Computer games affect the amount of gray matter in the hippocampus

Reduction and increase in the amount of gray matter in the hippocampus after 90 hours of play
Due to the great popularity of computer games, scientists are increasingly turning to the topic of how video games affect a person’s cognitive abilities. It is known, in particular, that the games in the genre of action improve the performance of the brain in various areas, including visual attention, visual short-term memory, organizing function, and procedural learning abilities. As a result, first-person and third-person shooters, such as Call of Duty, are now recommended for children , adults and older people to train the brain, namely, to develop certain abilities, such as visual attention.
There have been theories that video games affect the gray matter in the hippocampus, an important brain region that is involved in the formation of emotions, the consolidation of memory (that is, the transition of short-term memory into long-term memory) and generates a theta rhythm while maintaining attention. The hippocampus plays an important role in the work of the brain throughout human life.
Spatial learning (spatial learning) depends on the gray matter in the hippocampus, when a person remembers the relationship between objects in the surrounding space. An alternative orientation strategy in space is behavioral learning (response learning), in which the caudate nucleus is activated, and navigation is performed by memorizing a series of actions, starting from the starting point. It is important that people who are prone to behavioral learning have less gray matter in the hippocampus than people with a tendency to spatial learning.
')
Memory systems in the hippocampus and caudate nucleus contribute to optimal task performance. For example, the hippocampus is directly involved in spatial navigation, episodic memory and stress management. On the other hand, the striatum with the caudate nucleus is more involved in the formation of habits and procedural memory with the training of skills to bypass consciousness (for example, cycling).
Recent studies in humans and rats have shown that the amount of gray matter in the hippocampus is inversely proportional to the amount of gray matter in the caudate nucleus. The functional activity of these two areas of the brain also has an inverse relationship in the process of navigation. That is, if one of these two areas is more involved, the second is less involved. Moreover, if you actively use one of the structures (for example, the caudate nucleus to teach different skills to bypass consciousness), then there is a real risk of atrophy of the hippocampus. And this is serious, given the importance of the hippocampus throughout a person’s life. It is known that a low level of gray matter in the hippocampus is a risk factor for the development of a number of neuropsychiatric diseases, that is, mental diseases resulting from disturbances in the nervous structure and function of the nervous system.
Some scientists believe that it is important to maintain a balance between the activity of the hippocampus and the caudate nucleus. It is known that some factors - stress, routine, reward - stimulate the activity of the caudate nucleus, which is why the hippocampus suffers. The question is how video games affect the amount of gray matter in the hippocampus.
Considering all the above, a group of scientists from the Center for Neuropsychology and Consciousness at the University of Montreal and the Department of Psychiatry at the Douglas Hospital Research Center at McGill University (both Canada) conducted a study measuring the amount of gray matter in the hippocampus of people who constantly play video games and who do not play
During the experiment, 17 gamers and 16 non-gamers were scanned using magnetic resonance imaging. All of them also passed the 4-on-8 virtual maze (4 / 8VM) test in virtual reality to test the type of preferred navigation strategy: spatial learning or behavioral learning.
The first experiment confirmed the theory that video games reduce the amount of gray matter in the hippocampus. In fact, among regular gamers, there was more often a variant of behavioral rather than spatial learning in navigation. And the amount of gray matter in the left hippocampus was significantly less.
In the second experiment, scientists took a group of volunteers who do not play computer games, and forced them to play in the laboratory for 90 hours. Half played first-person shooter (Call of Duty: Modern Warfare 2), and the other half played games on a 3D platform (Super Mario games).
The research results are controversial. In general, there was no difference between the groups in the amount of gray matter of the hippocampus. But for those people who preferred behavioral strategies, after playing Call of Duty: Modern Warfare 2, there was a significant decrease in the amount of gray matter in the right hippocampus. In contrast, people with spatial learning strategies experienced an increase in the amount of gray matter in the left hippocampus.
Playing Super Mario had no negative effects for any group of subjects: people who preferred behavioral strategies significantly increased the amount of gray matter in the right hippocampus, and people with spatial learning strategies significantly increased the amount of gray matter in the entorhinal cortex.
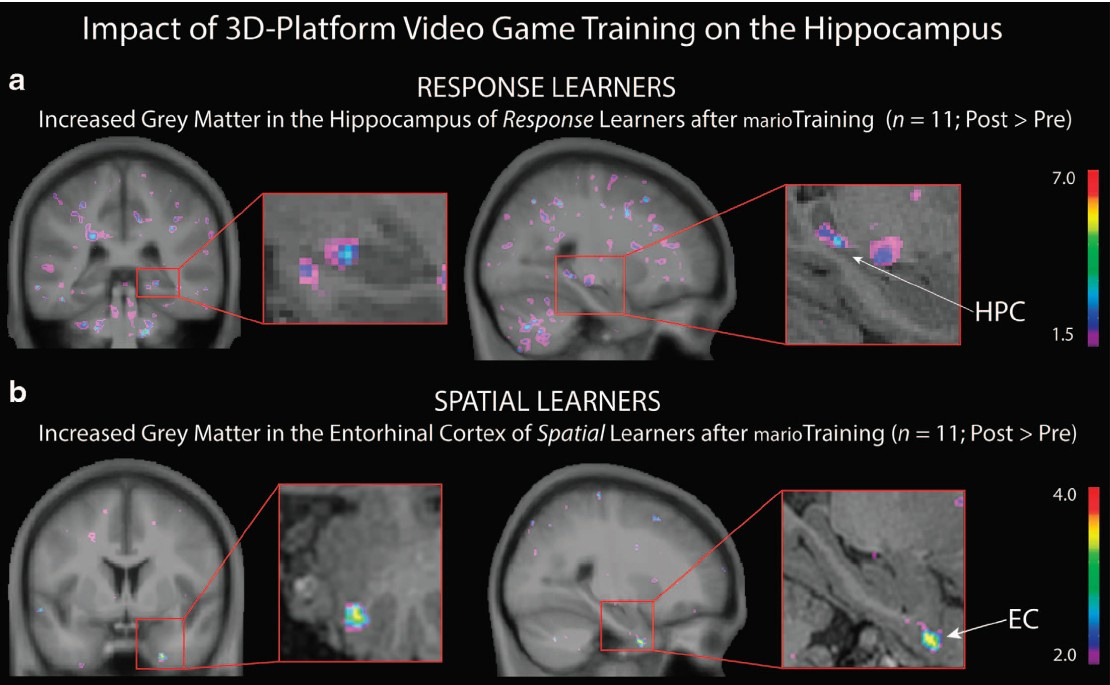
Thus, scientists conclude, although video games in the genre of action develop visual attention and other abilities of the brain, they have different effects on the amount of gray matter in the hippocampus in different people, depending on what type of navigation in space the person spontaneously leans to. If a person in life remembers the relationship between objects in the surrounding space, activating the hippocampus, then in the game he subconsciously does the same, thereby increasing the amount of gray matter in the hippocampus. If a person navigates in space by memorizing a series of actions, starting from the starting point, then video games of this type will even more atrophy his hippocampus. Studies show that in the action genre there are more of the second type of players, therefore, on average , their hippocampus is more atrophied than in normal people , but the caudate nucleus is more developed.
The scientific article was published on August 8, 2017 in the journal Molecular P (doi: 10.1038 / mp.2017.155, pdf ).
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/373709/
All Articles