Meet the 6th generation Intel Core processor (Skylake)

6th generation Intel Core processors (Skylake) appeared in 2015. Thanks to a number of improvements at the core level, “system on chip” and at the platform level, compared to the previous-generation 14-nm processor (Broadwell), the Skylake processor is very popular in a wide variety of devices designed for work, creativity and games. This article provides an overview of key features and enhancements of Skylake, as well as new usage patterns, such as waking up by voice commands and logging into the system using biometric data in Windows 10.
Skylake architecture
6th generation Intel Core processors are manufactured using 14nm technology, taking into account the more compact size of the processor and the entire platform for use in devices of various types. At the same time, the performance of the architecture and graphics has been improved, and enhanced security tools have been implemented. In fig. Figure 1 shows these new and improved features. Actual configuration in OEM devices may vary.

Figure 1. Skylake architecture and summary of improvements [1]
')
The main directions of development of processors
▍Performance
Increased productivity is directly due to the provision of more instructions to the executing unit: more instructions are executed for each clock cycle. This result is achieved through improvements in four categories [Ibid].
- Improved external interface. Due to more accurate branch prediction and increased capacity, instruction decoding speed increases, and prefetching is faster and more efficient.
- Improved paralleling instructions. For each clock cycle, more instructions are processed, and parallel execution of the instruction is improved due to more efficient buffering.
- Improved execution units (IB). The performance of execution units is improved compared to previous generations by the following measures:
- Shortened delays.
- Increased the number of IB.
- Improved power efficiency by disabling unused units.
- Increased speed of execution of security algorithms.
- Improved memory subsystem. In addition to improving the external interface, parallel processing of instructions and execution units, the memory subsystem has been improved in accordance with the bandwidth and performance requirements of the above components. The following measures were used for this:
- Increased bandwidth loading and saving.
- Improved prefetch module.
- Storage at a deeper level.
- Fill and write back buffers.
- Improved handling of page slips.
- Increased throughput with second level cache misses.
- New cache management instructions.
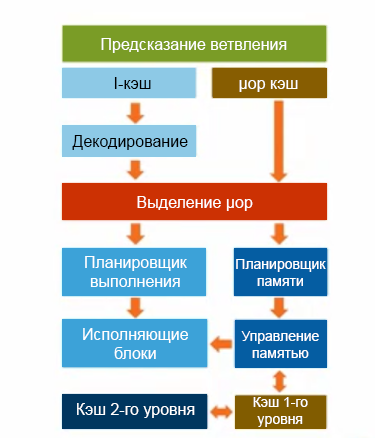
Figure 2. Skylake core microarchitecture diagram
In fig. Figure 3 shows the improvement in parallel processing in Skylake processors compared to processors of previous generations (Sandy Bridge is the second, and Haswell is the fourth generation of Intel Core processors).

Figure 3. Improved paralleling compared to previous generations of processors.
Thanks to the improvements shown in fig. 3, processor performance increased by 60% compared to a five-year-old PC, while video transcoding is performed 6 times faster, and graphics performance has increased 11 times.

Figure 4. The performance of the Intel Core processor 6th generation compared to a PC five years ago
- Source: Intel Corporation. Based on the results of Intel Core i5-6500 and Intel Core i5-650 processors in the SYSmark * 2014 test.
- Source: Intel Corporation. Based on the results of Intel Core i5-6500 and Intel Core i5-650 processors in the Handbrake test with QSV.
- Source: Intel Corporation. Based on the results of Intel Core i5-6500 and Intel Core i5-650 processors in the 3DMark * Cloud Gate test.
For detailed results of benchmarking desktop and laptop performance, see the following links:
▍Electricity saving
Setting up resources based on dynamic consumption
Outdated systems use Intel SpeedStep technology to balance performance and power consumption using an on-demand connection algorithm. This algorithm is controlled by the operating system. This approach is not bad for a constant load, but it is not optimal with a sharp increase in load. In Skylake processors, Intel Speed Shift technology transfers control to hardware instead of an operating system and allows the processor to switch to the maximum clock frequency in about 1 ms, providing more accurate power management [3].
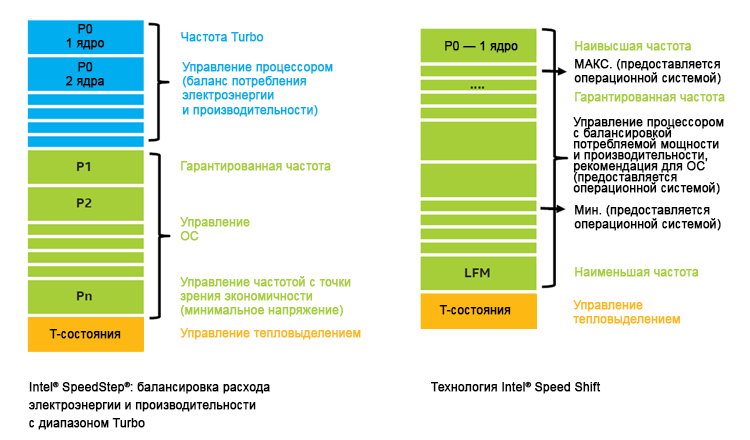
Figure 5. Comparison of Intel Speed Shift and Intel SpeedStep Technologies
The figures below show the responsiveness of the Intel Core i5 6200U processor with Intel Speed Shift technology compared to Intel SpeedStep technology.
- The response rate increased by 45%.
- Photo processing is 45% faster.
- Plotting is 31% faster.
- Local notes are 22% faster.
- The average response rate increased by 20%.
According to the results of WebXPRT * 2015 test by Principled Technologies *, which measures the performance of web applications in general and in specific areas, such as photo processing, note taking, and graphing. For more information, see the website .
Additional power optimization is achieved by dynamically adjusting resources based on their consumption: by reducing the power of unused resources by limiting the power of the Intel AVX2 vector extensions when they are not used, and also by reducing the power consumption when idle.
▍Multimedia and graphics
Intel HD Graphics video card embodies a number of improvements in terms of 3D graphics processing, media processing, display, performance, power, customization and scaling. This is a very powerful device in the family of graphics adapters integrated into the processor (first introduced in second-generation Intel Core processors). In fig. 6 compares some of these enhancements that provide more than 100 times the performance of graphics [2].

Figure 6. Graphics subsystem capabilities in different processor generations
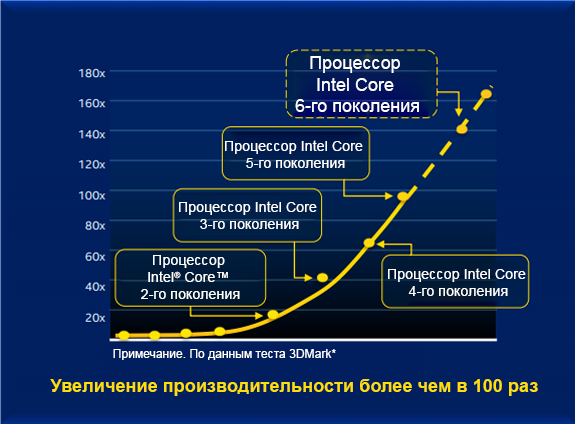
Figure 7. Improved graphics and multimedia processing across generations.
9th generation microarchitecture
The 9th generation graphics architecture is similar to the graphics architecture of the 8th generation of Intel Core Broadwell processors (5th generation), but improved in terms of performance and scalability. In fig. 8 shows a block diagram of generation 9 microarchitecture [8], consisting of three main components.
- Screen. From the left side.
- Beyond the cut. L-shaped part in the middle. Includes a streamline command handler, a global thread manager and a graphical user interface (GTI).
- Slice. Includes execution units (IB).
Compared to the 8th generation, the 9th generation microarchitecture has a higher maximum performance of 1 W, increased throughput and a separate power supply / clock circuit for a component outside the slice. This allows you to more effectively manage the power supply in such usage modes as when playing multimedia. The slice is a customizable component. For example, GT3 supports up to two slices (each slice with 24 execution units), GT4 (Halo) can support up to 3 sections (the number after the letters GT means the number of execution units based on their use: GT1 supports 12 execution units, GT2 - 24, GT3 - 48, and GT4 - 72 performing blocks). The architecture allows adjustment in a wide enough range to use the minimum number of execution units in low load scenarios, so power consumption can be from 4 to more than 65 watts. API support for 9th generation GPUs is available in DirectX * 12, OpenCL 2.x, OpenGL * 5.x and Vulkan *.
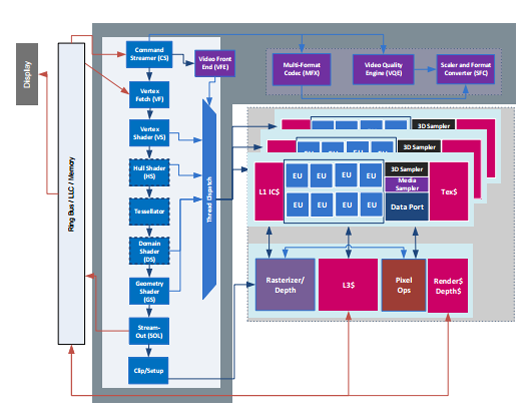
Figure 8. 9th generation GPU architecture
For more information about these components, see.
Improvements and multimedia processing capabilities include the following [2]:
- Consumption is less than 1 W, consumption is 1 W during video conferencing.
- Accelerate playback of unprocessed video from the camera (in RAW format) using new VQE features to support RAW video playback with a resolution of up to 4K60 on mobile platforms.
- New mode New Intel Quick Sync Video with fixed functions (FF).
- Support for a wide range of codecs with fixed functions, acceleration of decoding using GP.
In fig. Figure 9 shows the generation 9 GPU codecs.
Note. Support for multimedia codecs and processing may not be available in all operating systems and applications.
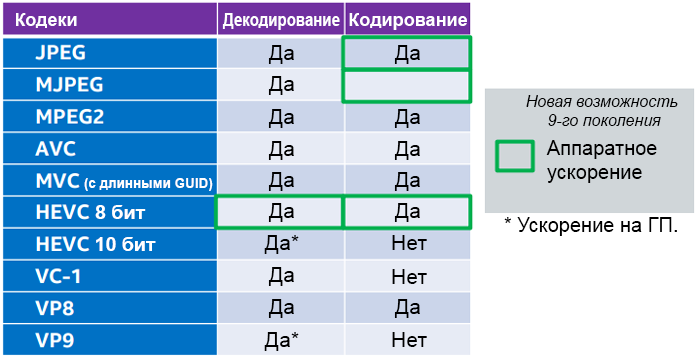
Figure 9. Codec support by Skylake processors
The improvements and screen capabilities include the following:
- Blend, scale, rotate and compress the image.
- Support for high pixel density (resolution over 4K).
- Support image transmission over a wireless connection with a resolution of up to 4K30.
- Self Update (PSR2).
- CUI XX - new features, improved performance.
The Intel Core I7-6700K processors provide the following features for gamers (see Figure 10). Intel Turbo Boost 2.0 technology, Intel Hyperthreading technology and overclocking are also supported. The performance gain compared to a PC five years ago reaches 80%. For more information, see this page .

Figure 10. Intel Core i7-6700K processor capabilities
- Source: Intel Corporation. Based on the results of Intel Core i7-6700K and Intel Core i7-875K processors in the SPECint * _rate_base2006 test (copy factor 8).
- Source: Intel Corporation. Based on the results of the Intel Core i7-6700K and Intel Core i7-3770K processors in the SPECint * _rate_base2006 test (copy factor 8).
- The features described are available in separate combinations of processors and chipsets. A warning. A change in the clock frequency and / or voltage can: (i) lead to a decrease in the stability of the system and a decrease in the lifetime of the system and processor; (ii) lead to a failure of the processor and other system components; (iii) reduce system performance; (iv) cause additional heat or other damage; (v) affect the integrity of data in the system. Intel does not test and does not guarantee the operation of processors with technical parameters other than those installed.
▍ Scalability
The Skylake microarchitecture is a customizable kernel: a single design for two directions, one for client devices, the other for servers without sacrificing the power and performance requirements of both segments. In fig. Figure 11 shows the various processor models and their efficiency in terms of power for use in devices of various sizes and types - from ultra-compact Compute Stick to powerful Intel Xeon-based workstations.

Figure 11. Availability of Intel Core processors for various types of devices
▍ Advanced security features
Intel Software Guard Extensions Extensions (Intel SGX): Intel SGX is a set of new instructions in Skylake processors, enabling application developers to protect sensitive data from unauthorized changes and access by unauthorized programs with higher rights. This enables applications to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of confidential information [1], [3]. Skylake supports instructions and streams for creating secure enclaves, allowing you to use trusted memory areas. For more information on the Intel SGX extensions, see this page .
Intel Memory Protection Extensions (Intel MPX): Intel MPX is a new set of instructions for checking for buffer overflow during runtime. These instructions allow you to check the boundaries of stack buffers and heap buffers before accessing memory, so that a process accessing memory has access only to the memory area assigned to it. Intel MPX support is implemented in Windows * 10 using the built-in Intel MPX functions in Microsoft Visual Studio * 2015. In most C / C ++ applications, you can use Intel MPX: to do this, recompile the applications without changing the source code and links to the outdated libraries. When running libraries that support Intel MPX, on systems that do not support Intel MPX (Intel Core processors 5th generation and earlier), the performance does not change: it does not increase, nor decreases. You can also dynamically enable and disable Intel MPX support [1], [3].
We reviewed improvements and enhancements to the Skylake architecture. In the next section, we look at Windows 10 components that are optimized to take advantage of the Intel Core architecture.
New features in Windows 10
The capabilities of the 6th generation Intel Core processors are complemented by the capabilities of the Windows 10 operating system. Below are some of the main features of the Intel hardware and Windows 10 OS, thanks to which Intel platforms running Windows 10 work more efficiently, more stable and faster [3].
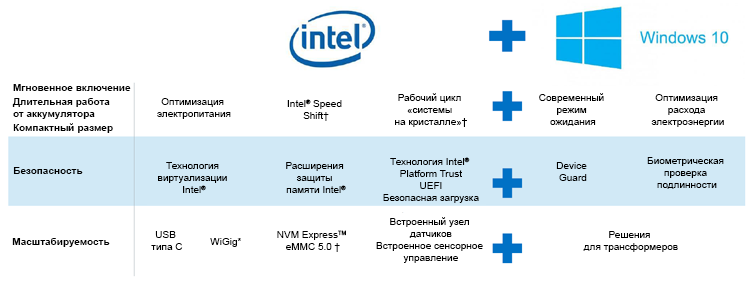
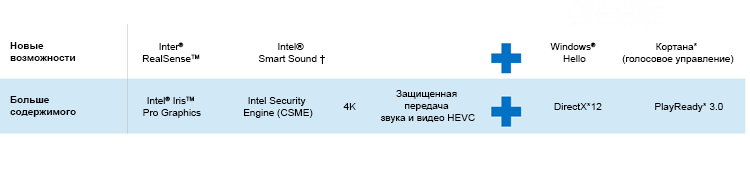
Intel Intel and Microsoft are working together to provide further support for Windows.
Figure 12. Skylake and Windows * 10 features
▍Cortana
Microsoft's Cortana Voice Assistant is available on Windows * 10 and gives you the ability to control your computer with your voice after you say the key phrase “Hello, Cortana!”. The voice command wake-up function uses the audio processing pipeline on the CPU to increase recognition accuracy, but you can transfer this function to a hardware-based digital sound signal processor with built-in support for Windows 10 [3].
▍Windows Hello *
With the help of biometric hardware and Microsoft Passport *, Windows Hello supports a variety of mechanisms for logging into your system using face, fingerprint, or iris recognition. The system, without installing any additional components, supports all these login capabilities without using a password. The Intel RealSense Front-View Camera (F200 / SR300) supports face recognition-based biometric authentication [3].

Figure 13. Windows * Hello with Intel RealSense technology
Photos on fig. 13 show how the focal points detected on the face by the F200 camera are used to identify the user and enter the system. Based on the location of 78 control points on the face, a face pattern is created when the user first attempts to log in using face recognition. On the next login attempt, the saved location of the reference points obtained by the camera is compared with the saved template. The capabilities of the Microsoft Passport service, combined with the capabilities of the camera, make it possible to achieve a security level with indicators of false admission to the system in 1 out of 100,000 cases and a false refusal in admission in 2-4% of cases.
Links
- A new generation of Intel microarchitecture called Skylake, by Julius Mandelblat
- Intel's new generation of microarchitecture called Skylake by David Blythe
- Intel Skylake Architecture and Windows * 10 - Better Together, by Shiv Koushik
- Skylake for gamers
- The best Intel processor
- Skylake Desktop Performance Test
- Skylake Laptop Performance Test
- Intel Gen9 processor computing architecture
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/394077/
All Articles