Will Russia save the Earth from an asteroid threat?

An employee of OAO State Academic Rocket Center named after Academician V.P. Makeev, Sabit Saitgaraev, told the TASS news agency about a plan developed in the center for the destruction of asteroids dangerous for the earth with modified intercontinental ballistic missiles.
“Most of the rockets use boiling fuel,” explains Saitgaraev. - Their refueling begins 10 days before the start, so they are not suitable for destroying meteorites similar in diameter to Chelyabinsk, which are detected several hours before approaching the Earth. For these purposes, fit intercontinental ballistic missiles that need to be upgraded. Improved rockets, for example, could be tested on the Apophis asteroid, which in 2036 will get close to the maximum distance from Earth. ”
')
To transform an intercontinental rocket into an interplanetary rocket, it will be necessary to install an additional upper stage. According to the expert, such technologies already exist, and it will only be necessary to test them in action - for example, on small celestial bodies approaching the Earth. Saitgaraev said that design work on this issue is already underway and estimated the cost of such a venture to be several million dollars.
From 2012 to 2015, the European Union, with the participation of Russia, conducted a research project NEOShield -1. In early January, from the Central Scientific Research Institute of Mechanical Engineering (TsNIIMash), which is under the jurisdiction of Roskosmos, it was reported that within the framework of this project, the tasks of studying various methods of influencing space objects dangerous for humanity were distributed among the countries. Russia got to study the possibility of rejecting dangerous asteroids through nuclear explosions. It is planned to deliver nuclear charges to asteroids by ballistic missiles.
Russian scientists believe that a nuclear explosion near a dangerous asteroid is the most effective way to prevent its collision with Earth, although nuclear explosions in space are now prohibited. “If, in connection with the asteroid threat, the question arises of a huge damage or even of the very existence of life on Earth, these prohibitions, naturally, will disappear,” noted TsNIIMash.
The institute also stressed that the safest way to conduct a nuclear explosion in deep space, when there is enough time until the asteroid gets closer to the Earth. “In this case, a nuclear explosion is made so that the asteroid does not collapse into parts, but a part of its substance is released, resulting in a jet thrust, which affects the change in the orbit of the object. This orbital change will fully manifest itself when the asteroid approaches the Earth later - it will be deflected from the planet when it travels to a safe distance, ”explained TsNIIMash.
A similar method of deflecting asteroids is being developed by Americans at the Livermore National Laboratory. True, they do not plan to use nuclear explosions to deflect asteroids - instead, according to their calculations, a rapidly moving artificial object can deflect an asteroid from a dangerous course, and the material knocked out of the asteroid after impact of the object will contribute to this deviation. Scientists confirm their calculations with the results of computer simulation.
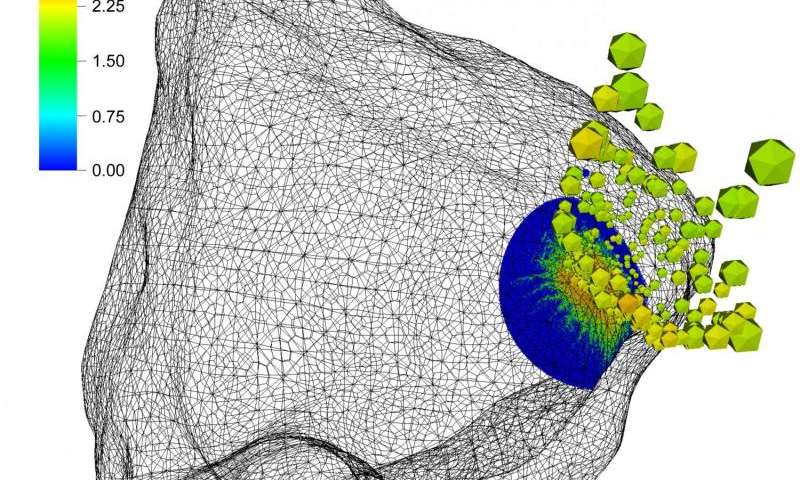
In their model, the 500-meter asteroid Golevka collides with a 10-ton vehicle, flying at a relative speed of 10 km / s. As a result, the asteroid's speed changes by 1 mm / s.
In 2016, the Ministry of Emergency Situations of Russia does not expect any dangerous rapprochement with asteroids. But sooner or later such a rapprochement will occur. The most potentially dangerous for all of us is the asteroid Apophis (99942 Apophis), having a diameter of 393 meters. On April 13, 2029, it will approach Earth at a distance of 38.4 thousand kilometers, which is close to the height of the orbits of geostationary satellites, and its speed of approach will be 7.42 kilometers per second. For comparison, the sensational Chelyabinsk meteorite in 2013 had dimensions of about 20 meters across.
But will Russia save the Earth from asteroids? It is possible that in the near future our country has other priorities. At the end of January, it became known that spending 1.75 billion rubles on the development of technology and software for detecting celestial bodies threatening the Earth was excluded from the project of the Federal Space Program for 2016–2025. On the other hand, Bruce Willis is already a little old, Superman is busy with Batman, and Wolverine is retiring. Then who, if not us?
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/390579/
All Articles