SpaceX successfully launched the observatory DSCOVR
The landing of the first step on the barge at sea this time had to be abandoned.
In the video, the Falcon 9 launch is very well shown. After about two and a half minutes, the engines are disconnected and the first stage is separated. Then the second stage begins to work, and the head fairings are separated.
At the appointed time, SpaceX successfully launched a Falcon 9 rocket with a satellite weather observation load, DSCOVR . Unfortunately, some secondary tasks had to be abandoned: the first stage of the rocket was not put on a special barge, instead it splashed down in the Atlantic Ocean.
Initially, the launch was planned for February 9 (or February 8 local time), but for reasons independent of SpaceX - the US Air Force had problems with the tracking system - it had to be postponed. Monday did not like the weather conditions, so the start was scheduled for 6:05 pm local time on Tuesday (that is, at two o'clock in the morning Wednesday night in Moscow). Yesterday the launch was postponed again due to strong wind.
This time the weather was perfect, the probability of violation of the start parameters is less than 10% . But a very strong storm began in the sea, the waves reached 9 meters in height. There could be no question of any landing of the first step on the sea platform specially created for this. In addition, the ship had only three out of four engines intact . Ilon Musk, the head and founder of SpaceX, said that the chances of a successful outcome are less than a percent.
')

After two missed starting windows it was no longer possible to postpone. Another cancellation would mean a shift in deadlines for February 20 due to the unfavorable position of the Moon and the associated conditions of gravity. Therefore, the rocket had to launch without landing the first stage on an unmanned ship. Musk also promised that the offshore platform will significantly update in the future, so that it was ready for almost everything. Testing the landing of the first stage of the Falcon 9 rocket means the potential to reduce the launch cost by a dozen times.
DSCOVR is an observatory that is designed to monitor the Earth’s atmosphere, the solar wind and coronal mass emissions. Observing solar activity is important because it adversely affects the operation of radio communication systems, satellites, and electrical power systems, and also increases the radiation dose received by the crew of the International Space Station. Without accurate predictions of solar activity, systems can fail at the most unfavorable moment. The cost of the program DSCOVR - 340 million dollars.
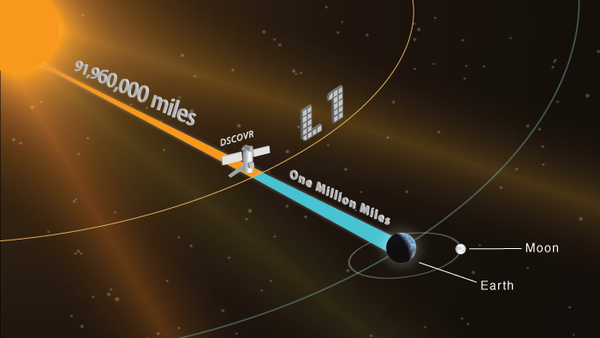 "/>
"/>For the operation of the device must be placed in the Lagrange L 1 in a million and a half kilometers from Earth. From there he will be able to constantly see the illuminated side of our planet and the sun. For SpaceX, this is the first launch of this nature; never before has the brainchild of Ilona Mask launched spacecraft beyond the limits of the earth's orbit. It will be possible to talk about the full success of the launch in about 110 days, when DSCOVR takes its location.
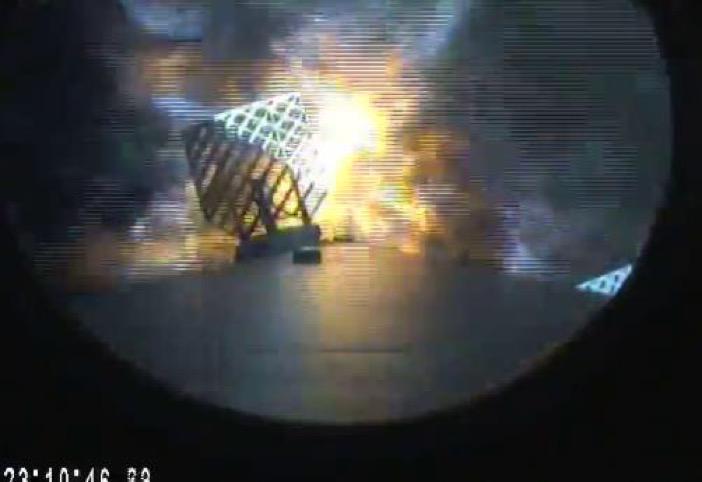

The first stage of Falcon 9 in storm conditions. The photo shows the trellis steering wheels, with the help of which the device controlled its position. The error was only 10 meters. If there were no stormy weather, and a landing platform would be in the sea, a successful outcome would be very likely.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/376399/
All Articles