Internet Analytics Digest (Issue # 1): Innovation and the Labor Market
The Internet and its associated markets are the most fertile ground for innovation. Innovations are now spoken everywhere - from school to government. At the same time, there are not so many materials that show how innovative economies are developing. The article below provides some relevant materials and research that will help you understand the current state of affairs.
At the end of 2015, the “National Report on Innovations in Russia 2015” was published by the Ministry of Economic Development with the participation of the expert council of the Russian government, RVC and The Boston Consulting Group.
Some excerpts:
- The share of innovative products in Russia in the total output is 8–9% (in the leading countries ~ 15%) and does not grow over the past 3 years.
- Labor productivity in the Russian economy as a whole is 2 or more times behind the leading countries, there is no positive dynamics.
- The results of Russian innovations still have low competitiveness - 0.4% of Russia's share in total global exports of high-tech goods - while there is a positive trend (in 2010, Russia's share was 0.21%).
- The number of working-age population is rapidly decreasing since 2006, and it is projected that by 2020 it will be 80.6 million people, which is about 10 million less than in 2006.
The main barriers to improving the efficiency of the innovation ecosystem of Russia are expressed as follows:
1. Experts and innovations “flow away” from Russia. Business projects grown by the local venture capital market do not find opportunities in Russia and leave the country.
2. The undeveloped institutional environment: the unpopularity of the professions of the scientist, the insufficient protection of the rights of owners of innovative companies.
3. There is no single vision of technological priorities, coordinated technological policy.
4. Innovation and technology policies are formed situationally and their development is coordinated at the document level.
5. Lack of a unified system for monitoring the innovation ecosystem and methods for assessing the volume, quality and cost-effectiveness of innovations.
')
Discussion of the report at the Gaidar Economic Forum:
At the same time, it is interesting to compare yourself with others. For example, with Israel, where in 2015, 18 local venture capital funds attracted a total of $ 1.52 billion (in 2014 - $ 1.2 billion). The report "The Israeli industry of innovation and venture capital: results of 2015, forecasts of 2016" covers not only the largest deals and funds, but also political events that directly affect the development of an innovative economy. And, if in the case of Russia, the lack of unity runs like a red thread through the entire report, then in Israel, associations and joint R & D sites with other countries are a driver of development.
In turn, changes in the traditional economy can be seen in the atlas created at Harvard University. The resource allows you to build an infographic, which clearly presents data on world trade. Below are pictures for Russia.
According to the atlas in 2014, Russian exports amounted to $ 555 billion. Crude and refined oil - 57% of exports, gas and coal - 10%. If we take into account more metals, then fuel and ore accounts for almost 80% of Russian exports. Imports of goods is about $ 300 billion a year.
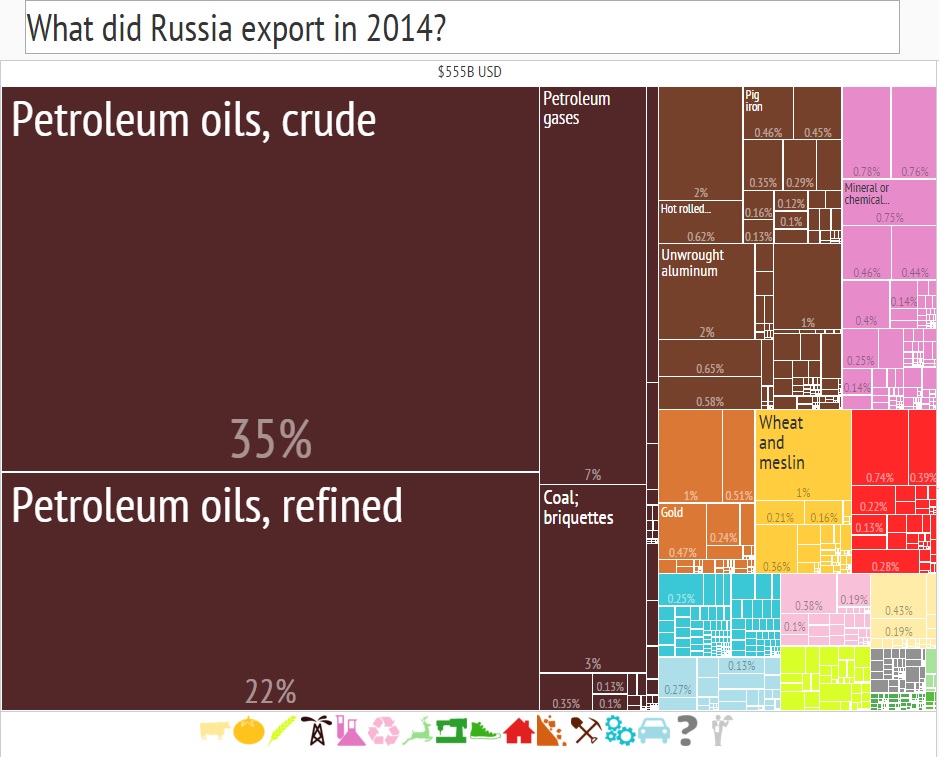
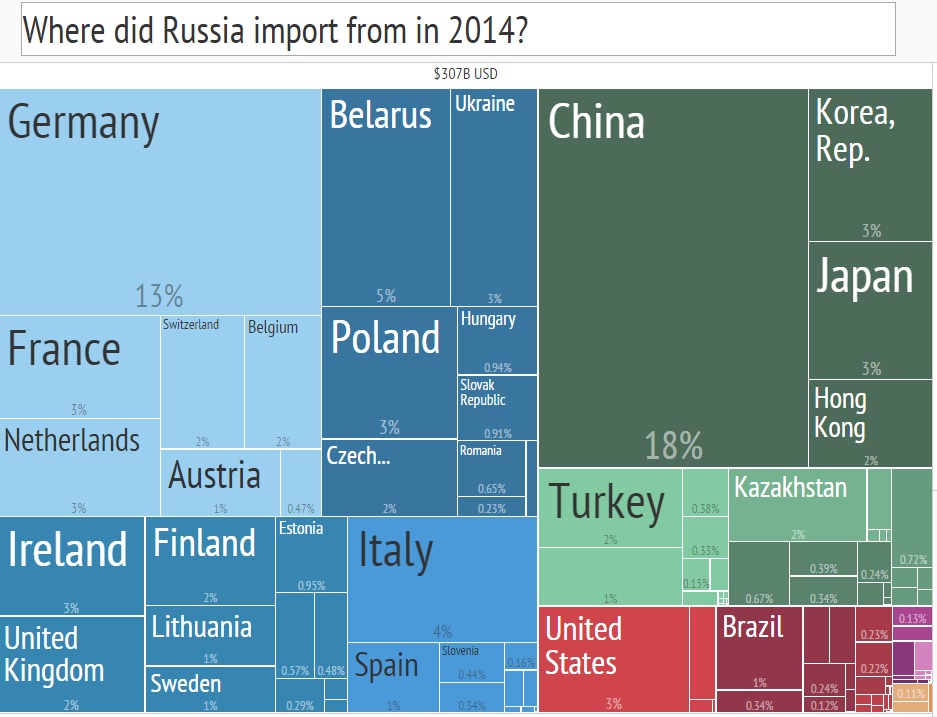
In fairness, it is worth noting that the Harvard data does not deal with the data of the Central Bank of Russia. According to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in 2014, Russia shipped goods for 498 billion dollars, and imported 308 billion. In 2015, the volume of both imports and exports decreased significantly, but official statistics have not yet been published. It must be admitted that Russia is losing its main trading partners and it is extremely difficult to build an “import substitution” in such conditions.
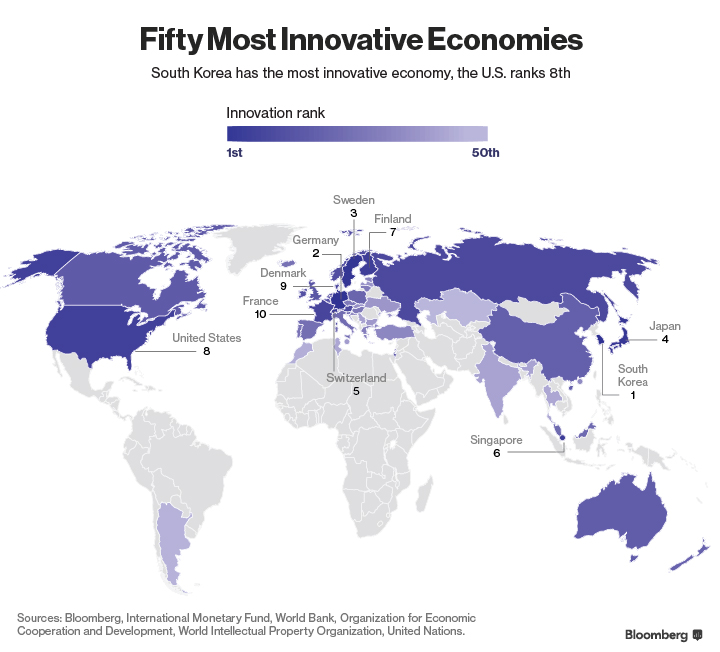
However, in mid-January, Bloomberg reported that Russia ranked 12th among the world's innovative economies in the Innovation Index. First place was taken by South Korea. It is followed by Germany, Sweden, Japan and Switzerland. The ten most innovative countries also include Singapore, Finland, USA, Denmark and France. Russia this year is on the 12th line, last year it was on the 14th. China took 21st place, which was explained by the fact of copying technology, but not by inventing its own.
Considering what is happening with the Russian economy, it is logical to complete the material with a description of the situation on the labor market. HeadHunter published a study on the results of 2015, in which they reported that the ideal candidate of 2015 is an experienced sales specialist. The most difficult period last year (and, probably, in this too) is spring: the number of vacancies decreased by 22%. The competition rose to 12 resumes per place. The IT sector is resistant to the crisis - the demand during the year did not fall lower than 25% even in the most difficult times. The trend for remote employment is increasing. 1C: Bitrix in their study speaks of the explosive growth of remote work in Russia in the next 5 years. By 2020, every fifth company employee will work remotely. The cumulative savings from this transition will be more than 1 trillion rubles. In addition, 68% of the surveyed companies state that the salary does not depend on whether an employee works in an office or not, and in 12% of companies, teleworkers receive even more office ones.
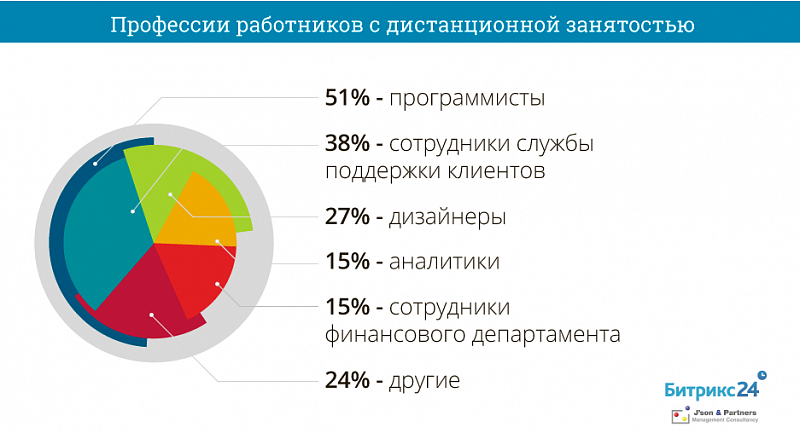
Remotely working programmers - 51%, customer support staff (38%), designers (27%), analysts (15%) and finance department (15%).

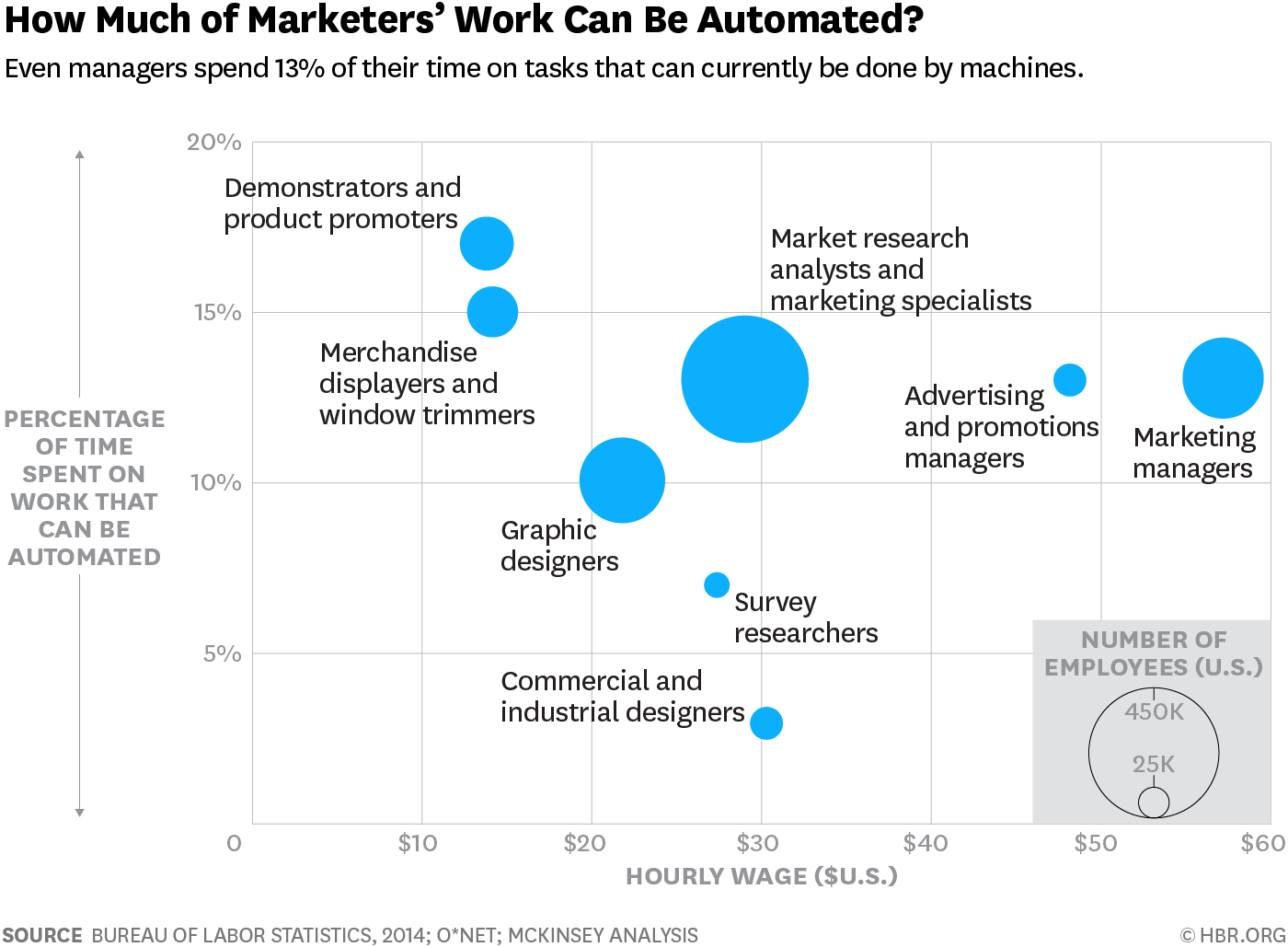
Along with distance employment, the problem of replacing human workers with robots is becoming ever more pronounced. McKinsey published a study , the main conclusion of which is the thesis that it is possible to automate not only 45% of work, but also 5% of jobs, which means that we will have to compete not only with each other, but also with robots who are not sleeping They do not go on vacation and on sick leave and do not ask for a salary increase. About who will have the hardest and easiest of all in this unequal struggle can be found in the article HBR .

A report on the future of the labor market was published at the World Economic Forum in Davos a week ago. Russia is expected not to be among the fifteen countries whose experience was studied at the research stage, but the findings are partly directly and some indirectly apply to Russia. The fourth industrial revolution is underway. New places are created, but more slowly than they disappear. In the next 5 years, we will lose about 5 million jobs - mostly employees of "mental" labor. The fourth industrial revolution differs in speed from the third and second. The change of the “regime” will happen in 5-10 years, and not in a generation, as before. “You need to run very fast to stay in place” ...
General information on global studies of the impact of the Internet on the economy can be found in the article “Internet analytics” (Zero issue)
At the end of 2015, the “National Report on Innovations in Russia 2015” was published by the Ministry of Economic Development with the participation of the expert council of the Russian government, RVC and The Boston Consulting Group.
Some excerpts:
- The share of innovative products in Russia in the total output is 8–9% (in the leading countries ~ 15%) and does not grow over the past 3 years.
- Labor productivity in the Russian economy as a whole is 2 or more times behind the leading countries, there is no positive dynamics.
- The results of Russian innovations still have low competitiveness - 0.4% of Russia's share in total global exports of high-tech goods - while there is a positive trend (in 2010, Russia's share was 0.21%).
- The number of working-age population is rapidly decreasing since 2006, and it is projected that by 2020 it will be 80.6 million people, which is about 10 million less than in 2006.
The main barriers to improving the efficiency of the innovation ecosystem of Russia are expressed as follows:
1. Experts and innovations “flow away” from Russia. Business projects grown by the local venture capital market do not find opportunities in Russia and leave the country.
2. The undeveloped institutional environment: the unpopularity of the professions of the scientist, the insufficient protection of the rights of owners of innovative companies.
3. There is no single vision of technological priorities, coordinated technological policy.
4. Innovation and technology policies are formed situationally and their development is coordinated at the document level.
5. Lack of a unified system for monitoring the innovation ecosystem and methods for assessing the volume, quality and cost-effectiveness of innovations.
')
Discussion of the report at the Gaidar Economic Forum:
At the same time, it is interesting to compare yourself with others. For example, with Israel, where in 2015, 18 local venture capital funds attracted a total of $ 1.52 billion (in 2014 - $ 1.2 billion). The report "The Israeli industry of innovation and venture capital: results of 2015, forecasts of 2016" covers not only the largest deals and funds, but also political events that directly affect the development of an innovative economy. And, if in the case of Russia, the lack of unity runs like a red thread through the entire report, then in Israel, associations and joint R & D sites with other countries are a driver of development.
In turn, changes in the traditional economy can be seen in the atlas created at Harvard University. The resource allows you to build an infographic, which clearly presents data on world trade. Below are pictures for Russia.
According to the atlas in 2014, Russian exports amounted to $ 555 billion. Crude and refined oil - 57% of exports, gas and coal - 10%. If we take into account more metals, then fuel and ore accounts for almost 80% of Russian exports. Imports of goods is about $ 300 billion a year.


In fairness, it is worth noting that the Harvard data does not deal with the data of the Central Bank of Russia. According to the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in 2014, Russia shipped goods for 498 billion dollars, and imported 308 billion. In 2015, the volume of both imports and exports decreased significantly, but official statistics have not yet been published. It must be admitted that Russia is losing its main trading partners and it is extremely difficult to build an “import substitution” in such conditions.
However, in mid-January, Bloomberg reported that Russia ranked 12th among the world's innovative economies in the Innovation Index. First place was taken by South Korea. It is followed by Germany, Sweden, Japan and Switzerland. The ten most innovative countries also include Singapore, Finland, USA, Denmark and France. Russia this year is on the 12th line, last year it was on the 14th. China took 21st place, which was explained by the fact of copying technology, but not by inventing its own.

Considering what is happening with the Russian economy, it is logical to complete the material with a description of the situation on the labor market. HeadHunter published a study on the results of 2015, in which they reported that the ideal candidate of 2015 is an experienced sales specialist. The most difficult period last year (and, probably, in this too) is spring: the number of vacancies decreased by 22%. The competition rose to 12 resumes per place. The IT sector is resistant to the crisis - the demand during the year did not fall lower than 25% even in the most difficult times. The trend for remote employment is increasing. 1C: Bitrix in their study speaks of the explosive growth of remote work in Russia in the next 5 years. By 2020, every fifth company employee will work remotely. The cumulative savings from this transition will be more than 1 trillion rubles. In addition, 68% of the surveyed companies state that the salary does not depend on whether an employee works in an office or not, and in 12% of companies, teleworkers receive even more office ones.
Remotely working programmers - 51%, customer support staff (38%), designers (27%), analysts (15%) and finance department (15%).


Along with distance employment, the problem of replacing human workers with robots is becoming ever more pronounced. McKinsey published a study , the main conclusion of which is the thesis that it is possible to automate not only 45% of work, but also 5% of jobs, which means that we will have to compete not only with each other, but also with robots who are not sleeping They do not go on vacation and on sick leave and do not ask for a salary increase. About who will have the hardest and easiest of all in this unequal struggle can be found in the article HBR .


A report on the future of the labor market was published at the World Economic Forum in Davos a week ago. Russia is expected not to be among the fifteen countries whose experience was studied at the research stage, but the findings are partly directly and some indirectly apply to Russia. The fourth industrial revolution is underway. New places are created, but more slowly than they disappear. In the next 5 years, we will lose about 5 million jobs - mostly employees of "mental" labor. The fourth industrial revolution differs in speed from the third and second. The change of the “regime” will happen in 5-10 years, and not in a generation, as before. “You need to run very fast to stay in place” ...
General information on global studies of the impact of the Internet on the economy can be found in the article “Internet analytics” (Zero issue)
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/389961/
All Articles