How to repair nuclear reactors
RBMK reactors are known primarily for the Chernobyl accident . At one time, the idea of using the proven technology of industrial plutonium-producing reactors to create a simple nuclear power unit seemed to be quite sound and economical, especially in the early stages of nuclear power development, because by 2000 the USSR planned to build 400 gigawatts of fast sodium reactors.
However, the reality turned out to be quite different - simplicity turned into catastrophic miscalculations in the design, and it is necessary to operate these reactor units longer than the original plans.
Reactor graphite has such an unpleasant feature that after a certain dose of neutron irradiation is set, it begins to swell. At the first block of the Leningrad NPP, launched at the end of 1973 in the mid-2000s, they began to observe how graphite masonry blocks grow and bend. By 2012, the process reached the limits of safe operation - the deflection of some technological channels exceeded 60-70 mm (at a length of 18 meters), some graphite blocks burst.
')
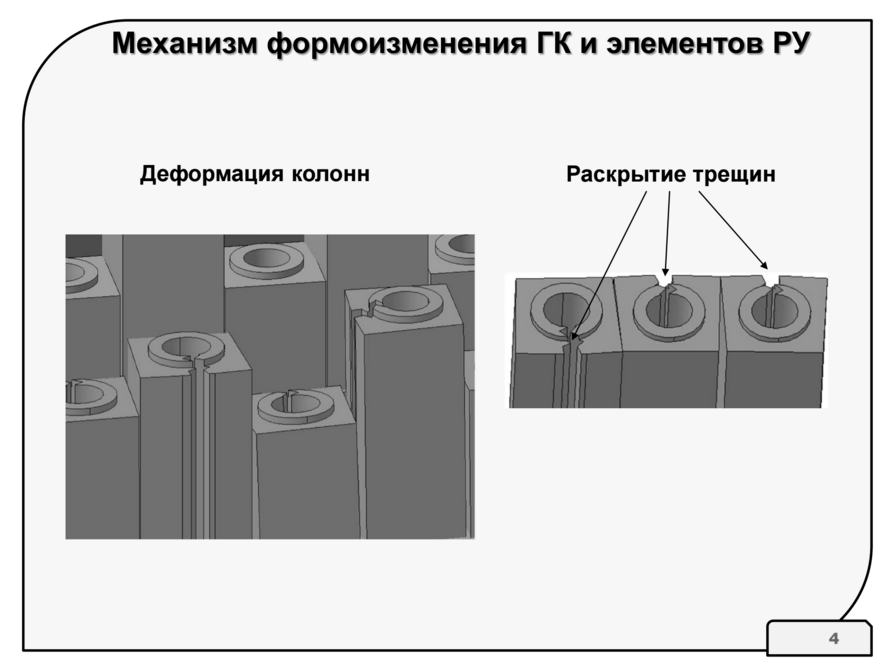

Since a fully depreciated RBMK unit in operation brings good money, it was decided to come up with some repair technology to modify the end of the permitted (extended) service life - 2018. The idea of taking and replacing the entire graphite stack did not pay off, so more sophisticated technology was used - trimming specific columns and pulling them into a vertical with the gradual assembly of a flat stack. Of course, given the high radioactivity of the masonry, this work is much more difficult than it sounds and required the development of various robots. The development of technology and equipment was carried out in 2011-2012, and in January 2013, work began on the first block of LNPP.

Far from all the cells were subjected to milling and processing, but a rather rather large amount.

Fuel was removed from all the cells being processed and the technological channel was withdrawn — a steel-zirconium tube to which water and steam-water communications were connected to the top and bottom, and the fuel and control rods of the control and protection systems were lowered inside. In total, there are 1,661 such technological channels on the RBMK-1000.

The TCs themselves went up with a shielded unloading-loading machine, however, in order to suppress the spread of radioactive dust and aerosols, a separate sanitary room was installed in the reactor hall (except for the general one at the NPP entrance) with changing clothes and wet cleaning was constantly carried out.
Equipment Ltd. "Prolog"

Equipment LLC "Diakont" - by the way manufacturers of very high-tech robots and cameras for work in nuclear reactors.


After the restoration of the shape of the columns, a hole was re-cut under the TC

A typical technology for the collection of radioactive dust, in principle, all the "special ventilation" of any radioisotope production ends up a little or more difficult.

Results of work: TO

AFTER:

As a result, work on the restoration of the reactor took 8 months - from January to August 2013. At the same time, we had to make several modifications of the technology, although in some aspects (for example, dose load), according to NIKIET, the result was even better than expected. On November 25, 2013, the upgrade of the capacity of the updated reactor began, and in January 2014, the Leningrad NPP brought the first power unit to full capacity, confirming the success of the repair, which cost "even cheaper than the original figure of 4.5 billion rubles".
Then this technique was applied on the second block of the Leningrad NPP and on the first and second block of the KuNPP.
However, the reality turned out to be quite different - simplicity turned into catastrophic miscalculations in the design, and it is necessary to operate these reactor units longer than the original plans.
Reactor graphite has such an unpleasant feature that after a certain dose of neutron irradiation is set, it begins to swell. At the first block of the Leningrad NPP, launched at the end of 1973 in the mid-2000s, they began to observe how graphite masonry blocks grow and bend. By 2012, the process reached the limits of safe operation - the deflection of some technological channels exceeded 60-70 mm (at a length of 18 meters), some graphite blocks burst.
')


Since a fully depreciated RBMK unit in operation brings good money, it was decided to come up with some repair technology to modify the end of the permitted (extended) service life - 2018. The idea of taking and replacing the entire graphite stack did not pay off, so more sophisticated technology was used - trimming specific columns and pulling them into a vertical with the gradual assembly of a flat stack. Of course, given the high radioactivity of the masonry, this work is much more difficult than it sounds and required the development of various robots. The development of technology and equipment was carried out in 2011-2012, and in January 2013, work began on the first block of LNPP.

Far from all the cells were subjected to milling and processing, but a rather rather large amount.

Fuel was removed from all the cells being processed and the technological channel was withdrawn — a steel-zirconium tube to which water and steam-water communications were connected to the top and bottom, and the fuel and control rods of the control and protection systems were lowered inside. In total, there are 1,661 such technological channels on the RBMK-1000.

The TCs themselves went up with a shielded unloading-loading machine, however, in order to suppress the spread of radioactive dust and aerosols, a separate sanitary room was installed in the reactor hall (except for the general one at the NPP entrance) with changing clothes and wet cleaning was constantly carried out.
Equipment Ltd. "Prolog"

Equipment LLC "Diakont" - by the way manufacturers of very high-tech robots and cameras for work in nuclear reactors.


After the restoration of the shape of the columns, a hole was re-cut under the TC

A typical technology for the collection of radioactive dust, in principle, all the "special ventilation" of any radioisotope production ends up a little or more difficult.

Results of work: TO

AFTER:

As a result, work on the restoration of the reactor took 8 months - from January to August 2013. At the same time, we had to make several modifications of the technology, although in some aspects (for example, dose load), according to NIKIET, the result was even better than expected. On November 25, 2013, the upgrade of the capacity of the updated reactor began, and in January 2014, the Leningrad NPP brought the first power unit to full capacity, confirming the success of the repair, which cost "even cheaper than the original figure of 4.5 billion rubles".
Then this technique was applied on the second block of the Leningrad NPP and on the first and second block of the KuNPP.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/393787/
All Articles