to that of China, none of the industry leaders considered financial instruments to be strategically important for business. At the same time, the Western banking system offered its customers more diverse services than the Chinese.
Fintech in emerging markets
In developing countries, a large proportion of the population does not have access to banking services, consumer banking is poorly developed, but at the same time there is a high level of mobile penetration. So, there are all conditions for active growth of fintech.
A vivid example is Kenya, where in 2007 the mobile cash service M-Pesa was launched. Today, the service has 23 million active customers in 11 countries. In neighboring Somalia, which has long and firmly been associated in the mass consciousness with wars and upheavals, and not with financial innovations, about 40% of the adult population use mobile money.
In the Asian region — India, Indonesia, and the Philippines — about 400 million people are not covered by traditional banking services. Truly a huge reserve for the development of mobile money services. It is here that mobile money is not a question of comfort, but a way to solve a serious social problem.
Please note that the transition to digital financial technology in each country took place differently. In Kenya, considerable funds were invested in the mobile money system, an extensive network of non-banking agents was built, and adequate legislative regulation played a significant role. In this sense, the example of Kenya is very different from the Chinese version, where the whole process was based on the largest Internet companies.
In India, the driver of change was the national biometric identification project AADHAAR , which was accompanied by the opening of more than 200 million bank accounts for the population. It should be noted separately that India, with its growing population exceeding 1.2 billion people, the low level of accessibility of banking services, the willingness of the authorities to increase the availability of financial services, the penetration of mobile communications at the level of 80% - a market of enormous opportunities.
Banks: under the threat of "uberization"
We all know what happened to the private transportation market under the influence of Uber . Many companies could not stand the competition and left the market, and the industry itself has irrevocably changed. More than likely, the banking industry will soon find itself in a similar situation.
First of all, Citigroup experts predict a serious reduction in the number of branches. In this regard, the Nordic countries were ahead of their neighbors. Scandinavian and Dutch banks have already reduced the total number of branches by about 50% compared with peak values. Citigroup estimates that in developed markets the number of branches will decrease by another 30-50% compared with 2013. American banks just have to do it. But against the background of universal availability of mobile Internet, pressure from fintech, stagnation of income and profitability - reductions are almost inevitable.
In the future, banking services should come down to consulting. The profitability of physical departments falls. Their maintenance costs today are too expensive, despite the fact that most of the costs can be reduced by automating the most common processes.
In Citigroup, it is estimated that until 2025, banks will have to reduce the number of staff by about 30% compared with the state in 2015. Potentially, by reducing the network of physical branches, European, American, and Japanese banks can cut their costs by about $ 175 billion a year.
Mobile money - FINTECH revolution in favor of consumers
Electronic money, refusal of cash and checks in favor of bank cards are all integral elements of the modern world. And if in developed countries, new financial technologists mostly struggle with the inconvenience of traditional banking services, in emerging markets they carry a serious social mission.
Mobile and electronic money make financial services as convenient and accessible as possible to the widest segments of the population:
- Increasing the availability of financial services .
As we wrote in one of the previous posts , 2 billion people in the world do not have access to official financial services. Most (but not all) of these two billions live in developing countries in Africa and Asia. Banking services covered only wealthy people, while mobile payments could provide access to financial services for even the poorest. In emerging markets, the most simple technical solutions are used and expensive smartphones are not needed to use mobile financial instruments, the simplest phone is enough. - Transboundary .
The world has become smaller. International payments are no longer the prerogative of big business. The share of payments from individuals and small businesses is constantly growing. The total volume of international remittances in annual terms exceeds 580 billion US dollars. Fintech greatly simplifies cross-border payments and transfers. - Payments for medium and small businesses .
Medium and small businesses are actively working with the cache, especially in emerging markets. According to IFC Mobile Money, here about 75% of all receipts and payments take place in cash, in developed markets - no more than 25%. Fintech companies provide micro and small business opportunities for accepting credit cards and working with non-cash funds.
In developing countries, electronic money is usually presented in the form of mobile means of payment. To put it simply, mobile money is nothing more than a monetary transaction conducted using a mobile phone. Most often they are used for local and international P2P transfers, quick loans and the purchase of goods and services.
According to Citigroup and Imperial College London, a ten percent increase in mobile money penetration will open access to official financial services to 220 million people. Funds in the amount of about $ 1 trillion will come out of the shadow, which will give about $ 100 billion of additional tax charges. In parallel, the retail sector will reduce the cost of working with cash by about 120 billion a year. And this is only part of the effects of a 10 percent increase!
Classic banks feed a huge army of employees, spend fabulous sums on the maintenance of offices, IT systems and physical call centers. In such conditions, the comfort of customers inevitably takes second place. Traditional banking is outdated, it is being replaced by more convenient, transparent and understandable technologies that have much less restrictions and are cheaper for the end user.
The Wirex service allows you to forget about the limitations of traditional financial institutions. Instant money transfers in USD, EUR, GBP and digital currency, conversion, the ability to order a virtual or plastic payment card - without going to the offices or communicating with the banking support service. Wirex provides its services worldwide, and in order to start using the service, it is enough to install the application on an Android or iOS device.
Prepared using Citi GPS materials.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/394227/
All Articles