A few words in defense of bio-impedance
Bioimpedance is a controversial and disputed, discussed and tested method of assessing an organism that has both proponents and critics.
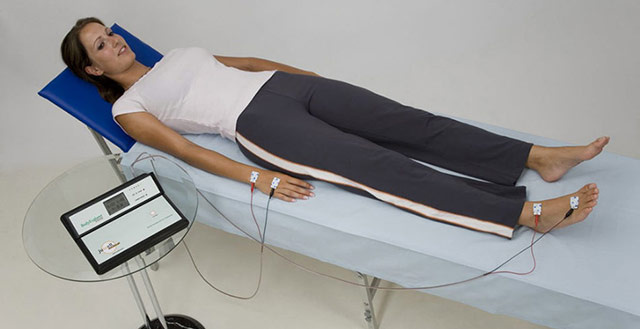
In clinical medicine, however, it is used, and not only for body composition analysis. We decided that it would not be superfluous to make a few comments about this technique.
Historically
')
As noted in a number of publications, the starting point for bio-impedance is the end of the 18th century. Ever since, its value has been equally exalted by some and disputed by others. At the same time, both “camps of the protesters” behave quite correctly, and the evidence base of the former can sometimes be read in favor of the latter and vice versa. In other words, straightforwardly sharp distortion of facts is not.
The method is based on the electrical resistance of tissues, therefore there are many formulas, physics, mathematics, in other words exact sciences, far from medicine, where there are many random factors. This, in fact, is the key argument of the antagonists: it is impossible to calculate and decompose the human body.
Indeed, there are observations that bioimpedancemetry on patients with light skin works differently than on patients with dark. And if you take factors such as height, weight, the presence of any chronic diseases ...
But here, in fairness, I must say that not only this diagnostic has such problems: not so long ago there was a case when the Polar optical heart rate monitors refused to accurately measure the pulse of black athletes.
Studied or not?
In Russia, this method is devoted to a book released by Science in 2009, which, of course, is more like a textbook on physics. There is also a large-scale article that explains the principles of bio-impedancemetry: Theory and the basics of bio-impedance in clinical diagnosis.
In the last article, there are some rather “radical” comparisons: there is no need to prove, the analysis with the help of current alone is necessary: there are ECGs and EEGs that are not in doubt; but they are not the only ones. Moreover, bioimpedance is divided into several "subspecies".
Why is it important? The most controversial "bioimpedance meter" is called modern smart scales . The fact is that many of them have been dubbed as “truncated”, “truncated”, “inferior” method. At that time, as in the above material, the classification is given: bioimpedancemetry can be carried out in three ways of applying electrodes: “hand to hand”, “hand to foot”, “foot to foot”. In other words, based on this text, scales are one of the ways that should also be considered complete.
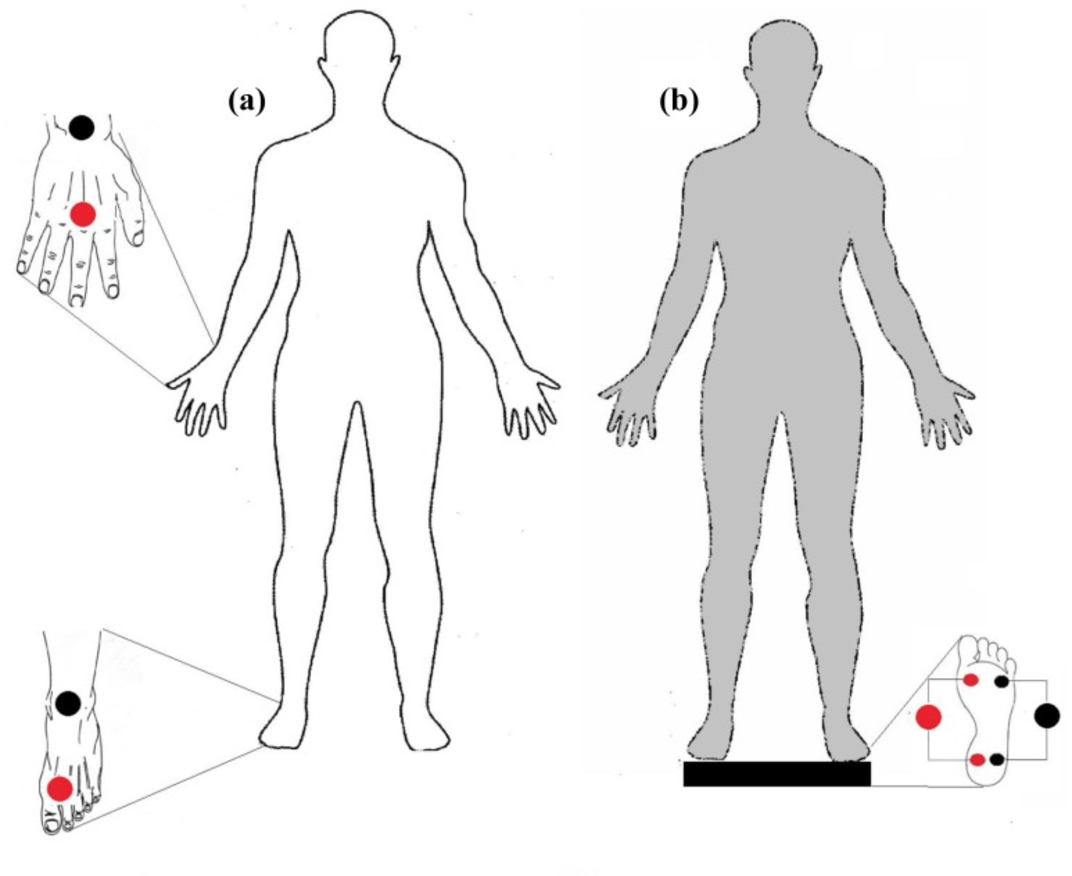
It is impossible not to add that the applicability of bio-impedance is wider than the task assigned to it by the manufacturers of modern gadgets: clinical tests are well-known, where bio-impedance acts as a diagnostic method for cervical cancer. Also in one of the studies it is argued that bio-impedance shows adequate results in the analysis of fat mass in HIV-positive patients. This is to say that there are too many exceptions that complicate diagnosis.
Body analysis
To date, bioimpedancemetry is the most popular method of diagnosing body composition, where parameters such as fat level, bone mineral composition, muscle mass, hydration, and some others are considered.
Virtually any material on this topic begins with a general quotation that this is a method with no alternative in terms of accuracy, speed, and availability as compared to others. That truth is true: faster and cheaper - only by eye or with the help of a caliper.
Accuracy is a debatable question. There are a number of supporting materials that state the accuracy of bio-impedance according to one of the indicators (important, of course) - the level of body fat. The error - where do without it - bioimpedance is estimated at 3 - 6%, which is considered acceptable.
Reproducibility - a critical component for science - is confirmed in studies with a larger sample, subject to a significant number of additional factors, such as race, age, gender.

Compare the bioimpedance with the reference body composition study DEXA (DXA, densitometry). Simply put, this is an x-ray of body composition. At the moment, it is argued that bioimpedancemetry gives comparable results in some indicators, primarily fat mass. Even in the article , where it seems as if this method “swears”, the same permissible error and deviation up to 6% is given.
The analysis of DEXA costs incomparable money, and if bio-impedance at home with the help of scales will cost an average of 2-3 thousand rubles forever, in a clinic - from 1000 rubles, then DEXA on average costs about 10 thousand. Often it is also not recommended to do it: some kind of radiation.
According to the analysis of the fat mass, the scales we tested also coincided with DEXA and the MEDASS bioimpedancemeter clinical apparatus.
The correlation of other results
Controversial, it's true. If in words, then the doctors who conduct the DEXA analysis openly negative about bio-impedance. Those who do bioimpedance, on the contrary, believe that it is permissible to rely on the results obtained in the diagnosis.
The main reason why the method causes distrust is a high degree of dependence on additional factors: for example, all other things being equal, two people may have different results because one of them drank a glass of water five minutes before the study.
At the same time, it is considered that the evaluation of hydration is also quite capable of a bioimpedance meter: at low sensitivity with a single measurement, the reproducibility of serial trends turned out to be convincing.
Thus, it must be said that most of the studies, articles and tests are devoted to the problem of obesity, and here bioimpedance shows good results, according to the authors. Even where it is difficult to identify additional factors: pharmacology at the time of the survey, medical history, situational (dehydration, or vice versa), we can talk about accurate results.
Some results
Face-to-face DEXA and bio-impedance are acceptable in some respects, if in both cases certain conditions are met. For example, two hours before bioimpedance analysis it is impossible to drink liquid, and one day to drink alcohol, this will increase the accuracy of calculations.
Bioimpedance has its advantages, some of which are outside of medicine: it is fast, it is available, it is cheap. At the same time, the data are reproducible and repeatable, but this method does not demonstrate ultrahigh sensitivity, therefore, it is more suitable for identifying trends in certain metabolic processes. DEXA - on the contrary: it is often impossible to do, it is expensive, without declaring a doctor some parameters cannot be deciphered.
To date, many scientific publications are devoted to bioimpedance analysis, because they see it as a cheap and accurate diagnostic alternative, but the method should still be recognized as “medical-physical-mathematical”, which is not always suitable for “spontaneous” processes that occur in the body. We also did both studies: bioimpedance is here , DEXA is here . The table is above.
In other words, we must nevertheless recognize that bioimpedance - exists, is a clinically confirmed method of diagnosis with a declared tolerance. The method is evaluated as accurate for identifying fat mass, and also coincides with a number of other parameters.
Home bio-impedance meters, or smart scales, are also part of this system, belong to the leg-to-foot bio-impedance meters class and show high accuracy of results with proper weighing and calibration. The test, which we passed, was carried out on the device DEXA from General Electric, the device "MEDASS" and the Bluetooth-scales MGB Body Fat Scale .

In clinical medicine, however, it is used, and not only for body composition analysis. We decided that it would not be superfluous to make a few comments about this technique.
Historically
')
As noted in a number of publications, the starting point for bio-impedance is the end of the 18th century. Ever since, its value has been equally exalted by some and disputed by others. At the same time, both “camps of the protesters” behave quite correctly, and the evidence base of the former can sometimes be read in favor of the latter and vice versa. In other words, straightforwardly sharp distortion of facts is not.
The method is based on the electrical resistance of tissues, therefore there are many formulas, physics, mathematics, in other words exact sciences, far from medicine, where there are many random factors. This, in fact, is the key argument of the antagonists: it is impossible to calculate and decompose the human body.
Indeed, there are observations that bioimpedancemetry on patients with light skin works differently than on patients with dark. And if you take factors such as height, weight, the presence of any chronic diseases ...
But here, in fairness, I must say that not only this diagnostic has such problems: not so long ago there was a case when the Polar optical heart rate monitors refused to accurately measure the pulse of black athletes.
Studied or not?
In Russia, this method is devoted to a book released by Science in 2009, which, of course, is more like a textbook on physics. There is also a large-scale article that explains the principles of bio-impedancemetry: Theory and the basics of bio-impedance in clinical diagnosis.
In the last article, there are some rather “radical” comparisons: there is no need to prove, the analysis with the help of current alone is necessary: there are ECGs and EEGs that are not in doubt; but they are not the only ones. Moreover, bioimpedance is divided into several "subspecies".
Why is it important? The most controversial "bioimpedance meter" is called modern smart scales . The fact is that many of them have been dubbed as “truncated”, “truncated”, “inferior” method. At that time, as in the above material, the classification is given: bioimpedancemetry can be carried out in three ways of applying electrodes: “hand to hand”, “hand to foot”, “foot to foot”. In other words, based on this text, scales are one of the ways that should also be considered complete.

It is impossible not to add that the applicability of bio-impedance is wider than the task assigned to it by the manufacturers of modern gadgets: clinical tests are well-known, where bio-impedance acts as a diagnostic method for cervical cancer. Also in one of the studies it is argued that bio-impedance shows adequate results in the analysis of fat mass in HIV-positive patients. This is to say that there are too many exceptions that complicate diagnosis.
Body analysis
To date, bioimpedancemetry is the most popular method of diagnosing body composition, where parameters such as fat level, bone mineral composition, muscle mass, hydration, and some others are considered.
Virtually any material on this topic begins with a general quotation that this is a method with no alternative in terms of accuracy, speed, and availability as compared to others. That truth is true: faster and cheaper - only by eye or with the help of a caliper.
Accuracy is a debatable question. There are a number of supporting materials that state the accuracy of bio-impedance according to one of the indicators (important, of course) - the level of body fat. The error - where do without it - bioimpedance is estimated at 3 - 6%, which is considered acceptable.
Reproducibility - a critical component for science - is confirmed in studies with a larger sample, subject to a significant number of additional factors, such as race, age, gender.

Compare the bioimpedance with the reference body composition study DEXA (DXA, densitometry). Simply put, this is an x-ray of body composition. At the moment, it is argued that bioimpedancemetry gives comparable results in some indicators, primarily fat mass. Even in the article , where it seems as if this method “swears”, the same permissible error and deviation up to 6% is given.
The analysis of DEXA costs incomparable money, and if bio-impedance at home with the help of scales will cost an average of 2-3 thousand rubles forever, in a clinic - from 1000 rubles, then DEXA on average costs about 10 thousand. Often it is also not recommended to do it: some kind of radiation.
According to the analysis of the fat mass, the scales we tested also coincided with DEXA and the MEDASS bioimpedancemeter clinical apparatus.
| Data | MEDASS | MGB | Dexa |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fat mass in% | 19.5 | 21.4 | 19.7 |
| Fat mass in kg | 12.5 | 13.6 | 11.9 |
| Muscle mass | 27.2 | 28.5 | Muscle mass + connective tissue + fluid - 48.6 |
| Metabolism | 1555 Kcal / day | 1348 Kcal / day | 1427 Kcal / day |
| Mineral composition | 2,652 kg | 2.5 kg | 2,773 kg |
The correlation of other results
Controversial, it's true. If in words, then the doctors who conduct the DEXA analysis openly negative about bio-impedance. Those who do bioimpedance, on the contrary, believe that it is permissible to rely on the results obtained in the diagnosis.
The main reason why the method causes distrust is a high degree of dependence on additional factors: for example, all other things being equal, two people may have different results because one of them drank a glass of water five minutes before the study.
At the same time, it is considered that the evaluation of hydration is also quite capable of a bioimpedance meter: at low sensitivity with a single measurement, the reproducibility of serial trends turned out to be convincing.
Thus, it must be said that most of the studies, articles and tests are devoted to the problem of obesity, and here bioimpedance shows good results, according to the authors. Even where it is difficult to identify additional factors: pharmacology at the time of the survey, medical history, situational (dehydration, or vice versa), we can talk about accurate results.
Some results
Face-to-face DEXA and bio-impedance are acceptable in some respects, if in both cases certain conditions are met. For example, two hours before bioimpedance analysis it is impossible to drink liquid, and one day to drink alcohol, this will increase the accuracy of calculations.
Bioimpedance has its advantages, some of which are outside of medicine: it is fast, it is available, it is cheap. At the same time, the data are reproducible and repeatable, but this method does not demonstrate ultrahigh sensitivity, therefore, it is more suitable for identifying trends in certain metabolic processes. DEXA - on the contrary: it is often impossible to do, it is expensive, without declaring a doctor some parameters cannot be deciphered.
To date, many scientific publications are devoted to bioimpedance analysis, because they see it as a cheap and accurate diagnostic alternative, but the method should still be recognized as “medical-physical-mathematical”, which is not always suitable for “spontaneous” processes that occur in the body. We also did both studies: bioimpedance is here , DEXA is here . The table is above.
In other words, we must nevertheless recognize that bioimpedance - exists, is a clinically confirmed method of diagnosis with a declared tolerance. The method is evaluated as accurate for identifying fat mass, and also coincides with a number of other parameters.
Home bio-impedance meters, or smart scales, are also part of this system, belong to the leg-to-foot bio-impedance meters class and show high accuracy of results with proper weighing and calibration. The test, which we passed, was carried out on the device DEXA from General Electric, the device "MEDASS" and the Bluetooth-scales MGB Body Fat Scale .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/373833/
All Articles