Date with ʻOumuamua. For the first time the interstellar object in the Solar System is open.
On October 19, 2017, while analyzing the Pan-STARRS telescope data, the long-awaited discovery occurred - the first interstellar object in the Solar System. Entire decades have been devoted to the search for interstellar small bodies (comets and asteroids), many articles where the upper limits on their number per unit of the Galaxy volume were calculated. And now - finally.

Since several days have passed since the discovery, and for some reason, Ethan is silent, he decided to write an article himself.
Actually the object itself, which was first called P10Ee5V, had a trajectory that demonstrated one unusual feature that had never before been seen by any of the hundreds of thousands of small bodies of the Solar System that are open to date. The calculated eccentricity of the “orbit” was equal to ~ 1.2 . The word “orbit” here was quoted, since with an eccentricity of more than 1, a closed circular or elliptical orbit turns into an open hyperbolic trajectory . But eccentricity alone is not enough. Previously, objects with an eccentricity of a little more than 1 were already detected, but it always turned out that this was due to disturbance from the planets of the Solar System or disturbances from the Oort Cloud by stars. Knowing the eccentricity and the perihelion distance (the minimum distance the object moves closer to the Sun), one can calculate the speed with which a certain celestial body moved when it was away from the Sun and the influence of the planets of the Solar System. For example, for comets from the Oort Cloud, this speed “at infinite distance” never exceeds ~ 200 m / s. For the recently opened object P10Ee5V, this speed was ~ 26 km / s . Since this velocity approximately coincides with the average relative velocity between the stars adjacent to the Sun, doubts that the object has an interstellar origin immediately disappeared. The object was called the first interstellar comet - C / 2017 U1 (Pan-STARRS).
The largest telescopes of the world were pulled out of their schedules and aimed at the earliest possible study of the temporary guest of the Solar System. Looking ahead - at the end of November, observations are scheduled by the space telescopes. Hubble and them. Spitzer.
')

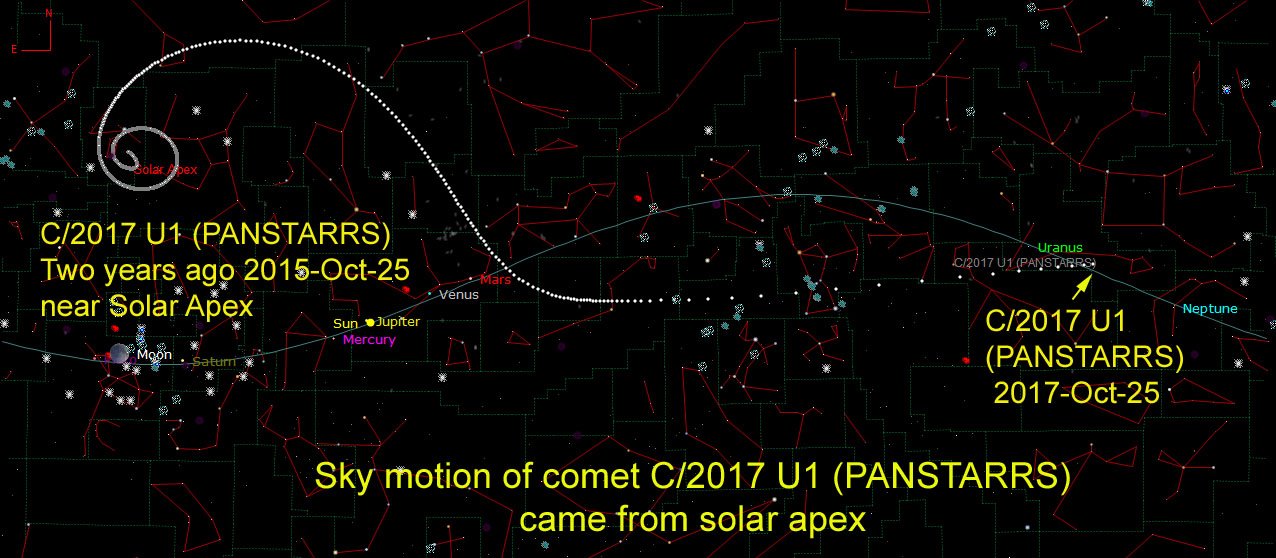
Interestingly, when the researchers “rewound” the object's position back in time, they found out that its trajectory leads from the Lyra constellation , that is, just in the direction of the Solar System movement relative to the averaged motion of neighboring stars, which also removes any doubts about the origin of this object.
A new object immediately threw a puzzle to astrophysicists - the absence of noticeable cometary activity. The object was to be formed in the same way as the objects of "our" Oort Cloud, and from the Oort Cloud, astronomers observe exactly comets. Actually from the category of comets C / 2017 U1 was demoted and a new designation was given - A / 2017 U1 (to emphasize the absence of cometary signs). A little later, astronomers introduced a new designation for interstellar objects and the object was designated 1I (I - “interstellar”), which clearly demonstrates all the commotion caused by this guest in the astronomical community. It was also given a name in Hawaiian - 'Oumuamua , which means something like "pioneer." In connection with the absolute unreadability of this name, here and hereinafter in the article, the hero of the occasion will be simply referred to as " U1 ".
It is worth noting that, before being open, on September 9, 2017, U1 got close to the Sun at a distance 4 times closer than the Earth. Then U1 began to move away from the Sun again and “whistled” unnoticed at a fairly small (by the Solar System standards) distance from the Earth on October 14 - just 0.16 AU. (one and a half times closer than the minimum distance to Venus, the closest planet to Earth). And only 5 days later, U1 was opened already receding at a distance of 0.2 AU. Later, U1 was nevertheless found in pictures taken on October 14 and 18, which made it possible to clarify its trajectory. The fact that astronomers have not been able to find a single interstellar object around for a long time, until they are practically “stuck” with their nose, suggests that there may be quite a lot of such objects right now in the Solar System, but interstellar objects are probably predominantly small. size and do not show noticeable comet activity, which would facilitate their detection at long distances.
From observations by a variety of telescopes, we managed to clarify some properties of U1. The size is most likely about 100 by 200 meters (judging by the light curve, it has an elongated shape with a ratio of 1: 2). By the standards of typical comets and asteroids, it is a rather small object. It was even possible to obtain spectra, but the errors are so large that it is not yet possible to draw an unambiguous conclusion about the composition of the surface. Everything suggests that U1 is similar in spectrum to comet nuclei and some asteroids that are rich in organics (the so-called spectral class "D"). However, rather stormy discussions are going on regarding the interpretation of the spectrum and other options cannot be completely ruled out yet.

An avalanche of articles devoted to this discovery has already begun in scientific journals, which will provide researchers with work for months and even years ahead. The mere mystery of the absence of cometary activity is worth a lot. Perhaps this is not a comet or even an asteroid at all? The famous science fiction writer Arthur Clarke has an equally well-known work “A Date with Rama” telling about the collision of mankind with an alien starship moving through the Solar System along a hyperbolic trajectory. Here is a small excerpt from the very beginning of the novel:
As can be seen from the graph of the number of discoveries of near-Earth asteroids over the years below, systematically “combing” outer space began around 1997:

Moreover, the growth in the number of open small bodies can be roughly considered linear. That is, over the past 20 years, the area of the “combed-out” space has grown. Considering the movement of the Sun among a multitude of interstellar objects and the movement of the Earth around the Sun, we can estimate the volume in which the first interstellar object was detected. The shape of this volume will look like a spiral, the thickness of which grows with each turn. The length of such a (unfolded) helix for 20 years will be ~ 1688 AE. Since U1 was detected at a distance of 0.2 AU from the Earth, the thickness of this spiral will increase from 0 to 0.2 AU. Then the resulting volume of space will be approximately 71 cubic meters. AE. This volume corresponds to a sphere with a radius of 2.57 AE, that is, in this radius, as a rule, there must always be at least one such object.
If we assume that the distribution of interstellar small bodies is exponential with an exponent of -3, then we can estimate how many more objects and what size should be nearby:
New observations indicate strong variability - the brightness of U1 changes 4-6 times with a period of about 8 hours and 2 peaks. In the Solar System, asteroids with such strong brightness variations are unknown that makes U1 even more mysterious.

Since several days have passed since the discovery, and for some reason, Ethan is silent, he decided to write an article himself.
Actually the object itself, which was first called P10Ee5V, had a trajectory that demonstrated one unusual feature that had never before been seen by any of the hundreds of thousands of small bodies of the Solar System that are open to date. The calculated eccentricity of the “orbit” was equal to ~ 1.2 . The word “orbit” here was quoted, since with an eccentricity of more than 1, a closed circular or elliptical orbit turns into an open hyperbolic trajectory . But eccentricity alone is not enough. Previously, objects with an eccentricity of a little more than 1 were already detected, but it always turned out that this was due to disturbance from the planets of the Solar System or disturbances from the Oort Cloud by stars. Knowing the eccentricity and the perihelion distance (the minimum distance the object moves closer to the Sun), one can calculate the speed with which a certain celestial body moved when it was away from the Sun and the influence of the planets of the Solar System. For example, for comets from the Oort Cloud, this speed “at infinite distance” never exceeds ~ 200 m / s. For the recently opened object P10Ee5V, this speed was ~ 26 km / s . Since this velocity approximately coincides with the average relative velocity between the stars adjacent to the Sun, doubts that the object has an interstellar origin immediately disappeared. The object was called the first interstellar comet - C / 2017 U1 (Pan-STARRS).
The largest telescopes of the world were pulled out of their schedules and aimed at the earliest possible study of the temporary guest of the Solar System. Looking ahead - at the end of November, observations are scheduled by the space telescopes. Hubble and them. Spitzer.
')

Interestingly, when the researchers “rewound” the object's position back in time, they found out that its trajectory leads from the Lyra constellation , that is, just in the direction of the Solar System movement relative to the averaged motion of neighboring stars, which also removes any doubts about the origin of this object.

A new object immediately threw a puzzle to astrophysicists - the absence of noticeable cometary activity. The object was to be formed in the same way as the objects of "our" Oort Cloud, and from the Oort Cloud, astronomers observe exactly comets. Actually from the category of comets C / 2017 U1 was demoted and a new designation was given - A / 2017 U1 (to emphasize the absence of cometary signs). A little later, astronomers introduced a new designation for interstellar objects and the object was designated 1I (I - “interstellar”), which clearly demonstrates all the commotion caused by this guest in the astronomical community. It was also given a name in Hawaiian - 'Oumuamua , which means something like "pioneer." In connection with the absolute unreadability of this name, here and hereinafter in the article, the hero of the occasion will be simply referred to as " U1 ".
It is worth noting that, before being open, on September 9, 2017, U1 got close to the Sun at a distance 4 times closer than the Earth. Then U1 began to move away from the Sun again and “whistled” unnoticed at a fairly small (by the Solar System standards) distance from the Earth on October 14 - just 0.16 AU. (one and a half times closer than the minimum distance to Venus, the closest planet to Earth). And only 5 days later, U1 was opened already receding at a distance of 0.2 AU. Later, U1 was nevertheless found in pictures taken on October 14 and 18, which made it possible to clarify its trajectory. The fact that astronomers have not been able to find a single interstellar object around for a long time, until they are practically “stuck” with their nose, suggests that there may be quite a lot of such objects right now in the Solar System, but interstellar objects are probably predominantly small. size and do not show noticeable comet activity, which would facilitate their detection at long distances.
What is U1
From observations by a variety of telescopes, we managed to clarify some properties of U1. The size is most likely about 100 by 200 meters (judging by the light curve, it has an elongated shape with a ratio of 1: 2). By the standards of typical comets and asteroids, it is a rather small object. It was even possible to obtain spectra, but the errors are so large that it is not yet possible to draw an unambiguous conclusion about the composition of the surface. Everything suggests that U1 is similar in spectrum to comet nuclei and some asteroids that are rich in organics (the so-called spectral class "D"). However, rather stormy discussions are going on regarding the interpretation of the spectrum and other options cannot be completely ruled out yet.

An avalanche of articles devoted to this discovery has already begun in scientific journals, which will provide researchers with work for months and even years ahead. The mere mystery of the absence of cometary activity is worth a lot. Perhaps this is not a comet or even an asteroid at all? The famous science fiction writer Arthur Clarke has an equally well-known work “A Date with Rama” telling about the collision of mankind with an alien starship moving through the Solar System along a hyperbolic trajectory. Here is a small excerpt from the very beginning of the novel:
...
When the orbital elements of a new asteroid have been calculated, the mystery seems to be
resolved, but it was replaced by another, more substantial.
The number 31/439 was not at all an ordinary asteroid running along
elliptical orbit and repeating it with precision clockwork
every few years. He turned out to be a lonely interstellar wanderer
visited the solar system for the first and last time, and moved like that
rapidly, that even the gravitational field of the sun was not capable
take him prisoner. Piercing the orbits of Jupiter, Mars, Earth, Venus and
Mercury and continuously picking up speed, he had to in the end
go around the sun and go back into the unknown.
Then, having finished the calculations, the computers sent people signals:
"Attention! We dug up something interesting for you ", - and number 31/439
first attracted the attention of mankind. Light flurry of excitement in
the headquarters of the Space Patrol - and the interstellar tramp instead of the ordinary
The numbers honored their own. Astronomers have long been exhausted as
Greek as well as Roman mythology and now set about Hindu
pantheon. The number 31/439 was named Rama.
...
More about U1
- Wikipedia
- NASA: Small Asteroid or Comet 'Visits' from Beyond the Solar System
- A / 2017 U1, first interstellar asteroid ever detected!
UPDATE
As can be seen from the graph of the number of discoveries of near-Earth asteroids over the years below, systematically “combing” outer space began around 1997:

Moreover, the growth in the number of open small bodies can be roughly considered linear. That is, over the past 20 years, the area of the “combed-out” space has grown. Considering the movement of the Sun among a multitude of interstellar objects and the movement of the Earth around the Sun, we can estimate the volume in which the first interstellar object was detected. The shape of this volume will look like a spiral, the thickness of which grows with each turn. The length of such a (unfolded) helix for 20 years will be ~ 1688 AE. Since U1 was detected at a distance of 0.2 AU from the Earth, the thickness of this spiral will increase from 0 to 0.2 AU. Then the resulting volume of space will be approximately 71 cubic meters. AE. This volume corresponds to a sphere with a radius of 2.57 AE, that is, in this radius, as a rule, there must always be at least one such object.
If we assume that the distribution of interstellar small bodies is exponential with an exponent of -3, then we can estimate how many more objects and what size should be nearby:
- Within a radius of 5.13 AE from the Sun: ~ 8 objects no larger than 0.3 km in size
- Within a radius of 10.3 AE from the Sun: ~ 64 objects with a size of not more than 0.6 km
- Within a radius of 20.5 AE from the Sun: ~ 512 objects no larger than 1.2 km in size
- Within a radius of 41 AE from the Sun: ~ 2,048 objects no larger than 2.4 km in size
UPDATE 2
New observations indicate strong variability - the brightness of U1 changes 4-6 times with a period of about 8 hours and 2 peaks. In the Solar System, asteroids with such strong brightness variations are unknown that makes U1 even more mysterious.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/373985/
All Articles