Some of the history of specialized military computers
Mid-twentieth century, USSR. The main attention was paid to the creation of universal computers for solving complex mathematical computational problems, these were stationary machines that were oriented towards sequential or batch problem solving, apart from the real time scale and dynamic changes in the parameters of environmental objects. But by the end of the 50s, the Ministry of Defense of the country had an interest in using such computers to solve information processing and control problems in military systems. But immediately there were difficulties associated with the shortcomings of such universal machines when used in military systems for solving real-time control tasks. Therefore, the beginning of the rapidly developing direction of computing technology for military purposes.

Two classes of computers were clearly distinguished: stationary and mobile. Different types of customers contributed to the development of mobile computer types, since it was planned to use them in the ground, aviation, marine, and missile, and other systems in the defense industries and enterprises. Digital computer technology began to be used for anti-aircraft systems. and missile defense, to control outer space and control flights in aviation and in space. Stationary worked indoors, and mobile, therefore, had to be transportable.
Due to the secrecy of the "neck", the exchange of information on the development of specialized computers between specialists in various industries and enterprises in the USSR was sharply limited, there was almost no information on the technical characteristics and principal features of such specialized machines across the border. The development of computers was costly because of this, since a great many architectures of such original machines were created. The centralized industry of electronic components for computers, too, was not.
')
Project Mobile Computing Point (PVP) or object "Platform"
Back in 1960, a series of mobile computers was developed and created for the army and frontline link, codenamed “Beta,” but the work never began.

mobile computing complex "Beta-3M"
In 1962, the mobile computer needed for the army was neither in the Ministry of Defense nor in the USSR. The General Staff issued the Directive as soon as possible (for the year) "... to design, order production, debug and put into operation the mobile Military Center, it was supposed to take one of the USSR-made computers and simply adapt it to the specific operating conditions. It is also necessary was "... to develop, program and debug a set of tasks for use during the command and control exercises (command and staff exercises) on the front (district) scale, with the participation of troops and military equipment, for command and staff games of headquarters, military academies and other educational events. "
The developers were oriented on the American Mobidik project (although already in the USSR a mobile, highly specialized Kurs-1 computer was developed for processing information from radar nodes, but everything was secret).

Here are some of the requirements for such a “Platform”: ensuring the necessary performance, reliability of work after moving along dirt roads, 100 hours of work in non-stop conditions, climatic conditions were set according to temperature from -30 to + 40 ° .
At the first stage, a suitable second-generation universal domestic computer on semiconductor elements was chosen, thanks to which the dimensions and power consumption of computers decreased, while such indicators as speed, the amount of RAM increased.
The computer was selected "Hrazdan-2" (produced in Yerevan, YerNIIMM plant). Started upgrading the machine. In order to ensure its operation in the "field" conditions, for operation in the troops and to make it mobile, it was necessary to increase its reliability, constructively modify the computer to place the equipment in a confined space, while ensuring its safety and operability during movement, protected from climatic conditions. impact. To all this it was necessary to choose the entire infrastructure of the mobile VC.

"Razdan"
This included a thermally insulated all-metal van-semi-trailer type 828 for equipment placement, a truck-mounted saddle of the type ZIL-157, powerful air conditioning, a mobile diesel power station with a power of 30 kW in a mobile version, with a fuel consumption of 8 liters / hour, connected radio and telegraph equipment.
A mobile computer center was created, two Hrazdan-2 computers were installed in one body, and all data preparation devices, communications, control and test equipment, various stands, an extended set of spare parts, cables and other equipment housed in the body of an army KUNG mounted on the chassis ZIL-157.
Climate protection to maintain the required temperature and humidity in the body was provided by the following main measures: an air conditioner with high cooling and heating capacity was installed in the body, computer racks of secondary power sources were carried out, additional fans were installed in a separate rack with an independent ventilation and cooling system. The optimum mode of operation of a computer at a temperature of + 20 to + 30 ° C.


In 1964, the modular EC "Platform" was taken to the "supply". After that, the project was still being upgraded, the OP of each computer was doubled due to a backup ferrite cube, a ROM on the ferrite cores was additionally built in, the implementation of the joint operation of two computers became possible.
cube of RAM on ferrite cores
The integration of two computers in the "Platform" in the hardware, software, information aspects was made for the first time in the USSR. In 1963-1968, the Mobile Platform Center was the first and only CC of this type.
COMPUTER "Granit"
A specialized computer was used for statistical processing of a large number of observations and was created by order of the Main Artillery Directorate of the USSR Ministry of Defense to increase the effectiveness of artillery firing. In 1957 she was sent to one of the artillery grounds of the Ministry of Defense. Used to shoot artillery guns.

The computer consisted of a computing device accumulating the sum of paired works, a set of devices for preparing a punched tape (35 mm wide film), an output perforator and a printing device, the power consumption was 4.5 kVA. I took such a computer 30 square meters.
Computer "Maple" and computing systems "Maple-1" and "Maple-2"
Starting from 1962 to 1968, the Klen computer and the Klen-1 and Klen-2 computer systems were created at the Research Institute of Electronic Mechanical Engineering (NIEM), and a distributed satellite information processing system worked on them. The goal of this development was to automate the processing of telemetric information coming from artificial earth satellites.
The unicast parallel action of the computer "Maple" operated with numbers, presented in a format with a comma fixed before the high-order bit. The numerical data was presented in a 27-bit grid, where 23 bits were occupied by the digital part, one digit was the sign of the number, and three bits were allotted for control modulo two. The team occupied 33 binary digits, 7 of them to provide an operation code, 16 - addresses, and 4 bits - a configuration code of numbers, 3 - for the address modification code, 3 bits - for control modulo two and three. Capacity of main memory of computer 8192 (8K) 27-bit words. The execution time of short operations, such as additions, transition operations was 4.5 μs, multiplication was performed in 25.5 μs. The system of computer commands "Maple" included 83 teams, which feature was the ability to work with different configurations of numbers.
In the computer "Maple" was the traditional input device with punch cards, 27 bit channels for communication with external subscribers, for data output - a printing device.
+5 to +40 degrees Celsius - temperature range for optimal machine operation.
Especially for the Klen machine, a pulse-potential system of elements with diode-resistive logic and a maximum operating frequency of 660 kHz was developed. The delay time of the logical elements of the system is 50 ns, the delay time of the elements of the system used in serial circuits is 20-30 ns. In the chains of adders and controls, special logic elements were used.
RAM in a computer was used on ferrite cores of type BT-7 with a cycle time of 6.0 μs and a reading time of 2.25 μs. As a long-term memory, a memory device on oxypher cores with constant firmware was used, the DZU cycle time was 4.5 μs, and the read time was 2.25 μs.

The capacity of the program DZU block could be from 8192 to 65536 codes, the magnetic random access memory (MOZU) of programs with a capacity of 4096 codes was used to debug programs before inserting into the DZU.
In the computer "Maple" there could be four blocks of the MOZU of numbers, with 8192 numbers in each block. The work of such units could be combined.

EVK "Maple-1" and "Maple-2" - modifications of the computer "Maple" with extended RAM and DZU with minimal additions in commands exchange with external devices. Magnetic tape memory and a developed system of external devices appeared as part of both complexes.

Computers differed only in the different configurations of internal chargers, tape drives and input-output devices. External devices "Maple-1" - input device for punched cards VU-700-2, 2 alphanumeric printing devices ATsPU-128-2. The external devices "Klen-2" included 4 printers ATsPU-128-2, the perforator of the PR results, the perforator tape PL-20-2.
From remote sources, data came from external highways at the Klen-1 computer complex, they were sorted, compressed, and eliminated redundant data. After that, the pre-processed data were transferred to the EEC "Maple-2", here they were final processing, cataloging, storage and issuance at the request of users.
Specialized computer "Diana-1", "Diana-2" .
S.A. Lebedev and the ITM team paid special attention to the work related to the country's defense, conducted research and development on automatic data acquisition from the radar (radar station) and automatic tracking of flying targets. An experiment was conducted on the simultaneous accompaniment of several real planes while anticipating the calculation of their trajectory. The Diana-1 computer was used for data entry in digital form, and the Diana-2 computer was used for tracking the targets. Such an experiment laid the foundation for the development of radar and missile systems on a new information - computational basis.
"Diana-1" -sequential machine with switched software processing, intended to work as part of the guidance systems of fighter aircraft at the target. The machine carried out automatic data acquisition from the radar with the selection of the object from noise, transferred them to a digital form and gave out the trajectories of movement of several targets on the screens.
“Diana-2” - a computer with a fixed comma, a digit capacity of 10, a unicast command system, with a number of commands - 14, a command memory of 256, a constant memory, random access memory on magnetostrictive delay lines.
Family of specialized computers "Karat"
In 1976, the unified Karat computer systems were accepted for supply for the USSR Navy. These were compact, reliable computers with high functional parameters. Their creation radically changed the situation in the marine instrument making.

The history of the creation of a unified computer "Karat" began in 1963 in the Kiev Research Institute of Radio Electronics under the direction of Plotnikov (the chief designer of the family of specialized computers "Karat"). In 1963, Plotnikov’s laboratory presented flat micromodules (PMM) as basic elements for new developments. It was the first serial-suitable universal element created in the USSR, which provided the opportunity to create computers and other digital equipment at a new, rather high level.
The thin-walled aluminum case of a flat micromodule was 17.5x9.5x6.3 mm, with a weight of 2 grams, such a PMM was assembled from microelements that were mounted on both sides with a printed microboard (9x17 mm), pin pins were installed perpendicular to the board in 4 mm increments.
But for the fleet, computers with elements smaller than the PMM were needed, therefore imperfect integrated circuits of domestic production began to be used to build computers. In the laboratory, Plotnikov began work on the creation of multichip integrated circuits. It was a completely new direction in the development of computer hardware components.

Hybrid large integrated circuits "Varduva" (GBIS) - this is how new multichip chips were named. The first model of "Karat" was a small-sized 24-bit machine on the GBIS "Varduva". The circuits of the functional units of the microcircuits were developed by Soviet scientists, proceeding from the computer logic circuits (8 register bits, 2 ALU bits, etc.) were placed in one case. This development for many years ahead of the creation of multi-chip circuits abroad (“multi-chips”).

The machine was used in more than 60 types of systems developed by enterprises of four ministries. In simple systems, a computer could be used in a minimal modification, and on the largest modern ships with several systems on board, 15 or more Karat computers could be found in the maximum version. In 1981, 15 modifications of the “Karat” family of cars were developed, software of 5 million teams was prepared. To process information from radar systems with phased antenna arrays, a modification of “Carat” was developed with a speed of 2.5 million operations per second. Later, the Karat-KM-E modification was developed on sectional microprocessor large integrated circuits. About 2 thousand cars were manufactured at the factories in the USSR.
Computer "Radon"
In 1964, the development of a computer for use in the air defense of the USSR was completed at the Research Institute of Electronic Mathematical Machines. It was a potential pulse with galvanic and transformer connections of second-generation computers based on transistors P16 and P601.
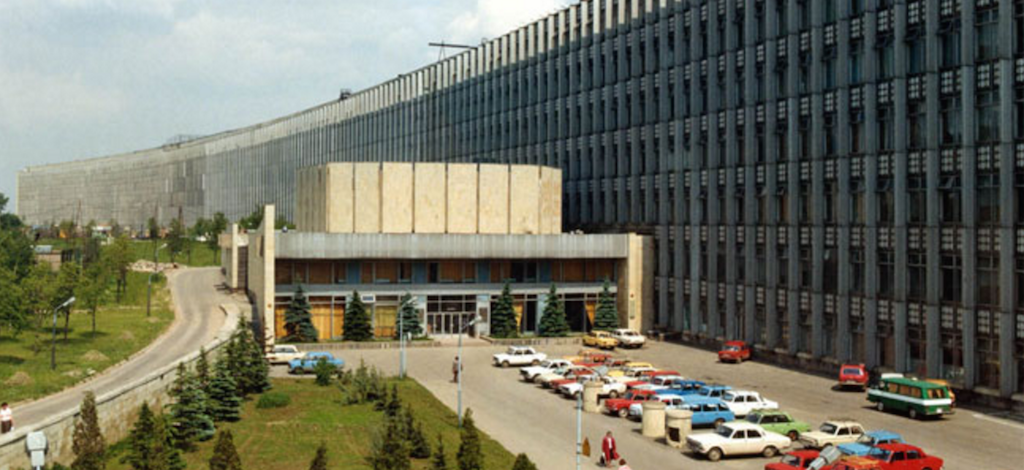

Scientific Research Institute of Electronic Mathematical Machines
The design of the computer consisted of 16 racks, each of the racks had its own power supply and control units, an interconnecting panel, including 320 “sheet” sockets (20 contacts each), which were connected by plugs located on the end of the cells containing from 4 to 8 items.

block diagram of the computer "Radon"
It was developed several modifications of the computer "Radon", which differed in the capacity of RAM, ROM. It was a two-machine complex with a bus connection organization. The computer was unicast, the commands were 24 (2 control), the operands were 20 (2 control), fixed point operations, the number of instruction codes was 64. Each computer processor had access to its memory, as well as to the memory of a paired computer , which made it possible to work not only in the two-machine mode, but also in the two-processor mode. Two computers were connected to a common exchange highway for communication with system control devices. For the initial loading, testing and display of information for analysis on the print used the periphery of the machine itself.
The Radon computer occupied an area of 150 square meters. It was reliable and with increased speed.
For the first time in the USSR in the car were implemented:
Acacia system
In 1982, the Acacia digital fire control system was developed. The system was created to generate data for the firing of the Granat strategic cruise missiles from submarines and submarines; the systems included 2 Archa, 2 RAM devices, 2 long-term memory devices, 2 data exchange devices, 2 reserve control devices. In order to increase the reliability of the Acacia system, all devices had a reserve, the reservation was made automatically.
The Arka CVM (specialized computer) was designed to work with the Ataka PCVM and was used to increase the capacity of the Ataka computer system.

The speed of such a PC for the mode of operation: with registers of 500 thousand short operations per second, while the register memory is 167 thousand short operations per second. Power consumption 1200 watts. The machine "Arka" had two exchange devices. Each device consisted of 8 consecutive channels. One exchange device with parallel multiplex channel. The average time between failures is 2000 hours.
CVM "Attack"

specialized digital computer "Attack" (MVM-012)
The specialized attack machine “Ataka” (MVM-012) was created in 1974 at the NPO Agat. The dimensions of such a machine are 1800x1076x516 mm, the occupied area is 0.65 square meters. The Ataka CVM consisted of two cabinets, which were interconnected mechanically and electrically. The machine consisted of a command device, a command interrupt device, an exchange device, an arithmetic unit, microprogram control blocks, 16 general-purpose buffer registers, 16K words ferrite random-access memory, a hardware control device, a monitoring and control panel, and a power supply device.

The machine used a binary system for representing numbers, with a fixed comma, the number of digits - 32. Work with words of double length (64 bits), with half words (16 bits) and with eight-digit alphabetic information is provided.The command system was dual-core, the number of operations was 56, of which 16 were arithmetic operations, 7 logical operations, 19 transfer operations, 6 shift operations, 8 control operations.
It should be noted that the central computer was able to increase memory up to 256K words with connecting external memory devices 182-3 - RAM 64K, 183 - DZU 128K (2X64K), 184 - RAM 32K and DZU 64K or any other devices having electrical and information compatibility with MVM-012.
2 parallel, 2 serial exchange channels were provided. The exchange rate for the serial channel was 20 thousand words per second, for the parallel channel - 94 thousand words per second.
The power consumption from the mains is 1.5 kW, power is supplied from a three-phase ship AC mains with a voltage of 220 V and a frequency of 400 Hz. Network fluctuations are allowed: ± 5% with long-term deviations and from + 13% to -25% with short-term voltage deviations, and from + 4% to -6% in frequency.
Terms of Use:
The car was produced until 1990, 255 Ataka CVTs were manufactured.
Computer "Harp"
The development of the machine was started in 1979 and was intended to work in various ship control systems, as a controlling link in real time. The power supply of the machine was carried out from the ship's three-phase network 220V, 400 Hz, the power consumption was 1.7 kW. For cooling, a forced-air and exhaust ventilation with an inlet air temperature of 18 ° C was used. It was a computer with a binary system for representing numbers with a fixed and floating point, the speed was 550 thousand short operations per second when accessing operands in RAM, 1100 thousand short operations when accessing buffers and registers. The number of digits is 32, it was possible to work with words of double length (64 digits), with half words (16 digits) and with octal alphabetic information.
Together with the Arka and Ataka computers, this machine has compiled a number of third-generation software-compatible machines of the TsMNII Agat. Agat is a pioneer in the development of combat information and control systems for surface ships (More, Root) and submarines (Tucha, Almaz, Omnibus and others), as well as shipboard fire control systems missile systems, control systems and protection of nuclear power plants.
Computer "Tucha"

computer with remote control
COMPUTER “Tucha” is a machine with a binary system for representing numbers with a fixed comma and the number of digits - 25. The numbers were represented by a modified additional code. It was with a unicast system of commands, the width of the commands is 20. The speed of the “Tucha” computer is 62.5 thousand short operations per second. The computer consisted of 4 cabinets, which were connected mechanically and electrically. For cooling, a forced-air and exhaust ventilation system with an inlet air temperature of 18 ° C was used.

device converts analog data to digital and digital to analog
The basis of the design of the machine was a cabinet for electronic equipment of the original design, which allowed it to be loaded onto a submarine through a standard hatch with a diameter of 598 mm. The reliability of the CVC “Tucha” was estimated to be 650 hours between failures. The computer system "Tucha" consumed about 17 kW of electricity.
A number of computers "Lada 2"
In 1986, for surface ships and submarines, the computer was developed by the Lada-2, it consisted of three on-board universal electronic computers, was built on a modular principle, such an open system allows you to connect additional functional devices.
A number of computers were used to build computing systems in a wide variety of systems, to collect and process information in real time, to automatically control various objects, to automate design, to automate complex scientific research, to provide information and reference and training systems.
The row machines had from two to four modifications. COMPUTER "LADA 2" - 2 modifications, COMPUTER "LADA 2U" -3 modifications, COMPUTER "LADA 2M" - 4 modifications. They differed in the composition of the devices, the way of cooling, the design.
The main parameters of the computer "Lada 2": the width of the numbers with a fixed point -1, 8, 16, c floating point - 32 (4 hardware commands), speed -1200 operations per second. Memory: address space 256 KB, RAM - 256, ROM - 32, dimensions of the first modification of the series - 703 * 450 * 276 mm, the second 480 * 350 * 212 mm, power consumption - 330 W.
The Lada 2 computer with architectural and software compatibility with the commercial computer series of the SM series widely used in the USSR The computer (SM4, SM1420, “Electronics 100”, “Electronics 79”, “Electronics 60”, DVK, SM1600) provided the user with an opportunity to use his work a rich application software for a number of SM computers.
The main devices of the computer "Lada 2" ( NPO "Agat". Computer "Lada 2". KA3.031110. Technical description. 1986 ):

corps version of the computer "Lada 2"
In 1988, the Lada 2YU was created, in 1990 - the Lada 2M.
The mass production was adjusted, in total 65 such copies of various modifications were released.
Nowadays, there are practically no official materials, since they were destroyed after a certain time because of the secrecy in force in the USSR, especially in those things that somehow concerned military affairs and developments in it.
(1985-1989 )

Two classes of computers were clearly distinguished: stationary and mobile. Different types of customers contributed to the development of mobile computer types, since it was planned to use them in the ground, aviation, marine, and missile, and other systems in the defense industries and enterprises. Digital computer technology began to be used for anti-aircraft systems. and missile defense, to control outer space and control flights in aviation and in space. Stationary worked indoors, and mobile, therefore, had to be transportable.
Due to the secrecy of the "neck", the exchange of information on the development of specialized computers between specialists in various industries and enterprises in the USSR was sharply limited, there was almost no information on the technical characteristics and principal features of such specialized machines across the border. The development of computers was costly because of this, since a great many architectures of such original machines were created. The centralized industry of electronic components for computers, too, was not.
')
Specialized military computers
Project Mobile Computing Point (PVP) or object "Platform"
Back in 1960, a series of mobile computers was developed and created for the army and frontline link, codenamed “Beta,” but the work never began.

mobile computing complex "Beta-3M"
In 1962, the mobile computer needed for the army was neither in the Ministry of Defense nor in the USSR. The General Staff issued the Directive as soon as possible (for the year) "... to design, order production, debug and put into operation the mobile Military Center, it was supposed to take one of the USSR-made computers and simply adapt it to the specific operating conditions. It is also necessary was "... to develop, program and debug a set of tasks for use during the command and control exercises (command and staff exercises) on the front (district) scale, with the participation of troops and military equipment, for command and staff games of headquarters, military academies and other educational events. "
The developers were oriented on the American Mobidik project (although already in the USSR a mobile, highly specialized Kurs-1 computer was developed for processing information from radar nodes, but everything was secret).

Here are some of the requirements for such a “Platform”: ensuring the necessary performance, reliability of work after moving along dirt roads, 100 hours of work in non-stop conditions, climatic conditions were set according to temperature from -30 to + 40 ° .
At the first stage, a suitable second-generation universal domestic computer on semiconductor elements was chosen, thanks to which the dimensions and power consumption of computers decreased, while such indicators as speed, the amount of RAM increased.
The computer was selected "Hrazdan-2" (produced in Yerevan, YerNIIMM plant). Started upgrading the machine. In order to ensure its operation in the "field" conditions, for operation in the troops and to make it mobile, it was necessary to increase its reliability, constructively modify the computer to place the equipment in a confined space, while ensuring its safety and operability during movement, protected from climatic conditions. impact. To all this it was necessary to choose the entire infrastructure of the mobile VC.

"Razdan"
This included a thermally insulated all-metal van-semi-trailer type 828 for equipment placement, a truck-mounted saddle of the type ZIL-157, powerful air conditioning, a mobile diesel power station with a power of 30 kW in a mobile version, with a fuel consumption of 8 liters / hour, connected radio and telegraph equipment.
A mobile computer center was created, two Hrazdan-2 computers were installed in one body, and all data preparation devices, communications, control and test equipment, various stands, an extended set of spare parts, cables and other equipment housed in the body of an army KUNG mounted on the chassis ZIL-157.
Climate protection to maintain the required temperature and humidity in the body was provided by the following main measures: an air conditioner with high cooling and heating capacity was installed in the body, computer racks of secondary power sources were carried out, additional fans were installed in a separate rack with an independent ventilation and cooling system. The optimum mode of operation of a computer at a temperature of + 20 to + 30 ° C.


In 1964, the modular EC "Platform" was taken to the "supply". After that, the project was still being upgraded, the OP of each computer was doubled due to a backup ferrite cube, a ROM on the ferrite cores was additionally built in, the implementation of the joint operation of two computers became possible.

cube of RAM on ferrite cores
The integration of two computers in the "Platform" in the hardware, software, information aspects was made for the first time in the USSR. In 1963-1968, the Mobile Platform Center was the first and only CC of this type.
COMPUTER "Granit"
A specialized computer was used for statistical processing of a large number of observations and was created by order of the Main Artillery Directorate of the USSR Ministry of Defense to increase the effectiveness of artillery firing. In 1957 she was sent to one of the artillery grounds of the Ministry of Defense. Used to shoot artillery guns.

The computer consisted of a computing device accumulating the sum of paired works, a set of devices for preparing a punched tape (35 mm wide film), an output perforator and a printing device, the power consumption was 4.5 kVA. I took such a computer 30 square meters.
Computer "Maple" and computing systems "Maple-1" and "Maple-2"
Starting from 1962 to 1968, the Klen computer and the Klen-1 and Klen-2 computer systems were created at the Research Institute of Electronic Mechanical Engineering (NIEM), and a distributed satellite information processing system worked on them. The goal of this development was to automate the processing of telemetric information coming from artificial earth satellites.
The unicast parallel action of the computer "Maple" operated with numbers, presented in a format with a comma fixed before the high-order bit. The numerical data was presented in a 27-bit grid, where 23 bits were occupied by the digital part, one digit was the sign of the number, and three bits were allotted for control modulo two. The team occupied 33 binary digits, 7 of them to provide an operation code, 16 - addresses, and 4 bits - a configuration code of numbers, 3 - for the address modification code, 3 bits - for control modulo two and three. Capacity of main memory of computer 8192 (8K) 27-bit words. The execution time of short operations, such as additions, transition operations was 4.5 μs, multiplication was performed in 25.5 μs. The system of computer commands "Maple" included 83 teams, which feature was the ability to work with different configurations of numbers.
In the computer "Maple" was the traditional input device with punch cards, 27 bit channels for communication with external subscribers, for data output - a printing device.
+5 to +40 degrees Celsius - temperature range for optimal machine operation.
Especially for the Klen machine, a pulse-potential system of elements with diode-resistive logic and a maximum operating frequency of 660 kHz was developed. The delay time of the logical elements of the system is 50 ns, the delay time of the elements of the system used in serial circuits is 20-30 ns. In the chains of adders and controls, special logic elements were used.
RAM in a computer was used on ferrite cores of type BT-7 with a cycle time of 6.0 μs and a reading time of 2.25 μs. As a long-term memory, a memory device on oxypher cores with constant firmware was used, the DZU cycle time was 4.5 μs, and the read time was 2.25 μs.

The capacity of the program DZU block could be from 8192 to 65536 codes, the magnetic random access memory (MOZU) of programs with a capacity of 4096 codes was used to debug programs before inserting into the DZU.
In the computer "Maple" there could be four blocks of the MOZU of numbers, with 8192 numbers in each block. The work of such units could be combined.

EVK "Maple-1" and "Maple-2" - modifications of the computer "Maple" with extended RAM and DZU with minimal additions in commands exchange with external devices. Magnetic tape memory and a developed system of external devices appeared as part of both complexes.

Computers differed only in the different configurations of internal chargers, tape drives and input-output devices. External devices "Maple-1" - input device for punched cards VU-700-2, 2 alphanumeric printing devices ATsPU-128-2. The external devices "Klen-2" included 4 printers ATsPU-128-2, the perforator of the PR results, the perforator tape PL-20-2.
From remote sources, data came from external highways at the Klen-1 computer complex, they were sorted, compressed, and eliminated redundant data. After that, the pre-processed data were transferred to the EEC "Maple-2", here they were final processing, cataloging, storage and issuance at the request of users.
Specialized computer "Diana-1", "Diana-2" .
S.A. Lebedev and the ITM team paid special attention to the work related to the country's defense, conducted research and development on automatic data acquisition from the radar (radar station) and automatic tracking of flying targets. An experiment was conducted on the simultaneous accompaniment of several real planes while anticipating the calculation of their trajectory. The Diana-1 computer was used for data entry in digital form, and the Diana-2 computer was used for tracking the targets. Such an experiment laid the foundation for the development of radar and missile systems on a new information - computational basis.
"Diana-1" -sequential machine with switched software processing, intended to work as part of the guidance systems of fighter aircraft at the target. The machine carried out automatic data acquisition from the radar with the selection of the object from noise, transferred them to a digital form and gave out the trajectories of movement of several targets on the screens.
“Diana-2” - a computer with a fixed comma, a digit capacity of 10, a unicast command system, with a number of commands - 14, a command memory of 256, a constant memory, random access memory on magnetostrictive delay lines.
Burtsev's experience in developing Diana-1 and Diana-2 enabled him to create a high-performance computer network including small computers of radar stations, an anti-missile radar, M40 and M-50. Management of all combat processes was automated. The main thing was the computer and the combat program implemented in it. Information from radars arrived asynchronously over duplex radio relay communication lines (such lines connected objects located at a distance from 100 to 200 km.). For its processing, Vsevolod Sergeevich for the first time introduced a developed system of interruptions in M-40 and M-50 and for the first time in the Soviet Union developed a device for receiving and transmitting data using the principle of operation of a powerful multiplex channel.
Family of specialized computers "Karat"
In 1976, the unified Karat computer systems were accepted for supply for the USSR Navy. These were compact, reliable computers with high functional parameters. Their creation radically changed the situation in the marine instrument making.

The history of the creation of a unified computer "Karat" began in 1963 in the Kiev Research Institute of Radio Electronics under the direction of Plotnikov (the chief designer of the family of specialized computers "Karat"). In 1963, Plotnikov’s laboratory presented flat micromodules (PMM) as basic elements for new developments. It was the first serial-suitable universal element created in the USSR, which provided the opportunity to create computers and other digital equipment at a new, rather high level.
The thin-walled aluminum case of a flat micromodule was 17.5x9.5x6.3 mm, with a weight of 2 grams, such a PMM was assembled from microelements that were mounted on both sides with a printed microboard (9x17 mm), pin pins were installed perpendicular to the board in 4 mm increments.
But for the fleet, computers with elements smaller than the PMM were needed, therefore imperfect integrated circuits of domestic production began to be used to build computers. In the laboratory, Plotnikov began work on the creation of multichip integrated circuits. It was a completely new direction in the development of computer hardware components.

Hybrid large integrated circuits "Varduva" (GBIS) - this is how new multichip chips were named. The first model of "Karat" was a small-sized 24-bit machine on the GBIS "Varduva". The circuits of the functional units of the microcircuits were developed by Soviet scientists, proceeding from the computer logic circuits (8 register bits, 2 ALU bits, etc.) were placed in one case. This development for many years ahead of the creation of multi-chip circuits abroad (“multi-chips”).

The machine was used in more than 60 types of systems developed by enterprises of four ministries. In simple systems, a computer could be used in a minimal modification, and on the largest modern ships with several systems on board, 15 or more Karat computers could be found in the maximum version. In 1981, 15 modifications of the “Karat” family of cars were developed, software of 5 million teams was prepared. To process information from radar systems with phased antenna arrays, a modification of “Carat” was developed with a speed of 2.5 million operations per second. Later, the Karat-KM-E modification was developed on sectional microprocessor large integrated circuits. About 2 thousand cars were manufactured at the factories in the USSR.
Computer "Radon"
In 1964, the development of a computer for use in the air defense of the USSR was completed at the Research Institute of Electronic Mathematical Machines. It was a potential pulse with galvanic and transformer connections of second-generation computers based on transistors P16 and P601.

Scientific Research Institute of Electronic Mathematical Machines
The design of the computer consisted of 16 racks, each of the racks had its own power supply and control units, an interconnecting panel, including 320 “sheet” sockets (20 contacts each), which were connected by plugs located on the end of the cells containing from 4 to 8 items.

block diagram of the computer "Radon"
It was developed several modifications of the computer "Radon", which differed in the capacity of RAM, ROM. It was a two-machine complex with a bus connection organization. The computer was unicast, the commands were 24 (2 control), the operands were 20 (2 control), fixed point operations, the number of instruction codes was 64. Each computer processor had access to its memory, as well as to the memory of a paired computer , which made it possible to work not only in the two-machine mode, but also in the two-processor mode. Two computers were connected to a common exchange highway for communication with system control devices. For the initial loading, testing and display of information for analysis on the print used the periphery of the machine itself.
The Radon computer occupied an area of 150 square meters. It was reliable and with increased speed.
For the first time in the USSR in the car were implemented:
- RAM and ROM using transistors;
- the processor contained two index registers;
- an effective system of integrated hardware control in combination with software tools for automatic recovery of the system after the impact of an error in the computer and system;
- the combination of the execution time of operations (pipeline);
- system interrupt and priority switching programs;
- dual-processor and dual-engine operating modes.
Acacia system
In 1982, the Acacia digital fire control system was developed. The system was created to generate data for the firing of the Granat strategic cruise missiles from submarines and submarines; the systems included 2 Archa, 2 RAM devices, 2 long-term memory devices, 2 data exchange devices, 2 reserve control devices. In order to increase the reliability of the Acacia system, all devices had a reserve, the reservation was made automatically.
The Arka CVM (specialized computer) was designed to work with the Ataka PCVM and was used to increase the capacity of the Ataka computer system.

The speed of such a PC for the mode of operation: with registers of 500 thousand short operations per second, while the register memory is 167 thousand short operations per second. Power consumption 1200 watts. The machine "Arka" had two exchange devices. Each device consisted of 8 consecutive channels. One exchange device with parallel multiplex channel. The average time between failures is 2000 hours.
CVM "Attack"

specialized digital computer "Attack" (MVM-012)
The specialized attack machine “Ataka” (MVM-012) was created in 1974 at the NPO Agat. The dimensions of such a machine are 1800x1076x516 mm, the occupied area is 0.65 square meters. The Ataka CVM consisted of two cabinets, which were interconnected mechanically and electrically. The machine consisted of a command device, a command interrupt device, an exchange device, an arithmetic unit, microprogram control blocks, 16 general-purpose buffer registers, 16K words ferrite random-access memory, a hardware control device, a monitoring and control panel, and a power supply device.

The machine used a binary system for representing numbers, with a fixed comma, the number of digits - 32. Work with words of double length (64 bits), with half words (16 bits) and with eight-digit alphabetic information is provided.The command system was dual-core, the number of operations was 56, of which 16 were arithmetic operations, 7 logical operations, 19 transfer operations, 6 shift operations, 8 control operations.
It should be noted that the central computer was able to increase memory up to 256K words with connecting external memory devices 182-3 - RAM 64K, 183 - DZU 128K (2X64K), 184 - RAM 32K and DZU 64K or any other devices having electrical and information compatibility with MVM-012.
2 parallel, 2 serial exchange channels were provided. The exchange rate for the serial channel was 20 thousand words per second, for the parallel channel - 94 thousand words per second.
The power consumption from the mains is 1.5 kW, power is supplied from a three-phase ship AC mains with a voltage of 220 V and a frequency of 400 Hz. Network fluctuations are allowed: ± 5% with long-term deviations and from + 13% to -25% with short-term voltage deviations, and from + 4% to -6% in frequency.
Terms of Use:
- vibration resistance in the frequency range 5–120 Hz with acceleration 2g;
- the impact of single blows with an acceleration of 1000g;
- vibration strength in the frequency range of 20–120 Hz with acceleration of 2g;
- cyclic temperature change from +65 to -50 ° ;
- relative humidity 95–98% at a temperature of + 40 ° ;
- cold resistance at operating temperature of -10 ° C and extreme temperature of -50 ° C;
- exposure to frost and dew at -20 ± 5 ° ;
- heat resistance at operating temperature + 50 ° and maximum temperature + 65 ° ;
- exposure to sea fog at a temperature of + 27 ± 2 ° .
The car was produced until 1990, 255 Ataka CVTs were manufactured.
Computer "Harp"
The development of the machine was started in 1979 and was intended to work in various ship control systems, as a controlling link in real time. The power supply of the machine was carried out from the ship's three-phase network 220V, 400 Hz, the power consumption was 1.7 kW. For cooling, a forced-air and exhaust ventilation with an inlet air temperature of 18 ° C was used. It was a computer with a binary system for representing numbers with a fixed and floating point, the speed was 550 thousand short operations per second when accessing operands in RAM, 1100 thousand short operations when accessing buffers and registers. The number of digits is 32, it was possible to work with words of double length (64 digits), with half words (16 digits) and with octal alphabetic information.
Together with the Arka and Ataka computers, this machine has compiled a number of third-generation software-compatible machines of the TsMNII Agat. Agat is a pioneer in the development of combat information and control systems for surface ships (More, Root) and submarines (Tucha, Almaz, Omnibus and others), as well as shipboard fire control systems missile systems, control systems and protection of nuclear power plants.
Computer "Tucha"

computer with remote control
COMPUTER “Tucha” is a machine with a binary system for representing numbers with a fixed comma and the number of digits - 25. The numbers were represented by a modified additional code. It was with a unicast system of commands, the width of the commands is 20. The speed of the “Tucha” computer is 62.5 thousand short operations per second. The computer consisted of 4 cabinets, which were connected mechanically and electrically. For cooling, a forced-air and exhaust ventilation system with an inlet air temperature of 18 ° C was used.

device converts analog data to digital and digital to analog
The basis of the design of the machine was a cabinet for electronic equipment of the original design, which allowed it to be loaded onto a submarine through a standard hatch with a diameter of 598 mm. The reliability of the CVC “Tucha” was estimated to be 650 hours between failures. The computer system "Tucha" consumed about 17 kW of electricity.
A number of computers "Lada 2"
In 1986, for surface ships and submarines, the computer was developed by the Lada-2, it consisted of three on-board universal electronic computers, was built on a modular principle, such an open system allows you to connect additional functional devices.
A number of computers were used to build computing systems in a wide variety of systems, to collect and process information in real time, to automatically control various objects, to automate design, to automate complex scientific research, to provide information and reference and training systems.
The row machines had from two to four modifications. COMPUTER "LADA 2" - 2 modifications, COMPUTER "LADA 2U" -3 modifications, COMPUTER "LADA 2M" - 4 modifications. They differed in the composition of the devices, the way of cooling, the design.
The main parameters of the computer "Lada 2": the width of the numbers with a fixed point -1, 8, 16, c floating point - 32 (4 hardware commands), speed -1200 operations per second. Memory: address space 256 KB, RAM - 256, ROM - 32, dimensions of the first modification of the series - 703 * 450 * 276 mm, the second 480 * 350 * 212 mm, power consumption - 330 W.
The Lada 2 computer with architectural and software compatibility with the commercial computer series of the SM series widely used in the USSR The computer (SM4, SM1420, “Electronics 100”, “Electronics 79”, “Electronics 60”, DVK, SM1600) provided the user with an opportunity to use his work a rich application software for a number of SM computers.
The main devices of the computer "Lada 2" ( NPO "Agat". Computer "Lada 2". KA3.031110. Technical description. 1986 ):
- (), (1, 2), (1, 02), ;
- , - (-64) ;
- - , - (-16) ;
- - : - , 15-00-013 , « 7012», - ;
- , ;
- , ;
- the controller of communication with peripheral devices "Unity" KE (KE1 and KE2);
- unit, matching the output of the computer to the external line MPI;
- remote control machine PU, consisting of an electronic module PU and panel PU;
- UEP power supply device, consisting of a water supply unit control unit, a DFT power supply filter, a VPN 5/24 power supply stabilizer.

corps version of the computer "Lada 2"
In 1988, the Lada 2YU was created, in 1990 - the Lada 2M.
The mass production was adjusted, in total 65 such copies of various modifications were released.
Nowadays, there are practically no official materials, since they were destroyed after a certain time because of the secrecy in force in the USSR, especially in those things that somehow concerned military affairs and developments in it.
(1985-1989 )
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/389967/
All Articles