AI Google learned to recognize the voices of people from the random crowd chorus
The person has the ability to distinguish the voice of the interlocutor from the noise, for example, in a place where there is a large crowd of people. This ability is called the "cocktail party effect". Our brain loads unnecessary sounds. Automatic separation of sounds into individual tracks by computer has also been studied, but so far such work remains a challenge for the machine.
A team from Google introduced a self-learning system capable of “snatching” a person’s speech using simultaneous recognition of audio and video sequences, separating other voices and extraneous noise. The study is called “Looking to hear at a cocktail party” (“Looking to Listen at the Cocktail Party”).
A person is able to highlight the voice of the interlocutor he needs from the crowd, and if necessary, ignore the familiar voice and tune in to someone else. A 2013 study by a team of scientists at the University of Queens in Ontario (Canada) in practice proved the “cocktail party effect” with the help of a test for married couples aged 44 to 79 who were married for at least 18 years at the time of the study. Over the years of living together, people tune in to each other, are able to highlight the information spoken in the voice of the spouse in audio, or ignore that voice if necessary. Couples familiar for less than five years are able to recognize the voice of their half worse, but this does not exclude the possibility of focusing on any individual speaker in a noisy room or hearing their own name in the general flow of information.
')
The technology developed by Google Research allows you to edit video, amplifying the voice of the main speaker and eliminating background noise. The method works with regular videos with one audio track. The user is only required to select the face of the person to be heard, or to let the program do it automatically, focusing on the situation. The method can be applied in improving sound and voice recognition from audio to text, in conference applications, to improve hearing aids, as well as in other situations in which a large number of people simultaneously participate.

A feature of the technology is the simultaneous use of audio tracks and video sequences. The movement of the lips of the speaker must match his speech. The visual signal allows not only to highlight and strengthen the desired voice, but also to perform the reverse process - to compare the speech with a specific person in the video.
The program works with a video that is spoken simultaneously by several people. At the output, the method allows you to get two audio tracks - the desired voice and other sounds with noise.

For training the specialists used 100 thousand high quality videos with lectures and monologues on YouTube. Segments with pure speech, without sounds and music in the background, in which the speaker is in the frame, were taken from the commercials. The result was about 2000 hours of video fragments.
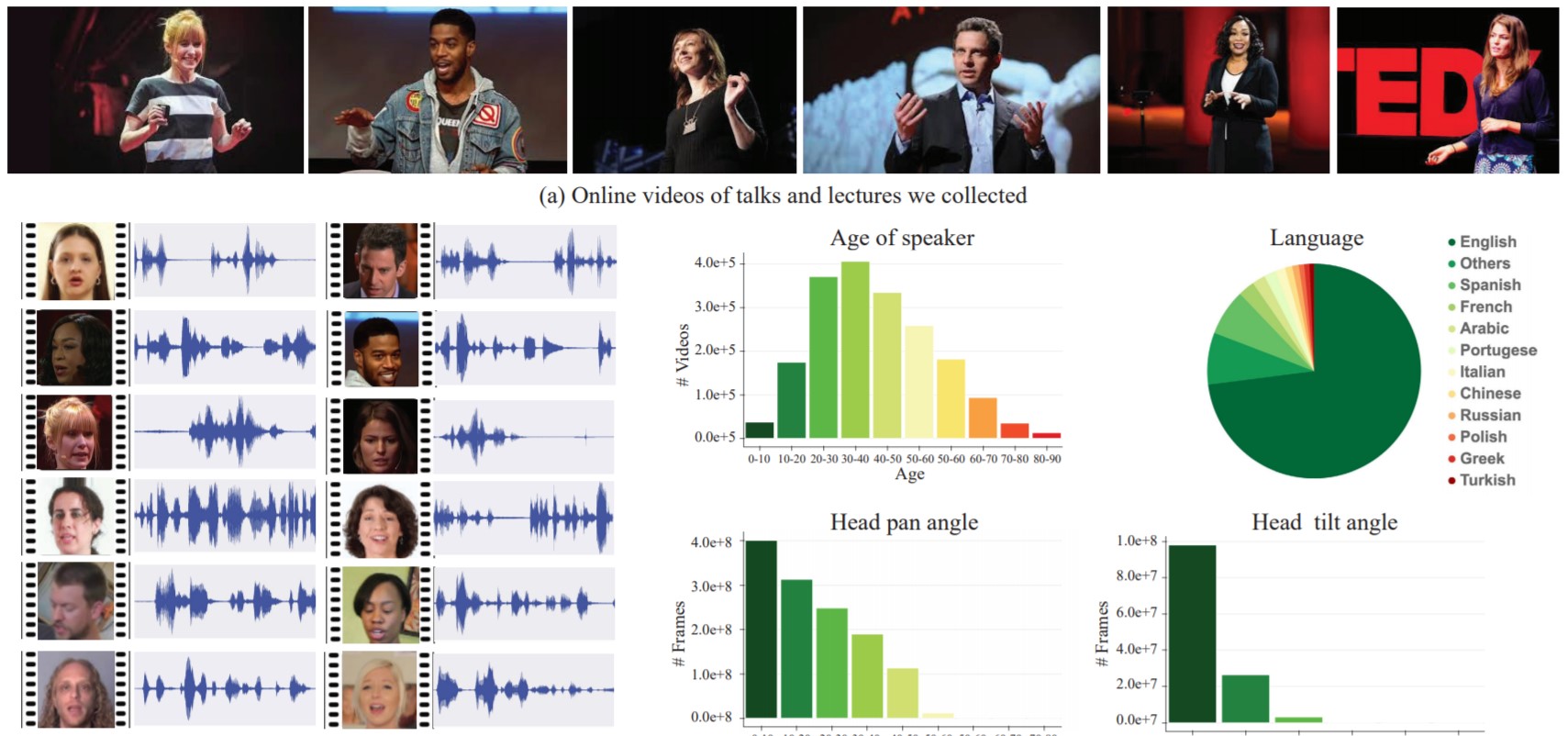
The materials used to create "artificial cocktail parties" along with the extraneous noise that they took from Audioset . The result was a video sequence, which many people speak at the same time. During training, the network compared separate audio tracks with individuals and made up a “mask” for each of the speakers.
Among the possible applications of technology, Google Research offers the use of more accurate automatic subtitling for video.
The work is published on the website of the Cornell University Library.
A team from Google introduced a self-learning system capable of “snatching” a person’s speech using simultaneous recognition of audio and video sequences, separating other voices and extraneous noise. The study is called “Looking to hear at a cocktail party” (“Looking to Listen at the Cocktail Party”).
A person is able to highlight the voice of the interlocutor he needs from the crowd, and if necessary, ignore the familiar voice and tune in to someone else. A 2013 study by a team of scientists at the University of Queens in Ontario (Canada) in practice proved the “cocktail party effect” with the help of a test for married couples aged 44 to 79 who were married for at least 18 years at the time of the study. Over the years of living together, people tune in to each other, are able to highlight the information spoken in the voice of the spouse in audio, or ignore that voice if necessary. Couples familiar for less than five years are able to recognize the voice of their half worse, but this does not exclude the possibility of focusing on any individual speaker in a noisy room or hearing their own name in the general flow of information.
')
The technology developed by Google Research allows you to edit video, amplifying the voice of the main speaker and eliminating background noise. The method works with regular videos with one audio track. The user is only required to select the face of the person to be heard, or to let the program do it automatically, focusing on the situation. The method can be applied in improving sound and voice recognition from audio to text, in conference applications, to improve hearing aids, as well as in other situations in which a large number of people simultaneously participate.

A feature of the technology is the simultaneous use of audio tracks and video sequences. The movement of the lips of the speaker must match his speech. The visual signal allows not only to highlight and strengthen the desired voice, but also to perform the reverse process - to compare the speech with a specific person in the video.
The program works with a video that is spoken simultaneously by several people. At the output, the method allows you to get two audio tracks - the desired voice and other sounds with noise.

For training the specialists used 100 thousand high quality videos with lectures and monologues on YouTube. Segments with pure speech, without sounds and music in the background, in which the speaker is in the frame, were taken from the commercials. The result was about 2000 hours of video fragments.

The materials used to create "artificial cocktail parties" along with the extraneous noise that they took from Audioset . The result was a video sequence, which many people speak at the same time. During training, the network compared separate audio tracks with individuals and made up a “mask” for each of the speakers.
Among the possible applications of technology, Google Research offers the use of more accurate automatic subtitling for video.
The work is published on the website of the Cornell University Library.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/374421/
All Articles