What caused the height and inclination of the ISS orbit
 The choice of some orbital parameters of the International Space Station is not always obvious . For example, the station can be at an altitude of 280 to 460 kilometers, and because of this, it constantly experiences the inhibitory effect of the upper layers of the atmosphere of our planet. Every day the ISS loses approximately 5 cm / s of speed and 100 meters in height. Therefore, from time to time it is necessary to raise the station, burning the fuel from the ATV and Progress trucks. Why is it impossible to raise the station higher to avoid these costs?
The choice of some orbital parameters of the International Space Station is not always obvious . For example, the station can be at an altitude of 280 to 460 kilometers, and because of this, it constantly experiences the inhibitory effect of the upper layers of the atmosphere of our planet. Every day the ISS loses approximately 5 cm / s of speed and 100 meters in height. Therefore, from time to time it is necessary to raise the station, burning the fuel from the ATV and Progress trucks. Why is it impossible to raise the station higher to avoid these costs?Pledged when designing the range and the current actual situation are dictated by several reasons. Every day, astronauts and cosmonauts receive high doses of radiation , and beyond the 500 km mark, its level rises sharply. And the limit for a six-month stay is only half a sievert, only a sievert is allotted for the whole career. Each sievert increases the risk of cancer by 5.5 percent.
On Earth, we are protected from cosmic rays by the radiation belt of the magnetosphere of our planet and the atmosphere, but they work less well in near space. In some parts of the orbit (the South Atlantic anomaly is such a spot of increased radiation) and strange effects can sometimes appear outside of it: outbreaks appear in closed eyes. These cosmic particles pass through the eyeballs, other interpretations claim that the particles excite the parts of the brain responsible for vision. This can not only interfere with sleep, but once again unpleasantly recalls the high level of radiation on the ISS.
In addition, "Soyuz" and "Progress", which are now the main ships change crew and supplies, certified to work at an altitude of 460 km. The higher the ISS, the less cargo can be delivered. Less will be able to bring and missiles that send new modules for the station. On the other hand, the lower the ISS, the more it is inhibited, that is, the more cargo delivered must be fuel for subsequent correction of the orbit.
')
Scientific tasks can be performed at an altitude of 400–460 kilometers. Finally, the position of the station is influenced by space debris - the failed satellites and their fragments, which have tremendous speed relative to the ISS, which makes a collision with them fatal.

The network has resources to monitor the parameters of the orbit of the International Space Station. You can get relatively accurate current data , or track their dynamics . At the time of this writing, the ISS was at an altitude of about 400 kilometers.
The elements located at the rear of the station can accelerate the ISS: these are Progress trucks (most often) and ATV, if necessary, the Zvezda service module (extremely rare). The European ATV is working on the illustration to Kata. The station is raised often and little by little: the correction occurs about once a month in small portions of the order of 900 seconds of the engine, while Progress uses smaller engines in order not to greatly influence the course of the experiments.
Engines can turn on once, thus increasing the height of flight on the other side of the planet. Such operations are used for small rises, since the eccentricity of the orbit changes.
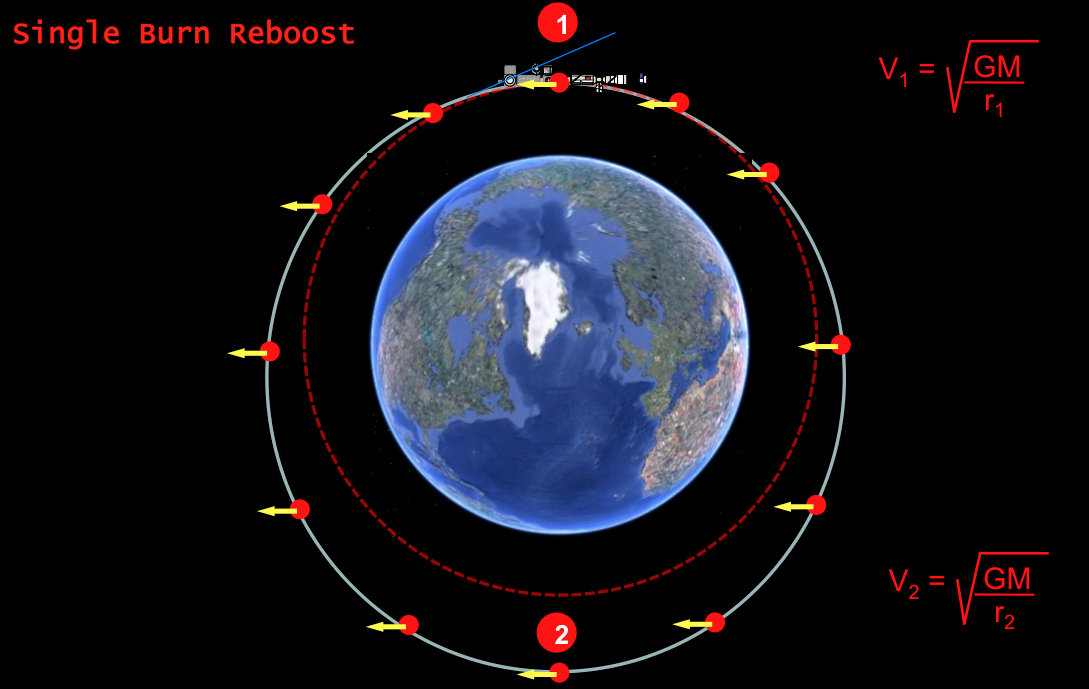
Correction with two inclusions is also possible, in which the second inclusion smooths the station orbit to a circle.

Some parameters are dictated not only by scientific data, but also by politics. It is possible for a spacecraft to be given any orientation, but at launch it will be more economical to use the speed that the rotation of the Earth gives. Thus, it is cheaper to launch the device into orbit with an inclination equal to the latitude, and maneuvers will require additional fuel consumption: more to move to the equator, less when moving to the poles. The inclination of the ISS orbit at 51.6 degrees may seem strange: NASA vehicles, launched from Cape Canaveral, traditionally have an inclination of about 28 degrees.

When the location of the future ISS station was discussed, it was decided that it would be more economical to give preference to the Russian side. Also, these orbital parameters allow you to see more of the surface of the Earth.
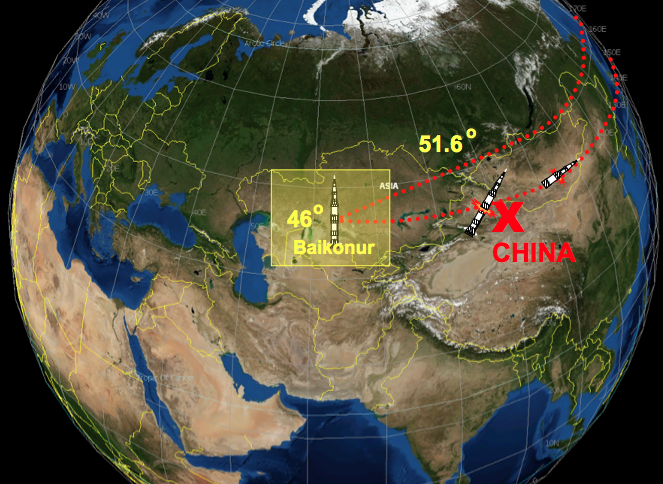
But Baikonur is at a latitude of about 46 degrees, why then is the usual inclination of 51.6 ° for Russian launches? The fact is that to the east there is a neighbor who is not too happy if something falls on him. Therefore, the orbit is tilted to 51.6 ° so that at launch no parts of the spacecraft could under any circumstances fall to China and Mongolia.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/374651/
All Articles