Created a prototype of a wearable device for the automatic diagnosis and correction of the blood glucose level of diabetics
Welcome to the pages of the blog iCover ! Effective diagnosis and treatment of diabetes - a problem that has touched millions of people on the planet, may be able to get closer to its solution in the very near future. This opinion is shared by scientists from South Korea and the United States who have developed an automatic wearable wireless device for this purpose. In more detail about the presented prototype, its advantages, the principle of work and the restrictions existing at the time of the announcement we will tell in this publication.
The problems with pancreas transplantation or its parts, associated with the rejection of the new graft by the immune system and the lack of transplanted tissues, became the reason for the bioengineers to find an alternative solution. One of the areas under consideration was the development of a mechanical robotic “analogue” of the pancreas, capable of compensating for changes in the level of glucose in the patient’s blood.
Over the past few years, the first partially automated systems have appeared on the market, the so-called. devices “with semi-annual closed loop”. Unfortunately, they proved their effectiveness only for insulin-dependent patients with type 1 diabetes (juvenile diabetes). This is the case when the body, due to the destruction of the beta cells of the pancreas, ceases to produce insulin and requires the introduction of the necessary doses from the outside. Such systems have tiny hypodermic needles for fixing glucose abnormalities, a computer system for analyzing the data obtained, and an insulin pump for subcutaneous injection of insulin with a super-thin pipette. All three elements communicate over a wireless interface. However, previously proposed commercial stations are not yet able to provide fully automatic correction of blood glucose level of type 1 diabetics, requiring at least partial monitoring and participation in the patient's process.
')
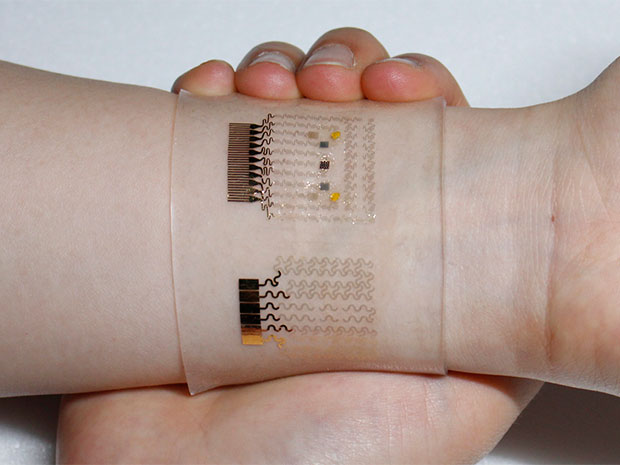
Type 2 diabetes, less severe and much more common, is the most suitable form for creating a fully automated closed-loop monitoring and corrective therapy system. At this stage of the disease, the pancreas of the patient still produces insulin and only needs some support. It is such a system for diagnosis and therapy that supplies the body with the purpose of supporting liver metformin was proposed by specialists from South Korea and the United States. A report on the work done was published on the Nature.com web portal on March 21, 2016. The device resembles a compact bracelet worn on a brush with active elements from graphene, switched with a smartphone via a wireless interface.
Due to the high carrier mobility, conductivity, flexibility, and optical transparency, graphene acquires the properties of a universal material, which is increasingly being used in both micro and macroelectronics. By creating a bracelet for diagnosing and treating diabetes, scientists were able to experimentally show that a graphene-doped sensor system of gold in microscopic concentrations combined with the finest gold mesh is capable of providing the level of electrochemical activity necessary to ensure automatic monitoring of the patient’s condition.
By itself, graphene does not react to glucose, but, being doped in a certain way, it can acquire a very useful set of electrochemical properties. The created prototype of the graphene-based system provides both fully automatic control and correction of the blood glucose level in patients with type 2 diabetes. Experiments carried out on laboratory mice demonstrated the stability of the transmission of electrical signals and the timeliness of delivery of a dose of metformin, which makes it possible to lower blood sugar levels in a short time.
When a certain threshold value is exceeded, the drug Metformin is injected into the blood by means of a built-in array of needles. And the most important component of the “wristband” is the sensor of the chemical composition of sweat, which allows to determine the level of glucose in the blood. As the scientists report in their reporting publication, the time during which changes in the composition of blood lead to changes in the composition of sweat, which can be estimated by the proposed method, does not exceed 15–20 minutes, which is not critical for people with type 2 diabetes.
The elastic bracelet is combined with sensors that allow to obtain all the necessary data on the current state of the patient in real time and quickly record the fact of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. The wearable device includes a system of operative therapy from an array of polymeric microneedles for subcutaneous injection, combined with capsules containing metformin and thermally activated.
Information collected via the wireless interface is read and analyzed by a special smartphone application, which, after analyzing the sensor data, also wirelessly gives the needle array a command to enter the required dose of the drug - metformin for type 2 diabetes or another drug prescribed to the patient.
After putting on the bracelet, the amount of sweat required for the analysis of biochemical parameters is collected by the adsorbent layer in 15-20 minutes. When they deviate from the norm, the patient is administered the required amount of metformin. During the experiment, the device confirmed its diagnostic capabilities in two volunteers. Therapeutic efficacy, due to some limitations of the technology, has so far been achieved in an experiment on transgenic mice suffering from type 2 diabetes.
Despite its effectiveness, the method in its current form has its limitations. As noted by Richard Guy, a pharmacologist at the British University of Bath, who called the development “a significant achievement,” the number of metformin in the current version of the device is insufficient to meet the daily needs of adult patients.
The bottlenecks of technology have not stopped scientists who are confident that they will be able to find solutions to the issue of lack of medication without a significant increase in the useful area of the device or the number of needles.
It is very important that in addition to the therapeutic effect, the proposed medical bracelet along with other similar devices will always quite accurately and absolutely painlessly be able to provide data on the amount of glucose in the blood, which, taking into account the possibilities of the application, will allow collecting complete statistics reflecting an objective picture of the disease in the time interval of interest. And for this purpose such a bracelet could be used now.
A source
Dear readers, we are always happy to meet and wait for you on the pages of our blog. We are ready to continue to share with you the latest news, review materials and other publications, and we will try to do everything possible so that the time spent with us will be useful for you. And, of course, do not forget to subscribe to our headings .
Our other articles and events

The problems with pancreas transplantation or its parts, associated with the rejection of the new graft by the immune system and the lack of transplanted tissues, became the reason for the bioengineers to find an alternative solution. One of the areas under consideration was the development of a mechanical robotic “analogue” of the pancreas, capable of compensating for changes in the level of glucose in the patient’s blood.
Over the past few years, the first partially automated systems have appeared on the market, the so-called. devices “with semi-annual closed loop”. Unfortunately, they proved their effectiveness only for insulin-dependent patients with type 1 diabetes (juvenile diabetes). This is the case when the body, due to the destruction of the beta cells of the pancreas, ceases to produce insulin and requires the introduction of the necessary doses from the outside. Such systems have tiny hypodermic needles for fixing glucose abnormalities, a computer system for analyzing the data obtained, and an insulin pump for subcutaneous injection of insulin with a super-thin pipette. All three elements communicate over a wireless interface. However, previously proposed commercial stations are not yet able to provide fully automatic correction of blood glucose level of type 1 diabetics, requiring at least partial monitoring and participation in the patient's process.
')
Type 2 diabetes, less severe and much more common, is the most suitable form for creating a fully automated closed-loop monitoring and corrective therapy system. At this stage of the disease, the pancreas of the patient still produces insulin and only needs some support. It is such a system for diagnosis and therapy that supplies the body with the purpose of supporting liver metformin was proposed by specialists from South Korea and the United States. A report on the work done was published on the Nature.com web portal on March 21, 2016. The device resembles a compact bracelet worn on a brush with active elements from graphene, switched with a smartphone via a wireless interface.
How the system works
Due to the high carrier mobility, conductivity, flexibility, and optical transparency, graphene acquires the properties of a universal material, which is increasingly being used in both micro and macroelectronics. By creating a bracelet for diagnosing and treating diabetes, scientists were able to experimentally show that a graphene-doped sensor system of gold in microscopic concentrations combined with the finest gold mesh is capable of providing the level of electrochemical activity necessary to ensure automatic monitoring of the patient’s condition.
By itself, graphene does not react to glucose, but, being doped in a certain way, it can acquire a very useful set of electrochemical properties. The created prototype of the graphene-based system provides both fully automatic control and correction of the blood glucose level in patients with type 2 diabetes. Experiments carried out on laboratory mice demonstrated the stability of the transmission of electrical signals and the timeliness of delivery of a dose of metformin, which makes it possible to lower blood sugar levels in a short time.
When a certain threshold value is exceeded, the drug Metformin is injected into the blood by means of a built-in array of needles. And the most important component of the “wristband” is the sensor of the chemical composition of sweat, which allows to determine the level of glucose in the blood. As the scientists report in their reporting publication, the time during which changes in the composition of blood lead to changes in the composition of sweat, which can be estimated by the proposed method, does not exceed 15–20 minutes, which is not critical for people with type 2 diabetes.
The elastic bracelet is combined with sensors that allow to obtain all the necessary data on the current state of the patient in real time and quickly record the fact of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. The wearable device includes a system of operative therapy from an array of polymeric microneedles for subcutaneous injection, combined with capsules containing metformin and thermally activated.
Information collected via the wireless interface is read and analyzed by a special smartphone application, which, after analyzing the sensor data, also wirelessly gives the needle array a command to enter the required dose of the drug - metformin for type 2 diabetes or another drug prescribed to the patient.
After putting on the bracelet, the amount of sweat required for the analysis of biochemical parameters is collected by the adsorbent layer in 15-20 minutes. When they deviate from the norm, the patient is administered the required amount of metformin. During the experiment, the device confirmed its diagnostic capabilities in two volunteers. Therapeutic efficacy, due to some limitations of the technology, has so far been achieved in an experiment on transgenic mice suffering from type 2 diabetes.
Technology limitations
Despite its effectiveness, the method in its current form has its limitations. As noted by Richard Guy, a pharmacologist at the British University of Bath, who called the development “a significant achievement,” the number of metformin in the current version of the device is insufficient to meet the daily needs of adult patients.
The bottlenecks of technology have not stopped scientists who are confident that they will be able to find solutions to the issue of lack of medication without a significant increase in the useful area of the device or the number of needles.
It is very important that in addition to the therapeutic effect, the proposed medical bracelet along with other similar devices will always quite accurately and absolutely painlessly be able to provide data on the amount of glucose in the blood, which, taking into account the possibilities of the application, will allow collecting complete statistics reflecting an objective picture of the disease in the time interval of interest. And for this purpose such a bracelet could be used now.
A source
Dear readers, we are always happy to meet and wait for you on the pages of our blog. We are ready to continue to share with you the latest news, review materials and other publications, and we will try to do everything possible so that the time spent with us will be useful for you. And, of course, do not forget to subscribe to our headings .
Our other articles and events
- Gator Caref Watch. Caring for your child
- Spring discounts from KitchenAid
- Sale of useful gadgets and interesting pieces
- Logitech Expands Color-Illuminated Mechanical Gaming Keyboards
- A selection of smart watches today. What changed?
- Perfect gadget backpack for father family
- How the case did not save my iPhone. Choose right
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/392085/
All Articles