Engineers have developed a generator without moving parts, embedded in the sole
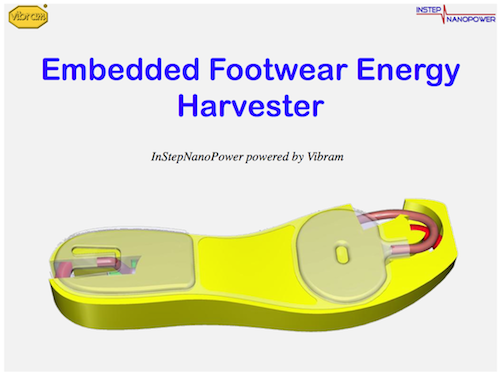
Engineers from the University of Wisconsin-Madison have developed an electricity generation system that fits in the sole of the boot. At the same time, unlike similar projects , the system has no mechanical moving parts. The electricity generated when walking is proposed to be used for charging gadgets.
Such a charger is well suited for military applications, tourists and residents of remote regions with problems with constant power supply.
')
According to one of the engineers, Tom Krupenkin, the power of the device in one boot can reach 10 W - that is, in the amount of 20 watts. According to the scientist, usually this energy is dissipated in the form of heat, while even 10% of this energy is enough to charge a typical smartphone.
The technology works on the principle of "reverse electrowetting" - a process that Krupenkin paired with Ashley Taylor opened in 2011 precisely in search of converting mechanical energy into electrical energy to collect the energy of human movement.
The device consists of two flat plates between which the conductive fluid circulates. Microscopic holes are made in the bottom plate and an electrode with insulation is connected to it. Under pressure, gas forms gas through the microperforations, which forms bubbles, which then collapse into larger bubbles. This repetitive process, occurring at high speed, moves the fluid around the circuit, which leads to the generation of electric current due to electrowetting .
The power of the experimental setup is 10 watts per square meter. Researchers claim that this power can be increased 1000 times. According to them, this bubble technology shows the highest energy density per unit area among devices for converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
By embedding such a system in shoes, you can accumulate energy in the battery and then charge the device. Or, as engineers suggest, integrate a WiFi repeater into the sole, which will reduce the power consumption of the smartphone by reducing the required power for transmitting the signal.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/390191/
All Articles