Aukey PB-T1 review - it's time to save time
We did not have time to look back, as the era of ordinary cell phones with fairly low power consumption changed the era of multifunctional smartphones and tablets with high-performance processors, large displays with high resolution and bright backlighting, Wi-Fi, accurate GPS, etc.
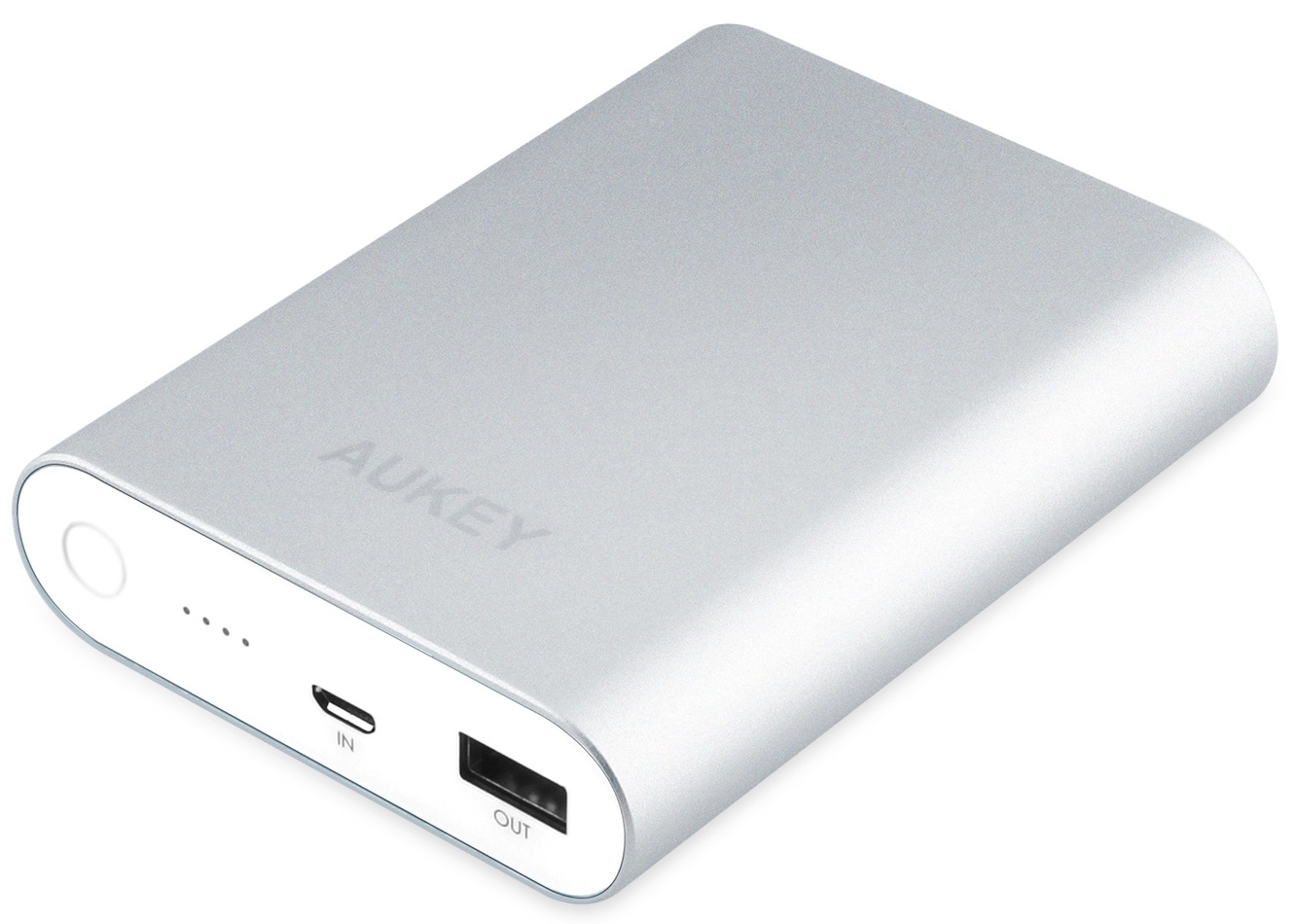

For servicing absolutely all the above-mentioned needs of the device, it became necessary for manufacturers to assemble the appropriate batteries when assembling in order to meet the needs of the phone and allow the device to work out some more, preferably longer, time until the next recharge. And still - not enough.
')
Today - about the little assistant PowerBank Aukey PB-T1 with the function of fast charging: test, compare, analyze.
As already mentioned, given the increasing demands of mobile devices due to increased intelligence due to the expansion of functionality, the development of operating systems and the installation of additional applications, even the most expensive models of batteries are not able to provide the right time for active and even moderate use of the above devices.
Being owners of volatile smartphones and tablets, we are more and more aware of how attached we are to having additional power sources with us, since work or the banal need to stay in touch all the time inevitably forces us to actively use our devices, which later to a rapid decrease in battery charge of the latter.
Those who follow the news of science and technology know that there are many serious and bold ideas and work on creating new types of batteries , increasing their capacity, changing the type of media or even, for example, inventing an E-Kaia device for charging gadgets using plants, in addition, there is the concept of a battery that allows you to charge your smartphone for 1 minute and many other inspirational ideas and ideas. Of course, there are some advances in these areas, but our reality is that all these technologies will not reach us in a short time, but we need to get out somehow now.
Considering the fact that after each discharge cycle, the batteries lose some of their capacity, we also “finish them off”, replacing the usual MP3 players with mobile music players of our smartphones and tablets, thereby helping to stay 10-20 by the evening % battery charge.
Portable chargers such as Power Bank of large capacity, which became fashionable and actively used several years ago, gave many people the chance to be constantly in touch, allowing even at the most critical moment to connect to the charger and, sighing with relief, continue to actively use the gadget.
However, it should be understood that even with a high-capacity Power Bank it is far from always convenient to dangle through the streets and shops, stroll or go on a hike with a wiring sticking out or with a phone (tablet) in a bag or briefcase, but already losing the ability to quickly respond to incoming calls and notifications .
With the same battery capacity and similar operating conditions, phones of some manufacturers may differ in longer battery life, which is associated with the optimization of the operating system and the features of the hardware used. Nevertheless, the game is not worth the candle, as it saves for a while.
Until recently, Power Bank devices gave the maximum output current of 2.1A at a voltage of 5V, which was decently large for relatively fast charging, but nevertheless the need to charge the device for 1.5 hours - 2 hours (or even more) was not for everyone soul
Qualcomm, not forcing us to languish in anticipation of the promising batteries of the future, has created a quick charge technology Quick Charge 2.0, followed by Power Integrations created the first AC-DC chip CHY100 with this technology on board for wall chargers, and Aukey without yawning, I integrated this microcircuit into my PB-T1 portable charger, thus opening a new era of portable chargers, thanks to which the time that we have to spend on recharging batteries significantly decreases lator.
In 1 minute, of course, until we manage to charge our devices, but up to 75% faster than conventional devices with integrated Qualcomm Quick Charge 2.0 technology is already guaranteed.
Incredibly fast by today's standards, charging quickly and, most importantly, reliably charge your devices in any geographic location and at any time.
You only need 30 minutes to use this technology to charge a standard battery of a tablet with Quick Charge 2.0 support to 60% or 40 minutes to charge a standard smartphone battery to 50%. This is due to the rated output current of 1.8 A at a voltage of 9 V for smartphones and a current of 1.35 A at a voltage of 12 V for tablets.
Qualcomm's proprietary fast charge technology is designed to safely, efficiently transfer as much power from a power source as possible, to charge the battery as quickly and efficiently as its chemical components support.
But, first of all, such a significant increase implies the use of batteries not only 5 V, but also with an output voltage of 9 V and 12 V, so the “stuffing” of your mobile device should include such a battery. What does this give?
This allows you to increase the power delivered by the battery charger. If at 5 V and 2.1 A the power is 5 V * 2.1 A = 10.5 W, then at 9 V and 1.8 A the power is 9 V * 1.8 A = 16.2 W, at 12 B and 1.35 A also amounts to 12 V * 1.35 A = 16.2 W. Those. The power supply increases by approximately 35%. And since we increase the power, with the same capacity the battery will charge faster, respectively, the battery, which gives more power.
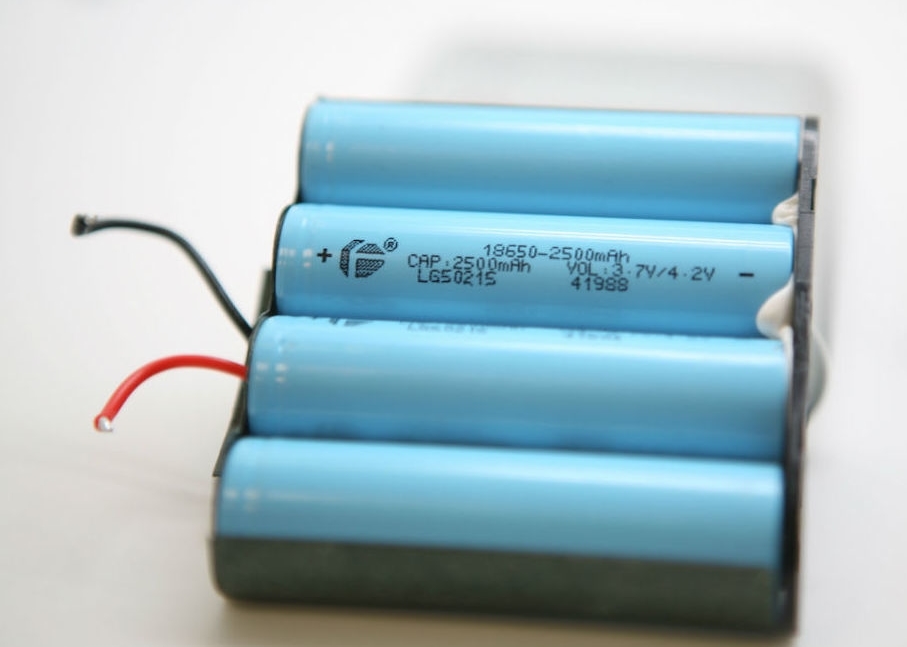
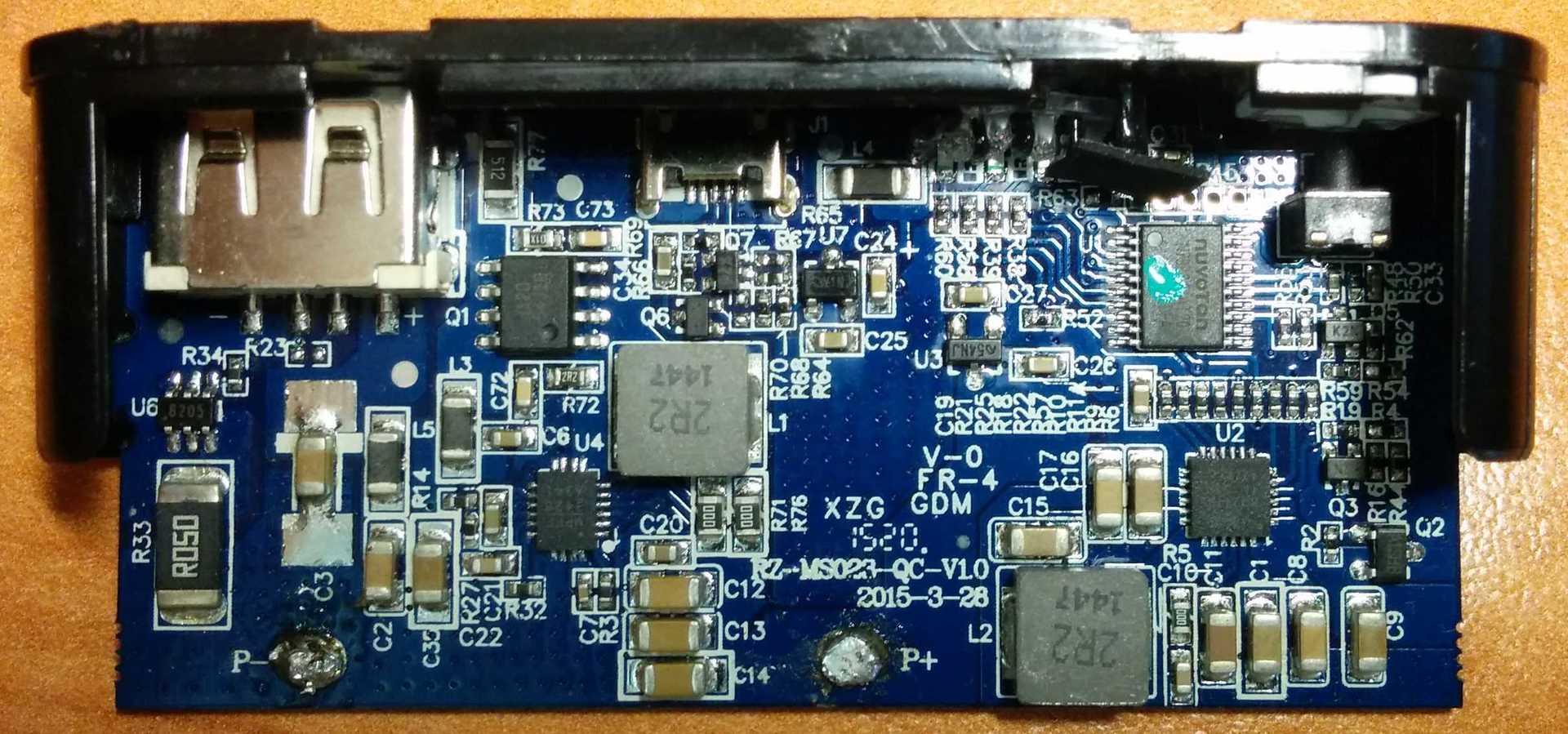
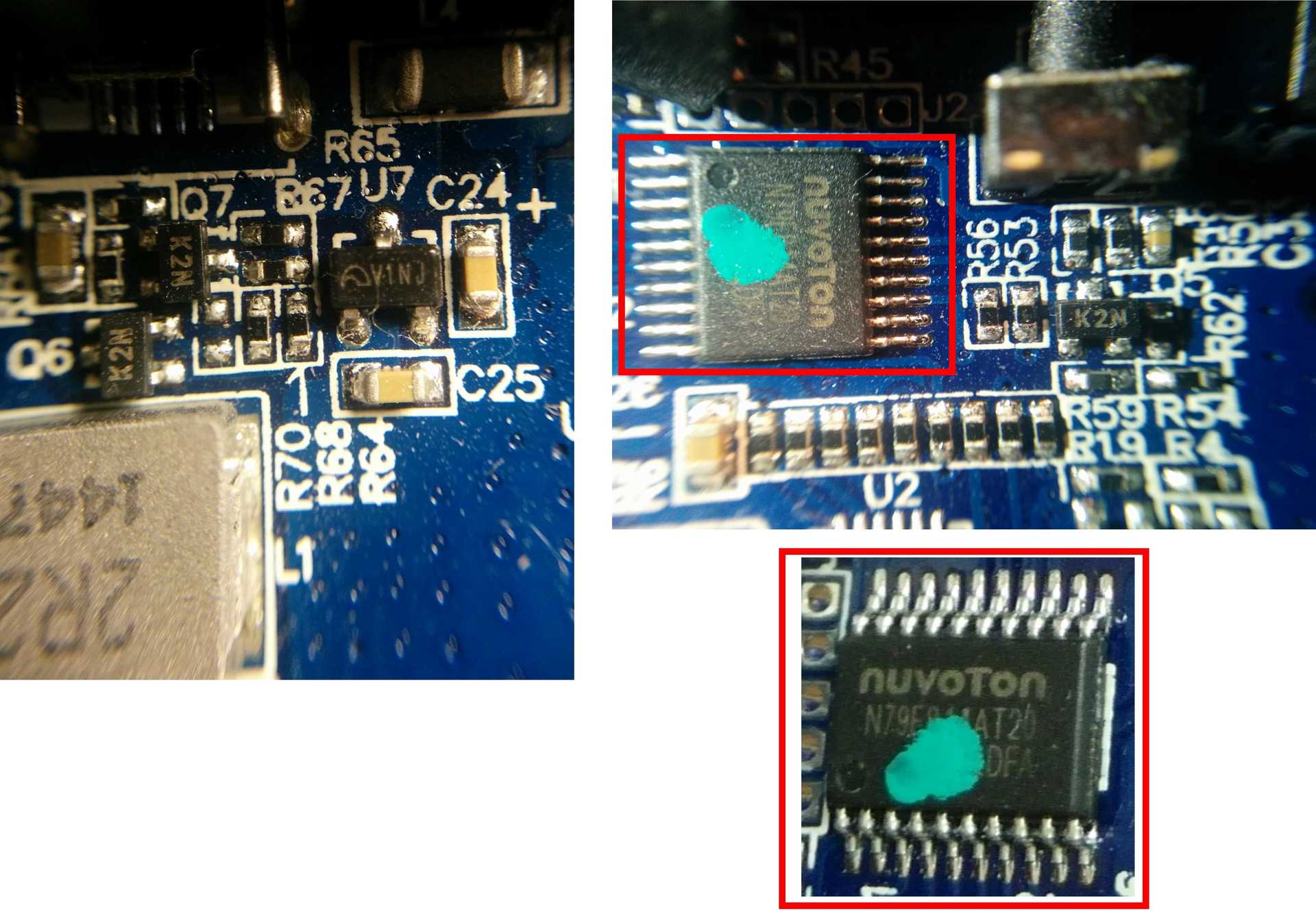
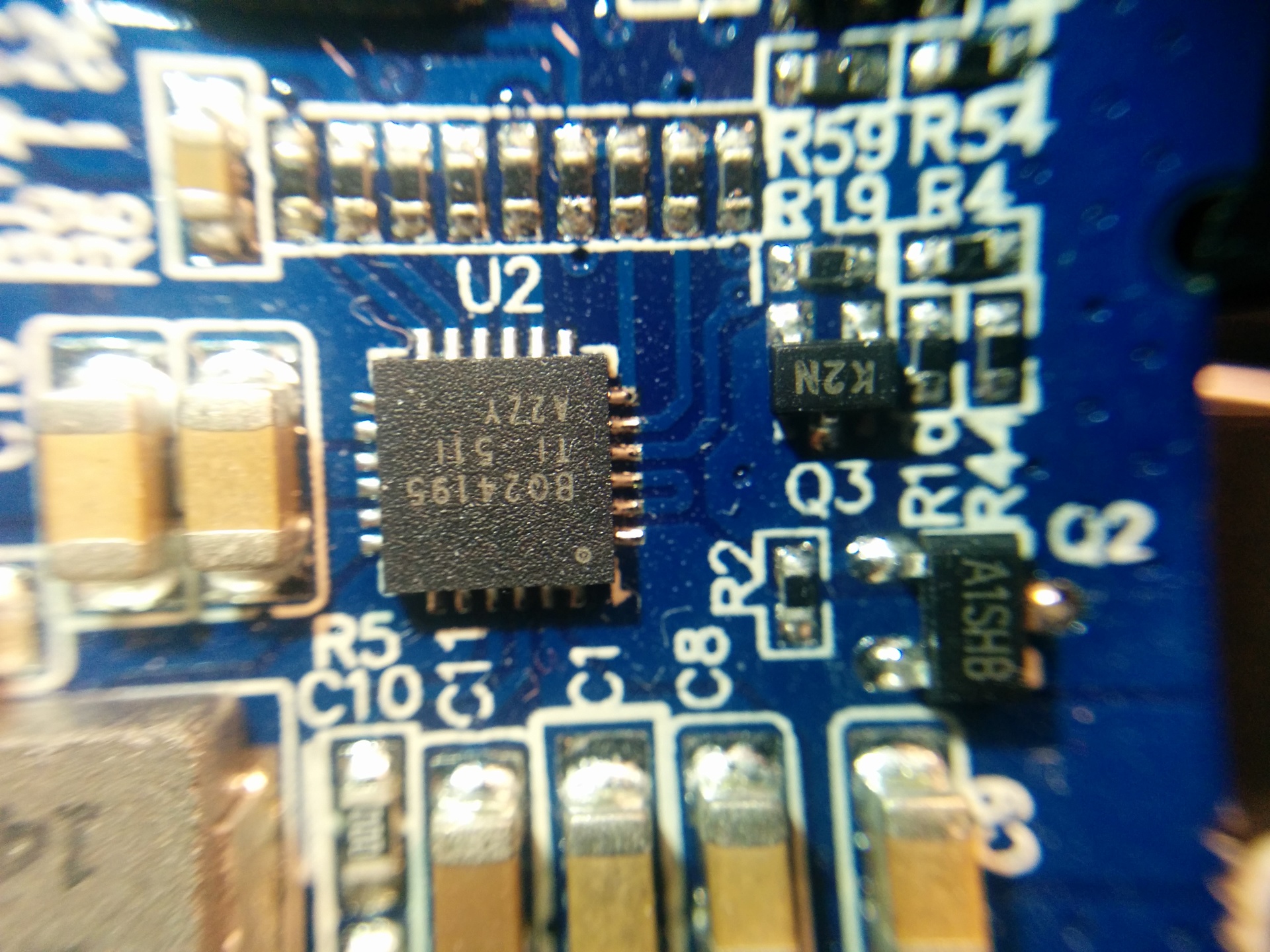
The device works on the basis of the NUVOTON N79E814AT20 8-bit microcontroller, for charging the batteries (2500 mAh, 3.7 V / 4.2 V, x4) the controller with the U2 marking on the BQ24195 board is responsible, and for charging and communicating with peripherals via USB and support for the Quick Charge technology 2.0 corresponds to a chip labeled U5 on the board, i.e. CHY100, which was mentioned above. The last chip is on the back of the board. More information about the principle of operation of this chip and about at what time and under what conditions the fast charging mode is activated can be found in the technical documentation for the chip itself .

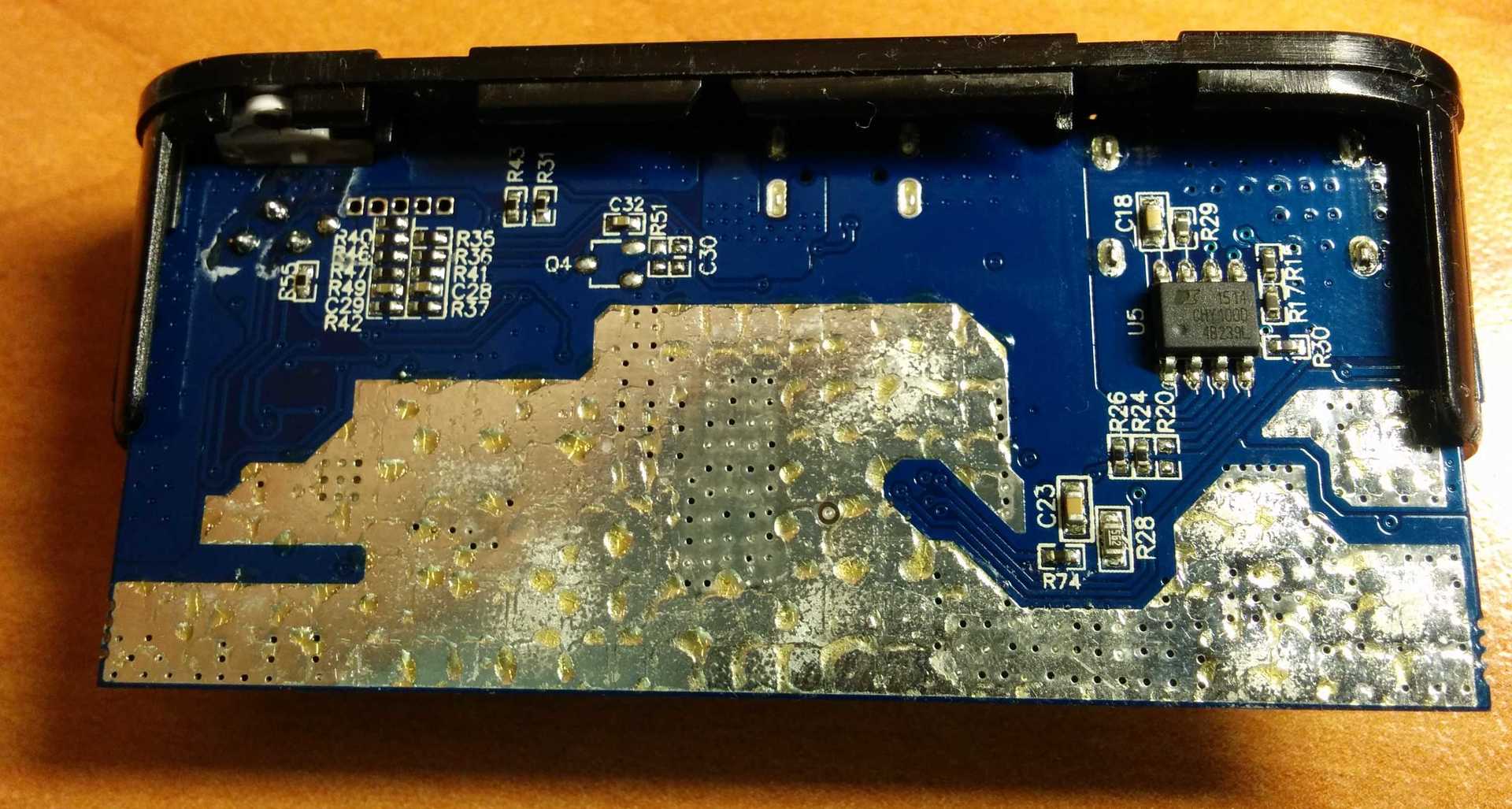
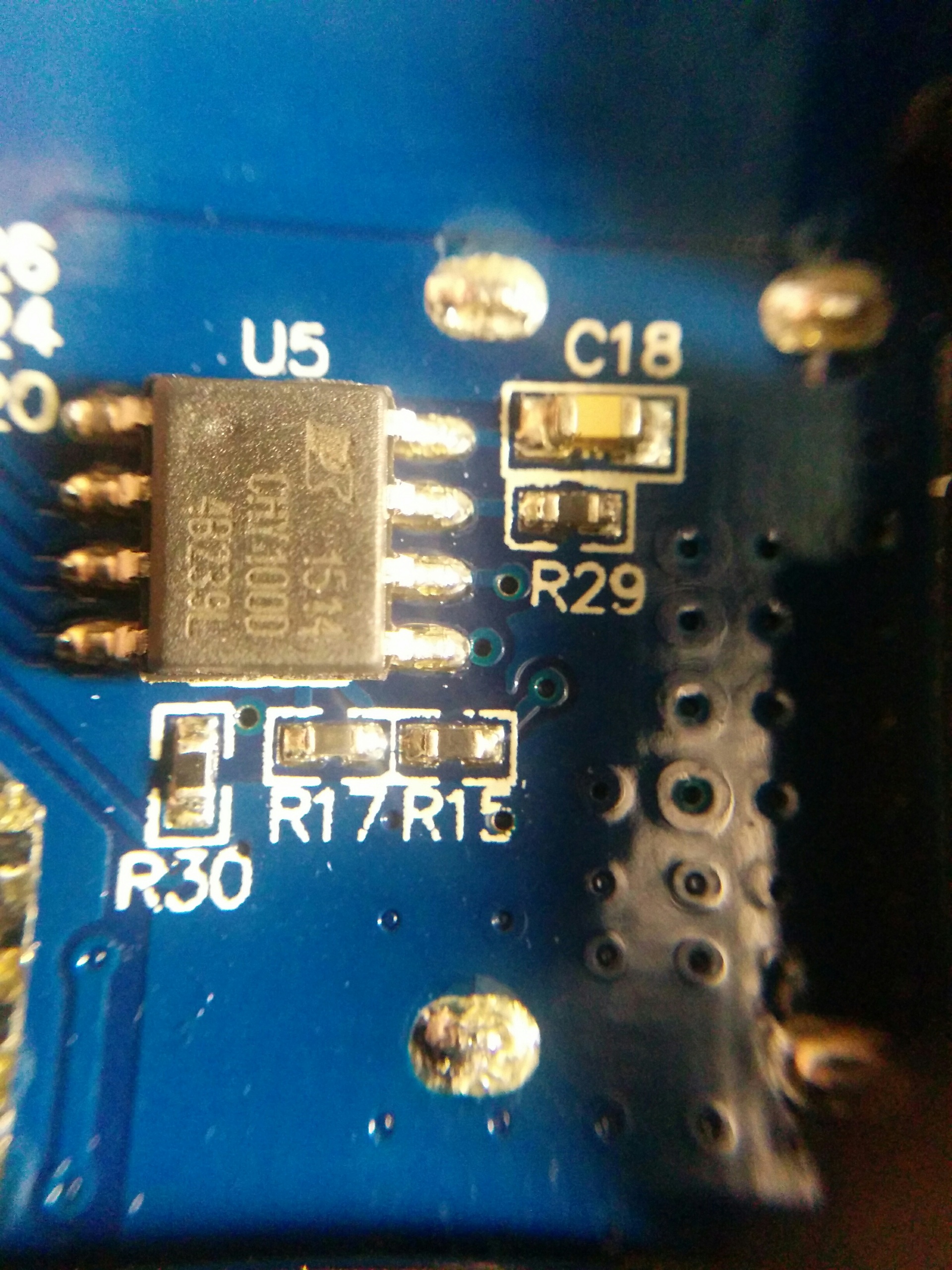
In order to avoid loss of power from the power source to the phone or tablet, you need to pay attention to the quality of the cable, its length, as well as the cross-sectional area, otherwise, even if your phone / tablet supports Quick Charge technology, the output voltage will not be 9 V or 12 V, and standard 5 V will be issued.
A special feature of the Aukey PB-T1 is that when you connect your mobile device to charging, the charger itself determines whether the connected device supports fast charging or not, first issuing standard 5V voltages and then delivering more voltage when the consumer, i.e. A mobile device battery will require increased voltage.
Another important point: if you try to charge low-power devices (smart watches, bracelets, etc.) with a classic portable charger, then this device will usually stop powering after 1-3 minutes, and With Aukey PB-T1, this is not to be feared at all. You will not need to press the power button again so that the power supply resumes or even remove the wire and reinsert it again.
For example, it became necessary to charge wireless headphones with low consumption:

Ordinary PowerBank after a minute refused to charge the device. Accordingly, by supplying power again, a minute later they received the same picture again, and with the Aukey PB-T1, the headphones were charged from beginning to end.
And thanks to the robust, anodized aluminum housing resistant to corrosion and scratches, you can not worry about the transportation and storage of the device, do not blow away the dust particles from the surface.
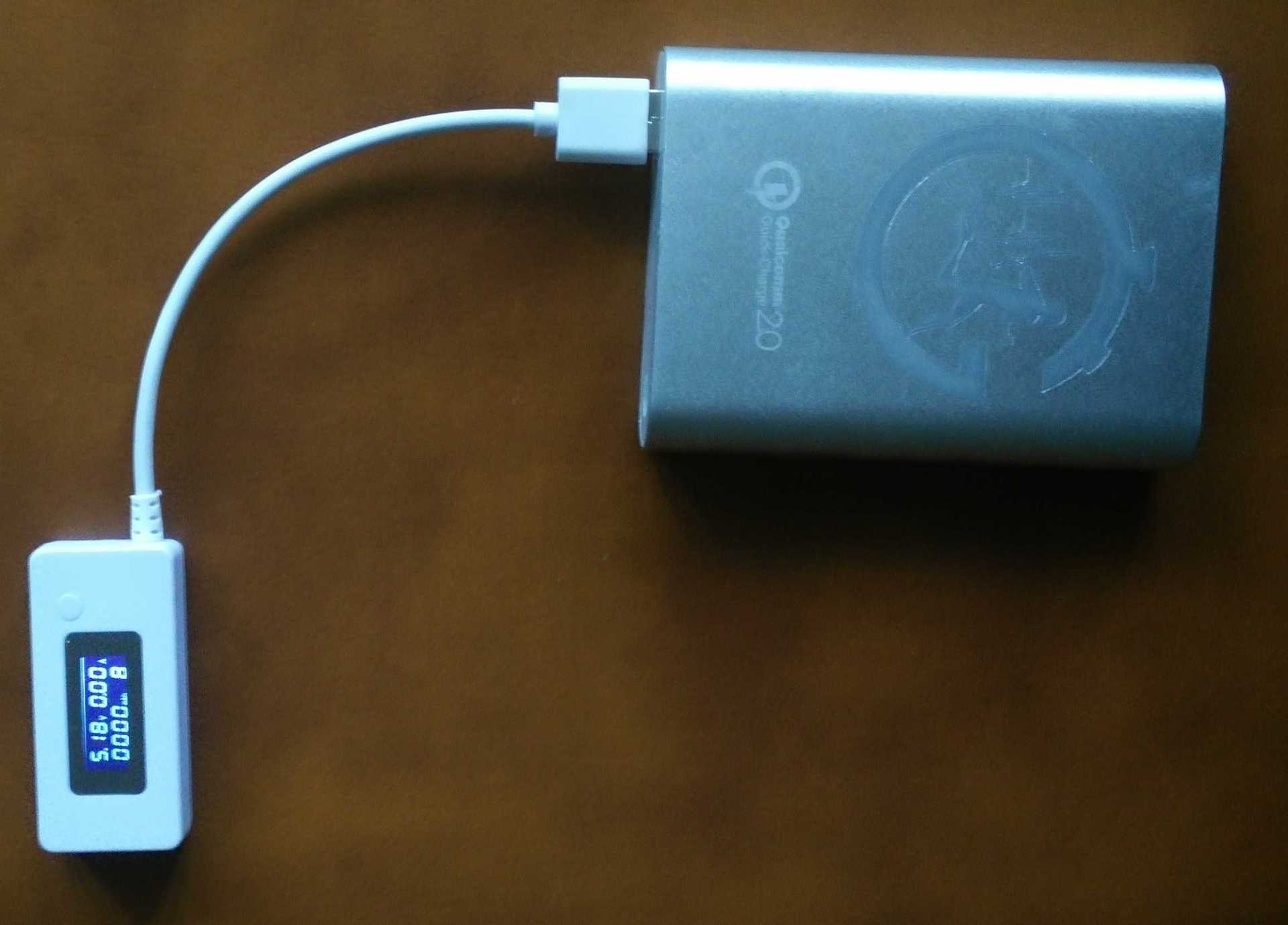
Let's move on to the practical part. Let's see how quickly we manage to charge the phone with Quick Charge 2.0 support. To control the output voltage and current, as well as control the battery charge, use the LCD USB Power Meter KCX-017:




As a “guinea pig”, we will use a mobile device that was on hand, namely the Motorola Nexus 6 with the declared support for Quick Charge 2.0. The battery is lithium-ion capacity of 3220 mAh.
We will charge from
1. Aukey PB-T1;

2. Classic Power Bank portable charger with the declared output characteristics of 5 V and 2100 mAh, which went 1.5 - 2 years ago;

3. A powerful desktop USB charging station Avantree PowerHouse , which has 4 ports, each of which gives the maximum output of the same 5V and 2.1A.
In each experiment, the mobile device is initially in a fully discharged state (battery charge is approximately 0%, “approximately” in the sense that if you try to turn on the smartphone, the vibration will work and then it will turn off again, that is, the charge slightly more than 0%, but less than 1%). Next, we will fix the first value in 15-30 seconds after connecting to charging, however, the phone at this time will still be in the disabled state, and after fixing the value we turn on the smartphone and we will record all subsequent values already in the on state.
We will also take into account that the smartphone was purchased about 3/4 years ago, i.e. Battery capacity is not the same as when you bought it.
Let us take into account the fact that a lot of applications are installed on the smartphone, there are 2 users, the second user is logged in, and in the background, 1 user account is additionally loaded by the smartphone, which in fact is formally considered the owner of the phone. Wi-Fi, GSM, mobile data transmission are also active, there are no active applications, but many services and processes are running in the background (regular updates of mail, letters of applications for instant messaging, letters in social networks, etc.), and these facts will lead to the fact that the smartphone battery will also be decently discharged.
The 2nd and subsequent values will be fixed when you press the unlock button so that the percentage of the current charge is visible on the smartphone display.
Values will be recorded with an interval of 5 minutes in the case of Aukey PB-T1 and Avantree PowerHouse and with an interval of 10 minutes in the case of PowerBank.
We also take into account that the time will be recorded not up to a second, but with an accuracy of ± 20 seconds with an interval of 5 minutes and ± 40 seconds with an interval of 10 minutes.
Considering all the above, we get the following experimental data:
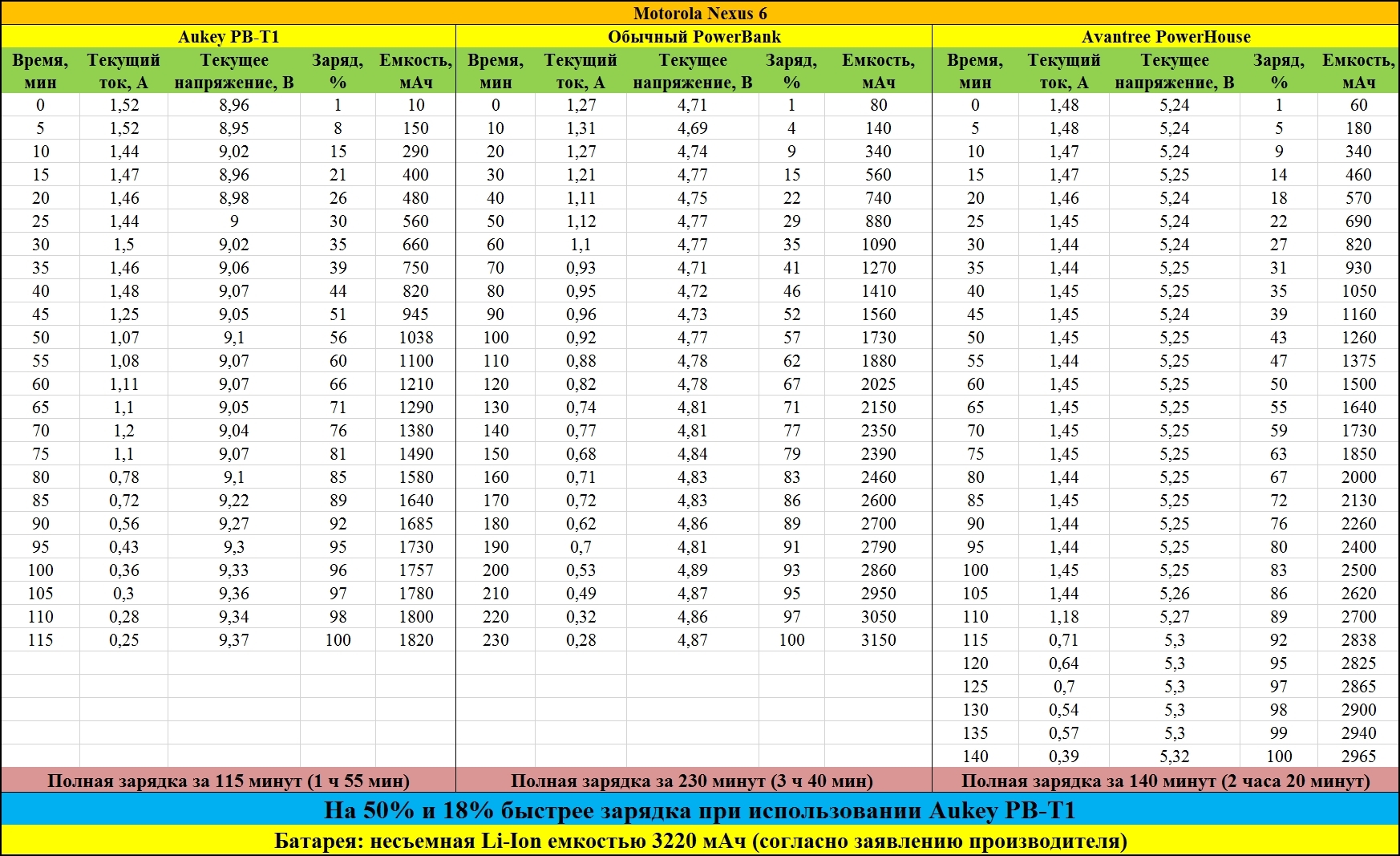
As you can see, the absolute leader was the Aukey PB-T1, he managed to charge the Nexus 6 in 115 minutes (1 hour 55 minutes). PB-T1 even managed to rip off the powerful Avantree PowerHouse station, the latter managed to charge our smartphone in 140 minutes (2 hours and 20 minutes), taking an honorable 2nd place.
Well, the third place was taken by PowerBank, charging the smartphone in 230 minutes (3 hours and 40 minutes).
For clarity, we construct the graphs of currents and voltages:
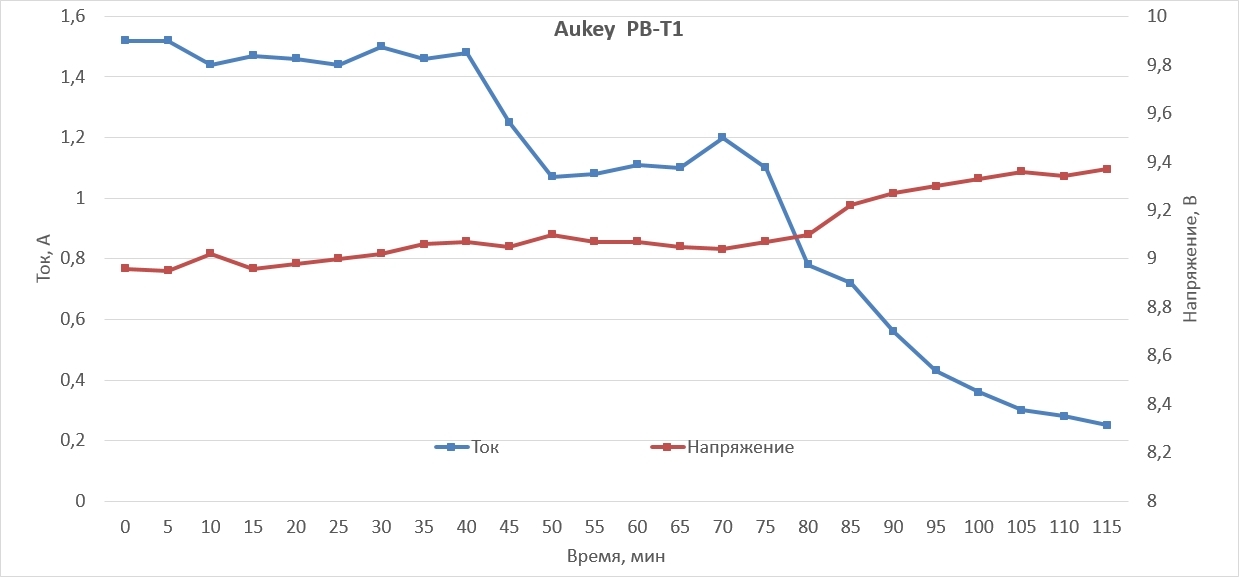
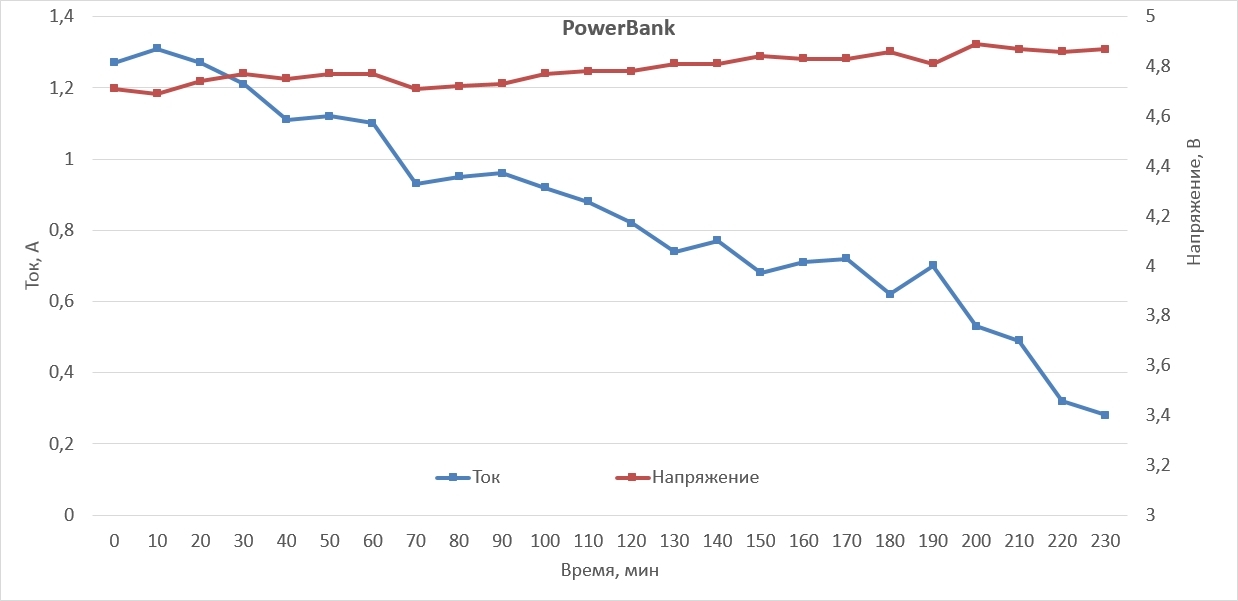
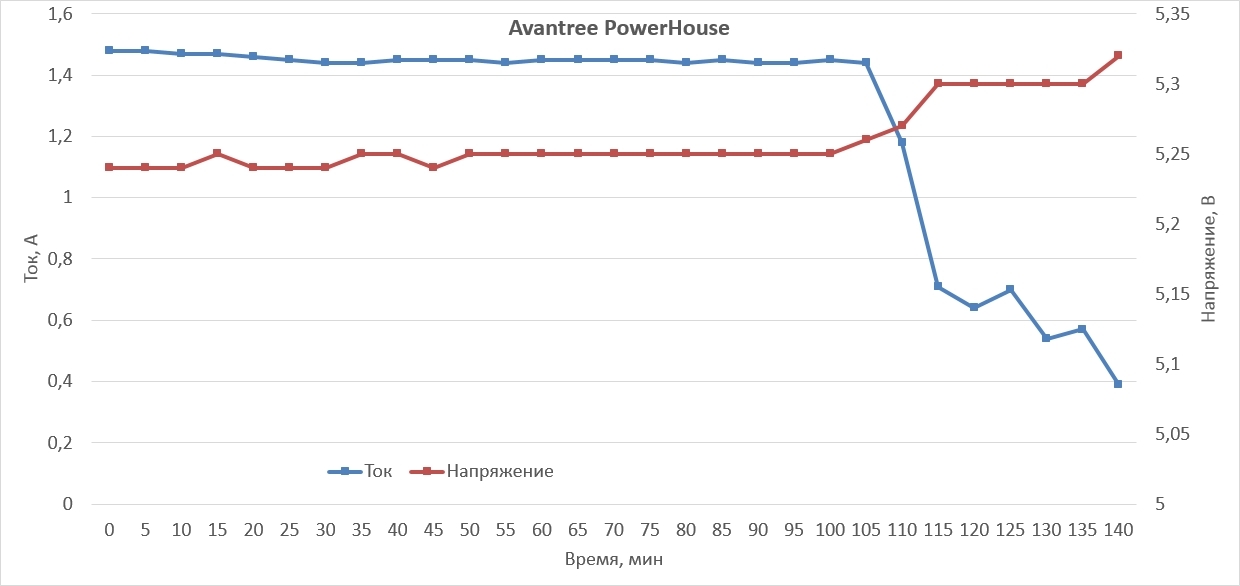
Of course, we are not dealing with an ideal case, so there are no “beautiful” graphs, a strict linear law at the initial stage of charging, no exponential decay at the subsequent stage of charging and smooth transitions, as the values constantly fluctuate. However, it is worth noting that portable devices could never boast stable values of the output current and voltage.
Thus, we gained 18% and 50% gains in charge rates compared to Avantree PowerHouse and PowerBank, respectively, using the Aukey PB-T1.
Of course, we could not completely get rid of the “wiring”, but we managed to charge almost 40% of the battery capacity in 40 minutes, which allowed us to continue to use our smartphone for quite a long time.
The following devices are compatible with Quick Charge 2.0:
A full list of supported devices can be found here .

For servicing absolutely all the above-mentioned needs of the device, it became necessary for manufacturers to assemble the appropriate batteries when assembling in order to meet the needs of the phone and allow the device to work out some more, preferably longer, time until the next recharge. And still - not enough.
')
Today - about the little assistant PowerBank Aukey PB-T1 with the function of fast charging: test, compare, analyze.
As already mentioned, given the increasing demands of mobile devices due to increased intelligence due to the expansion of functionality, the development of operating systems and the installation of additional applications, even the most expensive models of batteries are not able to provide the right time for active and even moderate use of the above devices.
Being owners of volatile smartphones and tablets, we are more and more aware of how attached we are to having additional power sources with us, since work or the banal need to stay in touch all the time inevitably forces us to actively use our devices, which later to a rapid decrease in battery charge of the latter.
Those who follow the news of science and technology know that there are many serious and bold ideas and work on creating new types of batteries , increasing their capacity, changing the type of media or even, for example, inventing an E-Kaia device for charging gadgets using plants, in addition, there is the concept of a battery that allows you to charge your smartphone for 1 minute and many other inspirational ideas and ideas. Of course, there are some advances in these areas, but our reality is that all these technologies will not reach us in a short time, but we need to get out somehow now.
Considering the fact that after each discharge cycle, the batteries lose some of their capacity, we also “finish them off”, replacing the usual MP3 players with mobile music players of our smartphones and tablets, thereby helping to stay 10-20 by the evening % battery charge.
Portable chargers such as Power Bank of large capacity, which became fashionable and actively used several years ago, gave many people the chance to be constantly in touch, allowing even at the most critical moment to connect to the charger and, sighing with relief, continue to actively use the gadget.
However, it should be understood that even with a high-capacity Power Bank it is far from always convenient to dangle through the streets and shops, stroll or go on a hike with a wiring sticking out or with a phone (tablet) in a bag or briefcase, but already losing the ability to quickly respond to incoming calls and notifications .
With the same battery capacity and similar operating conditions, phones of some manufacturers may differ in longer battery life, which is associated with the optimization of the operating system and the features of the hardware used. Nevertheless, the game is not worth the candle, as it saves for a while.
Until recently, Power Bank devices gave the maximum output current of 2.1A at a voltage of 5V, which was decently large for relatively fast charging, but nevertheless the need to charge the device for 1.5 hours - 2 hours (or even more) was not for everyone soul
Qualcomm, not forcing us to languish in anticipation of the promising batteries of the future, has created a quick charge technology Quick Charge 2.0, followed by Power Integrations created the first AC-DC chip CHY100 with this technology on board for wall chargers, and Aukey without yawning, I integrated this microcircuit into my PB-T1 portable charger, thus opening a new era of portable chargers, thanks to which the time that we have to spend on recharging batteries significantly decreases lator.
In 1 minute, of course, until we manage to charge our devices, but up to 75% faster than conventional devices with integrated Qualcomm Quick Charge 2.0 technology is already guaranteed.
Incredibly fast by today's standards, charging quickly and, most importantly, reliably charge your devices in any geographic location and at any time.
You only need 30 minutes to use this technology to charge a standard battery of a tablet with Quick Charge 2.0 support to 60% or 40 minutes to charge a standard smartphone battery to 50%. This is due to the rated output current of 1.8 A at a voltage of 9 V for smartphones and a current of 1.35 A at a voltage of 12 V for tablets.
Qualcomm's proprietary fast charge technology is designed to safely, efficiently transfer as much power from a power source as possible, to charge the battery as quickly and efficiently as its chemical components support.
But, first of all, such a significant increase implies the use of batteries not only 5 V, but also with an output voltage of 9 V and 12 V, so the “stuffing” of your mobile device should include such a battery. What does this give?
This allows you to increase the power delivered by the battery charger. If at 5 V and 2.1 A the power is 5 V * 2.1 A = 10.5 W, then at 9 V and 1.8 A the power is 9 V * 1.8 A = 16.2 W, at 12 B and 1.35 A also amounts to 12 V * 1.35 A = 16.2 W. Those. The power supply increases by approximately 35%. And since we increase the power, with the same capacity the battery will charge faster, respectively, the battery, which gives more power.
The device works on the basis of the NUVOTON N79E814AT20 8-bit microcontroller, for charging the batteries (2500 mAh, 3.7 V / 4.2 V, x4) the controller with the U2 marking on the BQ24195 board is responsible, and for charging and communicating with peripherals via USB and support for the Quick Charge technology 2.0 corresponds to a chip labeled U5 on the board, i.e. CHY100, which was mentioned above. The last chip is on the back of the board. More information about the principle of operation of this chip and about at what time and under what conditions the fast charging mode is activated can be found in the technical documentation for the chip itself .







In order to avoid loss of power from the power source to the phone or tablet, you need to pay attention to the quality of the cable, its length, as well as the cross-sectional area, otherwise, even if your phone / tablet supports Quick Charge technology, the output voltage will not be 9 V or 12 V, and standard 5 V will be issued.
A special feature of the Aukey PB-T1 is that when you connect your mobile device to charging, the charger itself determines whether the connected device supports fast charging or not, first issuing standard 5V voltages and then delivering more voltage when the consumer, i.e. A mobile device battery will require increased voltage.
Another important point: if you try to charge low-power devices (smart watches, bracelets, etc.) with a classic portable charger, then this device will usually stop powering after 1-3 minutes, and With Aukey PB-T1, this is not to be feared at all. You will not need to press the power button again so that the power supply resumes or even remove the wire and reinsert it again.
For example, it became necessary to charge wireless headphones with low consumption:

Ordinary PowerBank after a minute refused to charge the device. Accordingly, by supplying power again, a minute later they received the same picture again, and with the Aukey PB-T1, the headphones were charged from beginning to end.
And thanks to the robust, anodized aluminum housing resistant to corrosion and scratches, you can not worry about the transportation and storage of the device, do not blow away the dust particles from the surface.
Let's move on to the practical part. Let's see how quickly we manage to charge the phone with Quick Charge 2.0 support. To control the output voltage and current, as well as control the battery charge, use the LCD USB Power Meter KCX-017:




As a “guinea pig”, we will use a mobile device that was on hand, namely the Motorola Nexus 6 with the declared support for Quick Charge 2.0. The battery is lithium-ion capacity of 3220 mAh.
We will charge from
1. Aukey PB-T1;

2. Classic Power Bank portable charger with the declared output characteristics of 5 V and 2100 mAh, which went 1.5 - 2 years ago;

3. A powerful desktop USB charging station Avantree PowerHouse , which has 4 ports, each of which gives the maximum output of the same 5V and 2.1A.

In each experiment, the mobile device is initially in a fully discharged state (battery charge is approximately 0%, “approximately” in the sense that if you try to turn on the smartphone, the vibration will work and then it will turn off again, that is, the charge slightly more than 0%, but less than 1%). Next, we will fix the first value in 15-30 seconds after connecting to charging, however, the phone at this time will still be in the disabled state, and after fixing the value we turn on the smartphone and we will record all subsequent values already in the on state.
We will also take into account that the smartphone was purchased about 3/4 years ago, i.e. Battery capacity is not the same as when you bought it.
Let us take into account the fact that a lot of applications are installed on the smartphone, there are 2 users, the second user is logged in, and in the background, 1 user account is additionally loaded by the smartphone, which in fact is formally considered the owner of the phone. Wi-Fi, GSM, mobile data transmission are also active, there are no active applications, but many services and processes are running in the background (regular updates of mail, letters of applications for instant messaging, letters in social networks, etc.), and these facts will lead to the fact that the smartphone battery will also be decently discharged.
The 2nd and subsequent values will be fixed when you press the unlock button so that the percentage of the current charge is visible on the smartphone display.
Values will be recorded with an interval of 5 minutes in the case of Aukey PB-T1 and Avantree PowerHouse and with an interval of 10 minutes in the case of PowerBank.
We also take into account that the time will be recorded not up to a second, but with an accuracy of ± 20 seconds with an interval of 5 minutes and ± 40 seconds with an interval of 10 minutes.
Considering all the above, we get the following experimental data:

As you can see, the absolute leader was the Aukey PB-T1, he managed to charge the Nexus 6 in 115 minutes (1 hour 55 minutes). PB-T1 even managed to rip off the powerful Avantree PowerHouse station, the latter managed to charge our smartphone in 140 minutes (2 hours and 20 minutes), taking an honorable 2nd place.
Well, the third place was taken by PowerBank, charging the smartphone in 230 minutes (3 hours and 40 minutes).
For clarity, we construct the graphs of currents and voltages:



Of course, we are not dealing with an ideal case, so there are no “beautiful” graphs, a strict linear law at the initial stage of charging, no exponential decay at the subsequent stage of charging and smooth transitions, as the values constantly fluctuate. However, it is worth noting that portable devices could never boast stable values of the output current and voltage.
Thus, we gained 18% and 50% gains in charge rates compared to Avantree PowerHouse and PowerBank, respectively, using the Aukey PB-T1.
Of course, we could not completely get rid of the “wiring”, but we managed to charge almost 40% of the battery capacity in 40 minutes, which allowed us to continue to use our smartphone for quite a long time.
The following devices are compatible with Quick Charge 2.0:
- Asus: Transformer T100, Zenfone 2
- Droid Turbo by Motorola
- Eben 8848
- Fujitsu: Arrows NX, F-02G, F-03G, F-05F
- Google Nexus 6
- HTC: Butterfly 2, One (M8), One (M9)
- Kyocera Urbano L03
- LeTV: One Max, One Pro
- LG: G2 Flex 2, G4
- Moto: X Pure Edition, X Style, Moto X by Motorola
- Panasonic CM-1
- Ramos Mos1
- Samsung Galaxy Note 4, Note 5, Note Edge, S5 (Japan), S6, S6 Edge
- Sharp: Aquos Pad, Aquos Zeta, SH01G / 02G
- Sony Xperia: Z2 (Japan), Z2 Tablet (Japan), Z3, Z3 Compact, Z3 Tablet, Z3 +, Z4, Z4 Tablet, Z5, Z5 Compact
- Xiaomi: Mi 3, Mi 4, Mi Note, Mi Note Pro
- Yota Phone 2
- ZTE: Axon Pro, Nubia My Prague, Z9
A full list of supported devices can be found here .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/392137/
All Articles