How to see the ISS tonight

Many believe that the International Space Station (ISS) is flying somewhere very far away, and in order to see it (and even more so to take a picture) you need special equipment. However, this is not the case. Every day, the ISS rushes several times over our heads and seeing it is no more difficult than an ordinary passenger plane. You just need to know when and where to look. The brightness of the ISS can compete even with Jupiter and Venus, and its rapid movement through the sky attracts even more attention. In this article I want to tell how and when you can see the ISS tonight in Moscow , tell you how to find out the time of the ISS flight for any other place and date, and also touch on the subject of photo and video shooting of the ISS.
What is required for observation?
No telescopes and binoculars will help us, even more likely to harm. The fact is that the ISS is moving very quickly, it is difficult to catch and track it with an optical device with a high magnification. This gif gives some idea of its speed.
')

And we need a clear sky (tonight, everything is in order):
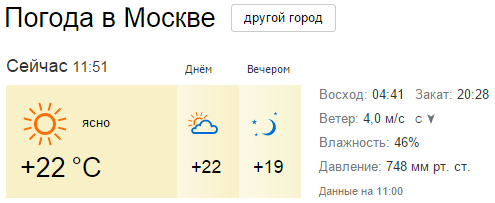
... and an open area with a good view of the south-west, south and south-east (for example, supermarket parking, sports ground, roof of the building, etc.). The proximity of bright lanterns does not hurt us, since the ISS is a very bright object. If you are too lazy to go out, you can get by with a balcony or a window facing south.
You also need a clock synchronized with the exact time, and a compass (in case you don’t know at least the approximate directions to the side of the world at a selected point for observations).
When and where to look?
The ISS makes one turn in about an hour and a half. This means that if the Earth did not rotate, we would see the ISS flying along the same trajectory every hour and a half. Since the Earth is still rotating, the "trace" of the ISS on the surface of the Earth shifts to the west with each turn. In addition, the ISS is visible only when it is illuminated by the Sun itself, while at the observer’s location it is already dark (you can manage to see the ISS even during the day , but this is more difficult). In order to calculate today's visible flights of the ISS over Moscow, I used the online service heavens-above.com (residents of other cities can easily get the ISS visibility conditions there on their own). The most favorable passage for observations is expected today at about 22:47 .
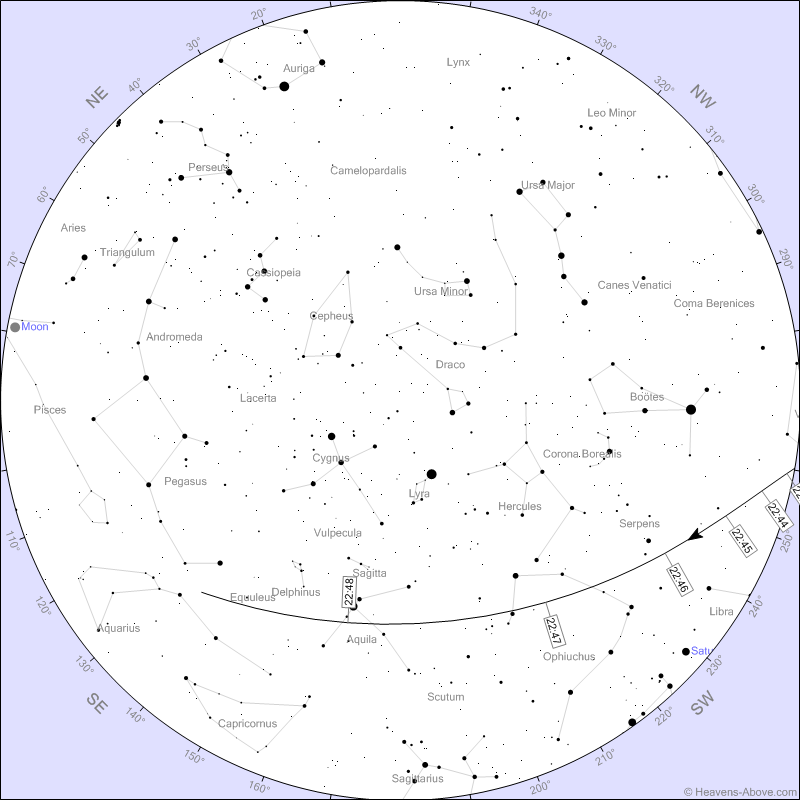
The stars on the map will not help us much as they are not so good in the city. It’s easier to navigate around the world using a compass. If there is no compass, look for the direction where the evening dawn is burning, there will be north-west.
The ISS will ascend at 22:42:30 , but it is still too early to start searching for it. On the very horizon, it is still not bright enough, and besides, trees, buildings and smoke can interfere with the view. It is better to wait until it rises at least 10 degrees above the horizon. It will happen at 22:44:38 , the ISS will be somewhere between the west and southwest. You will notice a dim, flicker-free sprocket that slowly moves to the left and up. This asterisk is the ISS flying somewhere over France at a distance of one and a half thousand kilometers. Do not be in a hurry to get upset if you did not manage to notice it at this moment - you could be prevented by light clouds at the horizon or you yourself miscalculated a little. The asterisk will move faster and faster, it will get brighter and brighter, and within a minute it will be much easier to find it. The station will reach a maximum height of 40 degrees at 10:47:43 , being practically in the south in azimuth. At this moment, the ISS will be located just below the Altair star, compared in brightness with Venus, and in angular velocity with a jet plane. The distance to it will be about 600 km. Then the ISS will decline, shifting to the east, and at 22:48:52 will enter the Earth's shadow. Due to the presence of the atmosphere, the brightness of the station will not fall instantly. It will fade away for a dozen seconds. Especially attentive observers will notice that before going out, the ISS will turn red. Indeed, at this moment astronauts on board will see the sunset, and at sunset the sun's rays redden. When the station finally disappears from view, look to the east and as a bonus you will see a rising moon.
Note: The above points in time will be accurate with second precision for an observer in Red Square. If you are far from the center, there will be differences in a few seconds. For example, in Reutov, the maximum height will be reached 2 seconds later. The entrance to the shadow, of course, will occur simultaneously for all observers.
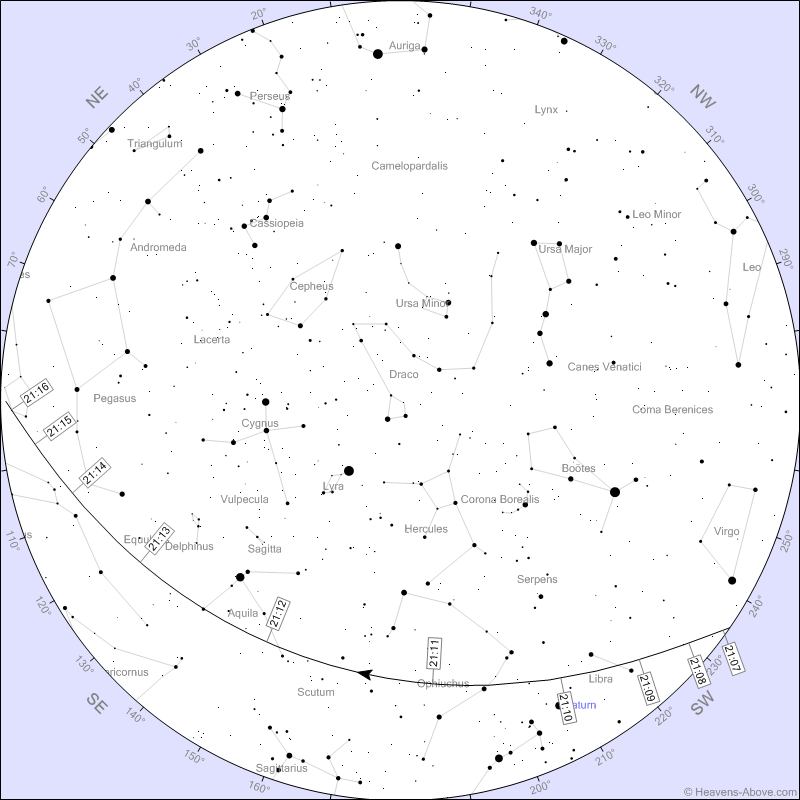
One more less convenient observation for observations will take place in a coil earlier, at 21:11 . You can try to observe it first, but at 9 pm it is still quite light and the ISS will be quite difficult to see against the background of a bright sky. In addition, the station will rise only 28 degrees.
How to take a picture of the ISS or shoot it on video?
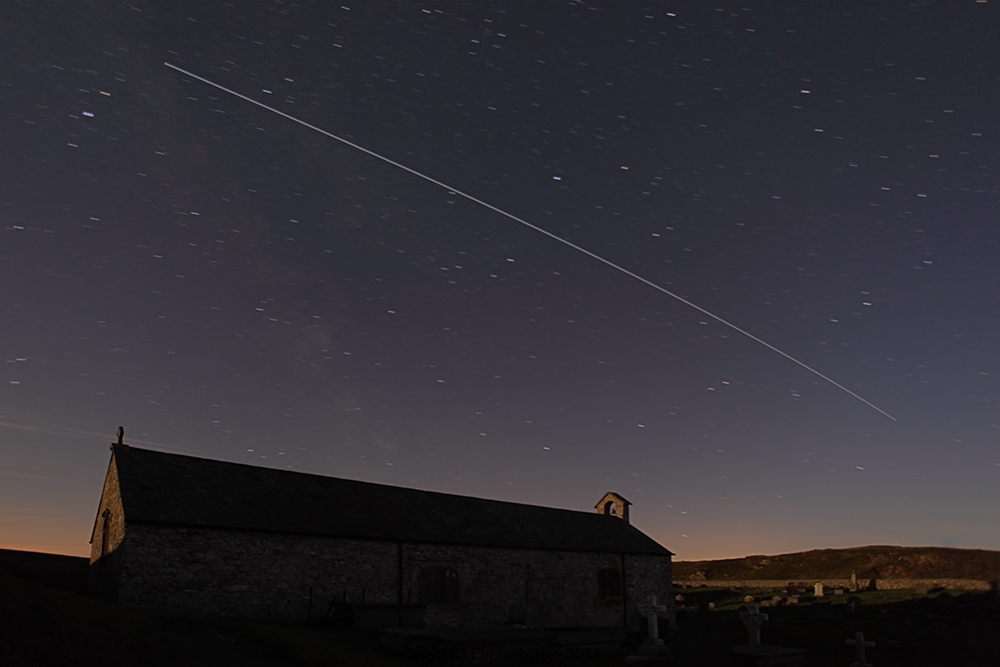
If you are going to observe the ISS for the first time, then I recommend not to be distracted by the photo. Look better with your eyes, get an idea of brightness and speed. Next time, for example, tomorrow , you can already go out with a camera. Set the long shutter speed to 10-30 seconds. Adjust the aperture and sensitivity so as not to flash the sky, but at the same time so that the stars can be seen. Mount the camera on a tripod and direct it to the part of the sky where the flight is expected. A few minutes earlier, you can take a test shot so that, guided by the stars, make sure that the desired part of the sky falls into the frame. As a result, you can get a frame like this (the photo is not mine, found in Google Images).

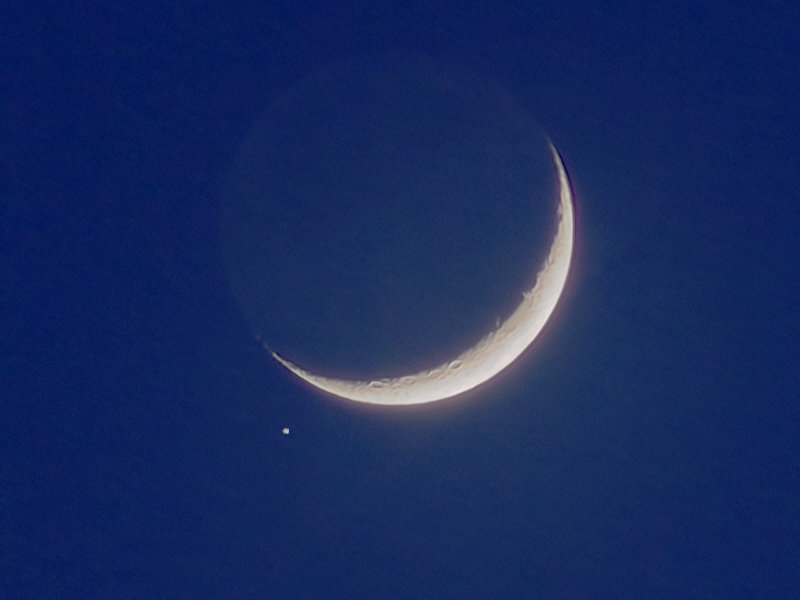
If you are expected to fly close to the moon, then you can catch an interesting frame. For example, I got this:

In the dynamics, it looked like this (shot on a compact camcorder Panasonic HDC-SD90).
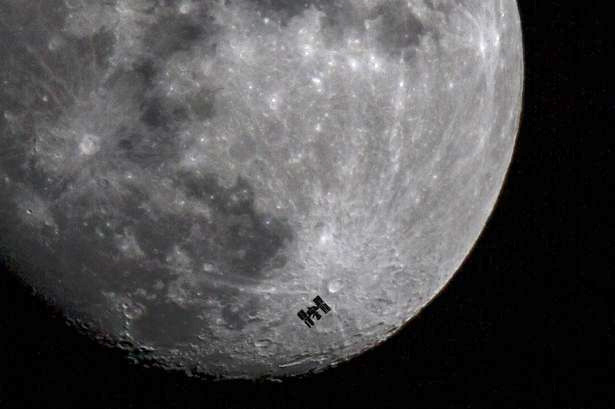
What about transits across the Moon and the Sun shown at the beginning of the article?
Recently, news portals circled the news that NASA has published unique shots of the ISS on the background of the moon. Even on Giktimes wrote this marks . In fact, in that photo there is nothing unusual, this can be seen by searching for the keyword " iss transit " in Google Images. I managed on the first attempt to make such a photo and video with quite modest equipment (the same as I used in the article Enjoying a solar eclipse together ):

Video is better to watch in full screen mode:
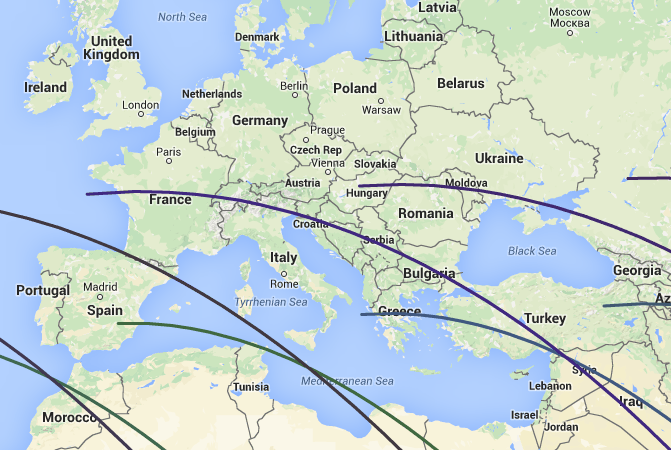
The main problem here is that the shadow (or rather the penumbra) cast by the ISS from the Sun or the Moon has dimensions of only a few kilometers. In an arbitrarily taken place, such a phenomenon happens extremely rarely, so you have to wait for the right moment, get in the car and drive a few tens of kilometers. To find out when and where to go, you can use the service calsky.com . There you can get a map showing where the shadow of the ISS will run over the next couple of days. Here, for example, a fragment of the map of the nearest transits on the Moon.
Conclusion
I hope that thanks to this article, many readers will come out on the street tonight and look at the sky. I propose to share impressions in the comments!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/376611/
All Articles