Astronautics 2018 - overview of missions and launches
2018 will be an interesting year. The great opposition of Mars, the launch of new carrier rockets, certification and possible first flight to the ISS of the Dragon and Starliner spacecraft, a telescope - the TESS planet hunter, missions to the Moon, Mars, Mercury and the Sun. Juno will be submerged in the atmosphere of Jupiter, Dawn is buried in the orbit of Ceres, and the probes of Hayabus II and OSIRIS-REx will approach the asteroids to study and collect the regolith. But let's start with Mars.
One of the main astronomical events of 2018 will be the great opposition of Mars. This close distance is also beneficial for space travel. So the Mars Foundation Inspiration was going to send two Americans on a 501 day expedition to fly around Mars. And SpaceX planned to land Red Dragon on the red planet. Both missions were supposed to fly on the SpaceX super-heavy rocket Falcon Heavy, the first launch of which was repeatedly transferred and scheduled for January 2018. Instead of Red Dragon, SpaceX will launch the Tesla Roadster on the trajectory of the passage past Mars, and nothing more is heard about the flight of Mars.
Instead, the previously canceled InSight research mission will be held to study the internal structure and composition of the red planet. The probe is built in the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) on the basis of the already proven design of the Phoenix landing probe. The launch will take place on May 5 on the ULA Altas V rocket, and arrival in November 2018.
')
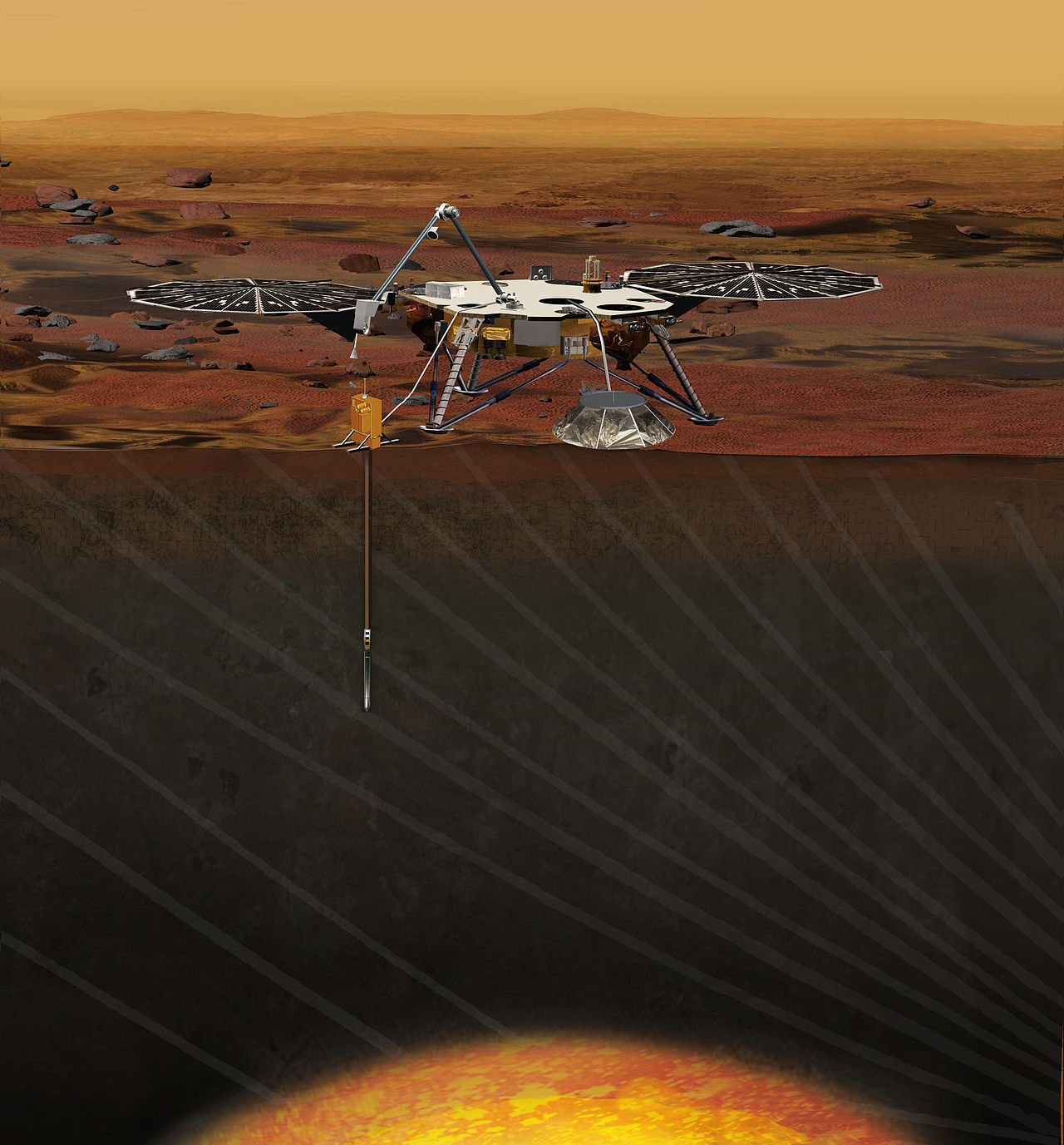

The probe is equipped with two cameras, a seismometer and a drill with the ability to dive to a depth of 6 m. The stationary probe will receive energy from solar batteries.
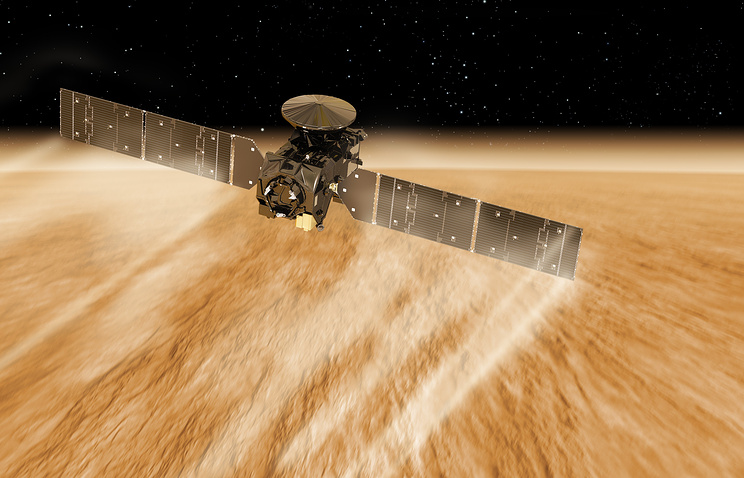

Since 2016, the TGO (Trace Gas Orbiter) orbital module of the Russian-European mission ExoMars gradually slows down against the atmosphere of Mars in order to move to a circular orbit and begin research in the spring of 2018. The device will investigate the origin of methane, other gases and water vapor in the atmosphere of Mars.
Also TGO will perform the functions of a repeater with the future rover Exomars 2020 .

In March, India plans to send its second mission to the moon - Chandrayan-2. The mission will consist of orbital and landing devices and even a small moon rover. Initially, the project was planned to be implemented jointly with Russia, but after the failure with Phobos-Grunt in 2011, India decided to launch the device on its own. The launch will take place on a rocket carrier GSLV Mk II, which limits the maximum mass of the lunar mission, which will be 3.25 tons. To achieve the lunar orbit, complex and lengthy maneuvers will be conducted. The first Indian lunar rover will weigh only 20 kg. and must work one lunar day.
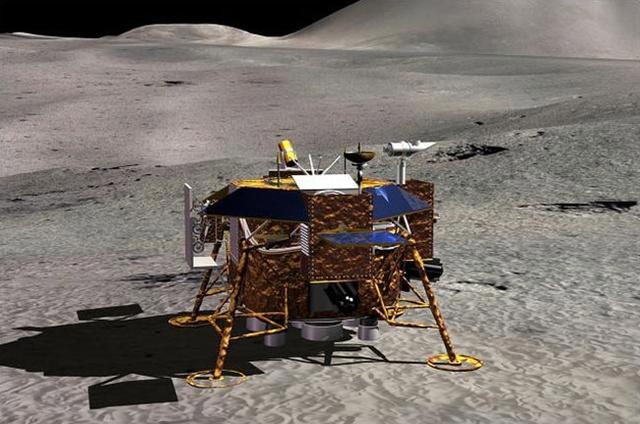

The goal of Chang'e-4 (duplication of the mission of Chang'e-3) is the first landing in history on the reverse side of the moon. To ensure communication with the landing module in July 2018, it is planned to launch the orbital module to the L2 position of the L2 . At the end of 2018 the launch of the landing module with a lunar rover is scheduled.
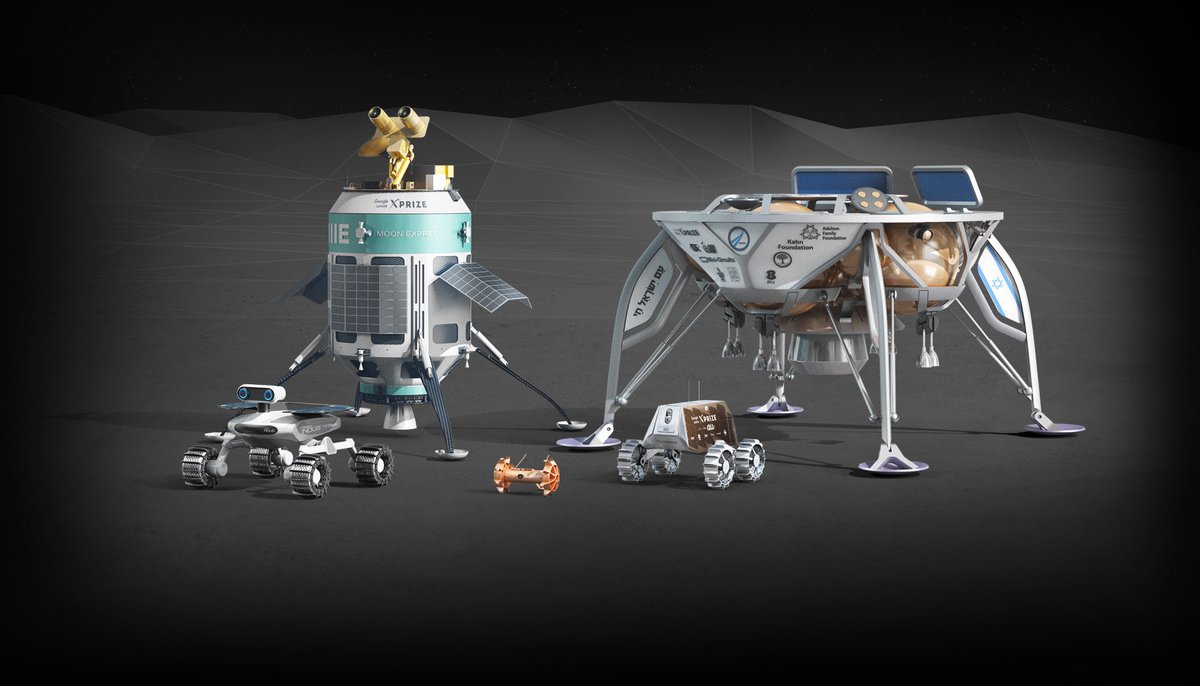

In addition to the two missions of the space agencies of India and China, in 2018, the 5 finalist teams of the Google Lunar Xprize contest are going to moonlight on the moon. In August 2017, the end date of the competition was finally moved to March 31, 2018, and the teams are at the finish line , but the prospects are dim.
Team Intus and Israeli SpaceIL are still raising money at the start. Japanese Hakuto gathered to fly with the Indians and depend on their launch. American Moon Express depends on Electron carrier rocket, the second test launch of which was postponed to January 2018.
International Synergy Moon will launch a launch on its own launch vehicle, which is not yet ready.
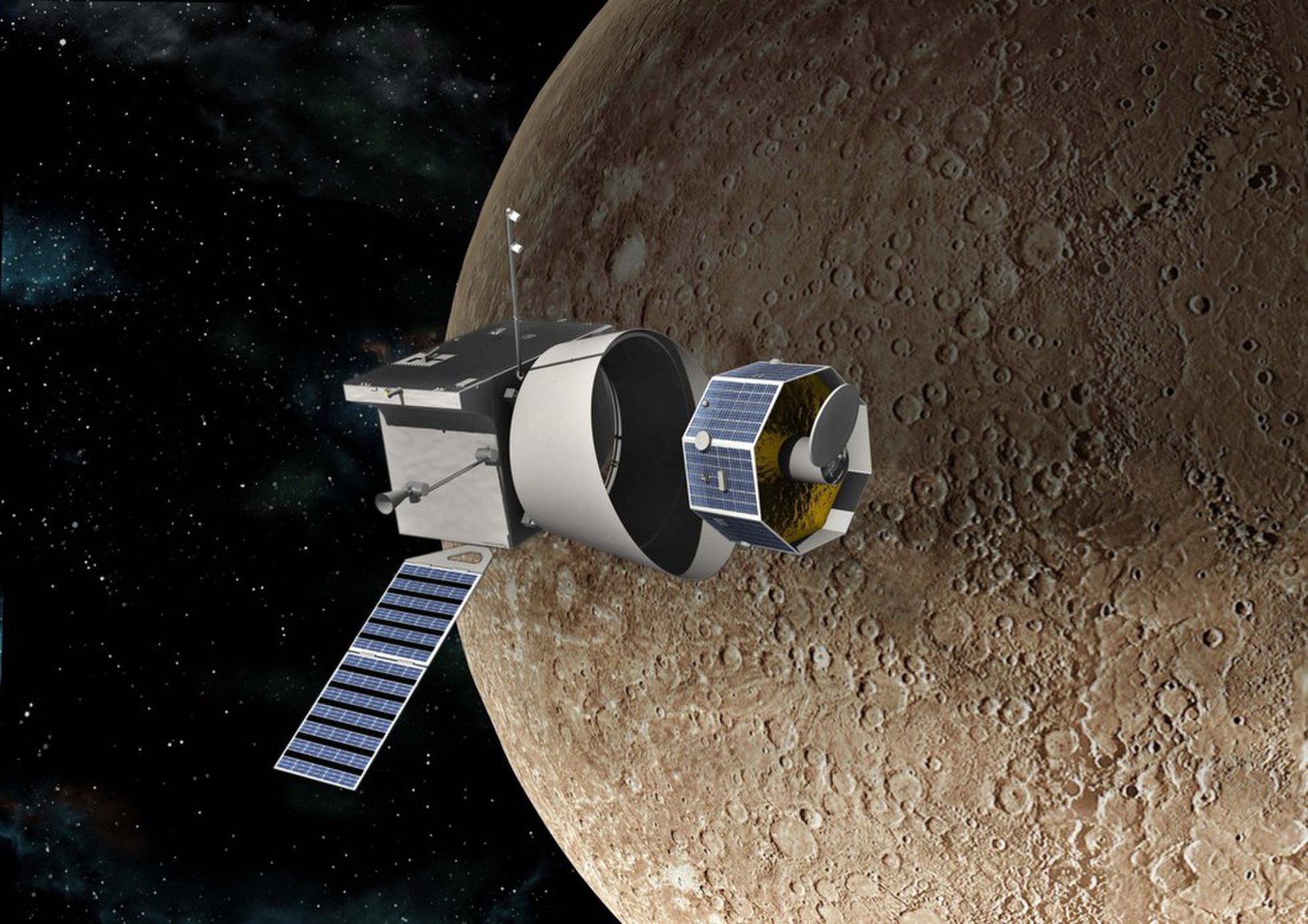
The joint project of the European ESA and the Japanese JAXA for the study of Mercury will consist of two satellites, with different orbits. The launch is scheduled for October 2018 on the European launch vehicle Ariane-5, and arrival in December 2025. To save fuel, as many as 17 gravitational maneuvers around the Earth, Venus and Mercury will be performed.
European Mercury Planetary Orbiter will study the surface and the internal structure of Mercury. The Japanese Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter will investigate the magnetic field and the Mercury magnetosphere.
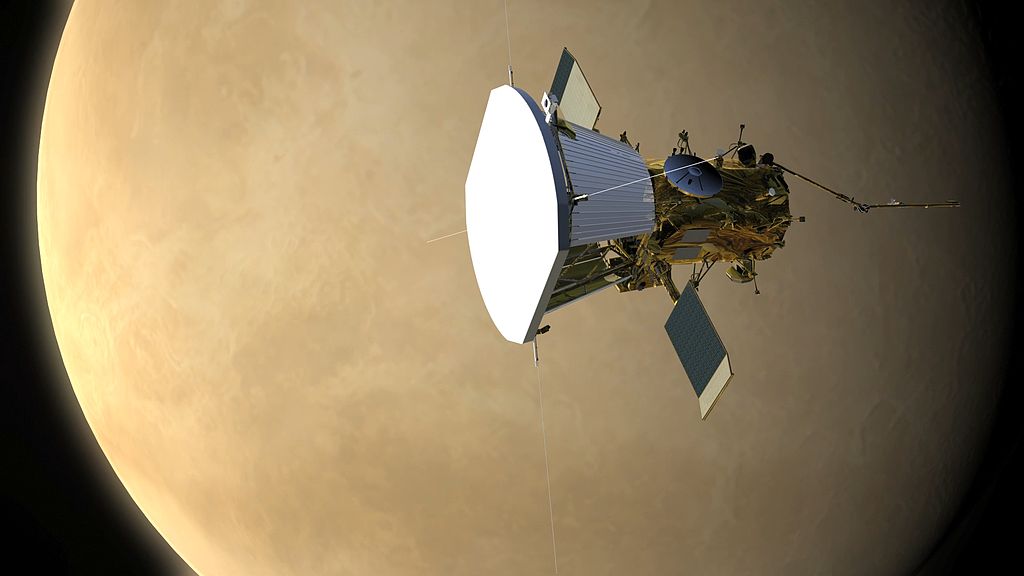

On July 31, 2018, the Solar Probe Plus will be launched on the Delta IV Heavy heavy rocket - a space probe to study the solar corona from an orbit at an altitude of 8.5 times the radius of the sun. The probe is equipped with a hexagonal shield behind which all instruments and solar panels are hidden. Magnetic fields, formation, acceleration of particles of the solar wind and the level of energy emitted by the solar corona are going to study. On December 19, 2024, the probe will have to reach the orbit of the Sun, for which it will perform 7 gravitational maneuvers near Venus.
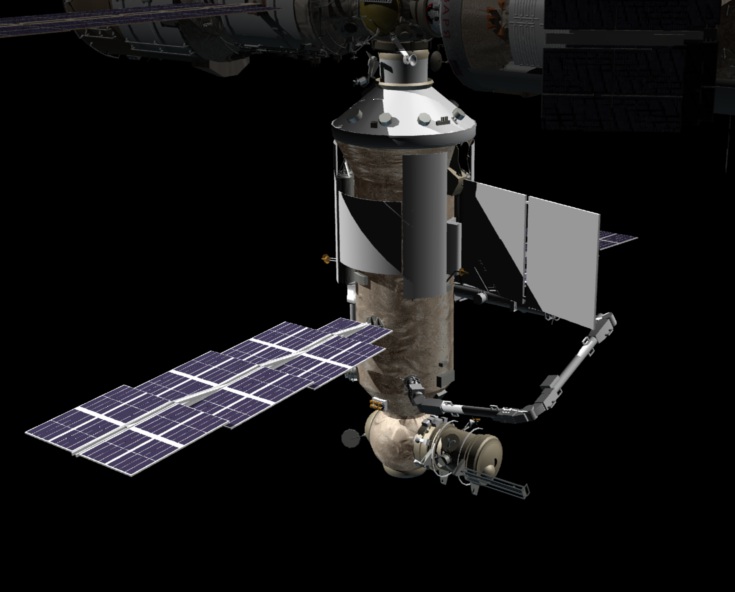

At the end of 2018, the launch of the 25-ton Russian multifunctional laboratory module " Science " should take place. The launch was repeatedly postponed, but this time Rosskosmos was determined.
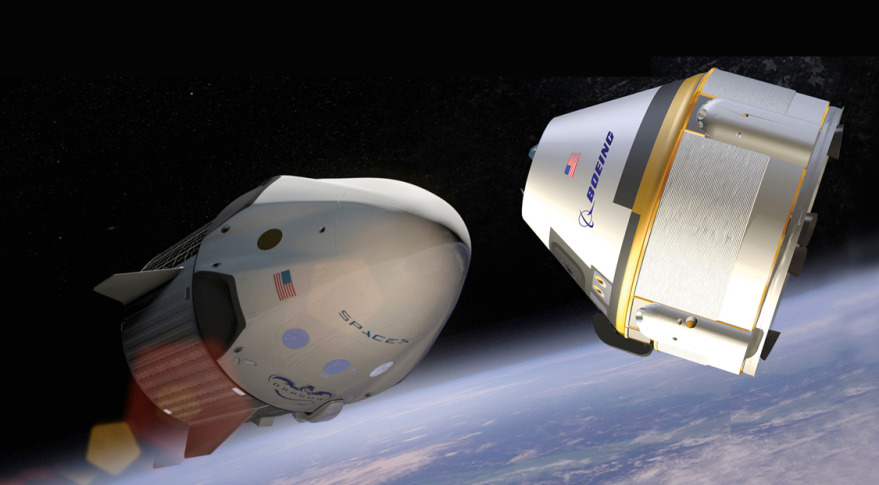

In 2014, SpaceX and Boeing became two winners in the competition for the delivery of astronauts to MSK and their return to earth. And in 2018 the first flights with people should take place.
Boeing plans to conduct flight tests of its CST-100 Starliner in August 2018. For SpaceX, the first demo launch of the Dragon V2 spacecraft to the ISS is scheduled for April 2018. The first manned flights to the ISS were postponed to 2019.
During the year, 4 manned MCs with interchangeable crews for the ISS will be launched.
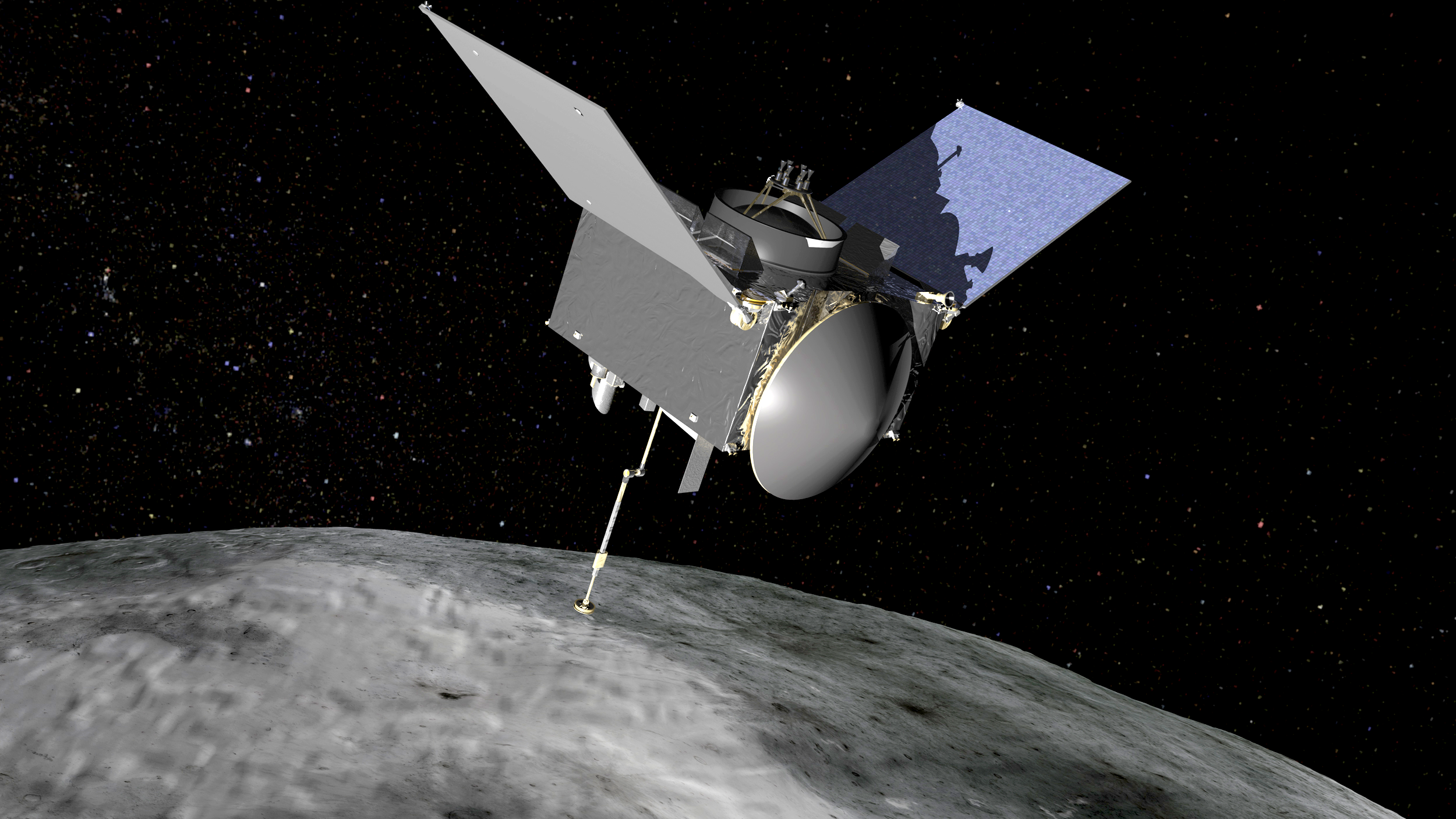

In September 2018, the OSIRIS-REx interplanetary station will arrive at the Bennu asteroid. After approaching, the device will begin to map the asteroid and measure the change in its orbit depending on the heating by the Sun. The results of the mapping will be used to select the ground location, the fence itself will be held in 2019, and return to Earth in 2023.
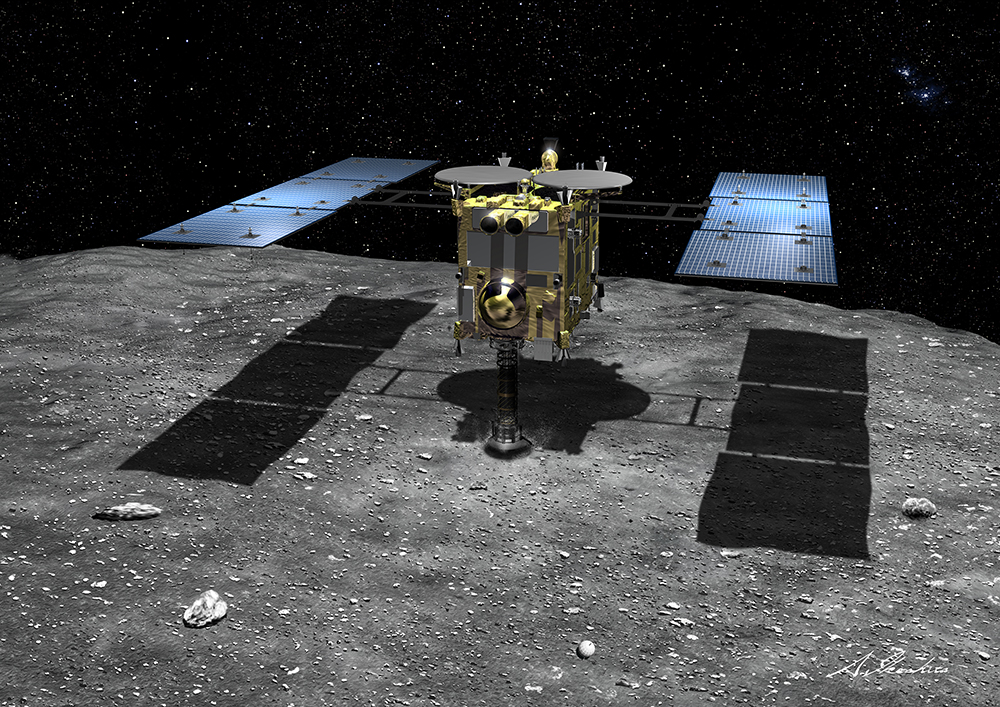
The Japanese Hayabusa-2 in July 2018 will arrive at the asteroid (162173) Ryugu . When approaching, it is planned to bombard the asteroid with a copper shell with a charge of explosives to form a shock crater and detect other rocks in it. MASCOT, a small, European-made descent vehicle, will descend for a more detailed survey. Like OSIRIS-REx, Hayabusa-2 will have to deliver a sample of rocks from the surface of the asteroid to Earth.
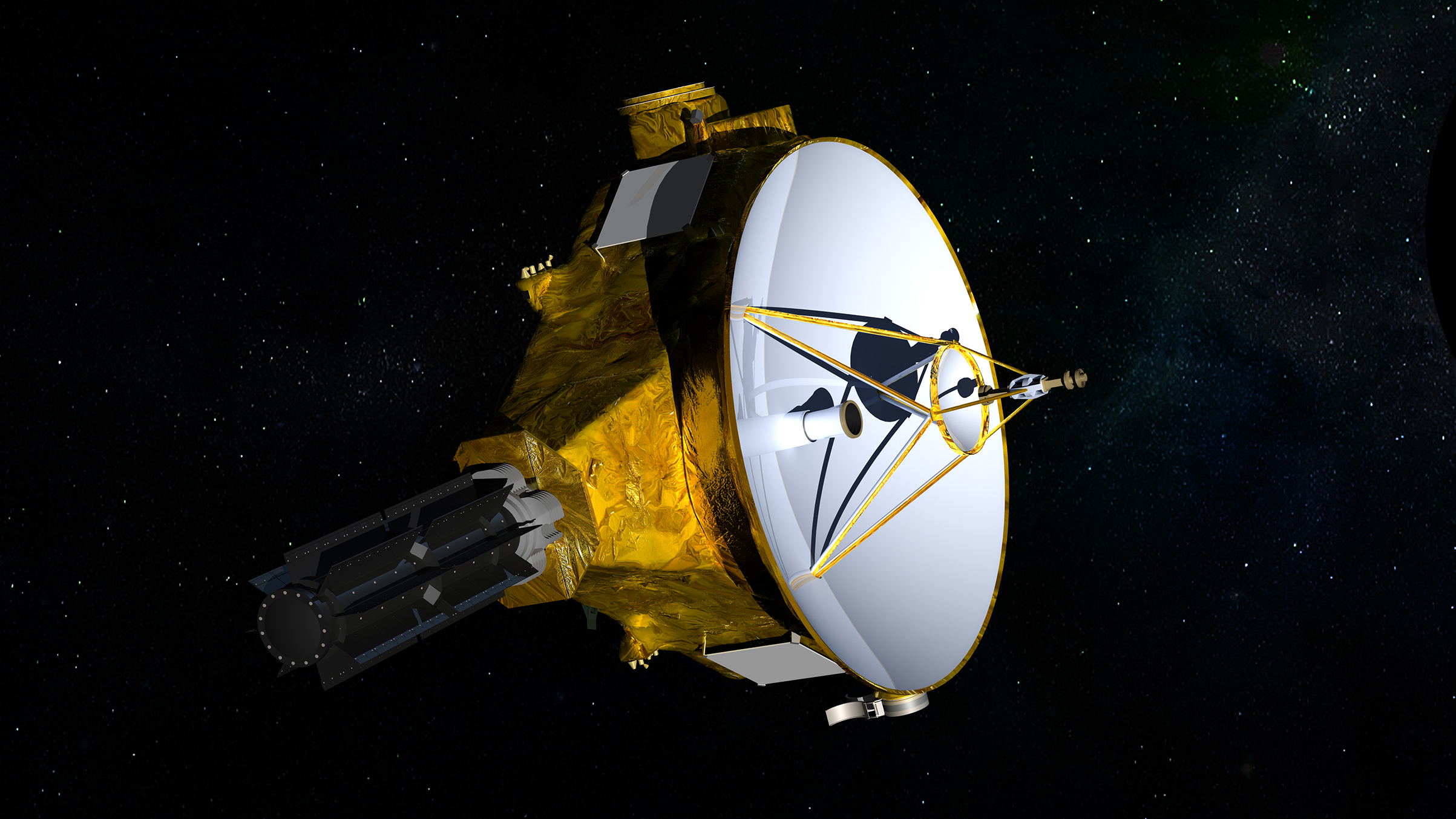

Launched in 2006, the New Horizons research station, located in the Kuiper belt, in June 2018 will exit hibernation and begin to approach the 2014 MU69 object, although the station will reach its minimum distance only in 2019. 2014 MU69 will be the most distant object in the solar system, which will visit the spacecraft created by people.
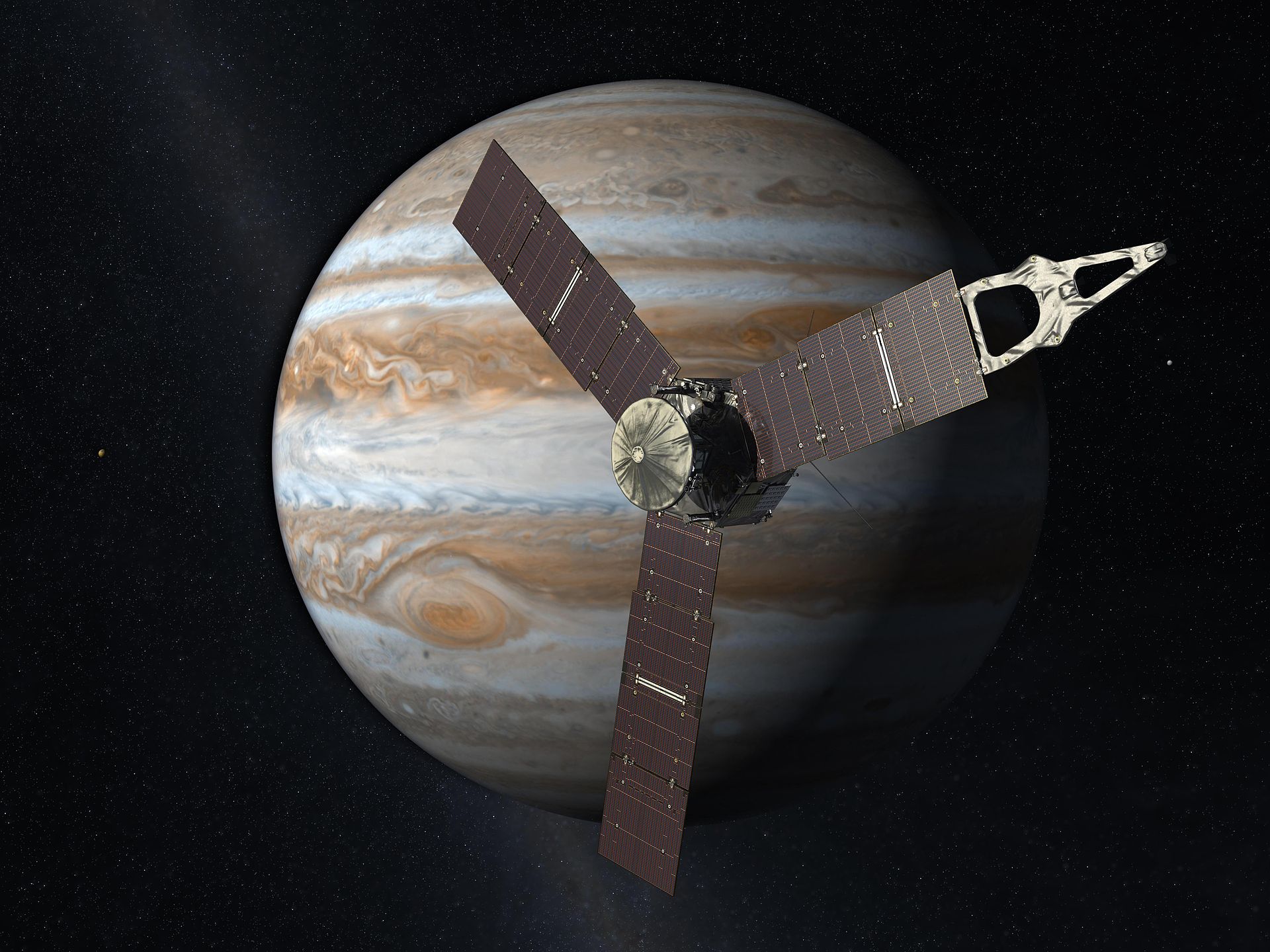

The fate of the grand finale of Cassini in 2017 will be repeated by Juno (Jupiter Polar Orbiter) in 2018. The satellite launched in 2011 has been exploring Jupiter since 2016 and will be submerged in the atmosphere in the summer of 2018.

The Dawn probe mission was extended until the second half of 2018, when its fuel reserves were finally exhausted. The probe will be buried in Ceres orbit to avoid contamination of the surface of Ceres with materials of terrestrial origin. The probe was launched in 2007 and explored the asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres .
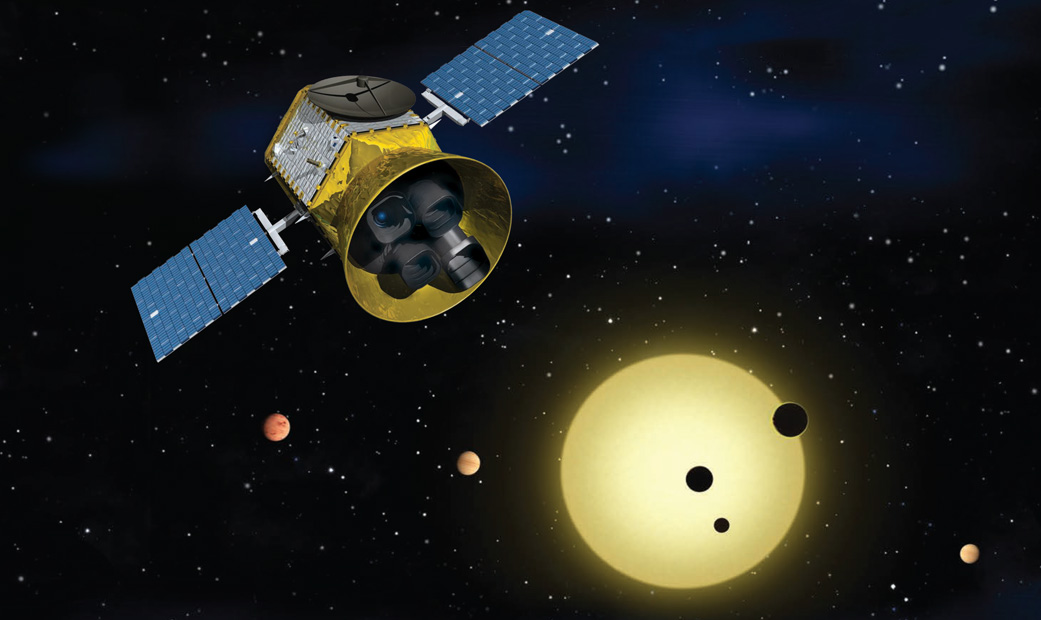

TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite) Planet Hunter will conduct research to investigate open and detect previously unknown transit exoplanets around bright stars. The data obtained by TESS will be used for further more detailed studies by other telescopes in the future. The initially privately-funded telescope from the second time hit the NASA program for the development of small research programs and will be launched in March 2018 on Falcon 9.
In May 2018, OneWeb will begin to deploy a constellation of about 2.5 thousand satellites that will provide Internet access throughout the planet. The launches will be carried out by the Unions in low orbit.
Sir Richard Branson, the founder of Virgin Galactic , expressed a desire to make the first flight of the SpaceShipTwo suborbital spacecraft with passengers in 2018. At the end of 2018, Blue Origin also plans to make the first flight of the New Shepard suborbital rocket system with people on board. After that, it is planned to finally begin commercial flights.
The test launches of Electron light rocket of the American Rocket Lab, Kuaizhou-1 of the Chinese company CASIC and the American LauncherOne of the Virgin Orbit company will continue.
For 2018, the first launch of the Stratolaunch is also planned , designed to launch orbital rockets from the Roc two-body aircraft.

The second launch of the Angara-A5 heavy rocket from the Plesetsk cosmodrome is scheduled for the very end of 2018, and SpaceX is going to send two tourists to fly around the moon.
UPD 1: Team Indus seems to be eliminated from the moon race (and with it the Japanese Hakuto), did not have time to raise money.
UPD 2: Postponed the flight dates of the new manned ships Dragon V2 and Starliner:
Boeing Orbital Flight Test (uncrewed): August 2018
Boeing Crew Flight Test (crewed): November 2018
SpaceX Demonstration Mission 1 (uncrewed): August 2018
SpaceX Demonstration Mission 2 (crewed): December 2018
Mars
One of the main astronomical events of 2018 will be the great opposition of Mars. This close distance is also beneficial for space travel. So the Mars Foundation Inspiration was going to send two Americans on a 501 day expedition to fly around Mars. And SpaceX planned to land Red Dragon on the red planet. Both missions were supposed to fly on the SpaceX super-heavy rocket Falcon Heavy, the first launch of which was repeatedly transferred and scheduled for January 2018. Instead of Red Dragon, SpaceX will launch the Tesla Roadster on the trajectory of the passage past Mars, and nothing more is heard about the flight of Mars.
Insight
Instead, the previously canceled InSight research mission will be held to study the internal structure and composition of the red planet. The probe is built in the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) on the basis of the already proven design of the Phoenix landing probe. The launch will take place on May 5 on the ULA Altas V rocket, and arrival in November 2018.
')

The probe is equipped with two cameras, a seismometer and a drill with the ability to dive to a depth of 6 m. The stationary probe will receive energy from solar batteries.
ExoMars: TGO

Since 2016, the TGO (Trace Gas Orbiter) orbital module of the Russian-European mission ExoMars gradually slows down against the atmosphere of Mars in order to move to a circular orbit and begin research in the spring of 2018. The device will investigate the origin of methane, other gases and water vapor in the atmosphere of Mars.
Also TGO will perform the functions of a repeater with the future rover Exomars 2020 .
Moon
Chandrayaan 2

In March, India plans to send its second mission to the moon - Chandrayan-2. The mission will consist of orbital and landing devices and even a small moon rover. Initially, the project was planned to be implemented jointly with Russia, but after the failure with Phobos-Grunt in 2011, India decided to launch the device on its own. The launch will take place on a rocket carrier GSLV Mk II, which limits the maximum mass of the lunar mission, which will be 3.25 tons. To achieve the lunar orbit, complex and lengthy maneuvers will be conducted. The first Indian lunar rover will weigh only 20 kg. and must work one lunar day.
Chang'e-4

The goal of Chang'e-4 (duplication of the mission of Chang'e-3) is the first landing in history on the reverse side of the moon. To ensure communication with the landing module in July 2018, it is planned to launch the orbital module to the L2 position of the L2 . At the end of 2018 the launch of the landing module with a lunar rover is scheduled.
Google Lunar Xprize

In addition to the two missions of the space agencies of India and China, in 2018, the 5 finalist teams of the Google Lunar Xprize contest are going to moonlight on the moon. In August 2017, the end date of the competition was finally moved to March 31, 2018, and the teams are at the finish line , but the prospects are dim.
Team Intus and Israeli SpaceIL are still raising money at the start. Japanese Hakuto gathered to fly with the Indians and depend on their launch. American Moon Express depends on Electron carrier rocket, the second test launch of which was postponed to January 2018.
International Synergy Moon will launch a launch on its own launch vehicle, which is not yet ready.
Mercury

The joint project of the European ESA and the Japanese JAXA for the study of Mercury will consist of two satellites, with different orbits. The launch is scheduled for October 2018 on the European launch vehicle Ariane-5, and arrival in December 2025. To save fuel, as many as 17 gravitational maneuvers around the Earth, Venus and Mercury will be performed.
European Mercury Planetary Orbiter will study the surface and the internal structure of Mercury. The Japanese Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter will investigate the magnetic field and the Mercury magnetosphere.
The sun

On July 31, 2018, the Solar Probe Plus will be launched on the Delta IV Heavy heavy rocket - a space probe to study the solar corona from an orbit at an altitude of 8.5 times the radius of the sun. The probe is equipped with a hexagonal shield behind which all instruments and solar panels are hidden. Magnetic fields, formation, acceleration of particles of the solar wind and the level of energy emitted by the solar corona are going to study. On December 19, 2024, the probe will have to reach the orbit of the Sun, for which it will perform 7 gravitational maneuvers near Venus.
ISS
The science

At the end of 2018, the launch of the 25-ton Russian multifunctional laboratory module " Science " should take place. The launch was repeatedly postponed, but this time Rosskosmos was determined.
Dragon V2 and CST-100 Starliner

In 2014, SpaceX and Boeing became two winners in the competition for the delivery of astronauts to MSK and their return to earth. And in 2018 the first flights with people should take place.
Boeing plans to conduct flight tests of its CST-100 Starliner in August 2018. For SpaceX, the first demo launch of the Dragon V2 spacecraft to the ISS is scheduled for April 2018. The first manned flights to the ISS were postponed to 2019.
During the year, 4 manned MCs with interchangeable crews for the ISS will be launched.
Asteroids
OSIRIS-REx

In September 2018, the OSIRIS-REx interplanetary station will arrive at the Bennu asteroid. After approaching, the device will begin to map the asteroid and measure the change in its orbit depending on the heating by the Sun. The results of the mapping will be used to select the ground location, the fence itself will be held in 2019, and return to Earth in 2023.
Hayabusa-2

The Japanese Hayabusa-2 in July 2018 will arrive at the asteroid (162173) Ryugu . When approaching, it is planned to bombard the asteroid with a copper shell with a charge of explosives to form a shock crater and detect other rocks in it. MASCOT, a small, European-made descent vehicle, will descend for a more detailed survey. Like OSIRIS-REx, Hayabusa-2 will have to deliver a sample of rocks from the surface of the asteroid to Earth.
New horizons

Launched in 2006, the New Horizons research station, located in the Kuiper belt, in June 2018 will exit hibernation and begin to approach the 2014 MU69 object, although the station will reach its minimum distance only in 2019. 2014 MU69 will be the most distant object in the solar system, which will visit the spacecraft created by people.
Juno

The fate of the grand finale of Cassini in 2017 will be repeated by Juno (Jupiter Polar Orbiter) in 2018. The satellite launched in 2011 has been exploring Jupiter since 2016 and will be submerged in the atmosphere in the summer of 2018.
Dawn

The Dawn probe mission was extended until the second half of 2018, when its fuel reserves were finally exhausted. The probe will be buried in Ceres orbit to avoid contamination of the surface of Ceres with materials of terrestrial origin. The probe was launched in 2007 and explored the asteroid Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres .
Tess

TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite) Planet Hunter will conduct research to investigate open and detect previously unknown transit exoplanets around bright stars. The data obtained by TESS will be used for further more detailed studies by other telescopes in the future. The initially privately-funded telescope from the second time hit the NASA program for the development of small research programs and will be launched in March 2018 on Falcon 9.
Orbital, commercial and suborbital launches
In May 2018, OneWeb will begin to deploy a constellation of about 2.5 thousand satellites that will provide Internet access throughout the planet. The launches will be carried out by the Unions in low orbit.
Sir Richard Branson, the founder of Virgin Galactic , expressed a desire to make the first flight of the SpaceShipTwo suborbital spacecraft with passengers in 2018. At the end of 2018, Blue Origin also plans to make the first flight of the New Shepard suborbital rocket system with people on board. After that, it is planned to finally begin commercial flights.
The test launches of Electron light rocket of the American Rocket Lab, Kuaizhou-1 of the Chinese company CASIC and the American LauncherOne of the Virgin Orbit company will continue.
For 2018, the first launch of the Stratolaunch is also planned , designed to launch orbital rockets from the Roc two-body aircraft.

The second launch of the Angara-A5 heavy rocket from the Plesetsk cosmodrome is scheduled for the very end of 2018, and SpaceX is going to send two tourists to fly around the moon.
UPD 1: Team Indus seems to be eliminated from the moon race (and with it the Japanese Hakuto), did not have time to raise money.
UPD 2: Postponed the flight dates of the new manned ships Dragon V2 and Starliner:
Boeing Orbital Flight Test (uncrewed): August 2018
Boeing Crew Flight Test (crewed): November 2018
SpaceX Demonstration Mission 1 (uncrewed): August 2018
SpaceX Demonstration Mission 2 (crewed): December 2018
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/374145/
All Articles