AMD announced a 32-core server processor Naples
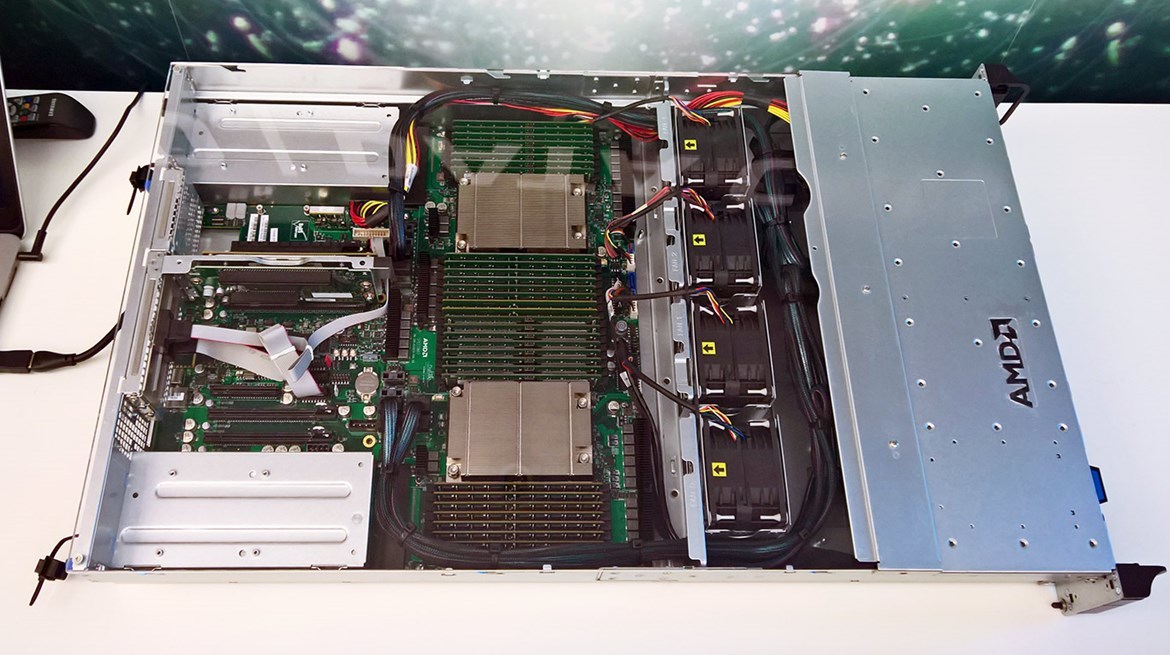
The AMD Naples dual-processor server supports up to 4 TB of RAM (16 DIMM modules per processor), data is exchanged between the memory and one CPU at 170 GB / s
Two weeks ago, AMD introduced a family of desktop processors Ryzen 7 , which are already on sale. The second stage of the Zen architecture should be server processors, and the third stage should be mobile APUs with integrated video accelerators.
Now it's time for stage number 2. On the server market and in data centers, AMD is going to just as well stir up the market and press down the hegemony of Intel Xeon, as it did with desktop processors. Yesterday, AMD announced high-end server-side processors Naples on the same Zen x86 architecture.
Naples has up to 32 cores / 64 threads with simultaneous multithreading (SMT) support. It is focused on corporate servers and data centers. The processor is manufactured according to the 14-nm technology standards, and is available for the socket SP3 socket.
')
Like all modern processors, Naples is designed in a system-on-a-chip (SoC) format, so the memory controller and most of the I / O is directly applied to the chip. The motherboard turns into a hub for connecting peripherals, which means a more elegant and simple design (see photo above). The processors are installed in the connectors, the memory modules are inserted right next to the processor, that is, in close proximity to the memory controller on the CPU. There is nothing superfluous. Very beautiful.
In addition to computing power, the processor supports high-performance I / O interfaces.
First, eight-channel DDR4-2400 memory controllers (up to 16 DIMMs per CPU). AMD officially announced support for 2 TB of memory per slot. Accordingly, 4 TB of RAM can be put in a dual-processor server.
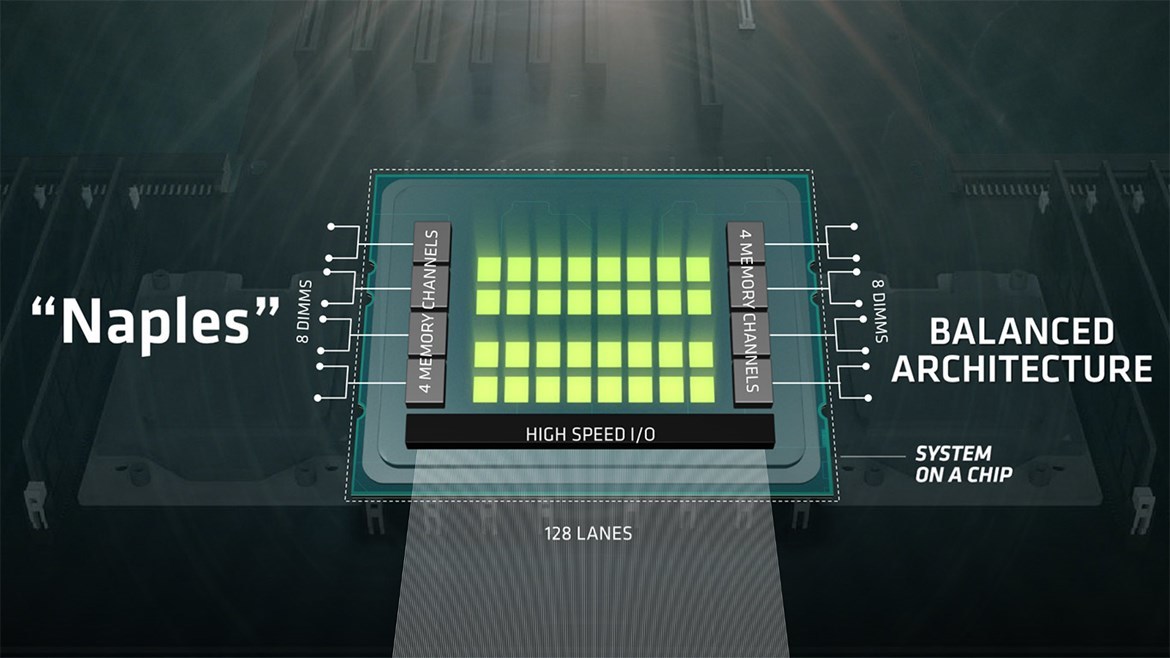
Secondly, a PCI Express 3.0 controller for 128 lines is integrated into the processor chip, which makes it possible to abandon the design in the server design of individual PCI Express components, which increase delays in data transfer.
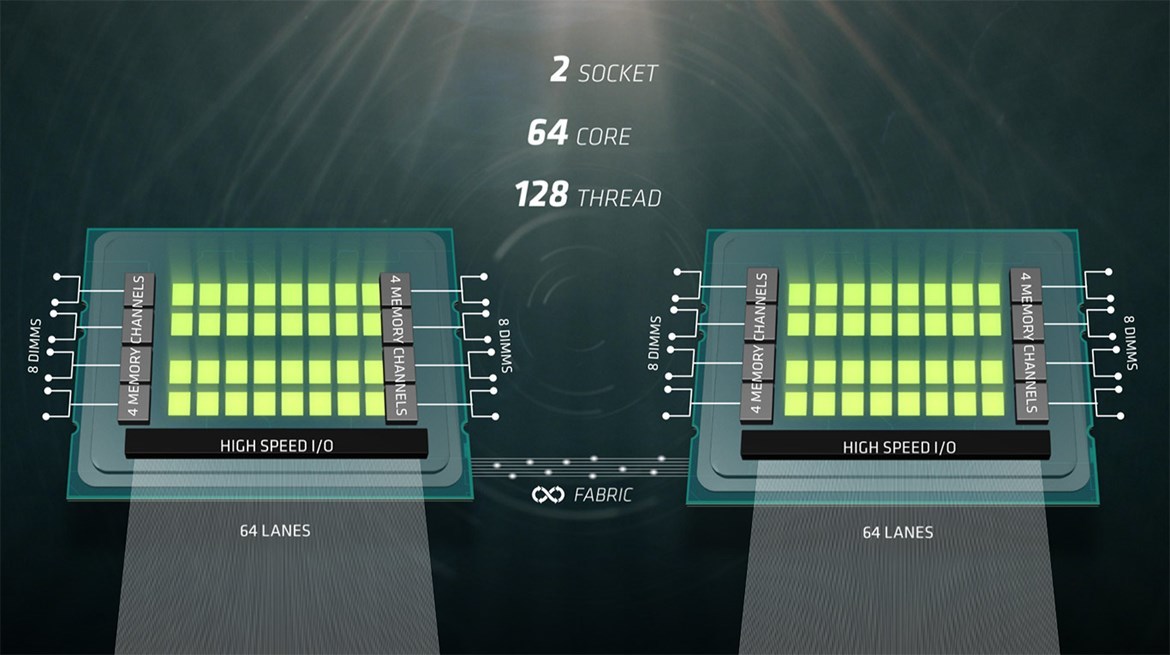
In a dual-processor configuration on motherboards with two sockets, 64 lines of the PCI Express bus are used to transfer data between processors - this bus AMD calls Infinity Fabric. In this case, on each processor, 64 lines are occupied for communication between processors, and the rest of the system has 64 lines from each CPU. In total, the same 128 PCIe lanes are obtained, as when using a single processor.
The physical dimensions of the processor at the event were not reported, but based on the size of a Zeppelin crystal of 195.2 mm² , of which there are four, you can deduce the chip size of 780 mm² and approximately 19.2 billion transistors. This is much more than anybody ever produced in the processor world.
If you compare Naples with a dual-processor server on the Intel Xeon E5-2699A V4, the AMD Naples server can have twice as many memory channels, much more cores (+20 physical cores, +40 threads) and 48 more free PCI Express lines.
Yesterday, at the official presentation, AMD shared the results of a comparative testing of the Naples dual-processor server and the Intel Xeon E5-2699A V4 server, a production model from one of the vendors. Obviously, because of the larger number of cores and memory modules, Naples immediately gains an advantage. In addition, it has a higher memory clock speed: 2400 MHz versus 1866 MHz in the Xeon E5-2699A V4.
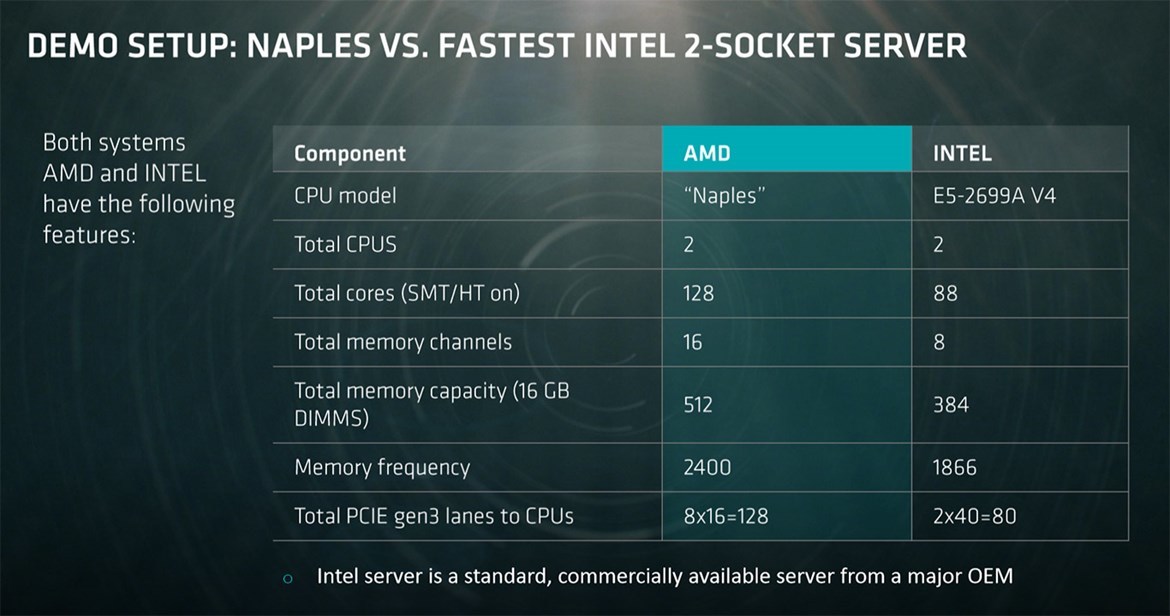
The higher computational power of the processor cores and the wider memory bus allow AMD to seriously outperform the Xeon processors in all tests. The clock frequency of AMD processors was not called (the company said that the final decision on clock frequencies has not yet been made). But this is not very important with such a serious advantage over the other characteristics.
Counting some kind of seismic analysis task that requires multiple calculations of 3D wave equations , the Naples server coped almost twice as fast as the Xeon server, even when, for justice, reduced the memory clock frequency to the same 1866 MHz and limited the use of cores to 44 cores on one processor systems.

According to the representative of AMD, a similar test with a real task loads all computer subsystems, including CPU, memory, and I / O subsystem. Calculations of wave equations in such problems are used in various problems, including in the analysis of geodetic data when searching for new mineral deposits, etc.
If you remove the limit on the number of cores and the memory clock speed - and let Naples go free, the difference in computation speed from Xeon increases to 2.5X.

The previous test was performed on a sample structure with 1 billion elements and performing 10 iterations to calculate the wave equations.
When the data set was quadrupled to 4 billion items, the Intel server could not load the task, and Naples managed in 54 seconds. However, this is a clear cheating from AMD, because it has more RAM installed in the server.

AMD marketers did not stop there. They said that a Naples server with four Radeon Instinct graphics cards corresponds to the computational power of a single human brain.
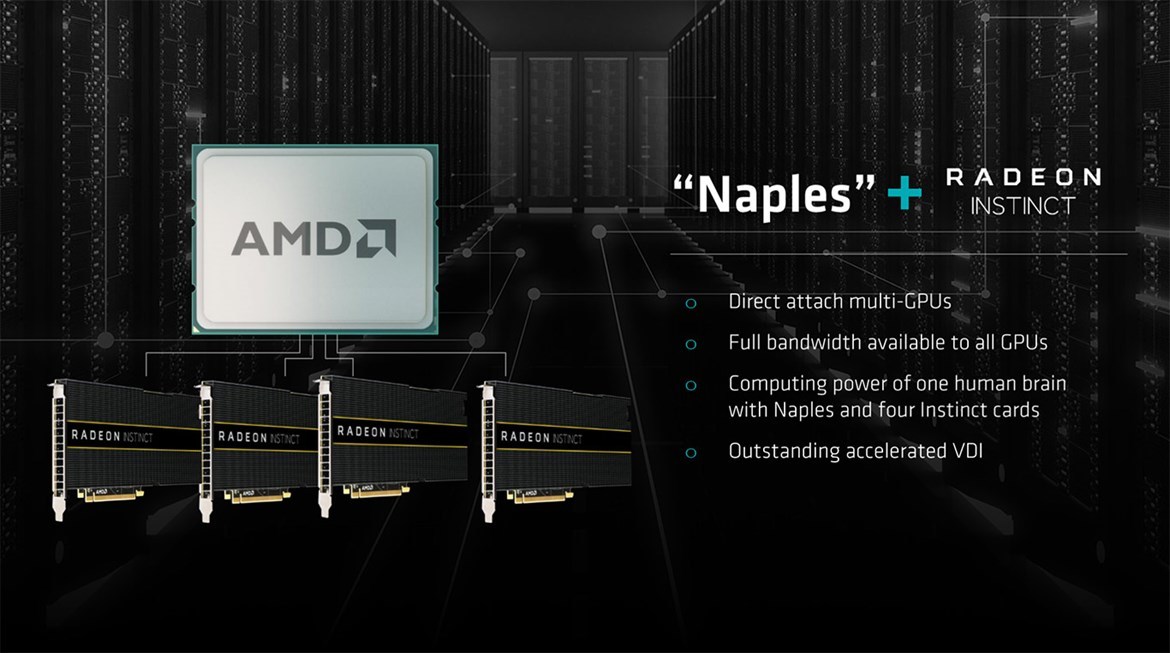
AMD did not disclose the cost of processors. If the company follows the same tactics as on the desktop processor market, then a more productive Naples server should cost even less than an Intel Xeon server.
Naples sales will begin in the II quarter. 2017, that is, until the end of June.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/373241/
All Articles