Standard settings - the most stupid. Why is the new fast drive failing and not “going” after the upgrade?
Hi% username%! You probably know for a long time why in UEFI you need to prefer AHCI, what is the catch of the Secure Boot and why the MBR is much worse than the GPT. If not, it's time to figure out the question of how to squeeze the maximum speed and stability from the drive using software.

Backward compatibility of technologies in the PC is an absolute good. With it, an elderly processor can be made to work in tandem with RAM from the “distant future”, and the new drive easily takes root in an old computer and makes it much faster even using old versions of the SATA interface.
And, if the legacy code can be treated differently, then outdated protocols and interfaces are almost always inferior to new developments. Only you will not know about it, because the new hardware in the new computer will be slowed down by default by the settings in favor of maximum compatibility. We find out which settings should be preferred so that the old drive does not interfere with the outdated standards for agood dancer , and why in the new computers the options for the outdated equipment are “confused”.
')
At the “iron” level, innovations in the interaction of the PC platform with the drives are extremely understandable: hard disks increased the recording density and increased the number of plates in the 3.5-inch form factor and filled the most capacious models with helium so that the disks began to work more stable. The future of HDD now depends on the pace of implementation of tiled magnetic recording technology or more radical changes (a jerk in the volume of drives) with thermally assisted magnetic recording .
SSD? Changed several types of memory, ceased to be a luxury in home computers, increased the volume to hundreds of gigabytes. Squeezed out all the juices from SATA-III, got PCI-E speeds and finally got a compact form factor .

Kingston DCP-1000 drive - up to 1 100 000 IOPS for reading and 200 000 IOPS for writing, for example
But the speed of the drives depends not only on the hardware, but also on the software component. And here is the time to recall the BIOS, which lingered on stage, as if idols of the ossified idols, which had become ossified in old age.
Today, in the minds of working people, UEFI is such a colorful alternative to “bios”, with gradients, beautiful menus, mouse support and, sometimes, Russified interfaces. All the more surprising that the motley EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface , then still without Unified in abbreviation), was originally developed by Intel back in 2003. And initially it was offered for Itanium server as a more flexible and fast interface for booting the OS and initializing / diagnosing components. There were a lot of weak points in the ancient 16-bit BIOS with 1 MB of addressable memory, so the replacement suggested itself. As is usually the case in the competition between the layers of abstraction and the performance of iron, UEFI became “harder” and turned into a mini-operating system with drivers and services, but the speed and stability were worth it.
UEFI came to mass computers in 2012-2013, and along with it, pleasant and not so new innovations appeared in the “pre-boot” interface. Let's start with the function of "defender" Windows 8, Secure Boot.
In the initiative to implement the Secure Boot feature in UEFI version 2.2 and higher, developers were well-intentioned, if you understand what we are talking about. The fact that Microsoft was the first to use this function (to secure the launch of Windows 8 and “strangle” bootloader activators) is another matter.
For a while, only Windows 8 was able to boot into Secure Boot mode, and users of all other OS had to disable the function in the UEFI BIOS, because the interface refused to execute unsigned files of not properly prepared systems.
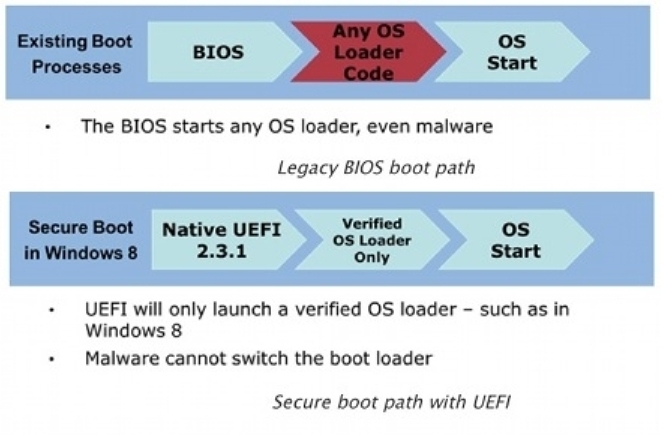
How does Secure Boot work?
The “softness” was that all new computers were supplied with Secure Boot at the request of Microsoft, so all fans of operating systems other than Win 8 soon learned about the new function (in not very pleasant circumstances of the “falling” system). And in some cases, the Microsoft update “just for fun” activated the Secure Boot in UEFI even in Windows 7 , which after such implantation safely “fell” on the next boot. This is another kind of "romantic" circumstances of acquaintance with the new function in past years.
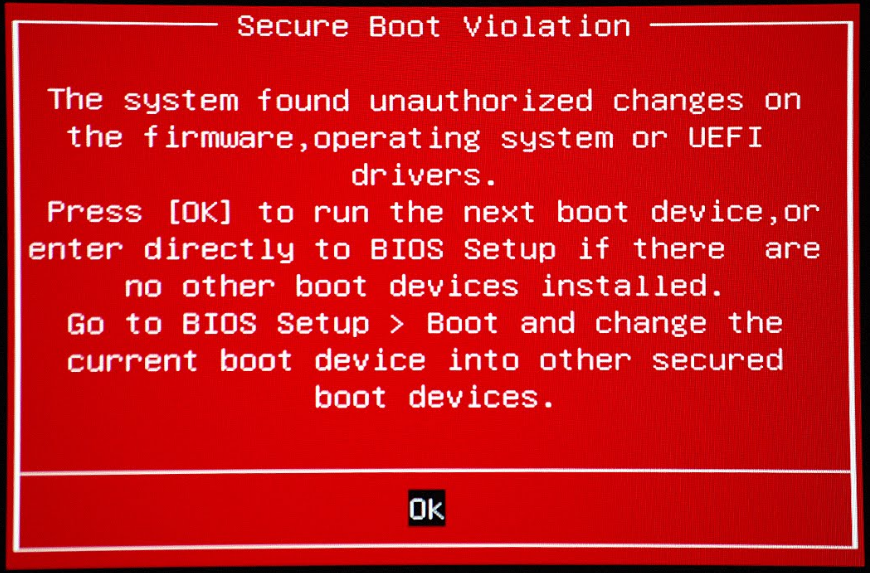
“I’ll show you what a safe boot is!”, As if the KB3133977 update tells us and includes an unsupported Windows 7 Secure Boot in ASUS motherboards
In fairness, it is worth noting that modern GNU / Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Fedora, Red Hat and openSUSE are among the first) quickly acquired a signature to be loaded into Secure Boot, but in 2016, with the Microsoft industry’s request, this standard is twice, let's say backed out.
The first time was when the Redmond team "lost" the master key from Secure Boot and compromised the protection for which they were so active. Not a regular key, but a master key, with which the bootloader becomes “naked and defenseless” in all released devices with the active Secure Boot, and attackers can easily and easily replace the operating system during the initial boot phase. There is no sadder story in the world than the story of the "golden keys" and debugging tools in the public domain.
And for the second time, Microsoft made a fuss when the above-mentioned backdoor began to be used for good as a means of “jailbreaking” tablets running Windows RT. The fact is that the Microsoft experiment with ARM systems ended in failure, and the steep and expensive (once) Surface tablets did not even receive support for UWP applications. That is, quite good from a constructive point of view, the devices have become hostages of the "dead" operating system. And there could be no other operating system in the tablet, because the Secure Boot on the tablets, at the request of Microsoft, was non-switchable. After the above-mentioned backdoor was in the public domain, ARM versions of Surface users were able for some time to launch an unauthorized bootloader and install an alternative OS. But the patch patch for Microsoft authorship arrived in time before the “heretics” had time to do something.

Microsoft Surface RT had a chance to get an alternative OS. Unfortunately, it did not come true ...
In a word, Secure Boot has already failed PC manufacturers and users, and there is a risk that this will happen again, so those who doubt its usefulness can be understood. Whether to use “secure boot” or not is an open question, as is the case with the “paranoia vs antivirus installed” approach when it comes to Windows. By default, this option is disabled in old non-branded PC motherboards, but weak protection is still better than none.
PS as part of the initiative to improve the quality of life, Microsoft has ensured that Secure Boot can become non-switchable even in desktop PCs, the choice remains on the conscience of the hardware manufacturer. Subscribing to custom binary files will cost $ 99.
But God bless them, with security features, are we here for the sake of the settings that eliminate the crutches in the drive? To them, and move on.
The list of obsolete technologies that nest in new motherboards for the sake of compatibility with the standards of past years, invariably featured IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) - a drive controller mode that was not “amputated” from new chipsets only for compatibility with old drives and software. In this mode, SATA 3.0 drives work with the speed of their PATA predecessors.
And the Extended Host Controller (AHCI) mode is turned off on demand even in the most advanced chipsets. And in vain, because only he will be able to unleash the potential of modern drives under high load.
In the olden days, the snag with the use of AHCI mode was that in the operating systems (Windows XP and Vista, for the most part) there were simply no drivers for most AHCI controllers in new chipsets, so the systems “fell into BSOD” immediately after installation . Today, Kulibins are introducing AHCI support even into these two outdated systems, and Windows 7/8 and 10 support the extended host controller to the full.

Drive in sequential read mode (IDE). Drive - Kingston SSD Now V +
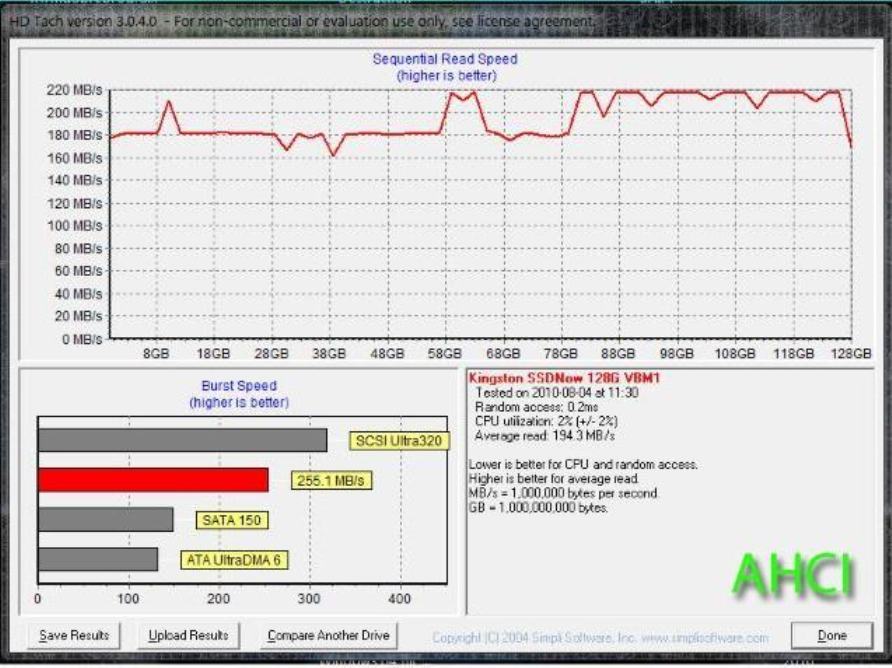
Sequential read drive (AHCI) (source: dobreprogramy.pl )
From the IDE mode, AHCI is distinguished by support for hot-swap drives (of little use in a home PC) and, more importantly, NQC. Native Command Queuing or “hardware sequencing of commands” is often considered a new development to improve the performance of SSD, although in fact it was developed taking into account the potential of mechanical drives.

NQC support in AHCI mode minimizes head movement in mechanical drives
NCQ “sorts” the commands when accessing the drive in such a way as to minimize head movements in the HDD and to use NAND cells in solid-state drives as efficiently as possible. In the case of SSD, AHCI mode is also important for the correct operation of TRIM and speed at the speed limit for SATA-III (and even inexpensive drives rest against the SATA ceiling, such as the Kingston UV400 , for example).

AHCI mode is vital for new SATA drives
Switching the mode of the controller is desirable before installing the operating system. You can and after, but then you have to "start" AHCI with unconventional, you know, medicine. In any case, make sure that your drives use a modern interface for data transfer. After all, the guarantee that, for example, Windows 98 will be able to interact with the drive is much less useful than a higher speed in modern operating systems and programs every day.
GPT markup support is another feature that has become universally used with the advent of UEFI. An important component of modern drives, and here's why.
Before the arrival of GUID Partition Table, PC users had to be content with the archaic method of placing partition tables - MBR or master boot record (master boot record), standard 1983, the same age as DOS 2.0.
An MBR is such a sector with an operating system loader and logical disk information. Supports work with disks up to 2 TB and only up to four main sections. If 2-terabyte HDDs have become “bottlenecks” in home PCs only recently, then the second factor has generated tricks like “extended partitions” since ancient times.
GPT works much more flexibly and assigns a global identifier to each partition, so there can be an unlimited number of partitions, and the problem of interaction with capacious drives is no longer relevant.

Loader - all
And most importantly, GPT is much more fault tolerant, because the loader and partition information are no longer stored “in the same basket”. If the MBR is damaged, your drive goes into “unconsciousness”, and the information from it will have to be recovered long and tedious. GPT stores copies of this information in different sectors of the disk and restores information if it is damaged.
In capacious HDD, GPT partitioning has become a harsh necessity, and new operating systems use it even for drives with capacities much less than 2 TB. The reasonable organization principle and reliability of GPT unequivocally outweigh its shortcomings, and there is no problem with support since Windows 8 (GNU / Linux is not deprived of support either), so it will not be superfluous to convert disks from MBR format to its follower.
Do not format the system disk under Windows XP in FAT32! If in GNU / Linux OS file systems “ bloom and smell ” and are introduced without a special bureaucracy, then the NTFS monopoly in Windows drives does not threaten anything. But over the past few years (for almost a quarter of a century, if we take the first version of the FS as the countdown), the shortcomings of NTFS have managed to “dry teeth” even Microsoft itself, therefore the Redmond people have developed and, partially, implemented the successor of their offspring - ReFS (Resilient File System).

ReFS file structure
The debut version of the "fault-tolerant file system" was published in beta versions of Windows 8 and its server counterparts. Its future in home PCs is still foggy, especially as a system partition, but Microsoft's key developments in this direction are already known today . Among them:
• Support for long names . Up to 32768 characters in the path instead of 255, as it was in NTFS
• Resistant to power supply interruptions . The data and the results of the changes will not be damaged, because the file system operates on metadata and restores information if it is damaged. For any operations, the file system first creates a new copy of metadata in free space, and only then, if successful, translates the link from the old metadata area to the new one. Here you have the safety of files without journaling.
• Storage redundancy for a larger drive resource.
• Higher speed due to reduced fragmentation.
ReFS is still not polished enough for widespread deployment, but if from somewhere it is worth waiting for innovations in the method of storing and operating files in Windows, then only from here.
The recommendation to choose the newest protocols and technologies available would be too naive - you should always weigh the pros and cons before ticking the UEFI or operating system. But still it is worth remembering that the upgrade of the old computer is the work of the owners of this computer. A PC with years of exposure is very rarely able to configure new hardware in the right way. And this means that after the upgrade, it will not be superfluous to check in which mode the new “piece of hardware” works - at least among those options that we talked about today. Make your SSD work "for all the money" at any opportunity!

Every new thing needs to be able to properly use
Proper configuration of the BIOS / UEFI and the operating system is good, and when it runs a new fast hardware, even better! For all fans to combine software pumping components with an immediate upgrade, we give 10% discount on HyperX SSD and DDR4 memory in DNS stores and 10% discount on HyperX Fury drives and DDR3 memory in Citylink ! The promotion is valid from March 21 to April 4 , this is a great opportunity to make your computer faster and save.
We are also pleased to announce that soon the subscriber of Kingston will become the owner of our newest flagship headset with surround sound. Therefore, if you are not yet signed, you need to fix the situation soon. :) We will choose the winner at random and announce thename of the lucky nickname on April 7th. Do not miss the chance to get the cinema level sound for your computer!
Subscribe and stay with us - it will be interesting!
For more information about Kingston and HyperX products, visit the company's official website . In choosing your kit HyperX help page with visual aids .

Backward compatibility of technologies in the PC is an absolute good. With it, an elderly processor can be made to work in tandem with RAM from the “distant future”, and the new drive easily takes root in an old computer and makes it much faster even using old versions of the SATA interface.
And, if the legacy code can be treated differently, then outdated protocols and interfaces are almost always inferior to new developments. Only you will not know about it, because the new hardware in the new computer will be slowed down by default by the settings in favor of maximum compatibility. We find out which settings should be preferred so that the old drive does not interfere with the outdated standards for a
')
UEFI is not an "alternatively talented BIOS", but the best method of hardware initialization
At the “iron” level, innovations in the interaction of the PC platform with the drives are extremely understandable: hard disks increased the recording density and increased the number of plates in the 3.5-inch form factor and filled the most capacious models with helium so that the disks began to work more stable. The future of HDD now depends on the pace of implementation of tiled magnetic recording technology or more radical changes (a jerk in the volume of drives) with thermally assisted magnetic recording .
SSD? Changed several types of memory, ceased to be a luxury in home computers, increased the volume to hundreds of gigabytes. Squeezed out all the juices from SATA-III, got PCI-E speeds and finally got a compact form factor .

Kingston DCP-1000 drive - up to 1 100 000 IOPS for reading and 200 000 IOPS for writing, for example
But the speed of the drives depends not only on the hardware, but also on the software component. And here is the time to recall the BIOS, which lingered on stage, as if idols of the ossified idols, which had become ossified in old age.
Today, in the minds of working people, UEFI is such a colorful alternative to “bios”, with gradients, beautiful menus, mouse support and, sometimes, Russified interfaces. All the more surprising that the motley EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface , then still without Unified in abbreviation), was originally developed by Intel back in 2003. And initially it was offered for Itanium server as a more flexible and fast interface for booting the OS and initializing / diagnosing components. There were a lot of weak points in the ancient 16-bit BIOS with 1 MB of addressable memory, so the replacement suggested itself. As is usually the case in the competition between the layers of abstraction and the performance of iron, UEFI became “harder” and turned into a mini-operating system with drivers and services, but the speed and stability were worth it.
UEFI came to mass computers in 2012-2013, and along with it, pleasant and not so new innovations appeared in the “pre-boot” interface. Let's start with the function of "defender" Windows 8, Secure Boot.
Secure Boot - long-suffering protection against "intermediaries" between the OS and UEFI
In the initiative to implement the Secure Boot feature in UEFI version 2.2 and higher, developers were well-intentioned, if you understand what we are talking about. The fact that Microsoft was the first to use this function (to secure the launch of Windows 8 and “strangle” bootloader activators) is another matter.
For a while, only Windows 8 was able to boot into Secure Boot mode, and users of all other OS had to disable the function in the UEFI BIOS, because the interface refused to execute unsigned files of not properly prepared systems.

How does Secure Boot work?
The “softness” was that all new computers were supplied with Secure Boot at the request of Microsoft, so all fans of operating systems other than Win 8 soon learned about the new function (in not very pleasant circumstances of the “falling” system). And in some cases, the Microsoft update “just for fun” activated the Secure Boot in UEFI even in Windows 7 , which after such implantation safely “fell” on the next boot. This is another kind of "romantic" circumstances of acquaintance with the new function in past years.

“I’ll show you what a safe boot is!”, As if the KB3133977 update tells us and includes an unsupported Windows 7 Secure Boot in ASUS motherboards
In fairness, it is worth noting that modern GNU / Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Fedora, Red Hat and openSUSE are among the first) quickly acquired a signature to be loaded into Secure Boot, but in 2016, with the Microsoft industry’s request, this standard is twice, let's say backed out.
The first time was when the Redmond team "lost" the master key from Secure Boot and compromised the protection for which they were so active. Not a regular key, but a master key, with which the bootloader becomes “naked and defenseless” in all released devices with the active Secure Boot, and attackers can easily and easily replace the operating system during the initial boot phase. There is no sadder story in the world than the story of the "golden keys" and debugging tools in the public domain.
And for the second time, Microsoft made a fuss when the above-mentioned backdoor began to be used for good as a means of “jailbreaking” tablets running Windows RT. The fact is that the Microsoft experiment with ARM systems ended in failure, and the steep and expensive (once) Surface tablets did not even receive support for UWP applications. That is, quite good from a constructive point of view, the devices have become hostages of the "dead" operating system. And there could be no other operating system in the tablet, because the Secure Boot on the tablets, at the request of Microsoft, was non-switchable. After the above-mentioned backdoor was in the public domain, ARM versions of Surface users were able for some time to launch an unauthorized bootloader and install an alternative OS. But the patch patch for Microsoft authorship arrived in time before the “heretics” had time to do something.

Microsoft Surface RT had a chance to get an alternative OS. Unfortunately, it did not come true ...
In a word, Secure Boot has already failed PC manufacturers and users, and there is a risk that this will happen again, so those who doubt its usefulness can be understood. Whether to use “secure boot” or not is an open question, as is the case with the “paranoia vs antivirus installed” approach when it comes to Windows. By default, this option is disabled in old non-branded PC motherboards, but weak protection is still better than none.
PS as part of the initiative to improve the quality of life, Microsoft has ensured that Secure Boot can become non-switchable even in desktop PCs, the choice remains on the conscience of the hardware manufacturer. Subscribing to custom binary files will cost $ 99.
But God bless them, with security features, are we here for the sake of the settings that eliminate the crutches in the drive? To them, and move on.
Outdated and slower interface for reasons that “if something didn't work out”
The list of obsolete technologies that nest in new motherboards for the sake of compatibility with the standards of past years, invariably featured IDE (Integrated Drive Electronics) - a drive controller mode that was not “amputated” from new chipsets only for compatibility with old drives and software. In this mode, SATA 3.0 drives work with the speed of their PATA predecessors.
And the Extended Host Controller (AHCI) mode is turned off on demand even in the most advanced chipsets. And in vain, because only he will be able to unleash the potential of modern drives under high load.
In the olden days, the snag with the use of AHCI mode was that in the operating systems (Windows XP and Vista, for the most part) there were simply no drivers for most AHCI controllers in new chipsets, so the systems “fell into BSOD” immediately after installation . Today, Kulibins are introducing AHCI support even into these two outdated systems, and Windows 7/8 and 10 support the extended host controller to the full.

Drive in sequential read mode (IDE). Drive - Kingston SSD Now V +

Sequential read drive (AHCI) (source: dobreprogramy.pl )
From the IDE mode, AHCI is distinguished by support for hot-swap drives (of little use in a home PC) and, more importantly, NQC. Native Command Queuing or “hardware sequencing of commands” is often considered a new development to improve the performance of SSD, although in fact it was developed taking into account the potential of mechanical drives.

NQC support in AHCI mode minimizes head movement in mechanical drives
NCQ “sorts” the commands when accessing the drive in such a way as to minimize head movements in the HDD and to use NAND cells in solid-state drives as efficiently as possible. In the case of SSD, AHCI mode is also important for the correct operation of TRIM and speed at the speed limit for SATA-III (and even inexpensive drives rest against the SATA ceiling, such as the Kingston UV400 , for example).

AHCI mode is vital for new SATA drives
Switching the mode of the controller is desirable before installing the operating system. You can and after, but then you have to "start" AHCI with unconventional, you know, medicine. In any case, make sure that your drives use a modern interface for data transfer. After all, the guarantee that, for example, Windows 98 will be able to interact with the drive is much less useful than a higher speed in modern operating systems and programs every day.
NTLDR is missing if you don’t use GPT markup
GPT markup support is another feature that has become universally used with the advent of UEFI. An important component of modern drives, and here's why.
Before the arrival of GUID Partition Table, PC users had to be content with the archaic method of placing partition tables - MBR or master boot record (master boot record), standard 1983, the same age as DOS 2.0.
An MBR is such a sector with an operating system loader and logical disk information. Supports work with disks up to 2 TB and only up to four main sections. If 2-terabyte HDDs have become “bottlenecks” in home PCs only recently, then the second factor has generated tricks like “extended partitions” since ancient times.
GPT works much more flexibly and assigns a global identifier to each partition, so there can be an unlimited number of partitions, and the problem of interaction with capacious drives is no longer relevant.

Loader - all
And most importantly, GPT is much more fault tolerant, because the loader and partition information are no longer stored “in the same basket”. If the MBR is damaged, your drive goes into “unconsciousness”, and the information from it will have to be recovered long and tedious. GPT stores copies of this information in different sectors of the disk and restores information if it is damaged.
In capacious HDD, GPT partitioning has become a harsh necessity, and new operating systems use it even for drives with capacities much less than 2 TB. The reasonable organization principle and reliability of GPT unequivocally outweigh its shortcomings, and there is no problem with support since Windows 8 (GNU / Linux is not deprived of support either), so it will not be superfluous to convert disks from MBR format to its follower.
File systems: you are ready for ReFS, but it’s not for you

ReFS file structure
The debut version of the "fault-tolerant file system" was published in beta versions of Windows 8 and its server counterparts. Its future in home PCs is still foggy, especially as a system partition, but Microsoft's key developments in this direction are already known today . Among them:
• Support for long names . Up to 32768 characters in the path instead of 255, as it was in NTFS
• Resistant to power supply interruptions . The data and the results of the changes will not be damaged, because the file system operates on metadata and restores information if it is damaged. For any operations, the file system first creates a new copy of metadata in free space, and only then, if successful, translates the link from the old metadata area to the new one. Here you have the safety of files without journaling.
• Storage redundancy for a larger drive resource.
• Higher speed due to reduced fragmentation.
ReFS is still not polished enough for widespread deployment, but if from somewhere it is worth waiting for innovations in the method of storing and operating files in Windows, then only from here.
New means the best?
The recommendation to choose the newest protocols and technologies available would be too naive - you should always weigh the pros and cons before ticking the UEFI or operating system. But still it is worth remembering that the upgrade of the old computer is the work of the owners of this computer. A PC with years of exposure is very rarely able to configure new hardware in the right way. And this means that after the upgrade, it will not be superfluous to check in which mode the new “piece of hardware” works - at least among those options that we talked about today. Make your SSD work "for all the money" at any opportunity!

Every new thing needs to be able to properly use
Proper configuration of the BIOS / UEFI and the operating system is good, and when it runs a new fast hardware, even better! For all fans to combine software pumping components with an immediate upgrade, we give 10% discount on HyperX SSD and DDR4 memory in DNS stores and 10% discount on HyperX Fury drives and DDR3 memory in Citylink ! The promotion is valid from March 21 to April 4 , this is a great opportunity to make your computer faster and save.
We are also pleased to announce that soon the subscriber of Kingston will become the owner of our newest flagship headset with surround sound. Therefore, if you are not yet signed, you need to fix the situation soon. :) We will choose the winner at random and announce the
Subscribe and stay with us - it will be interesting!
For more information about Kingston and HyperX products, visit the company's official website . In choosing your kit HyperX help page with visual aids .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/373301/
All Articles