NASA's mission for the first time observed and detailed the process of reconnection of the magnetic fields of the Sun and the Earth.
The MMS ( Magnetospheric Multiscale ) mission organized by NASA, for the first time since its launch in March 2015, was able to capture and describe in detail the phenomenon of magnetic reconnection arising from the interaction of the magnetic fields of the Earth and the Sun. More information about the event, which astrophysicists have been waiting for almost half a century, we will tell in our publication.
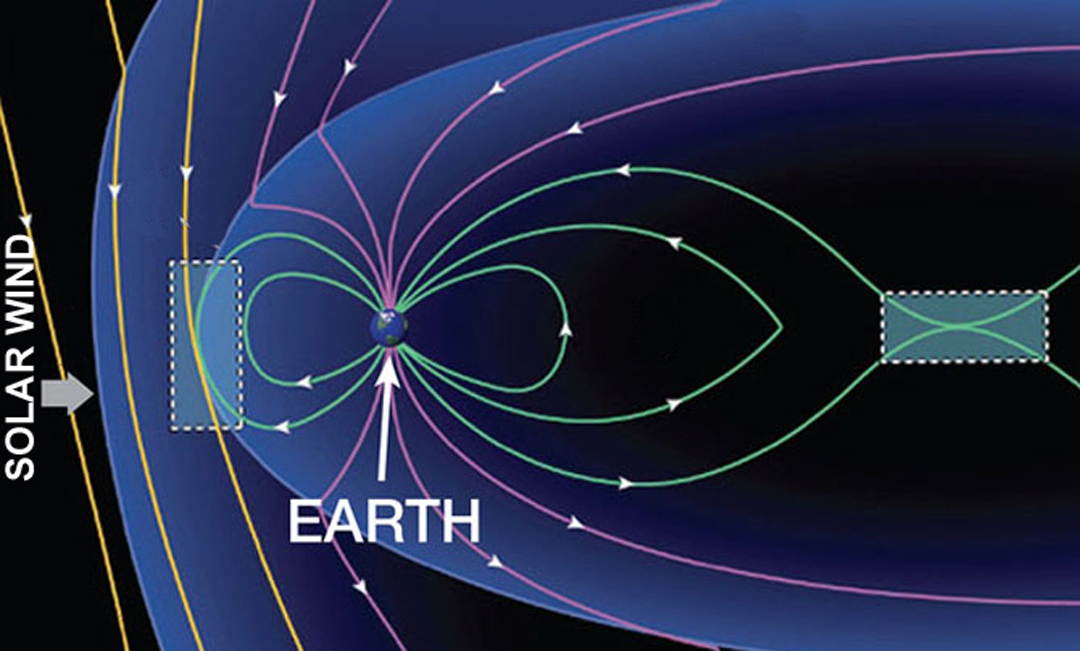
The sun gives rise to a stream of charged particles flying at colossal speed, called the solar wind. It is mainly represented by electrons, protons and helium nuclei (alpha particles). Astrophysicists believe that one of the mechanisms that cause the acceleration of these particles is associated with the so-called. magnetic reconnection, occurring at the moment when two oppositely directed magnetic field lines of different domains meet, break and re-connect with each other, forming loops that diverge with tremendous speed. The energy of the magnetic field accumulated at this moment passes into the kinetic and thermal energy of moving particles, which are fired as if from a catapult.

')
The magnetic reconnection mechanism described above also works when the magnetic lines of the Earth's field interact with the magnetic lines of the Sun “accompanying” the movement of the solar wind at the boundary of the magnetosphere. The study of the influence of this phenomenon on the planet is extremely important, since its consequences most directly affect the life of all living things. As is known, the magnetic field of the Earth creates a protective barrier that prevents the passage of particles of the solar wind to the surface of the planet. The meeting of cosmic radiation with the magnetic lines of the Earth at the boundary of the magnetosphere leads to a deviation of particle fluxes to the poles of the planet, as a result of which we observe auroras and record magnetic storms. At the moment of magnetic reconnection, accompanied by the release of energy and the rupture of magnetic field lines, the protective effect of the shield weakens and the particles are able to penetrate into near-earth space for a distance that can be dangerous both for human health and for satellites in Earth orbit.
Attempts to obtain an exhaustive, experimentally confirmed material associated with the phenomenon of magnetic reconnection have been made for almost half a century, both in laboratory and in cosmic plasma. And only now this phenomenon was directly observed in the Earth’s magnetosphere within the framework of the MMS (NASA) mission. The details of the event are reflected in the publication of the journal Science on May 12, 2016.
The main problem that complicates the actual detection of the phenomenon of magnetic reconnection is related to the fact that it occurs in a limited region of space. Thus, to obtain the necessary information, space probes moving at high speed must be at the right time in the right place. The first practical evidence of the existence of the magnetic reconnection effect in the MMS program was obtained in October 2015. Then, research stations in just a few seconds managed to make thousands of measurements, which subsequently provided the richest material for analyzing the phenomenon. Since that time, MMS probes crossed the borders of the Earth’s magnetosphere more than 4,000 times and recorded similar event fragments five times, but it was the first time to fully record the magnetic reconnection process in the atmosphere of our planet.
Astrophysicists are sure: studies of the magnetosphere will make it possible to understand other astrophysical phenomena that are accompanied by particle ejection, in particular, occurring in magnetors (neutron stars with an extremely strong magnetic field) or those that accompany the formation of high-energy cosmic particles coming from other galaxies. A lot of questions are still causing the mechanism of formation of the solar wind and the most solar activity.
It is clear that the processes occurring in the Earth’s magnetosphere, due to the relatively low energy level, cannot provide for researchers an exhaustive picture of the phenomena occurring in galactic space in more “energy-intensive” systems. At the same time, the magnetosphere of our planet provides scientists with a unique opportunity for experiments, since it allows directing space probes directly to the region where the reconnection takes place.
About MMS Mission
Launched in March 2015, the MMS program involves the study of information provided by four identical spacecraft located at the vertices of the pyramid at a distance of 10 km from each other. Each of them contains 25 sensors that collect and analyze data on the state of the electromagnetic field and the behavior of electron fluxes with a scan interval of 30 milliseconds. This frequency provides unprecedented accuracy and informative measurements in the entire history of studying the phenomenon of magnetic reconnection.
Despite the cardinal breakthrough associated with the latest events aboard the mission, there are still a lot of questions to be studied. So it is necessary to find out why in some cases the magnetic reconnection has an explosive character, in others it proceeds evenly, and in the third it does not occur at all. Studies of the drop-like tail of the Earth’s magnetosphere located on the part of the planet’s hemisphere opposite to the Sun look very promising. The investigations carried out by the mission at this point are associated with a portion of the field of the magnetosphere, which is being formed from the “solar” side.
That's all, with you there was a simple service for choosing sophisticated Dronk.Ru equipment. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog , there will be many more interesting ...

LetyShops cashback service sponsor . Return money for any purchases on the Internet. Read more about what a cashback service is in our article. We choose a cashback service for the 6th anniversary of Aliexpress.

The sun gives rise to a stream of charged particles flying at colossal speed, called the solar wind. It is mainly represented by electrons, protons and helium nuclei (alpha particles). Astrophysicists believe that one of the mechanisms that cause the acceleration of these particles is associated with the so-called. magnetic reconnection, occurring at the moment when two oppositely directed magnetic field lines of different domains meet, break and re-connect with each other, forming loops that diverge with tremendous speed. The energy of the magnetic field accumulated at this moment passes into the kinetic and thermal energy of moving particles, which are fired as if from a catapult.

')
The magnetic reconnection mechanism described above also works when the magnetic lines of the Earth's field interact with the magnetic lines of the Sun “accompanying” the movement of the solar wind at the boundary of the magnetosphere. The study of the influence of this phenomenon on the planet is extremely important, since its consequences most directly affect the life of all living things. As is known, the magnetic field of the Earth creates a protective barrier that prevents the passage of particles of the solar wind to the surface of the planet. The meeting of cosmic radiation with the magnetic lines of the Earth at the boundary of the magnetosphere leads to a deviation of particle fluxes to the poles of the planet, as a result of which we observe auroras and record magnetic storms. At the moment of magnetic reconnection, accompanied by the release of energy and the rupture of magnetic field lines, the protective effect of the shield weakens and the particles are able to penetrate into near-earth space for a distance that can be dangerous both for human health and for satellites in Earth orbit.
Attempts to obtain an exhaustive, experimentally confirmed material associated with the phenomenon of magnetic reconnection have been made for almost half a century, both in laboratory and in cosmic plasma. And only now this phenomenon was directly observed in the Earth’s magnetosphere within the framework of the MMS (NASA) mission. The details of the event are reflected in the publication of the journal Science on May 12, 2016.
The main problem that complicates the actual detection of the phenomenon of magnetic reconnection is related to the fact that it occurs in a limited region of space. Thus, to obtain the necessary information, space probes moving at high speed must be at the right time in the right place. The first practical evidence of the existence of the magnetic reconnection effect in the MMS program was obtained in October 2015. Then, research stations in just a few seconds managed to make thousands of measurements, which subsequently provided the richest material for analyzing the phenomenon. Since that time, MMS probes crossed the borders of the Earth’s magnetosphere more than 4,000 times and recorded similar event fragments five times, but it was the first time to fully record the magnetic reconnection process in the atmosphere of our planet.
Astrophysicists are sure: studies of the magnetosphere will make it possible to understand other astrophysical phenomena that are accompanied by particle ejection, in particular, occurring in magnetors (neutron stars with an extremely strong magnetic field) or those that accompany the formation of high-energy cosmic particles coming from other galaxies. A lot of questions are still causing the mechanism of formation of the solar wind and the most solar activity.
It is clear that the processes occurring in the Earth’s magnetosphere, due to the relatively low energy level, cannot provide for researchers an exhaustive picture of the phenomena occurring in galactic space in more “energy-intensive” systems. At the same time, the magnetosphere of our planet provides scientists with a unique opportunity for experiments, since it allows directing space probes directly to the region where the reconnection takes place.
About MMS Mission
Launched in March 2015, the MMS program involves the study of information provided by four identical spacecraft located at the vertices of the pyramid at a distance of 10 km from each other. Each of them contains 25 sensors that collect and analyze data on the state of the electromagnetic field and the behavior of electron fluxes with a scan interval of 30 milliseconds. This frequency provides unprecedented accuracy and informative measurements in the entire history of studying the phenomenon of magnetic reconnection.
Despite the cardinal breakthrough associated with the latest events aboard the mission, there are still a lot of questions to be studied. So it is necessary to find out why in some cases the magnetic reconnection has an explosive character, in others it proceeds evenly, and in the third it does not occur at all. Studies of the drop-like tail of the Earth’s magnetosphere located on the part of the planet’s hemisphere opposite to the Sun look very promising. The investigations carried out by the mission at this point are associated with a portion of the field of the magnetosphere, which is being formed from the “solar” side.
That's all, with you there was a simple service for choosing sophisticated Dronk.Ru equipment. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog , there will be many more interesting ...

LetyShops cashback service sponsor . Return money for any purchases on the Internet. Read more about what a cashback service is in our article. We choose a cashback service for the 6th anniversary of Aliexpress.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/394193/
All Articles