Mercury
 The tendency of mercury to move from one form to another and the ability to accumulate accumulation is particularly important in its technogenesis. In addition, mercury is omnipresent, sulfophilic, hydrophilic, multifaceted and present in all environments and environmental types, has many forms of location, which makes it difficult to study it. It is supertoxic and superpatological, even in very low concentrations. Mercury is in the lithosphere and biosphere in the form of solid compounds, various gaseous phases and in dissolved form, each of which prevails under specific physicochemical conditions, but easily transform into each other. In technogenesis, mercury accumulates in the waste of many industries, possessing high rates and destructive biological activity, is capable of producing hidden anthropogenic clusters, but humanity cannot exist without this amazing metal. How is the monitoring and control of mercury, what methods and devices of its control exist - I suggest to get acquainted under the cut.
The tendency of mercury to move from one form to another and the ability to accumulate accumulation is particularly important in its technogenesis. In addition, mercury is omnipresent, sulfophilic, hydrophilic, multifaceted and present in all environments and environmental types, has many forms of location, which makes it difficult to study it. It is supertoxic and superpatological, even in very low concentrations. Mercury is in the lithosphere and biosphere in the form of solid compounds, various gaseous phases and in dissolved form, each of which prevails under specific physicochemical conditions, but easily transform into each other. In technogenesis, mercury accumulates in the waste of many industries, possessing high rates and destructive biological activity, is capable of producing hidden anthropogenic clusters, but humanity cannot exist without this amazing metal. How is the monitoring and control of mercury, what methods and devices of its control exist - I suggest to get acquainted under the cut.What is mercury produced from?
Take a look at this amazingly beautiful mineral that has interested people since ancient times. Until now, it is popular not only for its main purpose (mercury production), but for jewelers.

This cinnabar is mercury (II) sulfide. Mineral for the production of mercury. It contains about 85 percent of mercury, a fragile material with a characteristic red color. Since ancient times cinnabar has been used as a red paint, as a source for obtaining mercury and as the only reliable (albeit unsafe) means of treating infectious diseases that existed before the invention of antibiotics. As an indispensable bright scarlet mineral pigment, cinnabar was used already in ancient Egypt and in early Byzantium. Everywhere since then, as in our days, natural cinnabar is widely used in canonical icon painting. But, of course, the most important use of this mineral is the industrial production of mercury.
Mercury is definitely an amazing material. It is the only metal capable of existing in liquid form under normal conditions. It is metal, therefore, electrically conductive. But if you cool the mercury to minus 39 gr. - it becomes solid and does not really differ from other metals. It can even be forged and sharpened. The network has an interesting video with a story about this wonderful substance. Mercury is used in various technological processes, as well as in the production of gas-discharge lamps, in microelectronics and instrument making. Mercury is an extremely technologically demanded substance and if mercury were not so toxic, the spheres of its use would be even wider. I must say that by itself, mercury is not very dangerous - much more dangerous than its compounds and pairs. Here they are the sources of the main danger.
')
Mercury under control
Mercury can accumulate in soil, water, food, in humans and animals. Mercury in the form of vapor is always present in the ambient air, but its “background” concentrations are not large. By the way, what? Rather tough Russian standards for this case regulate the concentration of mercury in the air no more than 0.0003 mg / m 3 . Of course, recording and controlling such concentrations is not an easy task, and for this there are more than 25 registration methods.
Mercury Registration Methods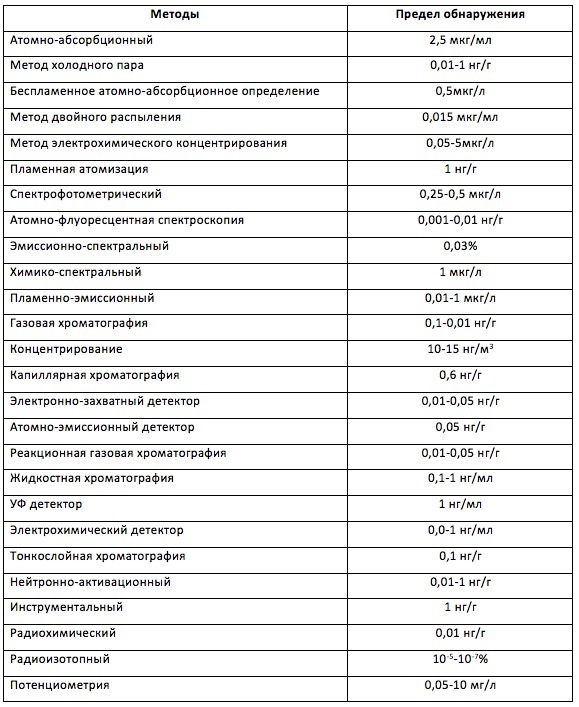

For example, chromatography. In this method, a separation process is carried out in which the test compound is distributed between the mobile phase (liquid or gas) and the stationary (solid or liquid). This method provides particularly valuable information on the qualitative and quantitative content of inorganic and organic forms of mercury. When analyzing mercury in natural objects, it is possible to determine the halides of methyl-, ethyl- and phenylmercury, as well as phenylmercury, dimethyl- and diethylmercury, as well as some other less common organic forms of mercury. The disadvantage of this method of analysis is technically complex laboratory equipment and is used mainly for determining the content of mercury in industrial and natural objects with a high content of mercury, as well as in the soil.

There are a number of methods associated with the use of radioisotopes. Despite the terrible name, such methods are quite safe, since radioisotopes are used in insignificant concentrations. For the analysis, a precisely known amount of the component to be detected, labeled with a radioactive isotope with a known radioactivity, is added to the test sample. After homogenization of the sample and the passage of isotopic metabolism, mercury is released from the medium (usually by chemical means) and its radioactivity is determined, from which the initial amount of mercury in the test medium is then calculated.
 This method has a fairly high sensitivity, does not require expensive equipment and allows you to work with low concentrations of mercury.
This method has a fairly high sensitivity, does not require expensive equipment and allows you to work with low concentrations of mercury.Radio-indicator analysis methods allow solving such tasks as determining trace amounts of mercury in substances, monitoring environmental pollution in analyzing the composition of atmospheric aerosols, natural and wastewater deposition, and analyzing soil and plant and animal objects. Radiation methods reliably guarantee the identification of mercury, have a sufficiently high sensitivity and allow to improve the accuracy and reproduce the results of the analysis. In addition, such methods do not require expensive equipment, allow working with a low level of radioactivity, which makes them indispensable for use in small laboratories, on research vessels, in conditions of high-altitude stations, in expeditionary and field conditions. The detection limit of methods - up to 10 -6 - 10 -8 %
If a good arsenal of control methods has been accumulated for determining mercury in liquid and solid media, it is much more difficult to analyze the concentration of mercury vapor in the air. First of all, due to low concentrations of vapor in the air and due to the lack of fairly simple registration methods. The most promising is the registration method based on the Zeeman method . Consider it in more detail.
Mercury in the air
The Zeeman effect is the splitting of atomic spectral lines in a strong magnetic field. Since any substance has its own spectrum, if we use the spectrum of a special mercury lamp, but in the presence of a strong magnetic field, such a spectrum will be distorted. Additional components will appear in the spectrum, which will be mirrored from the main spectrum. It looks like this

The initial spectrum (black curve) when the magnetic field is turned on is distorted by three. The central spectrum (blue) and two symmetrical lateral spectra (shown in red). The magnetic field induction in this case is 1.56 T. This effect basically allows for the implementation of a convenient mercury registration method. To do this, it is necessary to analyze the change in the amplitudes of the separated and main components, and the higher the mercury concentration in the test air, the higher will be one of the components of the split spectrum and, at the same time, the smaller the other. Of course, the air also has its own absorption spectrum at a wavelength of 254 nm (it is at this wavelength that the mercury lamp glows). This (in this case, "parasitic") spectrum must be removed. To do this, use the "reference" channel and special filters.

The reference channel either does not contain mercury at all, i.e. demercurated , or there is exactly the known value of the concentration of mercury in the form of the reference. The radiation of a split-spectrum mercury lamp passes through a reference and measuring cell, hits a filter that filters the parasitic spectra of other air molecules at a wavelength of 254 nm and enters the spectrometer. After the spectrometer, the reference and the studied spectra arrive at the matrix, which is often subjected to cooling in order to increase the sensitivity and for temperature stabilization. The resulting spectra are analyzed and the mercury concentration in the test air is finally determined.
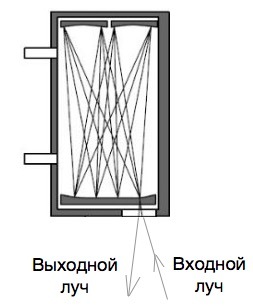 Of course, this is the most general representation of the scheme of such an instrument; in fact, due to the extremely low concentration of mercury in the sample, it is necessary that the optical radiation travels a long path in the measuring cell, for which various optical circuits of repeated transmission of optical radiation are used. This is done in order to achieve a significant increase in sensitivity due to repeated passage of the light beam, while maintaining the relatively small size of the device. This, in turn, greatly complicates and increases the cost of construction due to the need for “fine” adjustment of the device. The use of multipass cuvettes tightens the requirements for vibration, and there are already significant effects of temperature drops. However, these shortcomings are compensated by a significant increase in sensitivity, because the beam in a multipass cell can “run” a significant way. Sometimes tens of meters. Most modern instruments use exactly multi-pass cells.
Of course, this is the most general representation of the scheme of such an instrument; in fact, due to the extremely low concentration of mercury in the sample, it is necessary that the optical radiation travels a long path in the measuring cell, for which various optical circuits of repeated transmission of optical radiation are used. This is done in order to achieve a significant increase in sensitivity due to repeated passage of the light beam, while maintaining the relatively small size of the device. This, in turn, greatly complicates and increases the cost of construction due to the need for “fine” adjustment of the device. The use of multipass cuvettes tightens the requirements for vibration, and there are already significant effects of temperature drops. However, these shortcomings are compensated by a significant increase in sensitivity, because the beam in a multipass cell can “run” a significant way. Sometimes tens of meters. Most modern instruments use exactly multi-pass cells.
Mercury Convention
Despite the absolute demand for mercury for modern technologies, the issues of a sharp reduction in its use in the near future are being considered. In 2013, the UN adopted a rather tough and very controversial Minamata Convention on Mercury , which was supported by many countries. According to the convention, the use of mercury should be regulated, the production of some mercury-containing devices (medical, fluorescent lamps) should be reduced. Also limited to a number of industrial processes and industries, including mining (especially gold mining) and the production of cement.

Since 2020, the convention has banned the production, export and import of several different types of mercury-containing products, including electric batteries, electrical switches and relays, certain types of compact fluorescent lamps, cold cathode or external electrode fluorescent lamps, mercury thermometers and pressure gauges.
The initiators of the convention explain their intention to seriously limit the use of mercury in order to intensify the development of modern technologies in conditions when it will be impossible to use mercury and thereby significantly improve the environmental situation. However, some critics of the convention have expressed the opinion that this is only a reason to reconsider the global markets of mercury producers and oust many players from this market. After all, when the convention enters into force in 2020, the price for this metal may unexpectedly increase significantly, because humankind cannot refuse to fully use mercury.
Have a nice day, everyone!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/372837/
All Articles