Waste in revenue
 With this post, I continue the cycle ( one , second ) of articles on recycling technologies. The next step is the waste of food production, which can be used in the creation of various new materials. Today I will talk about an interesting technology for the production of chipboard using chipboard based on molasses and whey. The method developed in Tomsk is based on the process of producing an adhesive base by a specialized strain of microorganisms, while the biotechnology of obtaining an adhesive base allows you to create a particle board without using toxic formaldehyde resin. At the same time, the price of bio-adhesive is quite competitive, and the ecological chipboard can be obtained almost without changing the usual production technology - after all, the new material has passed the most stringent and serious technical tests.
With this post, I continue the cycle ( one , second ) of articles on recycling technologies. The next step is the waste of food production, which can be used in the creation of various new materials. Today I will talk about an interesting technology for the production of chipboard using chipboard based on molasses and whey. The method developed in Tomsk is based on the process of producing an adhesive base by a specialized strain of microorganisms, while the biotechnology of obtaining an adhesive base allows you to create a particle board without using toxic formaldehyde resin. At the same time, the price of bio-adhesive is quite competitive, and the ecological chipboard can be obtained almost without changing the usual production technology - after all, the new material has passed the most stringent and serious technical tests.Chemistry and life ...
I am sure that there are many specialists among the readers in one way or another connected with chemistry and chemical production. Indeed, modern achievements in the field of creating new materials and unique compounds are impressive. However, in addition to the rapid development of standard chemical technologies, the direction of "green" chemistry is actively developing. Especially in conjunction with advances in biotechnology. New materials are entering the arena, the production and use of which has a minimal impact on the environment. Ecology in a broad sense - from the idea and production - to use and subsequent disposal. But against this background, there are many technologies that are frozen in their development. These include the variety of materials and substances that use phenol-containing compounds and resins. If for specialized industrial materials (polymers, varnishes, adhesives, textolite, getinax, etc.) without them is not enough, then some materials for household applications can already be done without using such dangerous toxic compounds. First of all, in the production of furniture - after all, most of the budget cabinets, tables, office furniture are made of chipboard. Even in the State Duma, a scandal flared up not so long ago, due to the fact that the concentration of vapors of formaldehyde resin in MPs exceeds MPC several times.
Here is a small (45 seconds) video
What to say about schools, kindergartens and other budgetary institutions where furniture is supplied at the lowest prices, therefore its quality and environmental friendliness leaves much to be desired. I think many of you are now reading this article at a table in which formaldehyde emission continues, because this process takes about 4 years until the concentration of formaldehyde becomes close to the MPC. This is due to the fact that during the production of particleboard it is not possible to completely bind the resin during pressing and the non-hardened phenol-formaldehyde resin can contain up to 11% of free phenol . And this is a very dangerous trend. After all, formaldehyde resins are recognized as the strongest carcinogens, causing allergies, metabolic disorders, and the development of cancer may be the most terrible consequence for humans. This danger is understood by Western manufacturers, therefore, in the manufacture of chipboard, it is obligatory to cover with protective films (in the figure on the left) directly in production, but this significantly increases the cost of the final product. Most Russian manufacturers, unfortunately, do not.
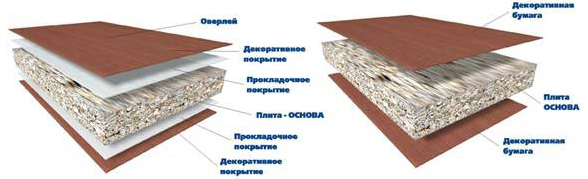
Although (by and large) it also does not save the situation. Packed in this way, the resin remains all in the plate and can be much more dangerous.
')
How do chipboard?
Let's talk a little about the production of chipboard. In fact, the technology is quite simple and well developed in many countries. Raw materials (wood, waste from the processing of industrial wood) are ground into dust, dried, mixed with formaldehyde resin and wax. Then the plate is formed and it is pre-pressed at a certain temperature for some time. Technological modes of pressing depend on the thickness of the plate, the quality of raw materials and the concentration of resin.

If the resin is low, the pressing process is much worse and longer. This leads to significant energy costs and equipment wear. Therefore, the resin often do not regret. Preformed plates are subjected to final pressing at a powerful finishing press. The finished slab is cut to size and sent to a ventilated warehouse for weathering within a few days. It is forbidden to ship a fresh plate. She is extremely smelly and dangerous. Chipboard production is not environmentally friendly. Talking about the good health of workers in such industries is also not necessary. Although there is a nice video of the chipboard production process in the USA, which was shot very beautifully, in which important moments are neatly missed and you will not see a single worker in the workshop of the final molding of the plate. Everything is automated! That, in principle, the most correct for such industries.
Alternatives and perspectives
As you already understand, the production of chipboard is not so difficult. If we imagine a situation that the formaldehyde adhesive base will be replaced by another one, then without changing the technological cycle, the plate can be made completely environmentally friendly. However, the requirements for the replaced adhesive composition must clearly comply with all technological requirements as in the case of formaldehyde resin. That is, the adhesive must be the same (as close as possible) according to different characteristics - consistency, adhesive ability, density, viscosity, pH, etc. And most importantly - to be competitive in price. It was possible to create such a substance to biotechnologists from Tomsk. The substance was obtained as a result of microbiological studies of special strains of microorganisms, which were subsequently studied and described. After conducting research on safety and lack of pathogenicity, the strain was deposited in the All-Russian Collection of Industrial Microorganisms (FGUP GosNII Genetics).
Certificate of Deposit

The approximate essence of the technology is as follows. In a special reactor at a temperature of 22 g. Food waste production of sugar is loaded with molasses and cheese cheese whey. Molasses is the basis of glue, whey is a source of microelements for the reproduction of microorganisms. A strain of microorganisms is added and within 2 days the biomass of bacteria produces an adhesive substance, destran . This is a complex polysaccharide with a huge molecular weight molecule.

After completion of the laboratory stage of research (with the support, by the way, I have a very respected Bortnik Foundation ), the stage of creating a semi-industrial reactor for the production of bio-adhesive was started, which was successfully completed by creating a pilot batch of bio-adhesive for industrial testing at one of the chipboard plants. The figure shows the scheme for obtaining bioglue.

Tests of glue at an industrial enterprise were successful. Samples of chipboard plates were obtained and new material was tested in accordance with GOST RF 10632-2007. New plates correspond to GOST, and even surpass it in some parameters. Some differences were still. In particular, the plates turned out somewhat darker than usual. The production at the time of pressing the plates began to spread the smell of fresh pastries, as in a bakery. And the workers immediately began to say that the scientists came again and would bake pies. Rospotrebnadzor checked the air quality and revealed no hazards, while the concentration of formaldehyde vapors in the workshop fell 80 times compared with standard production. Also, finished plates are not subjected to microbiological insemination, as they are not hydroscopic and retain low humidity throughout the entire life of a person.
The test results of plates and technological production drains



Important in this technology is the disposal of food waste. In particular, whey is a real scourge of dairy production. Despite the fact that many very useful and valuable substances are dissolved in this product, for example, albumin, but the processing of whey is an extremely complex process. Therefore, many dairies pour whey into the sewers, while paying decent environmental fines. Serum draining is dangerous and can cause serious biological contamination. Production of bio-adhesive for particleboard would reduce the environmental burden of dairy production, thereby increasing the production culture and environmental situation. Bio-adhesive obtained in Tomsk can also be used for the production of wood pellets, fabrics, and various fertilizers. As for the chipboard, it preserves its environmental friendliness for the whole period of its operation, and its utilization presents no problems. When hit in the ground, the plate is destroyed by soil microorganisms for several months, turning into fertilizer. In turn, the formaldehyde plate for microorganisms is toxic, so its utilization is difficult.
Technology perspectives
At the moment, the project is at the stage of readiness for industrial implementation. Until recent political events, foreign companies that work on the market for the production of environmentally friendly materials have shown serious interest in this technology. But these contacts were abruptly discontinued. The prospects for the development of this technology in Russia are difficult to estimate now, but the authors of the technology hope that there may be serious investors who will not allow another interesting Russian technology to lie on the shelf. Anyway, I, as a popularizer of science and technology, cannot remain indifferent. I am ready to answer your questions and comments, and if I have any questions that I can’t answer, I will pass them on personally to the team implementing this interesting project. I do not give direct links, as the Site Rules do not allow this. Write in a personal or on asmtomsk@gmail.com I will answer all!
A short video in conclusion
Have a good day and interesting technologies!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/376775/
All Articles