Charging and NFC in YotaPhone 2
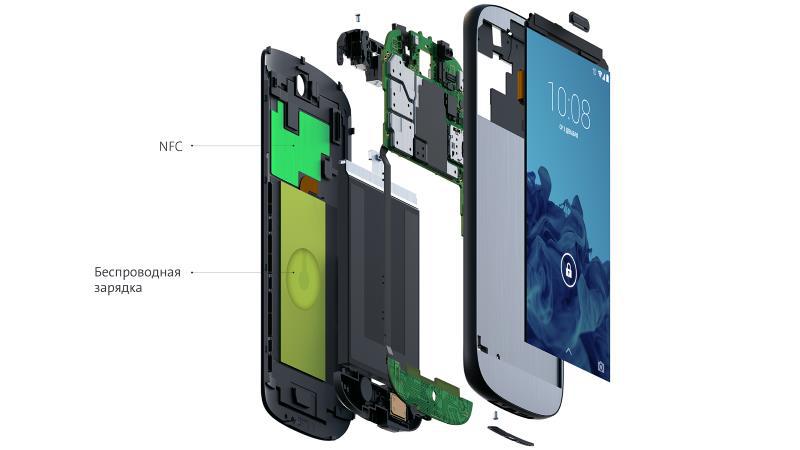
Since the start of sales of YOTAPHONE 2, users have been actively interested in using NFC and wireless charging. Therefore, we decided to tell you more about the technology, how we integrated these modules into the device, and about other features of these YOTAPHONE subsystems.
Wireless charging method
In the world there are several standards for wireless chargers, among which are Qi, PMI and A4WP. Yota Devices is a member of the Wireless Power Consortium (WPC) developing the Qi standard. This is by far the most common standard for wireless charging, and the YOTAPHONE 2 is compatible with it.
Wireless charging, also called inductive charging, was made possible by the law of induction discovered by Michael Faraday in 1831. After 60 years, Nikola Tesla has demonstrated in practice the possibility of wireless transmission of electricity from a generator to a consumer. This requires two coils - the receiving and transmitting, located very close to each other. The alternating current flowing through the transmitting coil generates a magnetic field. It, in turn, creates an induction electric current in the receiving coil. In YOTAPHONE 2, for example, control of the receiving part of the wireless charging is implemented on Toshiba IC (TC7763WBG) with a TDK coil.
')

Like any other approach, the method of electromagnetic induction has its own characteristics. In order for the energy transfer to proceed with the greatest efficiency, the coils should be located as close as possible to each other. This is not a problem in the laboratory, but in practice the distance between the coils in the smartphone and the charger is relatively large. After all, they are separated by the material of the housings of both devices and other structural elements. Moreover, in YOTAPHONE 2, unlike most other gadgets, the receiving coil is not located in the center, but somewhat shifted down. We had to go to this in order to place the NFC antenna without increasing the thickness of the device. Therefore, for regular work, you need to carefully combine the smartphone on the charger so that it does not hang down and does not lie at an angle.
In general, for better stability of the charging process, you can use chargers with three inductive coils (3 coil). However, this does not mean that charging with a smaller number of coils will not be able to charge the YotaPhone 2.
The use of wireless memory has no effect on the display on electronic ink, does not damage it and does not distort the image.
Wired charging method
 Wireless charging is not yet so widespread, and the vast majority use traditional chargers. With YOTAPHONE 2, you can use memory devices that support the Quick Charge 2.0 standard. In this case, the smartphone charges about 75% faster than when connected to a USB port of a laptop or desktop computer, and 30% faster than using Quick Charge 1.0 charging devices. In absolute terms, the full charge time of the YotaPhone 2 using the Quick Charge 2.0 charger is about 2 hours, since it is necessary to maintain the optimum temperature.
Wireless charging is not yet so widespread, and the vast majority use traditional chargers. With YOTAPHONE 2, you can use memory devices that support the Quick Charge 2.0 standard. In this case, the smartphone charges about 75% faster than when connected to a USB port of a laptop or desktop computer, and 30% faster than using Quick Charge 1.0 charging devices. In absolute terms, the full charge time of the YotaPhone 2 using the Quick Charge 2.0 charger is about 2 hours, since it is necessary to maintain the optimum temperature.The table provides a comparison of the effectiveness of different chargers when used with YOTAPHONE 2:
| Battery charge level | 50% | 90% | 100% |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOTAPHONE 2 charger (Quick Charge 2.0) | 42 min. | 1 h 18 min | 2 h |
| YotaPhone 1 memory (5 V / 1.5 A) | 46 min. | 1 h 35 min | 2 h 20 min. |
| USB charging (500 mA) | 2 h 30 min | 4 h 40 min. | 5 h 55 min. |

Another pleasant "side" property of Quick Charge 2.0 is the ability to use less thick wire compared to conventional USB charging (5 V, 2 A). The wire used by us is designed for 1.5 A (with a peak current of up to 1.8 A), and at a voltage of 9 V, this allows you to “skip” more power at the same current value, so a thicker wire is not needed.
By the way, there are two classes of chargers that support Quick Charge 2.0:
• Class A (5 V / 9 V / 12 V)
• Class B (5 V / 9 V / 12 V / 20 V).
The charger for YOTAPHONE 2 corresponds to Class A, while the main voltage for charging a smartphone is 9 V. This is quite enough to charge the batteries of smartphones, so this voltage is found most often in Quick Charge 2.0 chargers. Despite the fact that the maximum power of the charger is 13.5 W (current 1.5 A multiplied by 9 V = 13.5 W), in order to avoid overheating of a Li-Ion battery over 60 degrees, the maximum power had to be artificially limited. Our charger is the only one of all QC 2.0 that has an LED indicator that goes out when the battery is charging.
By the way, you can safely use Quick Charge 2.0 chargers with older devices. The memory itself determines whether a particular gadget supports the standard of fast charging, and selects the appropriate mode. If Quick Charge 2.0 is not supported, the charger produces 5 V with a maximum current of 1.5 A.
NFC
This abbreviation stands for Near Field Communication, which can be translated as "near contactless communication." This formulation hides a method of wireless transmission of information at short distances, no more than 10 cm. This is a promising and interesting technology, which in our country has not yet become widespread. However, I am glad that this new wireless standard is gradually finding new applications.
Today, the main areas of application for NFC are transport and payment systems. For example, this technology is known to residents of a number of cities under the guise of tickets that need to be attached to readers in transport. NFC can also be found in payment terminals of a number of mobile operators, as well as in plastic cards of some banks.
NFC is easy to use and allows you to save time and nerves today. For example, using a special application, you can check the remaining trips on a subway ticket on your smartphone.
You can also read NFC information tags on various products, pay for goods and services directly from your smartphone.
In addition, it is convenient to share information simply by attaching a smartphone to another: whether it is a photo, a map, a contact, in one word - all the most important and necessary.
Slimport
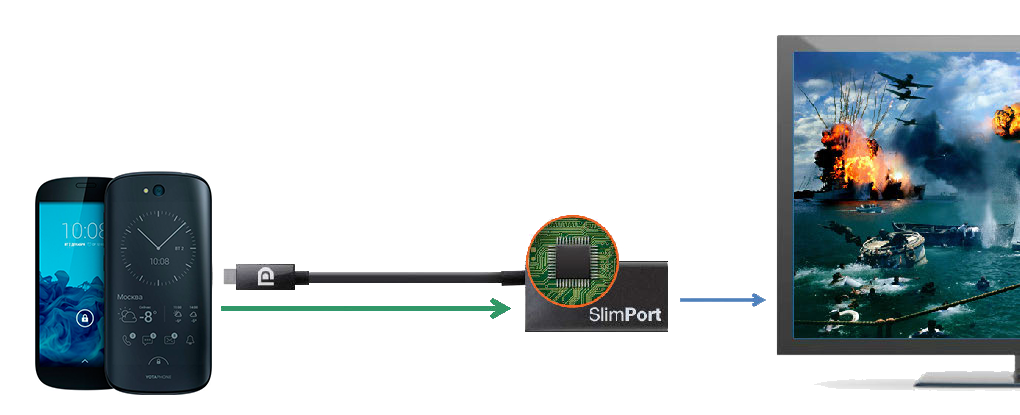
You can connect external display devices, monitors and televisions to YotaPhone 2. It is very convenient for viewing photos and videos. The connection is made using the adapter SlimPort-HDMI (sold separately) connected to the microUSB-connector of the smartphone. Or, you can connect an external device directly using the SlimPort-DisplayPort cable. The SlimPort controller in YOTAPHONE 2 uses an ANX7814 chip.

By the way, in the first YotaPhone for connecting external devices using the MHL interface. However, SlimPort has a number of advantages compared to it. For example, the color depth is 36 bpp instead of 16 at 1080p resolution and 60 frames per second, this difference is especially noticeable when displaying gradients. The average data transfer rate for SlimPort is 480 Mbps instead of 70 for MHL. This interface is more energy efficient and allows you to use Quick Charge 2.0 chargers, that is, charge your smartphone three times faster.
Conclusion
As new questions from YotaPhone 2 users arrive, we will post new posts like this. You can send your questions and suggestions on the topics of new publications to support@yotadevices.com or in a personal.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/375043/
All Articles