How to choose a communication standard for IoT network
The previous article did not discuss wireless networking standards.
The question of how the elements of the Internet of things communicate with each other, is one of the most important when building a network. Variants are possible here, and everything depends, of course, on the objectives of the project.
Key considerations when considering options for network connectivity:
The data are summarized in two tables.
')
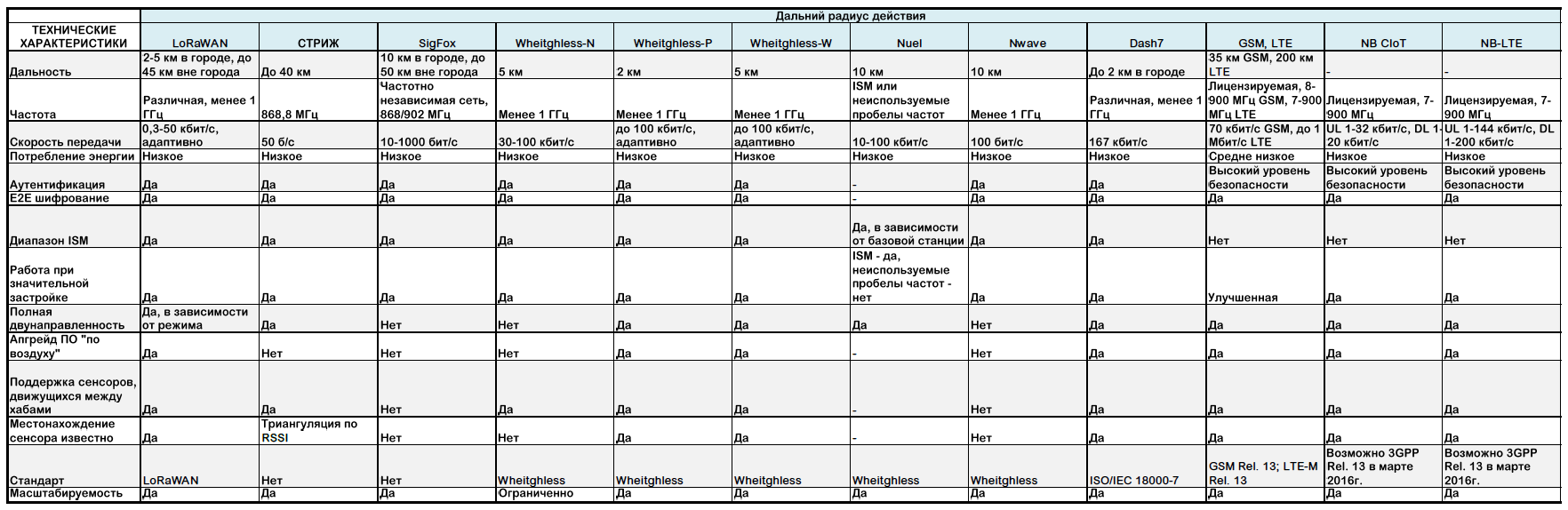
Long Range
LoRaWAN
The LoRaWAN or Long Range Wide Area Network was introduced as an energy efficient network technology by IBM Research and Semtech . The technology is based on a Semtech LoRa (™) PHY chip.
LoRa operates in the sub-GHz ISM bands (industrial, scientific and medical radio bands) of unlicensed frequencies. The network architecture is a star, end devices connect wirelessly to one or more gateways, and gateways connect to a network server via a standard IP connection.
In order to support and distribute technology, the LoRa Alliance was recently created, which includes many companies, including the Russian LACE .
Advantages of LoRa:
Disadvantages of LoRa:
Hubs for LoRa are supplied by companies such as MultiTech , and social networks have already been created, such as The Things Network .
Swift
The system is implemented by the Russian company STRIZH-Telematika, using its own protocol Marcato 2.0. The frequency can be adapted to the ISM range.
The technology is to a certain extent similar to LoRa technology with all the advantages and disadvantages of the latter. The principal difference is that LoRa uses wideband coding, and SWIF uses narrowband modulation. According to the company, this modulation makes it much more efficient to use a spectrum band, increase sensitivity and energy efficiency, and reduce costs.
The STRIZH wireless network is deployed in Moscow with 100% coverage, and also with partial coverage in the Moscow Region, St. Petersburg and some other cities and has more than 200 base stations. Radio modems, base stations, as well as meters and sensors with built-in modems are manufactured and sold.
Sigfox
The system was built by the company of the same name, founded in France in 2009. The technology used is Ultra Narrow Band (UNB), the same one that was used for communication between submarines during World War II. This technology was originally designed for communication at low data rates.
SigFox currently uses the most popular European ISM band at 868 MHz (as defined by the ETSI and CEP standards), and also 902 MHz in the USA (as defined by the FCC), depending on specific regional rules. The system is deployed using the capabilities of modern cellular networks.
The device can send up to 140 messages per day, and each message can contain up to 12 bytes of useful data. The 12 bytes cover the needs of devices that transmit data, such as device location, power consumption index, alarm, or any other type of basic sensory information. You can also send up to 4 messages from 8 bytes of useful data per device per day. In order to receive messages, the device must request data from the server, it must be programmed for specific events or for a specific time. 8 bytes sent to the device, allow you to send configuration data if necessary, you can optimize battery life. This is enough if there is no need for full-fledged two-way communication.
Unlike its competitors, the network is already deployed throughout Europe and North America and covers tens of thousands of devices. The company is certifying SigFox Ready ™ devices.
Advantages of SigFox:
Disadvantages of SigFox:
Wheitghless
Weightless is a group of open technology communications standards LPWAN (Low-Power Wide-Area Network) for exchanging data between a base station and devices. Standards are developed by the non-profit organization Weightless SIG. Currently, 3 standards are available - Weightless-N, Weightless-P and Weightless-W. Unlicensed frequencies of the sub-gigahertz range are used.
Weightless-N uses Ultra Narrow Band (UNB) technology, is a one-way communication standard. The most economical standard in the group, both in terms of costs and energy consumption.
Weightless-W uses TVWS frequencies (TV white space, unused frequencies of the television spectrum), where allowed by local rules. This increases the cost of the terminal and increases its power consumption.
Weightless-P - the last of the standards, introduced in July 2015, fully two-way, supports all major SRD / ISM ranges (short range devices / industrial, scientific and medical), the most productive in the group, has a number of additional features, like roaming, paging , adapted coding, etc. Therefore, it has a slightly shorter range and higher power consumption.
Weightless benefits:
Weightless Disadvantages:
Nuel
Neul is based on the Weightless protocol, uses unlicensed ISM and TVWS frequencies.
In September 2014, Neul was acquired by Huawei and became a subsidiary. It is stated that Neul and Huawei are working together on an innovative technology that allows the reuse of networks of mobile operators for a wide coverage of ultra-low communication power for IoT applications.
Advantages of Neul:
Neul Disadvantages:
Nwave
The British company with offices in London, the United States and Denmark is headed by a graduate of the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology Yuri Birchenko .
Nwave technology is similar to Neul because it is also based on the Weightless protocol, and is comparable to SigFox because it is proprietary. Nwave is sometimes described as a VPN (virtual private network) within public traffic using the Weightless-N standard. Uses Ultra Narrow Band (UNB) technology and unlicensed ISM frequencies.
The company manufactures and markets radio modems, base stations, as well as sensors with built-in modems and kits for developers.
The description of the technology and photo of Nwave equipment is extremely similar to the technology and equipment of the Russian company STRIZH-Telematics.
Advantages of Nwave:
Disadvantages of Nwave:
Dash7
The Dash7 Alliance Protocol (or D7A) is an open wireless protocol that operates on the 433 MHz, 868 MHz and 915 MHz unlicensed ISM / SRD frequencies. AES 128-bit encryption and data transfer up to 167 kbps is supported, with a maximum data packet of 256 bytes.
The protocol is promoted by the non-profit Alliance Dash7 Alliance with headquarters in Belgium. The protocol is based on the international standard ISO / IEC 18000-7, which describes the interface for active RFID and is used in US military logistics (NATO). The current version of the DASH7 protocol is no longer compatible with the ISO / IEC 18000-7 standard.
Advantages of Dash7:
Disadvantages of Dash7:
GSM, LTE
The 3GPP consortium (The 3rd Generation Partnership Project), which is developing specifications for mobile telephony, has long been working on improving GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications, originally Groupe Special Mobile) and LTE (Long-Term Evolution) in terms of IoT. These are primarily the answers to the challenges: penetrating power, low power consumption, efficiency and scalability. The upcoming improvements are related to Release 13, scheduled for March 2016, and declared as worthy of competition with LoRa and SigFox. According to the consortium, it was almost possible to solve all the stated problems, including energy efficiency. And the cost of the M2M module in 2016 should be $ 4.5 for GSM and $ 5 for LTE-M.
Advantages of GSM, LTE:
Disadvantages of GSM, LTE:
NB-LTE and NB-CIoT
Nokia Networks, Ericsson and Intel have teamed up to promote Narrow-Band Long-Term Evolution (NB-LTE) technology. Sprint, Verizon Wireless, Alcatel-Lucent, Qualcomm, Samsung, Sony and ZTE also became part of this initiative.
NB-LTE is seen by some experts as a direct challenge to Huawei Technologies, which is developing Narrowband Cellular IoT technology (NB-CIoT). NB-CIoT has already received the support of such heavyweights as Vodafone, T-Mobile, TeliaSonera and China Unicom.
The main difference between NB-LTE and NB-CIoT comes down to how much existing LTE networks can be reoriented to IoT. Huawei declined to comment on this, but critics of the clean slate approach (NB-CIoT) note that this technology requires new chipsets and does not seem to be backward compatible with LTE networks older than Release 13.
According to a Nokia representative, NB-LTE, by contrast, can be fully integrated into existing LTE networks and operates within existing LTE bands. In other words, NB-LTE uses the existing ecosystem and thus promises big economies of scale.
Otherwise, both technologies managed to solve the problem of energy saving: the declared duration of the device operation from the battery is 10 years. In addition, penetrating power in dense buildings has been improved several times, and the number of possible device connections has been increased by 2 orders of magnitude. The cost of the M2M module is estimated at $ 4 in 2016.
The advantages and disadvantages of these technologies naturally grow from GSM and LTE.
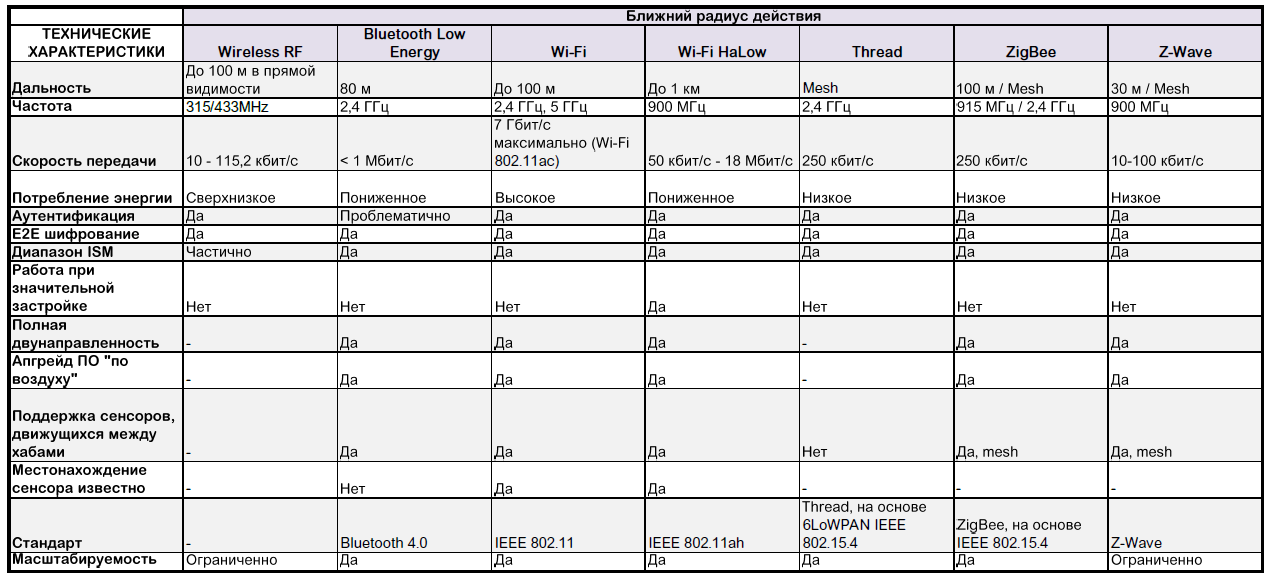
Short range
Wireless RF
Wireless radios (Wireless RF) sensors and actuators are cheap and easy to deploy. They are characterized by ultra-low power consumption. The range is up to 100 m in direct line of sight and up to 500m with external antennas. They usually operate at a frequency of 315 or 433 MHz at a speed of 10 - 115.2 kbit / s and support 128-bit AES encryption.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a wireless personal network technology developed and implemented using the Bluetooth Special Interest Group . At the moment, Bluetooth technology is present on all mobile platforms, BLE is equipped with millions of new devices. This technology is well supported and reliable for short-range communications. Often used for communication between smartphones and other personal, less commonly home electronic devices. On this technology, in particular, based technology iBeacon.
Benefits of BLE:
Disadvantages of BLE:
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi (or WiFi, originally from the English. Wireless Fidelity) is a local wireless network technology that allows electronic devices to connect to the network, mainly using the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz ISM radio frequencies. The technology is developing Wi-Fi Alliance on the basis of the standard IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) 802.11. Wi-Fi is a registered trademark of the same alliance, which includes more than 600 companies. This technology has become de facto almost ubiquitous, the world produces billions of Wi-Fi devices per year.
Wi-Fi was originally designed for local communication. Modern access points with stock antennas can provide a range of up to about 100 meters without obstructions. There are solutions using an amplifier and a semi-parabolic antenna with a range of over 20 km.
This technology does not stand still, constantly evolving. So, Wi-Fi Direct technology allows Wi-Fi devices to connect directly without an access point and a network. Devices can establish a connection with each other or with a group of several devices simultaneously. Connecting Wi-Fi Direct-certified devices is easy and simple: either two NFC-compatible devices together, or with a PIN. In addition, all direct Wi-Fi connections are protected by WPA2.
Wi-Fi connections may be impaired or connection speed may be reduced if there are other similar devices in the same area. Many 2.4 GHz 802.11b and 802.11g access points operate on the same channels by default on initial startup. Wi-Fi pollution can be a problem in high-density areas, such as large residential complexes or office buildings with many Wi-Fi access points. In addition, many other devices use the 2.4 GHz band: microwaves, ZigBee devices, Bluetooth devices, cordless phones, baby monitors, which can cause significant additional interference. This is also a problem when municipalities or other large sites (such as universities) seek to provide a larger Wi-Fi coverage area.
The recently released Cisco and Apple document “Enterprise Best Practices for Apple Devices on Cisco Wireless LAN” contains joint recommendations regarding the use of iPhone, iPad, iPod devices in networks (with an operating system of at least iOS 9.0). As stated in this document, “the 2.4 GHz band is not considered suitable for any business and / or critical enterprise applications.” For wireless networks using Apple devices, companies are recommended to use only 5 GHz frequencies (802.11a / n / ac standard). Nevertheless, the 2.4 GHz band is still the main, used by default for most mobile devices, besides the use of 5 GHz frequencies for Wi-Fi is not allowed in all countries.
The originally entered WEP encryption standard can be relatively easily cracked even with the correct configuration (due to the weakness of the algorithm). New devices support more advanced data encryption protocols WPA and WPA2. Many organizations use additional encryption to protect against intruders. At the moment, the main method of hacking WPA2 is the password selection, so it is recommended to use complex alphanumeric passwords in order to complicate the task of password selection as much as possible. In addition, Wi-Fi standards do not provide encryption of transmitted data in open networks. This means that all data transmitted over an open wireless connection can be listened to by attackers using sniffer programs. Therefore, when using free hot spots, you should not transfer critical data to the Internet.
Wi-Fi benefits:
Disadvantages of Wi-Fi:
Wi-Fi HaLow
Recently at the CES 2016, the Wi – Fi Alliance announced the development of a new wireless standard for the Internet of Things. The new standard is called HaLow and has not yet been approved by the IEEE 802.11ah specification. The certification of the first devices compatible with Wi-Fi HaLow will begin in 2018, but products with the support of the new specification will appear on the market earlier.
To connect the Wi-Fi HaLow will use the unlicensed frequency of 900 MHz. This will significantly increase the penetrating ability of the signal in urban areas, and its radius of action will be much larger than the current wireless standard - up to 1 kilometer. At the same time, the fee for the "long range" is a low signal power. The capacity of Wi-Fi HaLow will be much lower than the maximum Wi-Fi 802.11ac (7 Gb / s), the estimated speed: 50 kbps - 18 Mbps.
According to the alliance, HaLow will make extensive use of existing Wi-Fi protocols, which will ensure a high level of compatibility and security.
Thread
Thread Group , created by OSRAM, QUALCOMM, ARM, Samsung, Nest Labs and others (more than 200 companies) for one purpose - to develop the best way to connect and control devices in the house. This non-profit organization promotes the Networking Protocol (IP-based wireless network protocol) and certifies products. The first public release took place on July 13, 2015. (Revision 2.0). More than 30 devices will be certified in the near future.
Thread, implemented as an add-on to Wi-Fi, has clear limitations for home automation in terms of security and power consumption. The protocol is based on the 6LoWPAN (IPv6 over Low power Wireless Personal Area Networks) standard - an IPv6 interworking standard (new IP version with 128 bit address instead of 32 IPv4 address) over low-power IEEE802.15.4 wireless personal networks. For existing devices that support the IEEE802.15.4 standard, an upgrade to Thread can be made easily. The protocol provides AES banking class security in addition to the mesh network reliability designed specifically for home automation. 250+ authorized devices can be connected to the same network. Wide support for “sleep mode” allows for many years to operate the device even from one AA battery.
Thread Benefits:
Disadvantages of Thread:
Zigbee
ZigBee is a specification of top-level network protocols, which are regulated by the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, which appeared in 2003. ZigBee and IEEE 802.15.4 describe wireless personal area networks (WPAN, wireless personal area networks). The ZigBee specification is focused on applications that require guaranteed secure data transfer at relatively low speeds and the possibility of long-term operation of network devices from autonomous power sources. ZigBee technology supports not only simple network topologies (point-to-point, tree and star), but also self-organizing and self-healing mesh topology with relay and message routing.
ZigBee is developed by the ZigBee Alliance , which includes more than 300 companies. The Alliance also certifies equipment and devices. On December 16, 2015, the Alliance announced the ratification of ZigBee 3.0, which takes into account the current IoT requirements and supports all previous versions and hundreds of millions of devices already sold.
Advantages of ZigBee:
Disadvantages of ZigBee:
Z-wave
Z-Wave is a patented wireless communication protocol designed primarily for home automation. The technology uses low-power and miniature radio frequency modules that are embedded in consumer electronics and various devices. Z-Wave operates in the frequency range up to 1 GHz and is optimized for transmitting simple control commands with low latency. At the heart of the Z-Wave solution is a self-organizing mesh network (mesh network), in which each node or device can receive and transmit control signals to other network devices using intermediate neighboring nodes.
Z-Wave radio chips are supplied by Sigma Designs and Mitsumi. A distinctive feature of Z-Wave is that all these products are compatible with each other. Compatibility is confirmed by the Z-Wave or Z-Wave Plus certification process. The certification is carried out by Sigma Designs , which has certified over 1350 Z-Wave products. Globally, the protocol is supported by the Z-Wave Alliance , which unites more than 325 manufacturers.
Advantages of Z-Wave:
Disadvantages of Z-Wave:
Of course, in one article it is difficult to describe all existing protocols and technologies with all their diversity. So, for example, ANT + , WirelessHART , Ingenu , Telensa remained behind the scenes.
It should be noted that some manufacturers still seek to somehow bring together technology and their application. Dual-mode modules are available on the market, for example the Nemeus LoRa / Sigfox module . In addition, as the STRYZH-Telematics company claims, the SWIF technology provides full compatibility with LoRa.
Finally, according to Machina Research , the M2M advisory group, by 2024 there will be a total of 27 billion M2M connections in the world, 14% of which will be represented by LPWAN compounds like SigFox and its competitors such as LoRa and Neul.
Comments and amendments please leave in the comments.
The question of how the elements of the Internet of things communicate with each other, is one of the most important when building a network. Variants are possible here, and everything depends, of course, on the objectives of the project.
Key considerations when considering options for network connectivity:
- Range. Network to deploy in the office or in the whole city?
- Frequency. What penetration is necessary and how resistant to interference?
- Data transfer rate What bandwidth is required? How often is the data updated?
- Power supply Do devices operate on mains or battery?
- Security. Are devices involved in mission-critical applications?
The data are summarized in two tables.

')
Long Range
LoRaWAN
The LoRaWAN or Long Range Wide Area Network was introduced as an energy efficient network technology by IBM Research and Semtech . The technology is based on a Semtech LoRa (™) PHY chip.
LoRa operates in the sub-GHz ISM bands (industrial, scientific and medical radio bands) of unlicensed frequencies. The network architecture is a star, end devices connect wirelessly to one or more gateways, and gateways connect to a network server via a standard IP connection.
In order to support and distribute technology, the LoRa Alliance was recently created, which includes many companies, including the Russian LACE .
Advantages of LoRa:
- open standard
- long range
- high penetrating power in urban areas
- low power consumption, estimated up to 10 years of AA sensor operation
- various unlicensed frequencies such as 109 MHz, 433 MHz, 868 MHz, 915 MHz of the sub-GHz ISM bands
- adaptive data rate
- supports personal and social networks
- comprehensive security and embedded authentication and authentication
Disadvantages of LoRa:
- low data rate
- Semtech is the only chip supplier
- roaming is absent
Hubs for LoRa are supplied by companies such as MultiTech , and social networks have already been created, such as The Things Network .
Swift
The system is implemented by the Russian company STRIZH-Telematika, using its own protocol Marcato 2.0. The frequency can be adapted to the ISM range.
The technology is to a certain extent similar to LoRa technology with all the advantages and disadvantages of the latter. The principal difference is that LoRa uses wideband coding, and SWIF uses narrowband modulation. According to the company, this modulation makes it much more efficient to use a spectrum band, increase sensitivity and energy efficiency, and reduce costs.
The STRIZH wireless network is deployed in Moscow with 100% coverage, and also with partial coverage in the Moscow Region, St. Petersburg and some other cities and has more than 200 base stations. Radio modems, base stations, as well as meters and sensors with built-in modems are manufactured and sold.
Sigfox
The system was built by the company of the same name, founded in France in 2009. The technology used is Ultra Narrow Band (UNB), the same one that was used for communication between submarines during World War II. This technology was originally designed for communication at low data rates.
SigFox currently uses the most popular European ISM band at 868 MHz (as defined by the ETSI and CEP standards), and also 902 MHz in the USA (as defined by the FCC), depending on specific regional rules. The system is deployed using the capabilities of modern cellular networks.
The device can send up to 140 messages per day, and each message can contain up to 12 bytes of useful data. The 12 bytes cover the needs of devices that transmit data, such as device location, power consumption index, alarm, or any other type of basic sensory information. You can also send up to 4 messages from 8 bytes of useful data per device per day. In order to receive messages, the device must request data from the server, it must be programmed for specific events or for a specific time. 8 bytes sent to the device, allow you to send configuration data if necessary, you can optimize battery life. This is enough if there is no need for full-fledged two-way communication.
Unlike its competitors, the network is already deployed throughout Europe and North America and covers tens of thousands of devices. The company is certifying SigFox Ready ™ devices.
Advantages of SigFox:
- large coverage
- high penetrating power in urban areas
- ultra low power consumption, according to estimates, up to 20 years of sensor operation from 2 AA batteries
- flexibility in terms of antenna design
- SigFox protocol compatible with existing transceivers
- low cost
Disadvantages of SigFox:
- low data rate
- dependence on cellular infrastructure
- limited noise immunity
Wheitghless
Weightless is a group of open technology communications standards LPWAN (Low-Power Wide-Area Network) for exchanging data between a base station and devices. Standards are developed by the non-profit organization Weightless SIG. Currently, 3 standards are available - Weightless-N, Weightless-P and Weightless-W. Unlicensed frequencies of the sub-gigahertz range are used.
Weightless-N uses Ultra Narrow Band (UNB) technology, is a one-way communication standard. The most economical standard in the group, both in terms of costs and energy consumption.
Weightless-W uses TVWS frequencies (TV white space, unused frequencies of the television spectrum), where allowed by local rules. This increases the cost of the terminal and increases its power consumption.
Weightless-P - the last of the standards, introduced in July 2015, fully two-way, supports all major SRD / ISM ranges (short range devices / industrial, scientific and medical), the most productive in the group, has a number of additional features, like roaming, paging , adapted coding, etc. Therefore, it has a slightly shorter range and higher power consumption.
Weightless benefits:
- open standard
- long range
- high penetrating power in urban areas
- low power consumption, estimated up to 10 years of sensor operation (Weightless-N)
- various unlicensed frequencies (weightless-p)
- supports personal and social networks
- high security
- low cost (especially weightless-n)
Weightless Disadvantages:
- low data rate
Nuel
Neul is based on the Weightless protocol, uses unlicensed ISM and TVWS frequencies.
In September 2014, Neul was acquired by Huawei and became a subsidiary. It is stated that Neul and Huawei are working together on an innovative technology that allows the reuse of networks of mobile operators for a wide coverage of ultra-low communication power for IoT applications.
Advantages of Neul:
- long range
- high penetrating power in urban areas
- low power consumption, estimated up to 15 years of sensor operation
- blends well with other standards at neighboring frequencies
Neul Disadvantages:
- low data rate
- proprietary technology
Nwave
The British company with offices in London, the United States and Denmark is headed by a graduate of the Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology Yuri Birchenko .
Nwave technology is similar to Neul because it is also based on the Weightless protocol, and is comparable to SigFox because it is proprietary. Nwave is sometimes described as a VPN (virtual private network) within public traffic using the Weightless-N standard. Uses Ultra Narrow Band (UNB) technology and unlicensed ISM frequencies.
The company manufactures and markets radio modems, base stations, as well as sensors with built-in modems and kits for developers.
The description of the technology and photo of Nwave equipment is extremely similar to the technology and equipment of the Russian company STRIZH-Telematics.
Advantages of Nwave:
- long range
- high penetrating power in urban areas
- very low power consumption
- supports personal and social networks
- high security
- low cost
Disadvantages of Nwave:
- low data rate
- proprietary technology
Dash7
The Dash7 Alliance Protocol (or D7A) is an open wireless protocol that operates on the 433 MHz, 868 MHz and 915 MHz unlicensed ISM / SRD frequencies. AES 128-bit encryption and data transfer up to 167 kbps is supported, with a maximum data packet of 256 bytes.
The protocol is promoted by the non-profit Alliance Dash7 Alliance with headquarters in Belgium. The protocol is based on the international standard ISO / IEC 18000-7, which describes the interface for active RFID and is used in US military logistics (NATO). The current version of the DASH7 protocol is no longer compatible with the ISO / IEC 18000-7 standard.
Advantages of Dash7:
- open standard
- big enough range
- high penetrating power in urban areas
- low power consumption
- various unlicensed frequencies
Disadvantages of Dash7:
- low data rate
- average water penetration
- specific antenna requirements
GSM, LTE
The 3GPP consortium (The 3rd Generation Partnership Project), which is developing specifications for mobile telephony, has long been working on improving GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications, originally Groupe Special Mobile) and LTE (Long-Term Evolution) in terms of IoT. These are primarily the answers to the challenges: penetrating power, low power consumption, efficiency and scalability. The upcoming improvements are related to Release 13, scheduled for March 2016, and declared as worthy of competition with LoRa and SigFox. According to the consortium, it was almost possible to solve all the stated problems, including energy efficiency. And the cost of the M2M module in 2016 should be $ 4.5 for GSM and $ 5 for LTE-M.
Advantages of GSM, LTE:
- functioning on the existing infrastructure of cellular operators
- widespread in the world
- high data transfer rate
- support personal and social networks
- high comprehensive security
- roaming
Disadvantages of GSM, LTE:
- licensed frequencies
- high fares
NB-LTE and NB-CIoT
Nokia Networks, Ericsson and Intel have teamed up to promote Narrow-Band Long-Term Evolution (NB-LTE) technology. Sprint, Verizon Wireless, Alcatel-Lucent, Qualcomm, Samsung, Sony and ZTE also became part of this initiative.
NB-LTE is seen by some experts as a direct challenge to Huawei Technologies, which is developing Narrowband Cellular IoT technology (NB-CIoT). NB-CIoT has already received the support of such heavyweights as Vodafone, T-Mobile, TeliaSonera and China Unicom.
The main difference between NB-LTE and NB-CIoT comes down to how much existing LTE networks can be reoriented to IoT. Huawei declined to comment on this, but critics of the clean slate approach (NB-CIoT) note that this technology requires new chipsets and does not seem to be backward compatible with LTE networks older than Release 13.
According to a Nokia representative, NB-LTE, by contrast, can be fully integrated into existing LTE networks and operates within existing LTE bands. In other words, NB-LTE uses the existing ecosystem and thus promises big economies of scale.
Otherwise, both technologies managed to solve the problem of energy saving: the declared duration of the device operation from the battery is 10 years. In addition, penetrating power in dense buildings has been improved several times, and the number of possible device connections has been increased by 2 orders of magnitude. The cost of the M2M module is estimated at $ 4 in 2016.
The advantages and disadvantages of these technologies naturally grow from GSM and LTE.

Short range
Wireless RF
Wireless radios (Wireless RF) sensors and actuators are cheap and easy to deploy. They are characterized by ultra-low power consumption. The range is up to 100 m in direct line of sight and up to 500m with external antennas. They usually operate at a frequency of 315 or 433 MHz at a speed of 10 - 115.2 kbit / s and support 128-bit AES encryption.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a wireless personal network technology developed and implemented using the Bluetooth Special Interest Group . At the moment, Bluetooth technology is present on all mobile platforms, BLE is equipped with millions of new devices. This technology is well supported and reliable for short-range communications. Often used for communication between smartphones and other personal, less commonly home electronic devices. On this technology, in particular, based technology iBeacon.
Benefits of BLE:
- widespread in the world
- high data transfer rate
- high reliability
Disadvantages of BLE:
- some problems with authentication and privacy
- low penetrating power in urban areas
- device location is not determined
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi (or WiFi, originally from the English. Wireless Fidelity) is a local wireless network technology that allows electronic devices to connect to the network, mainly using the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz ISM radio frequencies. The technology is developing Wi-Fi Alliance on the basis of the standard IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) 802.11. Wi-Fi is a registered trademark of the same alliance, which includes more than 600 companies. This technology has become de facto almost ubiquitous, the world produces billions of Wi-Fi devices per year.
Wi-Fi was originally designed for local communication. Modern access points with stock antennas can provide a range of up to about 100 meters without obstructions. There are solutions using an amplifier and a semi-parabolic antenna with a range of over 20 km.
This technology does not stand still, constantly evolving. So, Wi-Fi Direct technology allows Wi-Fi devices to connect directly without an access point and a network. Devices can establish a connection with each other or with a group of several devices simultaneously. Connecting Wi-Fi Direct-certified devices is easy and simple: either two NFC-compatible devices together, or with a PIN. In addition, all direct Wi-Fi connections are protected by WPA2.
Wi-Fi connections may be impaired or connection speed may be reduced if there are other similar devices in the same area. Many 2.4 GHz 802.11b and 802.11g access points operate on the same channels by default on initial startup. Wi-Fi pollution can be a problem in high-density areas, such as large residential complexes or office buildings with many Wi-Fi access points. In addition, many other devices use the 2.4 GHz band: microwaves, ZigBee devices, Bluetooth devices, cordless phones, baby monitors, which can cause significant additional interference. This is also a problem when municipalities or other large sites (such as universities) seek to provide a larger Wi-Fi coverage area.
The recently released Cisco and Apple document “Enterprise Best Practices for Apple Devices on Cisco Wireless LAN” contains joint recommendations regarding the use of iPhone, iPad, iPod devices in networks (with an operating system of at least iOS 9.0). As stated in this document, “the 2.4 GHz band is not considered suitable for any business and / or critical enterprise applications.” For wireless networks using Apple devices, companies are recommended to use only 5 GHz frequencies (802.11a / n / ac standard). Nevertheless, the 2.4 GHz band is still the main, used by default for most mobile devices, besides the use of 5 GHz frequencies for Wi-Fi is not allowed in all countries.
The originally entered WEP encryption standard can be relatively easily cracked even with the correct configuration (due to the weakness of the algorithm). New devices support more advanced data encryption protocols WPA and WPA2. Many organizations use additional encryption to protect against intruders. At the moment, the main method of hacking WPA2 is the password selection, so it is recommended to use complex alphanumeric passwords in order to complicate the task of password selection as much as possible. In addition, Wi-Fi standards do not provide encryption of transmitted data in open networks. This means that all data transmitted over an open wireless connection can be listened to by attackers using sniffer programs. Therefore, when using free hot spots, you should not transfer critical data to the Internet.
Wi-Fi benefits:
- worldwide distribution in the world
- guaranteed compatibility
- high data transfer rate
- high reliability
Disadvantages of Wi-Fi:
- interference and interference
- some security issues
- low penetrating power in urban areas
- high energy intensity
- The range and limitations of different countries vary, many countries require the registration of Wi-Fi networks operating outdoors.
Wi-Fi HaLow
Recently at the CES 2016, the Wi – Fi Alliance announced the development of a new wireless standard for the Internet of Things. The new standard is called HaLow and has not yet been approved by the IEEE 802.11ah specification. The certification of the first devices compatible with Wi-Fi HaLow will begin in 2018, but products with the support of the new specification will appear on the market earlier.
To connect the Wi-Fi HaLow will use the unlicensed frequency of 900 MHz. This will significantly increase the penetrating ability of the signal in urban areas, and its radius of action will be much larger than the current wireless standard - up to 1 kilometer. At the same time, the fee for the "long range" is a low signal power. The capacity of Wi-Fi HaLow will be much lower than the maximum Wi-Fi 802.11ac (7 Gb / s), the estimated speed: 50 kbps - 18 Mbps.
According to the alliance, HaLow will make extensive use of existing Wi-Fi protocols, which will ensure a high level of compatibility and security.
Thread
Thread Group , created by OSRAM, QUALCOMM, ARM, Samsung, Nest Labs and others (more than 200 companies) for one purpose - to develop the best way to connect and control devices in the house. This non-profit organization promotes the Networking Protocol (IP-based wireless network protocol) and certifies products. The first public release took place on July 13, 2015. (Revision 2.0). More than 30 devices will be certified in the near future.
Thread, implemented as an add-on to Wi-Fi, has clear limitations for home automation in terms of security and power consumption. The protocol is based on the 6LoWPAN (IPv6 over Low power Wireless Personal Area Networks) standard - an IPv6 interworking standard (new IP version with 128 bit address instead of 32 IPv4 address) over low-power IEEE802.15.4 wireless personal networks. For existing devices that support the IEEE802.15.4 standard, an upgrade to Thread can be made easily. The protocol provides AES banking class security in addition to the mesh network reliability designed specifically for home automation. 250+ authorized devices can be connected to the same network. Wide support for “sleep mode” allows for many years to operate the device even from one AA battery.
Thread Benefits:
- addition to Wi-Fi
- design specifically for home electronics
- reliable self-healing network
- use of proven open standards
- high security
- low power consumption
Disadvantages of Thread:
- interference and interference
- low penetrating power in urban areas
- The range and limitations of different countries vary, many countries require the registration of Wi-Fi networks operating outdoors.
Zigbee
ZigBee is a specification of top-level network protocols, which are regulated by the IEEE 802.15.4 standard, which appeared in 2003. ZigBee and IEEE 802.15.4 describe wireless personal area networks (WPAN, wireless personal area networks). The ZigBee specification is focused on applications that require guaranteed secure data transfer at relatively low speeds and the possibility of long-term operation of network devices from autonomous power sources. ZigBee technology supports not only simple network topologies (point-to-point, tree and star), but also self-organizing and self-healing mesh topology with relay and message routing.
ZigBee is developed by the ZigBee Alliance , which includes more than 300 companies. The Alliance also certifies equipment and devices. On December 16, 2015, the Alliance announced the ratification of ZigBee 3.0, which takes into account the current IoT requirements and supports all previous versions and hundreds of millions of devices already sold.
Advantages of ZigBee:
- ability to self-organization and self-healing
- ease of deployment
- high noise immunity
- high security
- unlicensed frequency
- low power consumption (including “sleep” mode for devices)
Disadvantages of ZigBee:
- low speed
- most of the traffic is spent on the transmission of packets containing address information, synchronization information, etc.
- low penetrating power in urban areas
- insufficiently high level of standardization and the lack of a unified software and hardware platform for developing complex applications
Z-wave
Z-Wave is a patented wireless communication protocol designed primarily for home automation. The technology uses low-power and miniature radio frequency modules that are embedded in consumer electronics and various devices. Z-Wave operates in the frequency range up to 1 GHz and is optimized for transmitting simple control commands with low latency. At the heart of the Z-Wave solution is a self-organizing mesh network (mesh network), in which each node or device can receive and transmit control signals to other network devices using intermediate neighboring nodes.
Z-Wave radio chips are supplied by Sigma Designs and Mitsumi. A distinctive feature of Z-Wave is that all these products are compatible with each other. Compatibility is confirmed by the Z-Wave or Z-Wave Plus certification process. The certification is carried out by Sigma Designs , which has certified over 1350 Z-Wave products. Globally, the protocol is supported by the Z-Wave Alliance , which unites more than 325 manufacturers.
Advantages of Z-Wave:
- design specifically for home electronics
- ability to self-organization and self-healing
- ease of deployment
- high noise immunity
- high security
- unlicensed frequency
- no interference with multiple 2.4 GHz devices
- low power consumption
Disadvantages of Z-Wave:
- low speed
- for solutions with a need for more than 30 devices, Z-Wave begins to become more expensive than cable systems
- low penetrating power in urban areas
- Sigma Designs payments as a technology owner
Of course, in one article it is difficult to describe all existing protocols and technologies with all their diversity. So, for example, ANT + , WirelessHART , Ingenu , Telensa remained behind the scenes.
It should be noted that some manufacturers still seek to somehow bring together technology and their application. Dual-mode modules are available on the market, for example the Nemeus LoRa / Sigfox module . In addition, as the STRYZH-Telematics company claims, the SWIF technology provides full compatibility with LoRa.
Finally, according to Machina Research , the M2M advisory group, by 2024 there will be a total of 27 billion M2M connections in the world, 14% of which will be represented by LPWAN compounds like SigFox and its competitors such as LoRa and Neul.
Comments and amendments please leave in the comments.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/390825/
All Articles