Review and comparative testing of PC "Elbrus 401 ‑ PC". Part One - Hardware
An interesting guest recently visited us - a domestic personal computer with a 4-core Elbrus processor of the original architecture developed by the MCST company. After getting acquainted with its features and performance measurements, I would like to share my impressions and results.


')
Due to the large volume, the material is divided into four parts:
Enjoy reading!
First of all, we will clarify who buys this equipment and why. Computers of domestic development are used primarily in the defense industry, as well as everywhere where increased requirements are imposed on information security - where to put foreign counterparts completely or very undesirable. Recently, cautious steps have also been taken to introduce these products into the civilian sphere, but due to small production volumes and, accordingly, “biting” prices, few can afford this other than the military.
Specifically, our company bought this computer as part of an experiment. We designed and assembled a small series of operator consoles for the equipment simulation and debugging stand, and it was decided to build one of the consoles on the basis of the new Elbrus - to evaluate its performance and software compatibility. It should be noted that we already had a long experience of using earlier products of the MCST company, and, to be honest, neither the hardware nor the software had ever aroused any particularly warm feelings (you will learn why in the fourth part of the article). However, the novelty promised to be very interesting.
So, at the end of September 2015, our company addressed a request to the manufacturer - to the Moscow Center of SPARC-technologies. At that time, the conditions were as follows:
To understand where such a price level comes from, several factors should be kept in mind. Firstly, in addition to the cost of production of microcircuits, a significant proportion falls on the reimbursement of research and development costs and certification - the more significant the smaller the circulation, and they are still very small. Secondly, the processor model installed in the Elbrus 401 ‑ PC personal computer is the same 18918 chip (Elbrus-4), which is also used in the 4-processor servers of the MCST "Elbrus-4.4" and BitBlaze Elbrus 4400. There is a crystal level quad processor with RDMA channels for machine-to-machine interaction. If you look at similar offers from Intel in the Xeon MP line, skipping over 9000 price tags, you will get $ 1000–1500 for the younger models - presumably, the price for Elbrus for the end customer is exactly the same, assuming that the declared cost is 4 ‑ processor server is 8000 dollars, and the motherboard with the case and other stuff is also not free. And this is despite the fact that the production volumes of the MCST are a couple of orders of magnitude lower than those of world famous brands.
The computer complex is shipped in authentic packaging, the heat and clips of which eliminate any doubts about the origin and authenticity of the product.
Shipping container and its contents



Inside the box are found:
According to the documents, the computer is assembled at the Izhevsk Radio Factory, just a couple of kilometers from the production of Kalashnikov assault rifles and other harsh things; well, that explains a lot. But seriously, this company has a rich history of production of on-board computers and other radio equipment for the space industry.
The appearance of the system unit


The case of the Elbrus 401 ‑ PC system unit is an ordinary In-Win EMR034 mini-tower. And this is perhaps the only aesthetic flaw: it’s not even the fact that the domestic worker is dressed in a cheap robe of Chinese tailoring, but simply the look of this clothes doesn’t correspond to the status of a 4000-dollar computer. What prevented me from taking an inexpensive, but at least outwardly effective body, or elegantly strict (without the ridiculous combination of a glossy front with matte sides), remains a mystery to the author. After all, designers have had enough instinct to put quite decent components inside the system unit, for which at least it is not a shame.
Internal view of the system unit

There are no warranty seals on the case, so we can remove the wall and make sure that the insides in general correspond to the description:
Insignificant discrepancies between specifications and reality are possible as a result of a natural renewal of the market range of components: for example, the documentation stated a video card based on an older Radeon HD 6450 processor, other keyboard and mouse models were mentioned.
The layout of the elements on the motherboard
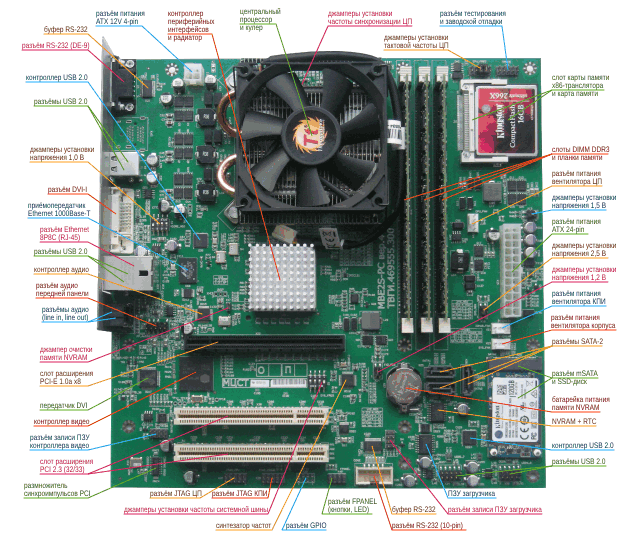
The Elbrus-4C 4-core processor (18918), formerly known as the Elbrus-2S, serves as the heart of the Elbrus 401-PC computer, as the model name suggests. It was decided to reassign the number index for marketing reasons. equal to the number of cores, and the role of the letter S, meaning system-on-chip constructive, is now performed by the Russian “C” (“system on chip”; the MCST interprets this term in its own way). There are several modifications that differ in frequency: 800 MHz (1891BM8), 750 MHz (18918), 600 MHz (18918), - the first of them is installed in the computer. Switches on the motherboard allow setting abnormal frequencies:
A few more switches serve to increase or decrease the supply voltages, but we didn’t experiment with overclocking, - who really wants to quickly, the announced Elbrus-8C can wait: the nominal frequency will be 1,300 MHz, and there will be twice as many cores.
Motherboard block diagram

The system exchange controller (“north bridge”) is embedded in the processor chip. It contains a 3-channel DDR3-1066 (PC3‑8500) memory controller with error correction support. The computer comes with 8-gigabyte registers of register memory, organized in the form of two banks. The maximum amount of local memory of each processor is 48 GB, but we did not check whether the “desktop” board is able to digest more than the 24 GB that it is installed into by the manufacturer. One thing is clear: since this is a single-processor computer, the interprocess communication channels remain unused, as well as the second IOLink I / O channel, intended either for communication with the peripheral interface controller or for remote access to the memory of other machines.
List of PCI devices ( fully on Pastebin )
List of USB devices ( fully on Pastebin )
The peripheral interface controller (“south bridge”) on the 1991VG1YA chip implements PCI and PCI Express buses, contains ATA 100 MB / s and SATA 300 MB / s controllers, as well as Ethernet 100/1000 Mbit / s. USB 2.0 and RS ‑ 232 interfaces are implemented by external controllers, as well as support for connecting the display, speakers and microphone. It is noteworthy that the controller of serial and parallel ports implements the IEEE 1284 interface, but there is no LPT port on the board. In addition, there is a layout for GPIO, but the connector itself is not soldered.
Since all other computer components are consumer goods, it makes no sense to consider them in detail. We note only one feature: with the overall democracy of the whole structure and even explicit permission to replace the external and internal components with any similar ones, the solid-state disk is screwed to the motherboard and sealed: paint is applied to the nuts. This greatly complicates the experiments, since all the system files and user data are located on this disk, we could not extract and make a backup on another computer, and we could not use any Live x86 disk, as well as launch full-time system in single-user mode with the connection of disks only for reading.
Sealed SS mount

Update as of 09.02.2016. The comments recall the existence of OST 107.460091.014 “Threaded connections. Ways and types of protection from self-loosening ”, suggesting that the RAC in the first place can serve as an additional stopper for nuts. It is possible that this is the case, but after all, there are alternative solutions in the world of fasteners that allow reusable use.
Also criticism deserves the cooling system. On the one hand, it does its job: even under long-term load, the processor's radiator does not heat up above 33 ° C (software for monitoring internal core temperature, such as mbmon or lmsensors , we were not found), and the fans of the south bridge and the case are simply not installed - probably, they are required only in severe climatic conditions. On the other hand, this system produces noise not so much, but it cannot claim the role of a quiet computer. We did not find out who is most guilty - the fan in the power supply or the fan on the processor - but note that all the connectors on the motherboard have 4 pins (which hints at the pulse speed control of the fan rotation speed), and the processor has a 3 ‑ pin cooler
Of the most minor flaws: on the motherboard, the assignment of the contacts of the front panel connector to which the power and reset buttons are connected, as well as the power and drive activity indicators are not signed. If you disconnect the cables, then it’s almost impossible to figure out what's what, it’s almost impossible - the enemy will not be able to turn on the computer, the country can sleep peacefully.
The documentation is made “according to the charter”: exclusively in hard copy, with a cover of wrapping paper, with handwritten marks, where appropriate. The hardware is described in some detail there, thanks to which you had the opportunity to familiarize yourself with the above schemes. But when it comes to the software part, the entire instruction manual fits on two pages and is formulated in the style “Give the order to shut down, wait until the execution of the order is completed and turn off the computing system” (how to act if the unconscious machine fails to follow the order, not reported; even such details, with what command or with what buttons to give this order, and to whom specifically to give it, perhaps, it is necessary to issue a general order for the garrison?). Coverage of a larger share of questions is reduced to sending to other documents, which, apparently, must be requested separately, - the documentation is not laid out in public access.
In the next part of the article we will look at the software - the Elbrus operating system with its applications.


')
Due to the large volume, the material is divided into four parts:
- hardware overview:
- Software review :
- launch of the operating system;
- staff software;
- development tools overview :
- architecture features;
- machine language;
- development tools;
- performance benchmarking :
- description of competing computers;
- benchmark results;
- summarizing.
Enjoy reading!
Acquisition
First of all, we will clarify who buys this equipment and why. Computers of domestic development are used primarily in the defense industry, as well as everywhere where increased requirements are imposed on information security - where to put foreign counterparts completely or very undesirable. Recently, cautious steps have also been taken to introduce these products into the civilian sphere, but due to small production volumes and, accordingly, “biting” prices, few can afford this other than the military.
Specifically, our company bought this computer as part of an experiment. We designed and assembled a small series of operator consoles for the equipment simulation and debugging stand, and it was decided to build one of the consoles on the basis of the new Elbrus - to evaluate its performance and software compatibility. It should be noted that we already had a long experience of using earlier products of the MCST company, and, to be honest, neither the hardware nor the software had ever aroused any particularly warm feelings (you will learn why in the fourth part of the article). However, the novelty promised to be very interesting.
So, at the end of September 2015, our company addressed a request to the manufacturer - to the Moscow Center of SPARC-technologies. At that time, the conditions were as follows:
- the company itself, the MCST only deals with legal entities, but is quite ready to release the goods by the piece;
- computers are collected in batches: when a sufficient number of applications are collected from those who wish, the price is announced and contracts are concluded - we were lucky to have time for the final receipt of orders for the first batch and get into the plan for October – November, so already on December 1 the finished computer was at our disposal ; in addition, a certain number of units of goods are made prozapas, and someone will be lucky enough to do without waiting and pay at the old price;
- The “Elbrus 401 ‑ PC” system unit comes with a monitor, keyboard and mouse, so far you have to buy all this “computing complex”, as the MCST officially calls it, even if you only need a motherboard with a processor (according to unofficial estimates, such a gentleman's set can be 2/3 full price);
- price per unit - was about 250 thousand rubles ($ 4,000, as promised earlier ) at the time of order ; forecasts for the future are still very cautious, but there is reason to believe that almost everything is determined by currency components, which means it will only increase in rubles, even if the price tag in dollars becomes thinner with an increase in production volumes.
To understand where such a price level comes from, several factors should be kept in mind. Firstly, in addition to the cost of production of microcircuits, a significant proportion falls on the reimbursement of research and development costs and certification - the more significant the smaller the circulation, and they are still very small. Secondly, the processor model installed in the Elbrus 401 ‑ PC personal computer is the same 18918 chip (Elbrus-4), which is also used in the 4-processor servers of the MCST "Elbrus-4.4" and BitBlaze Elbrus 4400. There is a crystal level quad processor with RDMA channels for machine-to-machine interaction. If you look at similar offers from Intel in the Xeon MP line, skipping over 9000 price tags, you will get $ 1000–1500 for the younger models - presumably, the price for Elbrus for the end customer is exactly the same, assuming that the declared cost is 4 ‑ processor server is 8000 dollars, and the motherboard with the case and other stuff is also not free. And this is despite the fact that the production volumes of the MCST are a couple of orders of magnitude lower than those of world famous brands.
Hardware
The computer complex is shipped in authentic packaging, the heat and clips of which eliminate any doubts about the origin and authenticity of the product.
Shipping container and its contents



Inside the box are found:
- system unit ("subunit" in the terminology of the manufacturer);
- Dell E2314H Monitor;
- keyboard Logitech K120 or equivalent;
- Logitech M100 mouse or equivalent;
- manual;
- product form;
- packing list with a list of the contents of the box.
According to the documents, the computer is assembled at the Izhevsk Radio Factory, just a couple of kilometers from the production of Kalashnikov assault rifles and other harsh things; well, that explains a lot. But seriously, this company has a rich history of production of on-board computers and other radio equipment for the space industry.
The appearance of the system unit


The case of the Elbrus 401 ‑ PC system unit is an ordinary In-Win EMR034 mini-tower. And this is perhaps the only aesthetic flaw: it’s not even the fact that the domestic worker is dressed in a cheap robe of Chinese tailoring, but simply the look of this clothes doesn’t correspond to the status of a 4000-dollar computer. What prevented me from taking an inexpensive, but at least outwardly effective body, or elegantly strict (without the ridiculous combination of a glossy front with matte sides), remains a mystery to the author. After all, designers have had enough instinct to put quite decent components inside the system unit, for which at least it is not a shame.
Internal view of the system unit

There are no warranty seals on the case, so we can remove the wall and make sure that the insides in general correspond to the description:
- microATX-MBE2S ‑ PC v4 motherboard with an integrated Elbrus-4C processor and Thermaltake Slim X3 II cooling system;
- Three levels of Kingston ValueRAM DDR3‑1600 registered ECC RAM with 8 GB capacity each (KVR16R11D8 / 8);
- 16 GB Kingston CompactFlash ultimate 266X memory card (CF / 16GB-U2) - for the needs of x86-broadcast;
- Kingston SSDNow mS200 solid-state drive with a capacity of 120 GB (SMS200S3 / 120G) - the main data carrier;
- WD Caviar Black 1 TB hard drive (WD1003FZEX-00MK2A0) - additional storage media that is not used by default;
- optical drive Lite-On iHAS124;
- Gigabyte Radeon R5 230 video card (GV-R523D3-1GL) - the main output device in addition to the integrated controller Silicon Motion SM718;
- power supply PowerRebel (PowerMan) IP ‑ S450HQ7‑0 rated power 450 watts.
Insignificant discrepancies between specifications and reality are possible as a result of a natural renewal of the market range of components: for example, the documentation stated a video card based on an older Radeon HD 6450 processor, other keyboard and mouse models were mentioned.
The layout of the elements on the motherboard

The Elbrus-4C 4-core processor (18918), formerly known as the Elbrus-2S, serves as the heart of the Elbrus 401-PC computer, as the model name suggests. It was decided to reassign the number index for marketing reasons. equal to the number of cores, and the role of the letter S, meaning system-on-chip constructive, is now performed by the Russian “C” (“system on chip”; the MCST interprets this term in its own way). There are several modifications that differ in frequency: 800 MHz (1891BM8), 750 MHz (18918), 600 MHz (18918), - the first of them is installed in the computer. Switches on the motherboard allow setting abnormal frequencies:
- for cores - 750, 800 (default), 900, 1000 MHz;
- for processor I / O channels - from 300 to 650 MHz in 50 MHz increments (default is 500 MHz);
- for system bus - from 340 MHz to 500 MHz (default) in 33 MHz increments;
- for core synchronization - 100 or 125 MHz (default).
A few more switches serve to increase or decrease the supply voltages, but we didn’t experiment with overclocking, - who really wants to quickly, the announced Elbrus-8C can wait: the nominal frequency will be 1,300 MHz, and there will be twice as many cores.
Motherboard block diagram

The system exchange controller (“north bridge”) is embedded in the processor chip. It contains a 3-channel DDR3-1066 (PC3‑8500) memory controller with error correction support. The computer comes with 8-gigabyte registers of register memory, organized in the form of two banks. The maximum amount of local memory of each processor is 48 GB, but we did not check whether the “desktop” board is able to digest more than the 24 GB that it is installed into by the manufacturer. One thing is clear: since this is a single-processor computer, the interprocess communication channels remain unused, as well as the second IOLink I / O channel, intended either for communication with the peripheral interface controller or for remote access to the memory of other machines.
List of PCI devices ( fully on Pastebin )
00: 00.0 PCI bridge: MCST PCI-Express Bridge (rev 01) 00: 01.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation Device e3e3 (rev 01) 01: 00.0 PCI bridge: MCST PCI-Bridge (rev 05) 01: 01.0 Ethernet controller: Intel Corporation Device 4d45 (rev 01) 01: 02.0 IDE interface: Intel Corporation Device 4d49 (rev 80) 01: 02.1 Multiport serial controller: Intel Corporation Device 0002 (rev 05) 01: 02.2 Communication controller: Intel Corporation Device 8000 01: 02.3 Multimedia audio controller: Cirrus Logic Crystal CS4281 PCI Audio (rev 01) 01: 03.0 SATA controller: Intel Corporation Device 4748 01: 04.0 USB controller: Intel Corporation Device 554f 01: 04.1 USB controller: Intel Corporation Device 5545 02: 03.0 VGA compatible controller: Silicon Motion, Inc. Device 0718 (rev a0) 03: 00.0 VGA compatible controller: Advanced Micro Devices [AMD] nee ATI Caicos [Radeon HD 6450] 03: 00.1 Audio device: Advanced Micro Devices [AMD] nee ATI Caicos HDMI Audio [Radeon HD 6400 Series]
List of USB devices ( fully on Pastebin )
Bus 001 Device 001: ID 1d6b: 0002 Linux Foundation 2.0 root hub Bus 001 Device 002: ID 04b4: 6560 Cypress Semiconductor Corp. CY7C65640 USB-2.0 "TetraHub" Bus 001 Device 003: ID 04b4: 6560 Cypress Semiconductor Corp. CY7C65640 USB-2.0 "TetraHub" Bus 002 Device 001: ID 1d6b: 0001 Linux Foundation 1.1 root hub
The peripheral interface controller (“south bridge”) on the 1991VG1YA chip implements PCI and PCI Express buses, contains ATA 100 MB / s and SATA 300 MB / s controllers, as well as Ethernet 100/1000 Mbit / s. USB 2.0 and RS ‑ 232 interfaces are implemented by external controllers, as well as support for connecting the display, speakers and microphone. It is noteworthy that the controller of serial and parallel ports implements the IEEE 1284 interface, but there is no LPT port on the board. In addition, there is a layout for GPIO, but the connector itself is not soldered.
Since all other computer components are consumer goods, it makes no sense to consider them in detail. We note only one feature: with the overall democracy of the whole structure and even explicit permission to replace the external and internal components with any similar ones, the solid-state disk is screwed to the motherboard and sealed: paint is applied to the nuts. This greatly complicates the experiments, since all the system files and user data are located on this disk, we could not extract and make a backup on another computer, and we could not use any Live x86 disk, as well as launch full-time system in single-user mode with the connection of disks only for reading.
Sealed SS mount

Update as of 09.02.2016. The comments recall the existence of OST 107.460091.014 “Threaded connections. Ways and types of protection from self-loosening ”, suggesting that the RAC in the first place can serve as an additional stopper for nuts. It is possible that this is the case, but after all, there are alternative solutions in the world of fasteners that allow reusable use.
Also criticism deserves the cooling system. On the one hand, it does its job: even under long-term load, the processor's radiator does not heat up above 33 ° C (software for monitoring internal core temperature, such as mbmon or lmsensors , we were not found), and the fans of the south bridge and the case are simply not installed - probably, they are required only in severe climatic conditions. On the other hand, this system produces noise not so much, but it cannot claim the role of a quiet computer. We did not find out who is most guilty - the fan in the power supply or the fan on the processor - but note that all the connectors on the motherboard have 4 pins (which hints at the pulse speed control of the fan rotation speed), and the processor has a 3 ‑ pin cooler
Of the most minor flaws: on the motherboard, the assignment of the contacts of the front panel connector to which the power and reset buttons are connected, as well as the power and drive activity indicators are not signed. If you disconnect the cables, then it’s almost impossible to figure out what's what, it’s almost impossible - the enemy will not be able to turn on the computer, the country can sleep peacefully.
The documentation is made “according to the charter”: exclusively in hard copy, with a cover of wrapping paper, with handwritten marks, where appropriate. The hardware is described in some detail there, thanks to which you had the opportunity to familiarize yourself with the above schemes. But when it comes to the software part, the entire instruction manual fits on two pages and is formulated in the style “Give the order to shut down, wait until the execution of the order is completed and turn off the computing system” (how to act if the unconscious machine fails to follow the order, not reported; even such details, with what command or with what buttons to give this order, and to whom specifically to give it, perhaps, it is necessary to issue a general order for the garrison?). Coverage of a larger share of questions is reduced to sending to other documents, which, apparently, must be requested separately, - the documentation is not laid out in public access.
In the next part of the article we will look at the software - the Elbrus operating system with its applications.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/390095/
All Articles