Space photos of the week
At first glance, this cosmic lilac-blue kaleidoscope is a strikingly beautiful snapshot of the cosmos. However, a multicolored “nebula” marks the intersection of two colliding galactic clusters, forming the only object known as MACS J0416.1-2403. This cluster is one of the six studied by astronomers.

NASA
')
The Martian gravitational map showing the thyroid volcano Farsis Dome (Tharsis Tholus) and the surrounding bends. White areas in the center show elevated gravity spots caused by large volcanoes. Blue areas indicate reduced gravity.
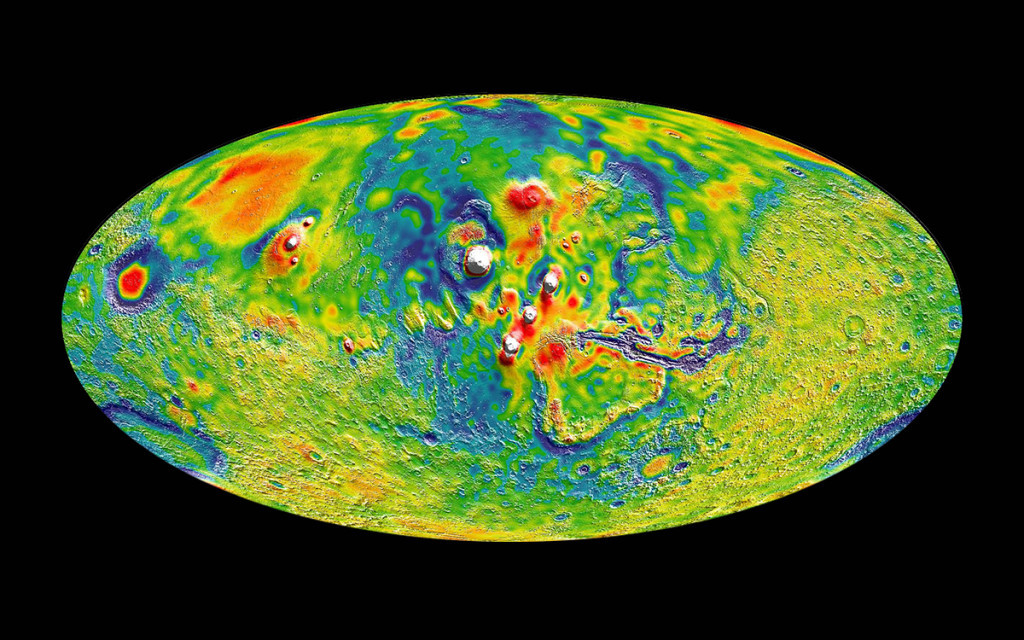
MIT / UMBC-CRESST / GSFC
On the stage is a solitary irregular galaxy known as Wolf-Landmark-Melott (abbreviated as WLM). It is a rather small and isolated galaxy that is so remote that it could never interact with any other cluster of galaxies of the Local Group.

Eso
The solar storms increased the X-ray spectrum of auroral auroras on Jupiter, which were about eight times brighter than usual and were hundreds of times more powerful than the Northern Lights of the Earth.
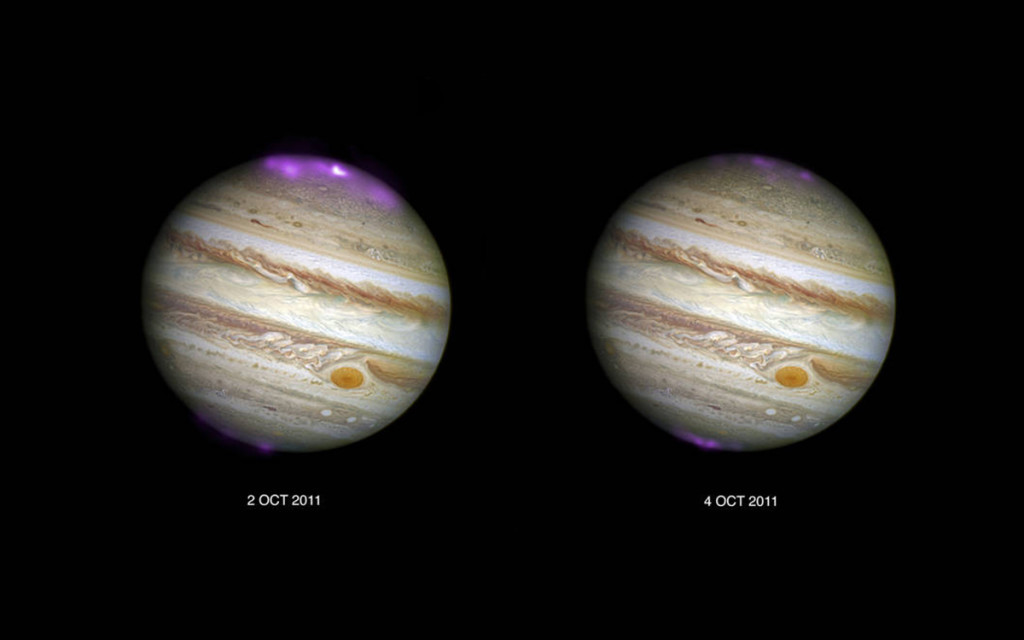
X-RAY: NASA / CXC / UCL / W.DUNN ET AL, OPTICAL: NASA / STSCI
Shaded areas that partially overlap the breathtaking image of a scattering of stars in the constellation Ophiuchus (Ophiuchus) - dense clouds of dust blocking the light.
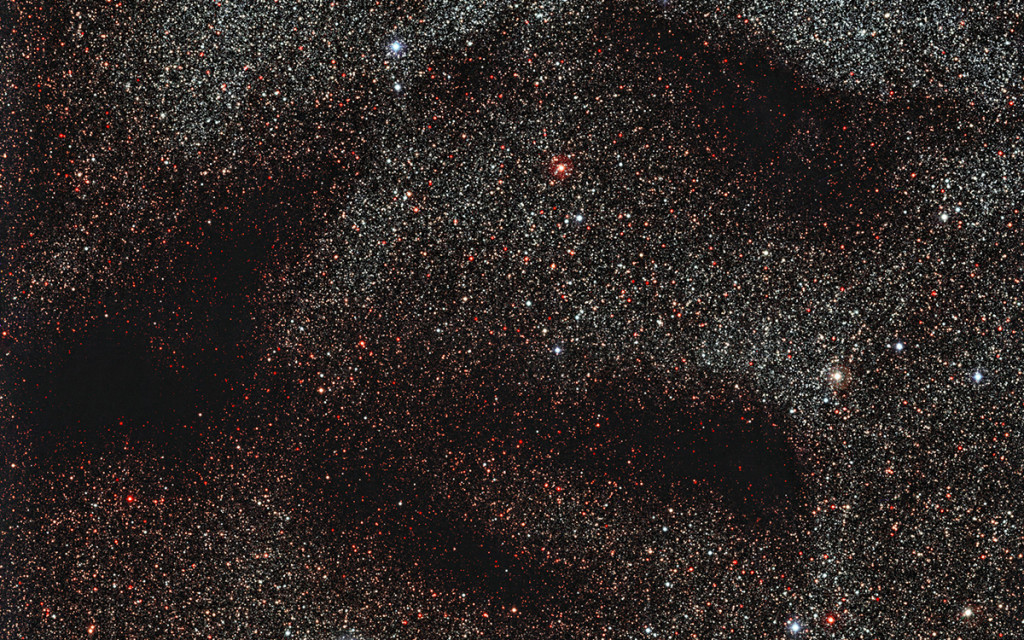

Eso
Alluvial fans are areas of alluvial (water-borne) sediments with a fan-shaped conical shape. One of the most popular is the Saheki Crater, which is located on Mars.
The picture was taken with a HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) camera. It will be used to measure fan depth and describe sedimentation history.

NASA / JPL-CALTECH / UNIV. OF ARIZONA

NASA
')
The Martian gravitational map showing the thyroid volcano Farsis Dome (Tharsis Tholus) and the surrounding bends. White areas in the center show elevated gravity spots caused by large volcanoes. Blue areas indicate reduced gravity.

MIT / UMBC-CRESST / GSFC
On the stage is a solitary irregular galaxy known as Wolf-Landmark-Melott (abbreviated as WLM). It is a rather small and isolated galaxy that is so remote that it could never interact with any other cluster of galaxies of the Local Group.

Eso
The solar storms increased the X-ray spectrum of auroral auroras on Jupiter, which were about eight times brighter than usual and were hundreds of times more powerful than the Northern Lights of the Earth.

X-RAY: NASA / CXC / UCL / W.DUNN ET AL, OPTICAL: NASA / STSCI
Shaded areas that partially overlap the breathtaking image of a scattering of stars in the constellation Ophiuchus (Ophiuchus) - dense clouds of dust blocking the light.

Eso
Alluvial fans are areas of alluvial (water-borne) sediments with a fan-shaped conical shape. One of the most popular is the Saheki Crater, which is located on Mars.
The picture was taken with a HiRISE (High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment) camera. It will be used to measure fan depth and describe sedimentation history.

NASA / JPL-CALTECH / UNIV. OF ARIZONA
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/392423/
All Articles