Peace atom?
“If you can use nuclear physics discoveries for peaceful purposes, this will open the way to a new paradise” - Albert Einstein

Atomic energy allows you to expand energy resources, which contributes to the conservation of fossil fuel resources, reduces the cost of electrical energy. This is important for areas that are far from fuel sources. The use of atomic electricity can reduce air pollution. After all, when NPPs operate, they do not consume fossil fuels, and, therefore, sulfur, nitrogen and carbon dioxide oxides are not emitted into the atmosphere, which in turn reduces the greenhouse effect, which leads to global climate change.
')

Soon April 26 is the famous date. This year marks 30 years from the moment when the word "Chernobyl" has become synonymous with a terrible man-made disaster, a global environmental disaster. The consequences of this accident felt the whole world.
Now the Chernobyl NPP has been stopped, decommissioning works are being carried out, objects of radioactive waste behavior have been erected on an industrial site, a shelter for spent nuclear fuel is being built. The construction of a new safe confinement is underway to isolate the destroyed power unit from the environment. The residual stage of overcoming the consequences of the accident should be the creation of the infrastructure for the processing of unstable structures and their dismantling, the removal of fuel-intensive materials from the Shelter object and their reliable burial.

The development of atomic energy in the USSR began in the post-war years, the First Main Directorate was created at the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR, it was entrusted with the task of creating the atomic industry and coordinating the country's scientific and technical and engineering developments of atomic weapons. In 1946, Kurchatov reports to Stalin about the possibility of the peaceful use of atomic energy. At the end of the same year, at the Institute of Atomic Energy (initially at Laboratory No. 2 of the USSR Academy of Sciences), the first F-1 nuclear reactor was launched in Europe and four years later the design of the world's first nuclear power plant began. The construction of such stations such problems as fuel transportation, gave many advantages - compact equipment, the ability to create power plants of large electrical unit capacity, such stations could be used on submarines, as there was no need for oxygen.

All set to implement the "plan". Were quickly created - a scientific base, design and construction organizations, industrial enterprises. A new branch of national economy has emerged - medium-sized machine building.
The first nuclear power plant was built in Obninsk (near Moscow) in 1954. Its power was only 5 MW. Thus began a new era - the era of nuclear energy.


The nuclear energy development program for 1956 foresaw the construction of nuclear power plants in the USSR with a total capacity of 2,175 MW.
The pace of development of nuclear energy was initially low, since attention was paid to the development of hydraulic and thermal power engineering. From 1948 to 1957, 9 industrial reactors, weapons-grade plutonium and one pilot NPP were commissioned. Actively engaged in the development of dual-purpose reactors that could generate energy and produce plutonium. Several experimental low-power nuclear power plants were put into operation (as an example, a 750-kW installation with an ARBUS reactor, an Arctic block installation).

Arctic block installation
The Soviet transistor device "Beta-1", as an example of a small nuclear installation for powering isolated consumers, was used for a radio meteorological station. In it, atomic energy for direct conversion into electric energy was supplied not by the fission of uranium or plutonium, but by the beta decay of cerium placed in a small container. The converter gave life to a 150-watt radio transmitter, which was equipped with a standard automatic weather station.
Beginning in 1957 began the construction of civilian nuclear power plants. Not only canal industrial uranium-graphite reactors were built, but also pressurized water-water reactors.
The next “plan” for the development of this industry involved the construction of nuclear power plants with a total capacity of 11.9 thousand MW. Until 1980, it was planned to increase the capacity of nuclear power plants to 26.8 thousand MW., The plan for the development of nuclear energy for the period of 1990 implied an even higher figure - 100 thousand MW. In 1982, construction of 143 power units with a unit capacity of 440, 500, 1000 and 1500 MW was approved. It can be said with confidence that at the beginning of the 80s in the USSR, the atomic energy industry began to develop at a very fast pace, the capacity of operating NPPs from 1981 to 1985 increased by 125%. The accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant forced to revise the program of development of nuclear energy ...
NPPs differ in the type of reactor installation and thermal circuit. The power unit layout of any NPP consists of a nuclear reactor, where the fission energy of uranium or plutonium nuclei is transferred to the coolant, cooling reactor, and a power steam turbine installation, where steam energy is converted into electrical energy.
At the First NPP, graphite was chosen as the moderator of the nuclear reactor, and water as the coolant. This choice was the result of studying various types of nuclear reactors: pressurized water reactors (PWR), boiling water reactors (BWR), and gas and sodium coolant.

Uranium-graphite channel reactors, which were cooled with boiling water, were economical. This type of reactor with an electrical capacity of 1000 MW or more is known as the “Soviet type”. Another type that formed the basis of the atomic power industry of the USSR is a tank reactor with pressurized water VVER (similar to PWR is a power reactor that uses plain water as a moderator of a nuclear reaction and a coolant). The representative of Soviet-type reactors is the RBMK-1000 with an electrical capacity of 1000 MW (for example, at the Lenin NPP named after VI Lenin).

The Leningrad NPP is located 80 km west of the city of St. Petersburg on the coast of the Gulf of Finland in the town of Sosnovy Bor. The best specialists of Minsredmash were thrown at the construction of LNPP, it was supposed to be the main one in the series of erected NPPs with RMBC reactors. After the approval of the technical design of the reactor RMBK - 1000, the construction of the station began (September 1967). In 1973, the reactor of the first power unit was ready for launch. In the main building of the first stage of LEAS there are two power units with an electrical power of 1000 MW with a common machine room and separate rooms for reactors, fuel transportation systems, control panels and a common room for gas cleaning and water purification of the primary circuit. In each power unit there is a RMBK reactor - 1000 with a heat capacity of 3200 MW with a condensation circuit and auxiliary systems, a steam and condensate-feed tracts and two turbogenerators with a power of 500 MW each. LNPP is the first station that uses sea water for cooling. In 1975, the second power unit was launched and construction of the second stage of the nuclear power plant began. In 1979, the third power unit, at the end of 1980 the reactor was launched in the fourth power unit. By August 1981, the total electrical capacity reached 4000 MW, due to which LNPP became the largest nuclear power plant in Europe of this type.
At the station sites, it was decided to store fuel assemblies and spent fuel (fuel assemblies, spent nuclear fuel) due to the lack of centralized places for storing or disposing of spent fuel from power units. Therefore, at the sites of stations with RBMK reactors
storage facilities for spent nuclear fuel were erected. Such “storage” turned out to be rather “deplorable”: the design capacities of the SNFS (a complex of buildings and structures with pools that have autonomous systems of special ventilation, water purification and cooling), and the design capacities of the reactor BV were quickly filled.
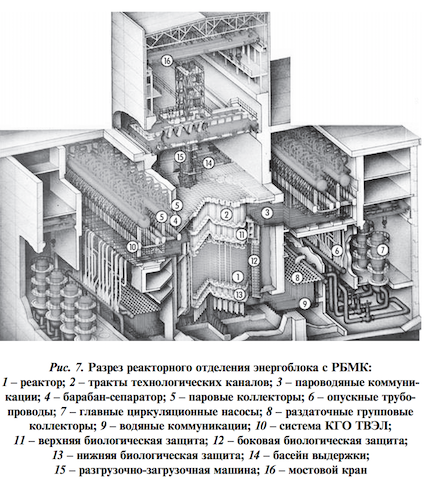
A long-term program to increase electricity production provided for the construction of nuclear power plants with RBMK reactors. Within 10 years after the launch of the first power unit of LNPP in the USSR, 12 power units with RBMK-1000 were launched at the Kursk, Chernobyl and Smolensk NPPs.
By 1986, 14 such units were launched.
It is worth noting that during the construction of the LNPP, an order was issued by Slavsky according to which "... the cost of a kilowatt of installed capacity should have been set at no more than 180 rubles." Therefore, we had to reduce the cost of the project by refraining from creating security systems beyond the required minimum. As a result, NPPs with RBMK-1000 at LNPP (and all subsequent NPP projects with this type of reactor) are simple - simply, in order to save, they did not provide for the containment of the reactor facility. It turns out that 200 tons of uranium and more than 1 ton of radioactive fission products "were located under the open sky", because the roof of the reactor compartment was as strong as the roof of an ordinary residential building.

In 1975, from 28 to 30 November, a serious radiation accident occurred at Leningrad NPP. The personnel of the first unit did not cope with the hardly controlled reactor, the power in the local area of the core increased several times, the temperature rose to 1600 C. Before that, there was 1 turbogenerator, the reactor power was at 50% of the nominal. Like at the Chernobyl NPP, before the accident, the power (due to operator error) dropped to zero, it was immediately lifted up. The emergency process lasted up to several hours during the rise of power from zero to 1,700 MW, and 30 fuel assemblies were destroyed, only one channel was destroyed.
In the accident at the Leningrad NPP, neutron-physical instability in the active zone itself played a significant role, and thermal-hydraulic processes of instability in the external reactor cooling circuit (MFC) played a much smaller role.
“Fortunately,” only two walls of the channels carrying the pressure of the coolant were destroyed. 1.5 million Ci of radioactivity was released into the external environment. The accident was hidden, instead of publicly recognizing the danger of the RBMK. Only in 1976 was the first time mentioned about this accident at the board of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the USSR, when it was reported about the request of the Government of Finland and Sweden regarding an increase in the radiation background over their territories.

In 1967, the USSR government decided to start the construction of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. In total, it was planned to build 6 power units with high-power uranium-graphite channel reactors - RBMK. In 1972, construction began on the first power unit. The site 4 km from the village of Kopachi, on the right bank of the Pripyat River, 12 km from the city of Chernobyl, was recommended by the State Commission for locating the nuclear power plant. Three variants of the project were developed for ChNPP (capacity 2000 MW): the first using the RBMK-1000 reactor, the second using the RK-1000 gas-graphite reactor, and the third using the WWER-1000 reactor. Initially, a variant using a gas-graphite reactor was chosen, but later it was replaced with an RBMK-1000 reactor. After Leningrad and Kursk, it was the third station with this type of reactors.
On December 14, 1977, the first Chernobyl NPP power unit was commissioned. On May 24, 1978, the first power unit was brought to a capacity of 1000 MW. On November 16, in 1978, the second power unit was launched, on December 3, in 1981, the fourth power unit. In November 1983, the first fuel assembly was loaded on the fourth power unit.
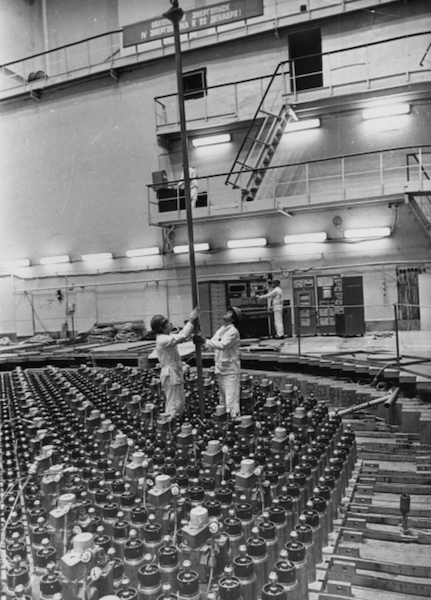

April 26 in 1986, the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. As a result, the core of the reactor installation and part of the building of the fourth block were destroyed, as well as the release of part of the radioactive products accumulated in the core to the atmosphere. Everything happened during the experiment to study the possibility of using the inertia of the rotor of the turbogenerator to generate any amount of electricity, if the reactor stops in the future.
The experiment was planned to be carried out at a reactor power of 700 MW, but before it began, the power level dropped to 30 MW. The operator tried to restore power, the experiment began at 200 MW. Within a few seconds, the reactor's power began to grow and the operator pressed the emergency protection button (the operator’s delay of several tens of seconds initially became the official version of the causes of the accident). Two explosions occurred at intervals of a few seconds, the reactor was completely destroyed.
After the destruction of the technological channels and the breakage of the steam and water communications from them, the steam entered the central hall, into the rooms of the drum separators on the right and left, into the sub-apparatus rooms of a firmly dense box. After the breakage of the lower communications, the reactor was completely dehydrated. The explosions began in the technological channels of the reactor, which began to destroy under increased pressure. The lower and upper communications of the reactor were destroyed, the pressure grew at lightning speed - 15 atmospheres per second (reached 250-300 atmospheres). The steam got into the reactor space - an explosion of metal construction occurred. The premises of the drum separators were destroyed, the drum separators themselves (weighing 130 tons) were shifted from the dead supports and cut off from the pipelines. This was followed by explosions in the underground pipeline mines. There was an explosion in the central hall, then (perhaps almost simultaneously) in the reactor itself, which was uncorked and full of hydrogen. The explosion in the core led to the release of a huge amount of activity and hot pieces of nuclear fuel. The fire started the roof. The explosion threw up and turned the slab of the top bio-protection to 500 tons, it collapsed on the machine in an inclined position, the active zone on the right and left remained slightly opened.
The first months after the accident, the main fault was laid on the operators. In 1991, almost all allegations were dropped from NPP personnel. One of the causes of the Chernobyl accident was the low quality of regulations and safety requirements. Yes, and the causes of the disaster were of a technical nature: the RBMK-1000 reactor that had exploded had a number of design flaws, which under certain conditions turned out to be dangerous, it simply did not comply with many nuclear safety rules.
As it was later stated (in 1993), before the accident, the fourth power unit of the Chernobyl NPP worked with a number of changed indicators - the reactor emergency cooling system turned off and the reduced reactivity margin (OPM).
According to experts, even the Chernobyl NPP personnel were not aware of the danger of working in the changed conditions. Before the accident, the ORM was less than the value allowed by the regulations, however, the operators did not know the current value of the ORM and, therefore, did not know that they were violating the regulations.
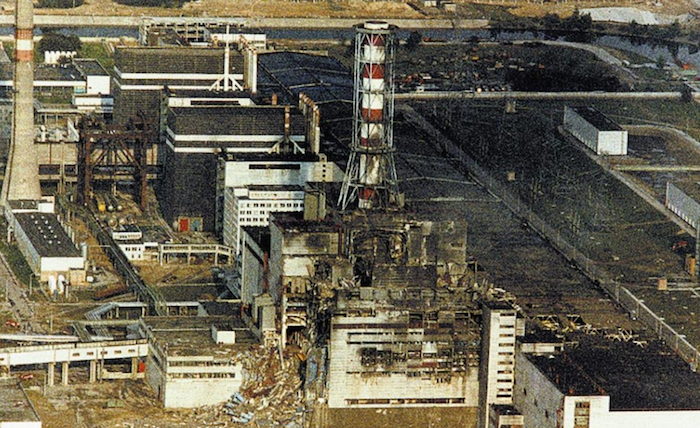

According to official data, 50 million Ci were thrown into the external environment. At the time of the accident, reactor 4 of the power unit was at full load, there were about 180 tons of fuel inside the reactor. The explosion blew off the reactor lid weighing almost 3 thousand tons, completely destroyed the roof, almost completely demolished the western and northern walls. According to rough estimates, from 30 to 100 tons of fuel were scattered around the “district”. Radiation levels around the destroyed block reached several thousand roentgens per hour (the permissible rate is 5 roentgens per year). In order to realistically assess the scale of the radioactive release: the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima weighed 4 and a half tons, the reactor of the fourth power unit threw 50 tons of evaporated fuel into the atmosphere. The explosion of the reactor led to a monstrous radiation contamination of the area (the territory of Ukraine, Belarus and some regions of Russia).
A 30-kilometer “exclusion zone” was created around the Chernobyl NPP, in which almost all the settlements were deliberately destroyed, and the population was evicted. The city of Pripyat (with a population of 50 thousand) added to the list of dead cities. All residents were evacuated, but no one was told the true reasons for the evacuation.

At the time of the explosion, 2 people died at the station (the body of one of them was never found), another died of burns in the hospital several hours after the accident. These people at the time of the explosion were located near the reactor and their death was not associated with radiation damage. Subsequently, 134 Chernobyl NPP employees and members of the rescue teams who were at the station during the explosion developed radiation sickness, 28 of which died within the next few months.
Vast territories were polluted in Ukraine (41.75 thousand square kilometers), Belarus (46.6 thousand square kilometers), the European part of Russia (57.1 thousand square kilometers). The disaster that happened was fatal for many thousands of innocent people ...
Nevertheless, in the fall of 1986, work at the Chernobyl NPP was resumed, the first power unit was launched on October 1, and the second one on November 5. The third power unit was launched in November 1987. But after a serious fire at the second power unit in 1991 and an unsuccessful attempt to restore it, the station was suspended by 1997.
As the main causes of the terrible accident at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant are considered to be the design flaws of the RBMK-1000 nuclear reactor. But after all, these reactors were not only at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, but also at several stations (Leningrad, Smolensk and Kursk).
So why was this type of reactor so popular in the USSR? .. Two types of reactors - high-power uranium-graphite channel (RBMK -1000) and water-cooled (VVER-1000), what type of RBMK nuclear reactor - 1000 or VVER-1000 What guided when choosing one type or another in our country? You can draw an analogy with the clock.
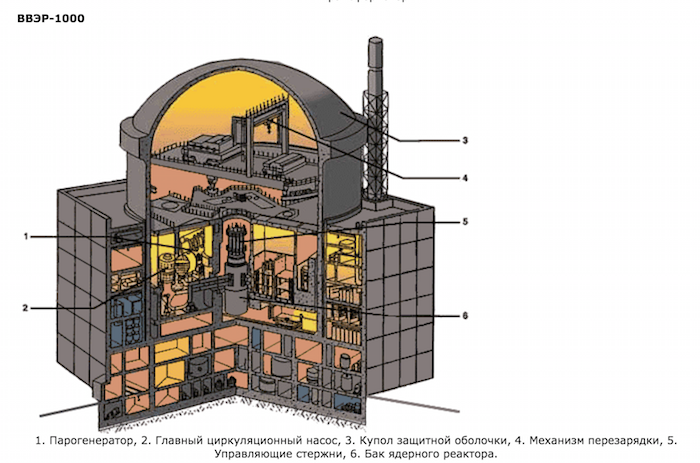
Imagine that a nuclear power plant at RBMK reactors is a person in expensive mechanical watches. This type of nuclear reactor could have almost unlimited power, and the replacement of spent nuclear fuel could be done without stopping it, that is, you could clean and repair the clock without removing it from your hand. Conveniently. Practical The use of RBMK type reactors always looked economically attractive. But for every convenience you have to pay some inconvenience. The disadvantages of uranium-graphite reactors are a whole package. Firstly, this is an increased requirement for safety, difficulty in operation, and secondly, exceptional requirements for service personnel; and finally, disciplined execution of instructions. A normative document strictly prescribes that if you twist the plant at least half a turn or reject the arrow by an extra degree - the clock will simply explode and tear off your hands.
The main qualitative advantage of the VVER reactor, as compared to RBMK, is its safety. This fact became apparent after the incident at the Chernobyl NPP. But there is a paradox why in the power engineering of the countries of the former USSR RBMK power units were more popular than WWER? Under this fact, oddly enough, there is also a serious science - economics. The fact is that before launching the Atommash plant (producing VVER rectors) at the end of the 70s, the USSR could produce only one vessel of this type of reactor per year.

The VVER-1000 basically does not have “positive feedbacks”, the very ones that led to the tragedy of April 26, 1986. In the case of out-of-control loss of control over the situation with coolant or core cooling, the chain reaction of burning nuclear fuel declines and quietly fades out like a burned campfire, and does not accelerate, as in the RBMK. There is no fuel (graphite) in the core of the VVER reactor, of which up to two thousand tons may be in the RBMK. It would seem that VVER is an ideal option, but our conditional character “man in a quartz watch” is also not perfect, his watch is heavier and more massive, such a brick on a strap. The VVER hull is gigantic in size, and its manufacture is very laborious. Dimensions are limited to achieving ultimate strength, since the mechanical stresses tearing the body are directly related to its diameter and internal pressure. An increase in unit capacity always leads to a reduction in the cost of 1 kW of installed capacity, since this increases such elements as MCP, steam generators (or drum-separators), a steam turbine with its entire complex economy, the specific cost of the automation system, water supply, etc. .
After the catastrophe at the Chernobyl NPP, the need to modernize the reactors became acute, the requirements for nuclear safety were tightened. Currently, 11 more RBMK-1000 reactors are operating.
The Chernobyl accident significantly slowed down the development of nuclear energy not only in the USSR, but throughout the world. In the USSR, they abandoned the construction of a number of nuclear power plants - Tatar, Bashkir, Kostroma, Odessa, Minsk, Krasnodar and others. The structure of the industry has been reorganized to meet international standards.
Now the Russian nuclear industry is one of the most advanced in the world in terms of scientific and technical developments in the design of reactors, nuclear fuel, operating experience of nuclear power plants, and qualifications of NPP personnel. The share of electricity generation by nuclear power plants is about 18.6% of the total electricity produced. Active construction of nine new NPP units, construction of Novovoronezh NPP-2, Leningrad NPP-2, Baltic NPP, the world's first floating NPP Akademik Lomonosov, is underway, the fourth power unit of the Beloyarsk NPP is being completed.

monument to the peaceful atom in Kurchatovka
Hopefully, the peaceful atom will remain peaceful ...

Atomic energy allows you to expand energy resources, which contributes to the conservation of fossil fuel resources, reduces the cost of electrical energy. This is important for areas that are far from fuel sources. The use of atomic electricity can reduce air pollution. After all, when NPPs operate, they do not consume fossil fuels, and, therefore, sulfur, nitrogen and carbon dioxide oxides are not emitted into the atmosphere, which in turn reduces the greenhouse effect, which leads to global climate change.
')
April 26 - 30 years from the date of the Chernobyl accident

Soon April 26 is the famous date. This year marks 30 years from the moment when the word "Chernobyl" has become synonymous with a terrible man-made disaster, a global environmental disaster. The consequences of this accident felt the whole world.
Now the Chernobyl NPP has been stopped, decommissioning works are being carried out, objects of radioactive waste behavior have been erected on an industrial site, a shelter for spent nuclear fuel is being built. The construction of a new safe confinement is underway to isolate the destroyed power unit from the environment. The residual stage of overcoming the consequences of the accident should be the creation of the infrastructure for the processing of unstable structures and their dismantling, the removal of fuel-intensive materials from the Shelter object and their reliable burial.
From the development of Soviet atomic energy

The development of atomic energy in the USSR began in the post-war years, the First Main Directorate was created at the Council of People's Commissars of the USSR, it was entrusted with the task of creating the atomic industry and coordinating the country's scientific and technical and engineering developments of atomic weapons. In 1946, Kurchatov reports to Stalin about the possibility of the peaceful use of atomic energy. At the end of the same year, at the Institute of Atomic Energy (initially at Laboratory No. 2 of the USSR Academy of Sciences), the first F-1 nuclear reactor was launched in Europe and four years later the design of the world's first nuclear power plant began. The construction of such stations such problems as fuel transportation, gave many advantages - compact equipment, the ability to create power plants of large electrical unit capacity, such stations could be used on submarines, as there was no need for oxygen.

All set to implement the "plan". Were quickly created - a scientific base, design and construction organizations, industrial enterprises. A new branch of national economy has emerged - medium-sized machine building.
Obninsk. A small green town near Moscow has become the capital of peaceful nuclear energy, a mecca for scientists and journalists all over the world. Just think: uranium-235, which flared up in a fierce, withering sun over Hiroshima, is now peacefully boiling water! Boils, turns it into steam, and he collapses a hot stream on the turbine blades. And the current runs along the wires, giving people light and heat, and the machine muscles - the power.
The first nuclear power plant was built in Obninsk (near Moscow) in 1954. Its power was only 5 MW. Thus began a new era - the era of nuclear energy.


The nuclear energy development program for 1956 foresaw the construction of nuclear power plants in the USSR with a total capacity of 2,175 MW.
The pace of development of nuclear energy was initially low, since attention was paid to the development of hydraulic and thermal power engineering. From 1948 to 1957, 9 industrial reactors, weapons-grade plutonium and one pilot NPP were commissioned. Actively engaged in the development of dual-purpose reactors that could generate energy and produce plutonium. Several experimental low-power nuclear power plants were put into operation (as an example, a 750-kW installation with an ARBUS reactor, an Arctic block installation).

Arctic block installation
In 1963, the ARBUS nuclear reactor reactor unit with a capacity of 750 kilowatts was commissioned - original in design and the first of its kind. Here, the role of a moderator and coolant is played well by gasoil - diesel fuel. Having been in the reactor, unlike water, it almost does not become infected with induced radioactivity.
The Soviet transistor device "Beta-1", as an example of a small nuclear installation for powering isolated consumers, was used for a radio meteorological station. In it, atomic energy for direct conversion into electric energy was supplied not by the fission of uranium or plutonium, but by the beta decay of cerium placed in a small container. The converter gave life to a 150-watt radio transmitter, which was equipped with a standard automatic weather station.
Beginning in 1957 began the construction of civilian nuclear power plants. Not only canal industrial uranium-graphite reactors were built, but also pressurized water-water reactors.
The next “plan” for the development of this industry involved the construction of nuclear power plants with a total capacity of 11.9 thousand MW. Until 1980, it was planned to increase the capacity of nuclear power plants to 26.8 thousand MW., The plan for the development of nuclear energy for the period of 1990 implied an even higher figure - 100 thousand MW. In 1982, construction of 143 power units with a unit capacity of 440, 500, 1000 and 1500 MW was approved. It can be said with confidence that at the beginning of the 80s in the USSR, the atomic energy industry began to develop at a very fast pace, the capacity of operating NPPs from 1981 to 1985 increased by 125%. The accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant forced to revise the program of development of nuclear energy ...
NPPs differ in the type of reactor installation and thermal circuit. The power unit layout of any NPP consists of a nuclear reactor, where the fission energy of uranium or plutonium nuclei is transferred to the coolant, cooling reactor, and a power steam turbine installation, where steam energy is converted into electrical energy.
At the First NPP, graphite was chosen as the moderator of the nuclear reactor, and water as the coolant. This choice was the result of studying various types of nuclear reactors: pressurized water reactors (PWR), boiling water reactors (BWR), and gas and sodium coolant.

Uranium-graphite channel reactors, which were cooled with boiling water, were economical. This type of reactor with an electrical capacity of 1000 MW or more is known as the “Soviet type”. Another type that formed the basis of the atomic power industry of the USSR is a tank reactor with pressurized water VVER (similar to PWR is a power reactor that uses plain water as a moderator of a nuclear reaction and a coolant). The representative of Soviet-type reactors is the RBMK-1000 with an electrical capacity of 1000 MW (for example, at the Lenin NPP named after VI Lenin).

LNPP
The Leningrad NPP is located 80 km west of the city of St. Petersburg on the coast of the Gulf of Finland in the town of Sosnovy Bor. The best specialists of Minsredmash were thrown at the construction of LNPP, it was supposed to be the main one in the series of erected NPPs with RMBC reactors. After the approval of the technical design of the reactor RMBK - 1000, the construction of the station began (September 1967). In 1973, the reactor of the first power unit was ready for launch. In the main building of the first stage of LEAS there are two power units with an electrical power of 1000 MW with a common machine room and separate rooms for reactors, fuel transportation systems, control panels and a common room for gas cleaning and water purification of the primary circuit. In each power unit there is a RMBK reactor - 1000 with a heat capacity of 3200 MW with a condensation circuit and auxiliary systems, a steam and condensate-feed tracts and two turbogenerators with a power of 500 MW each. LNPP is the first station that uses sea water for cooling. In 1975, the second power unit was launched and construction of the second stage of the nuclear power plant began. In 1979, the third power unit, at the end of 1980 the reactor was launched in the fourth power unit. By August 1981, the total electrical capacity reached 4000 MW, due to which LNPP became the largest nuclear power plant in Europe of this type.
Dear comrades! The Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union congratulates you on a great labor victory on the completion of construction and development in a short time of a design capacity of one million kilowatts of the first power unit of the Lenin Leningrad Nuclear Power Plant. Your heroic work created the world's largest nuclear power reactor, unique turbines and other equipment that embodies the latest achievements of science and technology and advanced production experience. The great organizational and political work of the party, trade union and Komsomol organizations in the development of socialist competition and the mobilization of workers for the assignments of the ninth five-year plan contributed greatly to the achievement of success. Commissioning of the first unit of the Leningrad Nuclear Power Plant. V. I. Lenin is a great contribution to the implementation of plans for the development of the nuclear power industry in our country. The Central Committee expresses confidence that the participants in the creation of the Leningrad Nuclear Power Plant. V. And Lenin will ensure successful construction and commissioning of new capacities, will multiply their contribution to the implementation of the directives of the XXIV Congress of the CPSU. We wish you, dear comrades, new successes in your work for the benefit of our socialist homeland. Moscow. Kremlin.
At the station sites, it was decided to store fuel assemblies and spent fuel (fuel assemblies, spent nuclear fuel) due to the lack of centralized places for storing or disposing of spent fuel from power units. Therefore, at the sites of stations with RBMK reactors
storage facilities for spent nuclear fuel were erected. Such “storage” turned out to be rather “deplorable”: the design capacities of the SNFS (a complex of buildings and structures with pools that have autonomous systems of special ventilation, water purification and cooling), and the design capacities of the reactor BV were quickly filled.

A long-term program to increase electricity production provided for the construction of nuclear power plants with RBMK reactors. Within 10 years after the launch of the first power unit of LNPP in the USSR, 12 power units with RBMK-1000 were launched at the Kursk, Chernobyl and Smolensk NPPs.
By 1986, 14 such units were launched.
It is worth noting that during the construction of the LNPP, an order was issued by Slavsky according to which "... the cost of a kilowatt of installed capacity should have been set at no more than 180 rubles." Therefore, we had to reduce the cost of the project by refraining from creating security systems beyond the required minimum. As a result, NPPs with RBMK-1000 at LNPP (and all subsequent NPP projects with this type of reactor) are simple - simply, in order to save, they did not provide for the containment of the reactor facility. It turns out that 200 tons of uranium and more than 1 ton of radioactive fission products "were located under the open sky", because the roof of the reactor compartment was as strong as the roof of an ordinary residential building.

"Rehearsal" of the Chernobyl accident in 1975
In 1975, from 28 to 30 November, a serious radiation accident occurred at Leningrad NPP. The personnel of the first unit did not cope with the hardly controlled reactor, the power in the local area of the core increased several times, the temperature rose to 1600 C. Before that, there was 1 turbogenerator, the reactor power was at 50% of the nominal. Like at the Chernobyl NPP, before the accident, the power (due to operator error) dropped to zero, it was immediately lifted up. The emergency process lasted up to several hours during the rise of power from zero to 1,700 MW, and 30 fuel assemblies were destroyed, only one channel was destroyed.
In the accident at the Leningrad NPP, neutron-physical instability in the active zone itself played a significant role, and thermal-hydraulic processes of instability in the external reactor cooling circuit (MFC) played a much smaller role.
“Fortunately,” only two walls of the channels carrying the pressure of the coolant were destroyed. 1.5 million Ci of radioactivity was released into the external environment. The accident was hidden, instead of publicly recognizing the danger of the RBMK. Only in 1976 was the first time mentioned about this accident at the board of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the USSR, when it was reported about the request of the Government of Finland and Sweden regarding an increase in the radiation background over their territories.
Chernobyl NPP

In 1967, the USSR government decided to start the construction of the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. In total, it was planned to build 6 power units with high-power uranium-graphite channel reactors - RBMK. In 1972, construction began on the first power unit. The site 4 km from the village of Kopachi, on the right bank of the Pripyat River, 12 km from the city of Chernobyl, was recommended by the State Commission for locating the nuclear power plant. Three variants of the project were developed for ChNPP (capacity 2000 MW): the first using the RBMK-1000 reactor, the second using the RK-1000 gas-graphite reactor, and the third using the WWER-1000 reactor. Initially, a variant using a gas-graphite reactor was chosen, but later it was replaced with an RBMK-1000 reactor. After Leningrad and Kursk, it was the third station with this type of reactors.
On December 14, 1977, the first Chernobyl NPP power unit was commissioned. On May 24, 1978, the first power unit was brought to a capacity of 1000 MW. On November 16, in 1978, the second power unit was launched, on December 3, in 1981, the fourth power unit. In November 1983, the first fuel assembly was loaded on the fourth power unit.

April 26 in 1986, the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. As a result, the core of the reactor installation and part of the building of the fourth block were destroyed, as well as the release of part of the radioactive products accumulated in the core to the atmosphere. Everything happened during the experiment to study the possibility of using the inertia of the rotor of the turbogenerator to generate any amount of electricity, if the reactor stops in the future.
The experiment was planned to be carried out at a reactor power of 700 MW, but before it began, the power level dropped to 30 MW. The operator tried to restore power, the experiment began at 200 MW. Within a few seconds, the reactor's power began to grow and the operator pressed the emergency protection button (the operator’s delay of several tens of seconds initially became the official version of the causes of the accident). Two explosions occurred at intervals of a few seconds, the reactor was completely destroyed.
After the destruction of the technological channels and the breakage of the steam and water communications from them, the steam entered the central hall, into the rooms of the drum separators on the right and left, into the sub-apparatus rooms of a firmly dense box. After the breakage of the lower communications, the reactor was completely dehydrated. The explosions began in the technological channels of the reactor, which began to destroy under increased pressure. The lower and upper communications of the reactor were destroyed, the pressure grew at lightning speed - 15 atmospheres per second (reached 250-300 atmospheres). The steam got into the reactor space - an explosion of metal construction occurred. The premises of the drum separators were destroyed, the drum separators themselves (weighing 130 tons) were shifted from the dead supports and cut off from the pipelines. This was followed by explosions in the underground pipeline mines. There was an explosion in the central hall, then (perhaps almost simultaneously) in the reactor itself, which was uncorked and full of hydrogen. The explosion in the core led to the release of a huge amount of activity and hot pieces of nuclear fuel. The fire started the roof. The explosion threw up and turned the slab of the top bio-protection to 500 tons, it collapsed on the machine in an inclined position, the active zone on the right and left remained slightly opened.
The first months after the accident, the main fault was laid on the operators. In 1991, almost all allegations were dropped from NPP personnel. One of the causes of the Chernobyl accident was the low quality of regulations and safety requirements. Yes, and the causes of the disaster were of a technical nature: the RBMK-1000 reactor that had exploded had a number of design flaws, which under certain conditions turned out to be dangerous, it simply did not comply with many nuclear safety rules.
As it was later stated (in 1993), before the accident, the fourth power unit of the Chernobyl NPP worked with a number of changed indicators - the reactor emergency cooling system turned off and the reduced reactivity margin (OPM).
According to experts, even the Chernobyl NPP personnel were not aware of the danger of working in the changed conditions. Before the accident, the ORM was less than the value allowed by the regulations, however, the operators did not know the current value of the ORM and, therefore, did not know that they were violating the regulations.
When I heard about the explosion, no one told us that the level of radiation was life-threatening. These were the times of the former Soviet Union, and the authorities kept information about the danger from us. The level of radiation where I worked was already very dangerous. I was in a group of 20 people, and only six of us are still alive.

According to official data, 50 million Ci were thrown into the external environment. At the time of the accident, reactor 4 of the power unit was at full load, there were about 180 tons of fuel inside the reactor. The explosion blew off the reactor lid weighing almost 3 thousand tons, completely destroyed the roof, almost completely demolished the western and northern walls. According to rough estimates, from 30 to 100 tons of fuel were scattered around the “district”. Radiation levels around the destroyed block reached several thousand roentgens per hour (the permissible rate is 5 roentgens per year). In order to realistically assess the scale of the radioactive release: the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima weighed 4 and a half tons, the reactor of the fourth power unit threw 50 tons of evaporated fuel into the atmosphere. The explosion of the reactor led to a monstrous radiation contamination of the area (the territory of Ukraine, Belarus and some regions of Russia).
A 30-kilometer “exclusion zone” was created around the Chernobyl NPP, in which almost all the settlements were deliberately destroyed, and the population was evicted. The city of Pripyat (with a population of 50 thousand) added to the list of dead cities. All residents were evacuated, but no one was told the true reasons for the evacuation.
“Dear comrades! .. In order to ensure complete safety of people, and, above all, children, there is a need to carry out a temporary evacuation of city residents to nearby settlements of the Kiev region. To do this, every apartment building today, April twenty-seventh, starting at fourteen zero-zero hours, will be served by buses, accompanied by police officers and representatives of the city executive committee. It is recommended to take with you documents, essential things, as well as, for the first time, food ... "

At the time of the explosion, 2 people died at the station (the body of one of them was never found), another died of burns in the hospital several hours after the accident. These people at the time of the explosion were located near the reactor and their death was not associated with radiation damage. Subsequently, 134 Chernobyl NPP employees and members of the rescue teams who were at the station during the explosion developed radiation sickness, 28 of which died within the next few months.
Vast territories were polluted in Ukraine (41.75 thousand square kilometers), Belarus (46.6 thousand square kilometers), the European part of Russia (57.1 thousand square kilometers). The disaster that happened was fatal for many thousands of innocent people ...
Nevertheless, in the fall of 1986, work at the Chernobyl NPP was resumed, the first power unit was launched on October 1, and the second one on November 5. The third power unit was launched in November 1987. But after a serious fire at the second power unit in 1991 and an unsuccessful attempt to restore it, the station was suspended by 1997.
As the main causes of the terrible accident at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant are considered to be the design flaws of the RBMK-1000 nuclear reactor. But after all, these reactors were not only at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, but also at several stations (Leningrad, Smolensk and Kursk).
RBMK - 1000 or VVER-1000
So why was this type of reactor so popular in the USSR? .. Two types of reactors - high-power uranium-graphite channel (RBMK -1000) and water-cooled (VVER-1000), what type of RBMK nuclear reactor - 1000 or VVER-1000 What guided when choosing one type or another in our country? You can draw an analogy with the clock.

Imagine that a nuclear power plant at RBMK reactors is a person in expensive mechanical watches. This type of nuclear reactor could have almost unlimited power, and the replacement of spent nuclear fuel could be done without stopping it, that is, you could clean and repair the clock without removing it from your hand. Conveniently. Practical The use of RBMK type reactors always looked economically attractive. But for every convenience you have to pay some inconvenience. The disadvantages of uranium-graphite reactors are a whole package. Firstly, this is an increased requirement for safety, difficulty in operation, and secondly, exceptional requirements for service personnel; and finally, disciplined execution of instructions. A normative document strictly prescribes that if you twist the plant at least half a turn or reject the arrow by an extra degree - the clock will simply explode and tear off your hands.
The main qualitative advantage of the VVER reactor, as compared to RBMK, is its safety. This fact became apparent after the incident at the Chernobyl NPP. But there is a paradox why in the power engineering of the countries of the former USSR RBMK power units were more popular than WWER? Under this fact, oddly enough, there is also a serious science - economics. The fact is that before launching the Atommash plant (producing VVER rectors) at the end of the 70s, the USSR could produce only one vessel of this type of reactor per year.

The VVER-1000 basically does not have “positive feedbacks”, the very ones that led to the tragedy of April 26, 1986. In the case of out-of-control loss of control over the situation with coolant or core cooling, the chain reaction of burning nuclear fuel declines and quietly fades out like a burned campfire, and does not accelerate, as in the RBMK. There is no fuel (graphite) in the core of the VVER reactor, of which up to two thousand tons may be in the RBMK. It would seem that VVER is an ideal option, but our conditional character “man in a quartz watch” is also not perfect, his watch is heavier and more massive, such a brick on a strap. The VVER hull is gigantic in size, and its manufacture is very laborious. Dimensions are limited to achieving ultimate strength, since the mechanical stresses tearing the body are directly related to its diameter and internal pressure. An increase in unit capacity always leads to a reduction in the cost of 1 kW of installed capacity, since this increases such elements as MCP, steam generators (or drum-separators), a steam turbine with its entire complex economy, the specific cost of the automation system, water supply, etc. .
After the catastrophe at the Chernobyl NPP, the need to modernize the reactors became acute, the requirements for nuclear safety were tightened. Currently, 11 more RBMK-1000 reactors are operating.
The Chernobyl accident significantly slowed down the development of nuclear energy not only in the USSR, but throughout the world. In the USSR, they abandoned the construction of a number of nuclear power plants - Tatar, Bashkir, Kostroma, Odessa, Minsk, Krasnodar and others. The structure of the industry has been reorganized to meet international standards.
Now the Russian nuclear industry is one of the most advanced in the world in terms of scientific and technical developments in the design of reactors, nuclear fuel, operating experience of nuclear power plants, and qualifications of NPP personnel. The share of electricity generation by nuclear power plants is about 18.6% of the total electricity produced. Active construction of nine new NPP units, construction of Novovoronezh NPP-2, Leningrad NPP-2, Baltic NPP, the world's first floating NPP Akademik Lomonosov, is underway, the fourth power unit of the Beloyarsk NPP is being completed.

monument to the peaceful atom in Kurchatovka
Hopefully, the peaceful atom will remain peaceful ...
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/392785/
All Articles