Virtual reality in medicine
Virtual reality is used in space and educational purposes. In medicine, she helps train the skills of surgeons and dentists, relieve pain in patients, treat phobias and post-traumatic syndrome. Learn more about how doctors can help people and save lives with the help of virtual reality - under Habrakat.
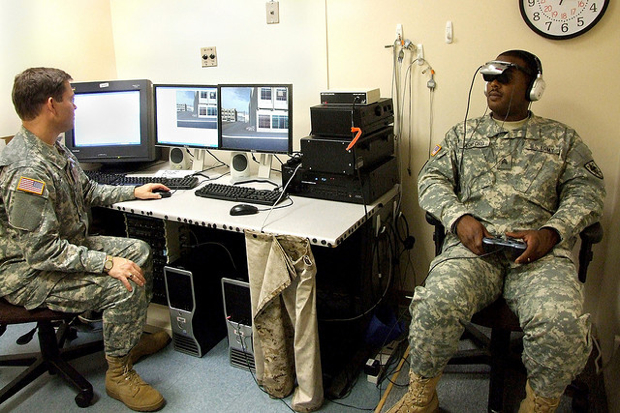

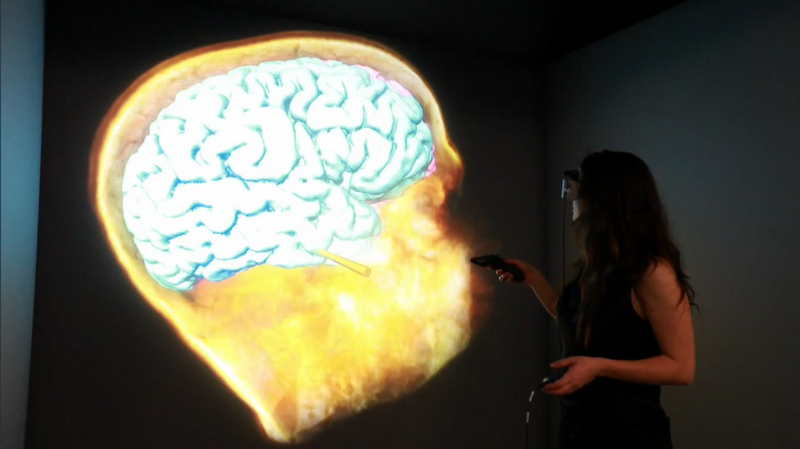
The surgeon can train his skills by performing simulator operations. In this case, patients do not go to the expense. Modern simulators have a graphic component and tactile feedback. In the photo below - the process of teaching students at the New York Medical College Weill Cornell, where a special virtual reality room is equipped.
')
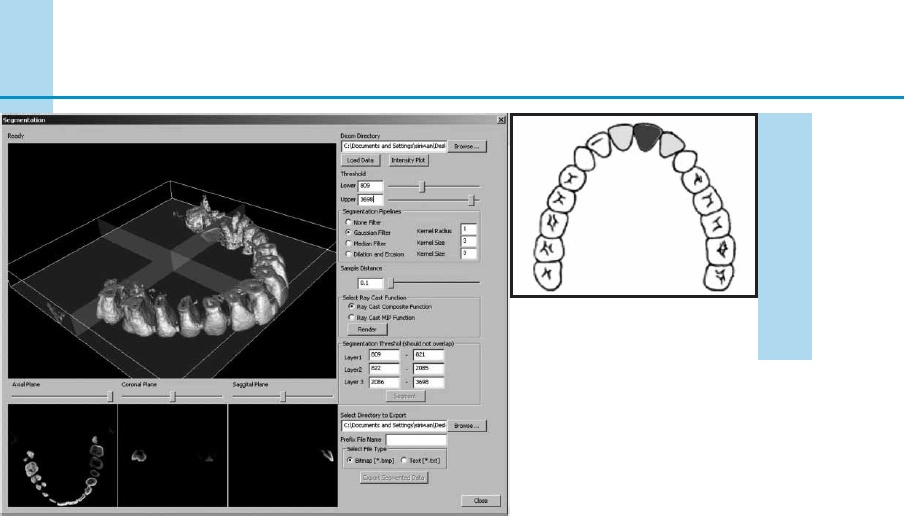
It looks like a simulator for dentists.
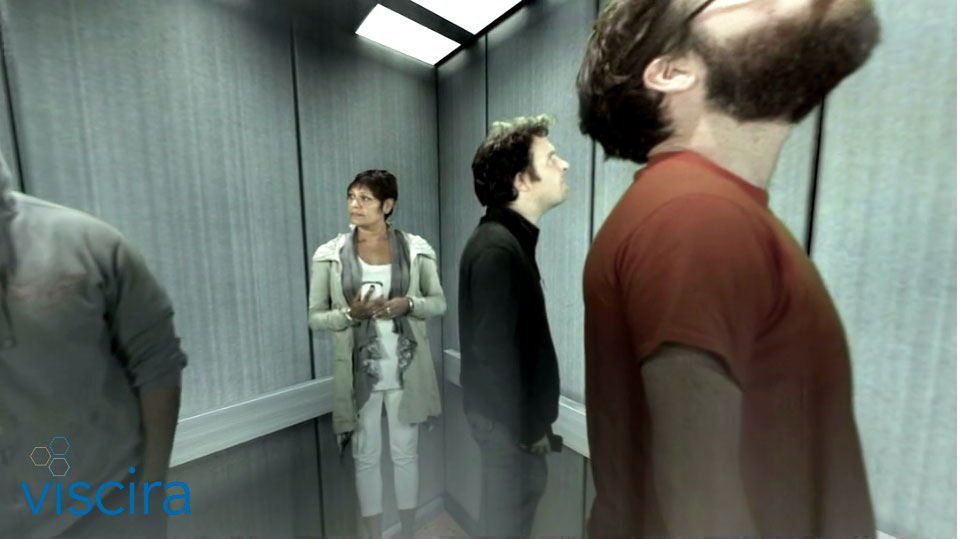
To understand the patient, sometimes you have to climb into his skin. Viscira's Mindscape application allows you to look at the world through the eyes of a person with productive symptoms of schizophrenia — delusions, auditory hallucinations, and thought disorder. The development is not intended for therapy, but for students of medical colleges, as well as relatives of patients - in order to understand what it is like to live with such a disease.

Viscira began working with virtual reality in 2011, and its first development was EyeMac, a simulation of age-related malaria degeneration: with this disease, lines and objects are distorted, and spots appear in the visual field. Ophthalmologists have experienced these symptoms.

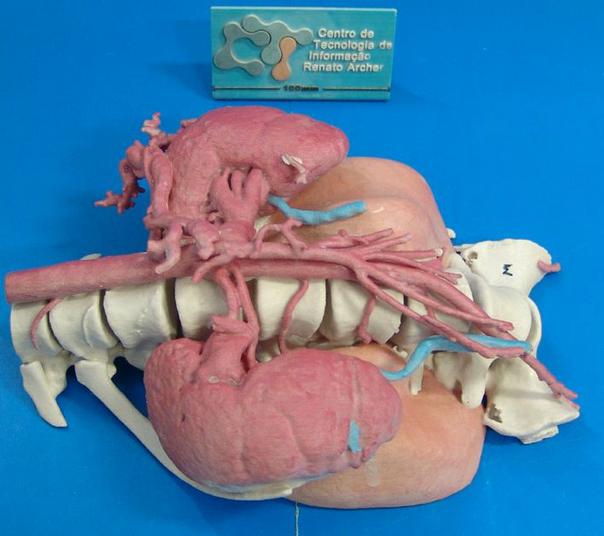
Surgeons, having before their eyes a three-dimensional model of the organ or organs to be operated on, can better plan the intervention, increasing the patient's chances even in the most difficult cases. In the photo below you see a 3D model of a tumor in the body of a twelve-year-old girl - an inoperable tumor located close to the spine and surrounded by healthy organs. This model helped surgeons save the girl.
Virtual reality along with 3D printing can be used to prepare for operations. The data obtained using tomography and three-dimensional data from X-ray machines and ultrasound, the doctor can see in the glasses of virtual reality.
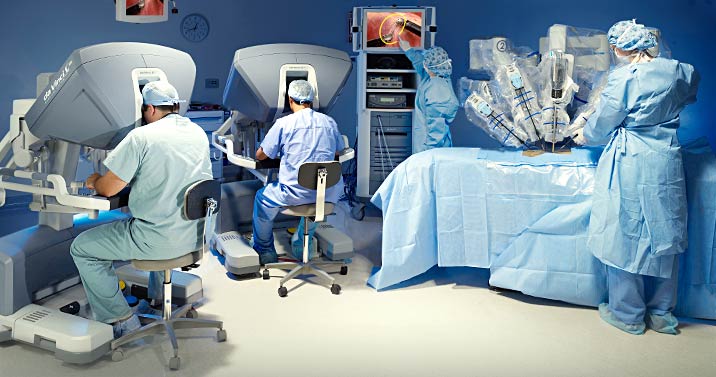
How can you not remember the medical robots , which include the robot surgeon Da Vinci, designed to perform operations at any distance. The system consists of two blocks - in fact, a four-armed robot, which performs the operation, and a block for the surgeon - a device with glasses in which the doctor sees the area in 3D format, and joysticks.
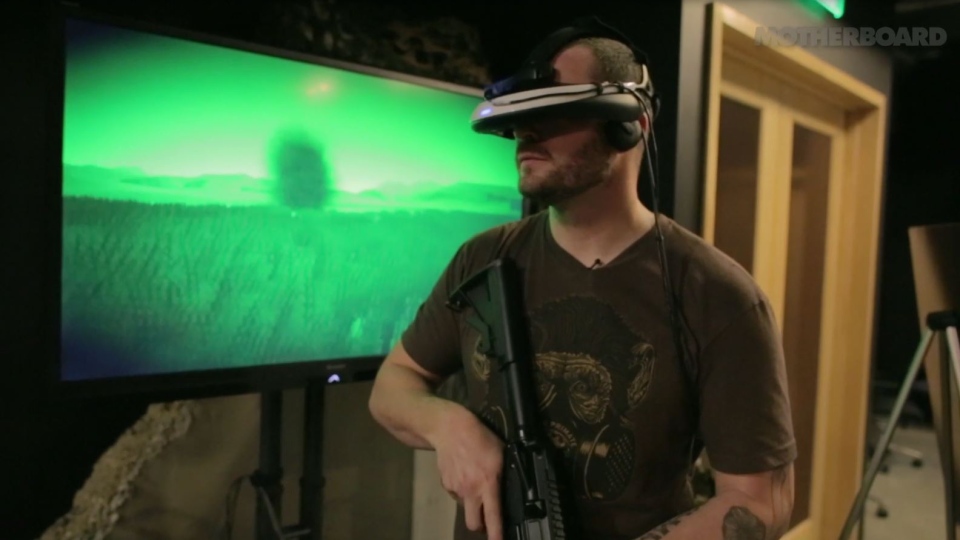
Some soldiers who have been in hot spots suffer from post-traumatic syndrome - sometimes he brings them to suicide. In Southern California at the Institute of Creative Technologies, veterans are helped with the help of a shooting game in which they reproduce a scene from life - they take as a basis the moment in which a person was injured. One of the patients was sure that he had not done enough to save a comrade in battle. Virtual reality has shown that he did everything he could, and this contributed to the improvement of his condition.

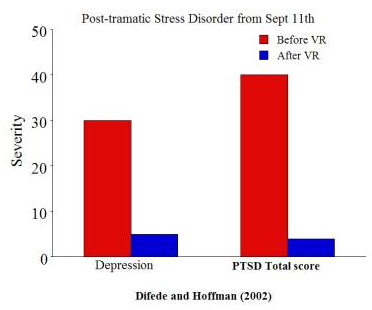
Post-traumatic syndrome was treated with the help of virtual reality in patients affected by the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001. On the image - a terrorist attack in virtual reality. The model was created to help the patient come to terms with this event.

How virtual reality affected depression in people who survived 9/11.
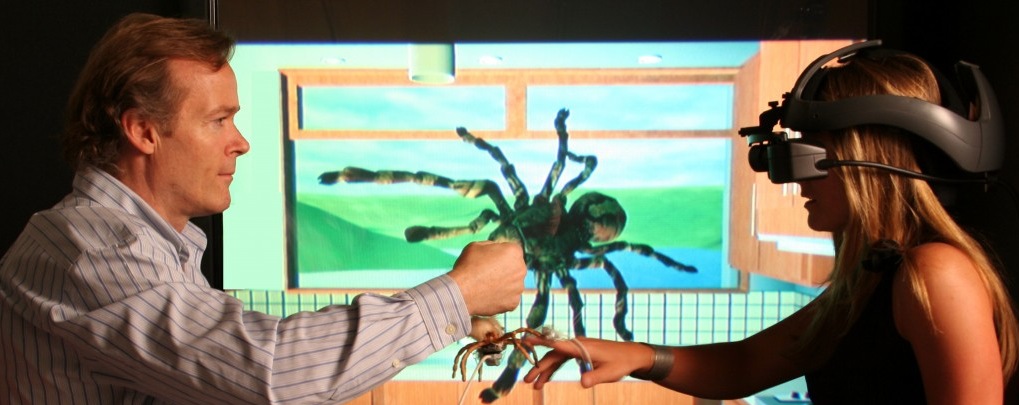
Virtual reality helps people cope with phobias. For example, the HITlab Spiderworld application is designed to treat arachnophobia - a wedge is knocked out with a wedge. The same developers made the SnowWorld application, where you can play snowballs, to reduce pain in patients with burns.



Virtual reality helps to cope with burns - throwing snowballs at penguins distracts and reduces pain.


Education
The surgeon can train his skills by performing simulator operations. In this case, patients do not go to the expense. Modern simulators have a graphic component and tactile feedback. In the photo below - the process of teaching students at the New York Medical College Weill Cornell, where a special virtual reality room is equipped.

')
It looks like a simulator for dentists.


To understand the patient, sometimes you have to climb into his skin. Viscira's Mindscape application allows you to look at the world through the eyes of a person with productive symptoms of schizophrenia — delusions, auditory hallucinations, and thought disorder. The development is not intended for therapy, but for students of medical colleges, as well as relatives of patients - in order to understand what it is like to live with such a disease.

Viscira began working with virtual reality in 2011, and its first development was EyeMac, a simulation of age-related malaria degeneration: with this disease, lines and objects are distorted, and spots appear in the visual field. Ophthalmologists have experienced these symptoms.

Preparation for operations
Surgeons, having before their eyes a three-dimensional model of the organ or organs to be operated on, can better plan the intervention, increasing the patient's chances even in the most difficult cases. In the photo below you see a 3D model of a tumor in the body of a twelve-year-old girl - an inoperable tumor located close to the spine and surrounded by healthy organs. This model helped surgeons save the girl.
Virtual reality along with 3D printing can be used to prepare for operations. The data obtained using tomography and three-dimensional data from X-ray machines and ultrasound, the doctor can see in the glasses of virtual reality.

Conducting operations
How can you not remember the medical robots , which include the robot surgeon Da Vinci, designed to perform operations at any distance. The system consists of two blocks - in fact, a four-armed robot, which performs the operation, and a block for the surgeon - a device with glasses in which the doctor sees the area in 3D format, and joysticks.

Therapy
Some soldiers who have been in hot spots suffer from post-traumatic syndrome - sometimes he brings them to suicide. In Southern California at the Institute of Creative Technologies, veterans are helped with the help of a shooting game in which they reproduce a scene from life - they take as a basis the moment in which a person was injured. One of the patients was sure that he had not done enough to save a comrade in battle. Virtual reality has shown that he did everything he could, and this contributed to the improvement of his condition.

Post-traumatic syndrome was treated with the help of virtual reality in patients affected by the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001. On the image - a terrorist attack in virtual reality. The model was created to help the patient come to terms with this event.

How virtual reality affected depression in people who survived 9/11.

Virtual reality helps people cope with phobias. For example, the HITlab Spiderworld application is designed to treat arachnophobia - a wedge is knocked out with a wedge. The same developers made the SnowWorld application, where you can play snowballs, to reduce pain in patients with burns.



Virtual reality helps to cope with burns - throwing snowballs at penguins distracts and reduces pain.

Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/376725/
All Articles