"Warned - armed" or what you need to know about a stroke, even if you are young
A sad and shocking turn of events: the star of social networks and model Katie died two weeks ago after a stroke. The New York Daily News reported that it may have had a “damaged neck” when it fell during a photo shoot at the end of January, and that Katie tweeted that she had a “nerve pinched” before she was hospitalized . But it turns out that such pain can be caused by a much more serious cause than a pinched nerve. But if a woman is so young (34 years old), who could match the pain in her neck with a stroke?
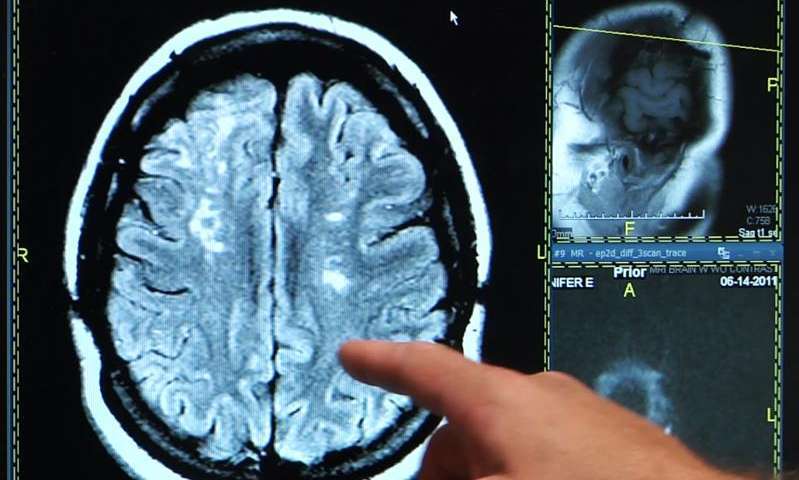
“When you are young and relatively healthy, you don’t think about a stroke, completely excluding this possibility,” says David Liebeskind, MD Medical Center of the University of Kalifonia. “But the reality is that a stroke can develop at any age.”
')
According to doctors, the model suffered from carotid artery dissection. It begins as a rupture in the artery wall, which can be caused by trauma and results in a blood clot blocking blood flow to the brain.
Although this type of stroke is rare, strokes are generally on the rise in younger people, probably due to factors such as hypertension. Between 1995 and 2008, the level of hospitalizations due to stroke in patients aged 15 to 44 years old jumped by 37% (!). What is most upsetting, the experts found that 73% of people under the age of 45 use the principle of “wait and see” when they experience symptoms of a stroke rather than rush to the hospital.
“But this is a catastrophic solution,” says Dr. Liebeskind, “because the first 3 hours after the onset of symptoms are a critical window for treatment.”
So what are the early signs? The two main ones are a sudden onset of dizziness or a severe headache. David Newman-Tokero, MD, assistant professor of neuroscience at Johns Hopkins University, said these are the most common symptoms in women under the age of 45, which are sometimes accompanied by hiccups or nausea.
Dr. Liebeskind adds a few more signs:
* temporary loss of speech,
* changes in vision,
* the inability to perform any ordinary actions
* other unusual sensations
* association of symptoms with pain in the neck or a recent fall.
“If you have a combination of symptoms, the likelihood of a stroke is high,” he said. “Dial„ 911 “. And if your doctor tries to diagnose something else for you (internal otitis or migraine) do not give up. Migraine does not kill you, but a stroke can, ”notes Dr. Liebeskind.
Dr. Newman-Tokero also advises asking the doctor this question: “Why do you think this is not a stroke? If he cannot answer in a clear voice, contact another doctor. ”
The first 3 hours after a person experiences the symptoms of a stroke is often called a “golden window”. This period of time is crucial for patients to restore blood supply to the brain and minimize or reverse brain damage.
"Timely treatment of stroke is probably more important than almost any other medical problem," said David Liebeskind, MD, professor of neurology, director of stroke treatment programs at Ronald Reagan Medical Center. "There is a very limited window in which, you can begin treatment, because the brain is very sensitive to a lack of blood flow, and the longer the patient waits, the more devastating the consequences. ”
Strokes occur at a fairly young age. “This is a real problem,” said Liebeskind. “We have to give young people information about the symptoms of a stroke and convince them of the urgency of the situation, because the statistics of stroke comes up.” Strokes in the US occur approximately every 40 seconds, bringing the total number of cases to 800,000 new patients per year.
In 2007, Jennifer Reilly was one of them. “I woke up in the middle of the night with a painful headache,” said Reilly. “I was 27 years old, I was very active, quite healthy and was not prone to headaches. I thought it was a really weird thing. "
Arriving at work that day, Reilly told a colleague about her story, who insisted that Reilly go to the hospital. Reilly eventually ended up at a medical center, where they determined that she had a stroke. “I was very skeptical,” said Reilly. “I didn’t have what I thought were the classic symptoms of a stroke. I was only 27. "
Reilly says that a week before the headache, she also experienced periodic numbness in one of her hands. “Half of my left hand went numb for just one second,” she said.
The majority of patients (about 85%) suffer from the so-called ischemic stroke, in which the arteries in the brain are blocked, blocking the access of oxygen to the brain. Ischemic stroke can happen to anyone at any age, and is often associated with high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking and obesity.
The faster a blood clot causing a stroke is removed, the lower the patient’s disability is the research data presented by the American Stroke Association at the International Conference on Stroke 2016.
In the current analysis, the researchers tested 83 patients who had had a blood clot removed. They found that:
* in patients to whom blood flow was restored within 2.5 hours after the onset of a stroke, 87% achieved functional independence (minimal disability or its complete absence).
* those who had blood flow restored between 2.5 and 3.5 hours after the onset of a stroke were 10% less likely to achieve functional independence;
* Every 60 minutes delay after 3.5 hours corresponded to a 15% decrease in functional independence.
Sleeping more than eight hours a day significantly increases your chances of a stroke - these are the research data.
A study of nearly 290,000 people found that 7–8 hours of sleep per day can reduce the likelihood of a stroke. But American researchers from New York University have shown that those who sleep longer increase the risk of stroke by 146%. Sleep less than 7 hours increases the risk by 22%. Scientists who presented their findings at a meeting of the American Stroke Association in Los Angeles on February 17, 2016
They took into account the many factors of health, lifestyle, age and ethnicity of 288,888 adults who took part in the survey from 2004 to 2013. The researchers also analyzed how long these people slept and how long they practiced walking, swimming, cycling or working in the garden. Sleep for 7–8 hours a day and exercise from 30 to 60 minutes 3–6 times a week gave the maximum benefit for the prevention of stroke.
Strokes occur either as a result of bleeding in the brain or when a blood clot cuts off blood flow to part of the brain. Every year in England, about 110,000 people suffer a stroke. This is the third most common cause of death after heart disease and cancer. They are the main cause of disability in the adult population.
Scientists also found that people who have 6 to 8 hours of sleep live longer and have better health, and those who get less than 6 hours of sleep are more likely to die prematurely.
Researchers don't know exactly why sleeping too much is problematic. One theory is that a longer sleep indicates a worse quality of sleep. All whose biological clocks are regularly violated (for example, nursing mothers and shift workers) are vulnerable.
The American Stroke Association writes that this year, more than 100,000 US women will get a stroke.
Stroke is not a geriatric disease. It is not limited to older people, overweight people, smokers or people with high cholesterol levels. “All of these are common risk factors,” says Stephen J. Kittner, MD, director of the Maryland Stroke Center at the University of Maryland in Baltimore. “But a stroke can hit anyone at any age. There are other risk factors for stroke that are especially important for women under 55. ”They include:
* Migraine
Recent studies show that women who suffer from migraines with aura (visual impairments such as flashing dots or white spots) may be up to 10 times more likely to suffer from a stroke, regardless of other risk factors.
* Birth control pills
Women taking birth control pills (even with low estrogen levels) may have a two-fold higher chance of stroke than those who do not use these drugs. And this risk may increase if other risk factors are present.
* Pre-eclampsia / Eclampsia
Women with a history of preeclampsia / eclampsia have an increased risk of future hypertension and stroke after delivery.
* Hypertension
Women with chronic primary or secondary hypertension, or a previous pregnancy associated with hypertension have an increased risk of stroke.
* Hormone replacement therapy
Women taking hormone replacement therapy may have an increased risk of stroke.
* Autoimmune diseases (diabetes, lupus) can increase the risk of stroke.
* Disorders of blood coagulation
Women who have had more than one miscarriage have a higher risk of blood clots, which may increase the likelihood of a stroke. Other signs of possible clotting may include a previous history of deep vein thrombosis or purple skin discoloration.
Dr. Kittner adds: “Risk factors are cumulative. Reducing even one risk can significantly reduce your chances of a stroke. ”

“When you are young and relatively healthy, you don’t think about a stroke, completely excluding this possibility,” says David Liebeskind, MD Medical Center of the University of Kalifonia. “But the reality is that a stroke can develop at any age.”
')
According to doctors, the model suffered from carotid artery dissection. It begins as a rupture in the artery wall, which can be caused by trauma and results in a blood clot blocking blood flow to the brain.
Although this type of stroke is rare, strokes are generally on the rise in younger people, probably due to factors such as hypertension. Between 1995 and 2008, the level of hospitalizations due to stroke in patients aged 15 to 44 years old jumped by 37% (!). What is most upsetting, the experts found that 73% of people under the age of 45 use the principle of “wait and see” when they experience symptoms of a stroke rather than rush to the hospital.
“But this is a catastrophic solution,” says Dr. Liebeskind, “because the first 3 hours after the onset of symptoms are a critical window for treatment.”
So what are the early signs? The two main ones are a sudden onset of dizziness or a severe headache. David Newman-Tokero, MD, assistant professor of neuroscience at Johns Hopkins University, said these are the most common symptoms in women under the age of 45, which are sometimes accompanied by hiccups or nausea.
Dr. Liebeskind adds a few more signs:
* temporary loss of speech,
* changes in vision,
* the inability to perform any ordinary actions
* other unusual sensations
* association of symptoms with pain in the neck or a recent fall.
“If you have a combination of symptoms, the likelihood of a stroke is high,” he said. “Dial„ 911 “. And if your doctor tries to diagnose something else for you (internal otitis or migraine) do not give up. Migraine does not kill you, but a stroke can, ”notes Dr. Liebeskind.
Dr. Newman-Tokero also advises asking the doctor this question: “Why do you think this is not a stroke? If he cannot answer in a clear voice, contact another doctor. ”
The first 3 hours after a person experiences the symptoms of a stroke is often called a “golden window”. This period of time is crucial for patients to restore blood supply to the brain and minimize or reverse brain damage.
"Timely treatment of stroke is probably more important than almost any other medical problem," said David Liebeskind, MD, professor of neurology, director of stroke treatment programs at Ronald Reagan Medical Center. "There is a very limited window in which, you can begin treatment, because the brain is very sensitive to a lack of blood flow, and the longer the patient waits, the more devastating the consequences. ”
Strokes occur at a fairly young age. “This is a real problem,” said Liebeskind. “We have to give young people information about the symptoms of a stroke and convince them of the urgency of the situation, because the statistics of stroke comes up.” Strokes in the US occur approximately every 40 seconds, bringing the total number of cases to 800,000 new patients per year.
In 2007, Jennifer Reilly was one of them. “I woke up in the middle of the night with a painful headache,” said Reilly. “I was 27 years old, I was very active, quite healthy and was not prone to headaches. I thought it was a really weird thing. "
Arriving at work that day, Reilly told a colleague about her story, who insisted that Reilly go to the hospital. Reilly eventually ended up at a medical center, where they determined that she had a stroke. “I was very skeptical,” said Reilly. “I didn’t have what I thought were the classic symptoms of a stroke. I was only 27. "
Reilly says that a week before the headache, she also experienced periodic numbness in one of her hands. “Half of my left hand went numb for just one second,” she said.
The majority of patients (about 85%) suffer from the so-called ischemic stroke, in which the arteries in the brain are blocked, blocking the access of oxygen to the brain. Ischemic stroke can happen to anyone at any age, and is often associated with high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking and obesity.
The faster a blood clot causing a stroke is removed, the lower the patient’s disability is the research data presented by the American Stroke Association at the International Conference on Stroke 2016.
In the current analysis, the researchers tested 83 patients who had had a blood clot removed. They found that:
* in patients to whom blood flow was restored within 2.5 hours after the onset of a stroke, 87% achieved functional independence (minimal disability or its complete absence).
* those who had blood flow restored between 2.5 and 3.5 hours after the onset of a stroke were 10% less likely to achieve functional independence;
* Every 60 minutes delay after 3.5 hours corresponded to a 15% decrease in functional independence.
Sleeping more than eight hours a day significantly increases your chances of a stroke - these are the research data.
A study of nearly 290,000 people found that 7–8 hours of sleep per day can reduce the likelihood of a stroke. But American researchers from New York University have shown that those who sleep longer increase the risk of stroke by 146%. Sleep less than 7 hours increases the risk by 22%. Scientists who presented their findings at a meeting of the American Stroke Association in Los Angeles on February 17, 2016
They took into account the many factors of health, lifestyle, age and ethnicity of 288,888 adults who took part in the survey from 2004 to 2013. The researchers also analyzed how long these people slept and how long they practiced walking, swimming, cycling or working in the garden. Sleep for 7–8 hours a day and exercise from 30 to 60 minutes 3–6 times a week gave the maximum benefit for the prevention of stroke.
Strokes occur either as a result of bleeding in the brain or when a blood clot cuts off blood flow to part of the brain. Every year in England, about 110,000 people suffer a stroke. This is the third most common cause of death after heart disease and cancer. They are the main cause of disability in the adult population.
Scientists also found that people who have 6 to 8 hours of sleep live longer and have better health, and those who get less than 6 hours of sleep are more likely to die prematurely.
Researchers don't know exactly why sleeping too much is problematic. One theory is that a longer sleep indicates a worse quality of sleep. All whose biological clocks are regularly violated (for example, nursing mothers and shift workers) are vulnerable.
The American Stroke Association writes that this year, more than 100,000 US women will get a stroke.
Stroke is not a geriatric disease. It is not limited to older people, overweight people, smokers or people with high cholesterol levels. “All of these are common risk factors,” says Stephen J. Kittner, MD, director of the Maryland Stroke Center at the University of Maryland in Baltimore. “But a stroke can hit anyone at any age. There are other risk factors for stroke that are especially important for women under 55. ”They include:
* Migraine
Recent studies show that women who suffer from migraines with aura (visual impairments such as flashing dots or white spots) may be up to 10 times more likely to suffer from a stroke, regardless of other risk factors.
* Birth control pills
Women taking birth control pills (even with low estrogen levels) may have a two-fold higher chance of stroke than those who do not use these drugs. And this risk may increase if other risk factors are present.
* Pre-eclampsia / Eclampsia
Women with a history of preeclampsia / eclampsia have an increased risk of future hypertension and stroke after delivery.
* Hypertension
Women with chronic primary or secondary hypertension, or a previous pregnancy associated with hypertension have an increased risk of stroke.
* Hormone replacement therapy
Women taking hormone replacement therapy may have an increased risk of stroke.
* Autoimmune diseases (diabetes, lupus) can increase the risk of stroke.
* Disorders of blood coagulation
Women who have had more than one miscarriage have a higher risk of blood clots, which may increase the likelihood of a stroke. Other signs of possible clotting may include a previous history of deep vein thrombosis or purple skin discoloration.
Dr. Kittner adds: “Risk factors are cumulative. Reducing even one risk can significantly reduce your chances of a stroke. ”
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/390827/
All Articles