An article by Russian scientists on the genetic factors in the development of psoriasis was published in the journal of the Nature group.
Scientists investigated the DNA of 14 patients with psoriasis to determine which genetic factors influence the development of the disease. They were able to determine the transcription factors involved in the formation of skin reactions during illness. 1564 genes associated with the disease have been identified. The data obtained will help in the diagnosis and development of treatment of the disease.
The study was published in the journal Experimental & Molecular Medicine (EMM), which is included in the group of journals Nature. Among the authors of the article are Ancha Baranova and Tatyana Tatarinova, researchers and consultants of the Atlas biomedical holding.
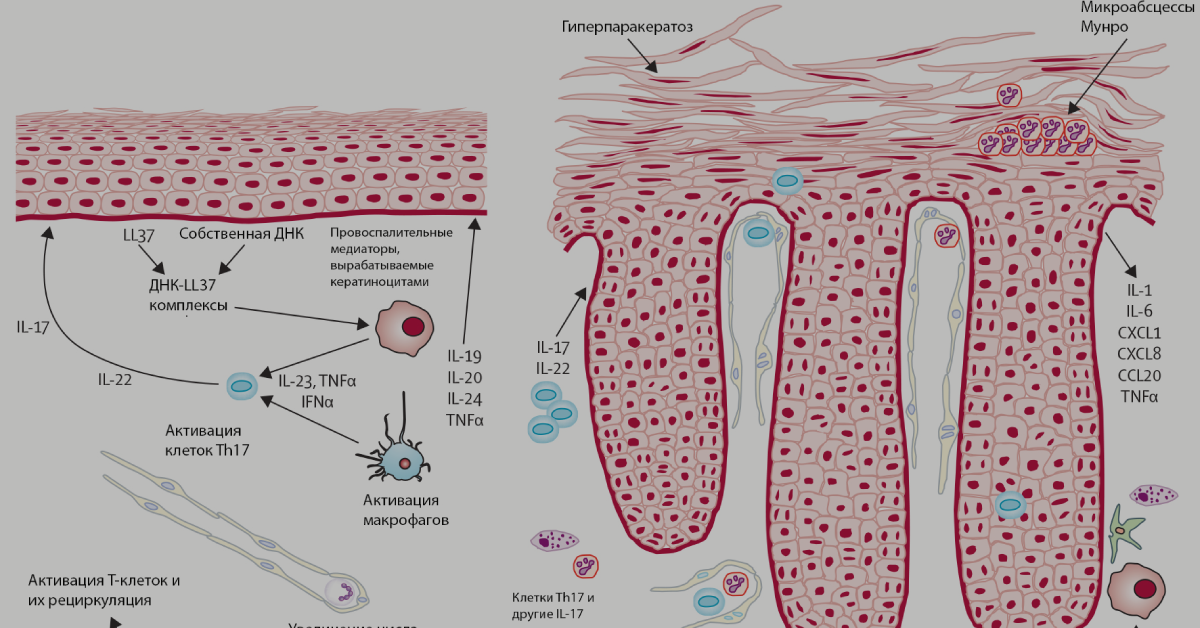
Psoriasis is a chronic immune-related genetic disease. Externally, it is manifested by the appearance on the skin of flaky red plaques. In some cases, plaques can cover large surfaces of the skin, in any case cause redness and itching and reduce the patient's quality of life.
')
At the cellular level, the disease is associated with impaired interaction between the cells of the epidermis and the immune system. Excessive synthesis of keratinocytes (cells of the epidermis) cause symptoms of psoriasis - keratinization and exfoliation of the skin. The second factor is the so-called “cytokine storm”: an increased number of cytokines, first in the skin cells, and then throughout the body. Cytokines are small peptide molecules that transmit a signal of inflammation between tissues. The “cytokine storm” causes comorbid diseases - stroke, diabetes and psoriatic arthritis, which occurs in 30% of cases of psoriasis.
To determine the beginning of the cascade reaction chain, a research team conducted RNA sequencing and analysis of transcriptome (all transcription factors) of skin cells in 14 patients with psoriasis.
The authors of the study identified 1564 genes with altered expression levels: 938 with elevated and 626 with reduced levels. Most genes with reduced expression are associated with lipid metabolism.
The skin serves as a barrier to pathogenic particles, so the irritation of receptors sensitive to pathogens activates antimicrobial protection. For carrying out this reaction are responsible including transcription factors. And although the desired antigen, which triggers a cascade of reactions, has not yet been found, scientists see many coincidences between the mechanisms of psoriasis and the reaction to pathogenic pathogens.
As a result of the analysis, researchers identified a list of transcription factors that play a key role in the development of psoriasis. These are primarily the genes of the FOX group, which are responsible for the group of DNA-binding proteins. They regulate cell growth and metabolism.
The study helps to better understand the mechanisms of cellular and genomic manifestations of psoriasis. These data will be useful for early diagnosis of the disease and the selection of therapy.
The study was published in the journal Experimental & Molecular Medicine (EMM), which is included in the group of journals Nature. Among the authors of the article are Ancha Baranova and Tatyana Tatarinova, researchers and consultants of the Atlas biomedical holding.

Nature of the disease
Psoriasis is a chronic immune-related genetic disease. Externally, it is manifested by the appearance on the skin of flaky red plaques. In some cases, plaques can cover large surfaces of the skin, in any case cause redness and itching and reduce the patient's quality of life.
')
At the cellular level, the disease is associated with impaired interaction between the cells of the epidermis and the immune system. Excessive synthesis of keratinocytes (cells of the epidermis) cause symptoms of psoriasis - keratinization and exfoliation of the skin. The second factor is the so-called “cytokine storm”: an increased number of cytokines, first in the skin cells, and then throughout the body. Cytokines are small peptide molecules that transmit a signal of inflammation between tissues. The “cytokine storm” causes comorbid diseases - stroke, diabetes and psoriatic arthritis, which occurs in 30% of cases of psoriasis.
Research of transcription factors
To determine the beginning of the cascade reaction chain, a research team conducted RNA sequencing and analysis of transcriptome (all transcription factors) of skin cells in 14 patients with psoriasis.
The authors of the study identified 1564 genes with altered expression levels: 938 with elevated and 626 with reduced levels. Most genes with reduced expression are associated with lipid metabolism.
The skin serves as a barrier to pathogenic particles, so the irritation of receptors sensitive to pathogens activates antimicrobial protection. For carrying out this reaction are responsible including transcription factors. And although the desired antigen, which triggers a cascade of reactions, has not yet been found, scientists see many coincidences between the mechanisms of psoriasis and the reaction to pathogenic pathogens.
As a result of the analysis, researchers identified a list of transcription factors that play a key role in the development of psoriasis. These are primarily the genes of the FOX group, which are responsible for the group of DNA-binding proteins. They regulate cell growth and metabolism.
The study helps to better understand the mechanisms of cellular and genomic manifestations of psoriasis. These data will be useful for early diagnosis of the disease and the selection of therapy.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/372937/
All Articles