Top 3D Expo 2018: Professional FDM printing. New materials. New horizons of application

Hello! With this material we are opening a series of articles on performances from Top 3D Expo 2018. In the first article, Evgeny Kopylov talks about the professional and industrial application of 3D printing using FDM / FFF technology.

Additive technology, as part of digital production, is one of the driving forces behind the fourth industrial revolution, and one of the main technologies is FDM.
')
Layer-by-layer fusion of polymers was the subject of this report.
About technology
Legend has it that FDM technology was developed by Scott Crump, the founder of Stratasys.

In 1989, a patent was filed, in 1992 the company received it, and before that, he experimented on his kitchen table with a glue gun on wax paper. After seven prototypes, the first car was created.
The RepRap enthusiast community changed the terminology somewhat, naming the FFF technology - Fusing Filament Fabrication, to bypass patent restrictions and develop the technology independently of Stratasys.
The technology is widely known - the polymer, extruded in a heated form, stacks in layers and forms the product.
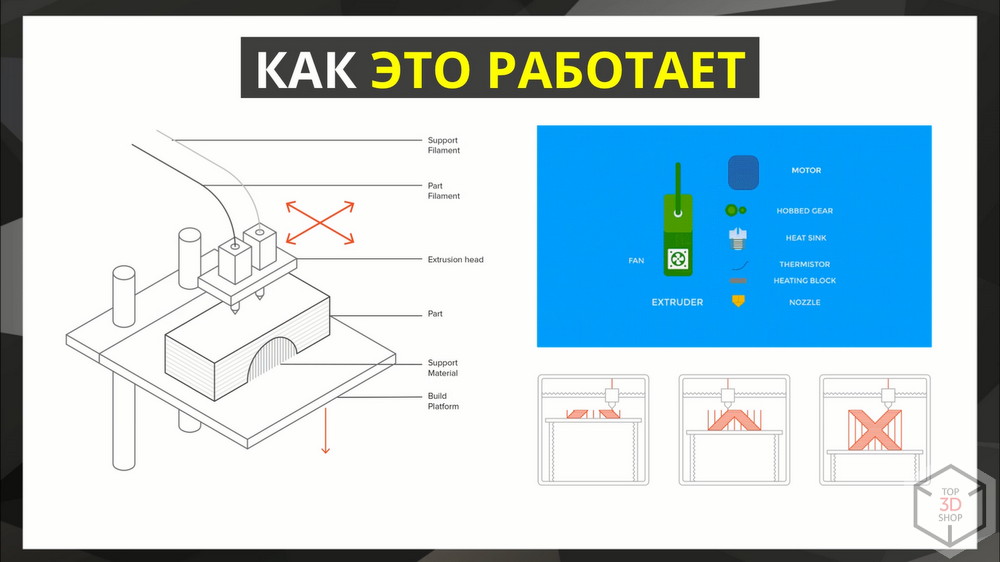
About printers
Designs are divided into two large groups - by the presence or absence of a thermostatic chamber - a closed body with adjustable temperature.

Kinematic systems more.
Cartesian and Delta
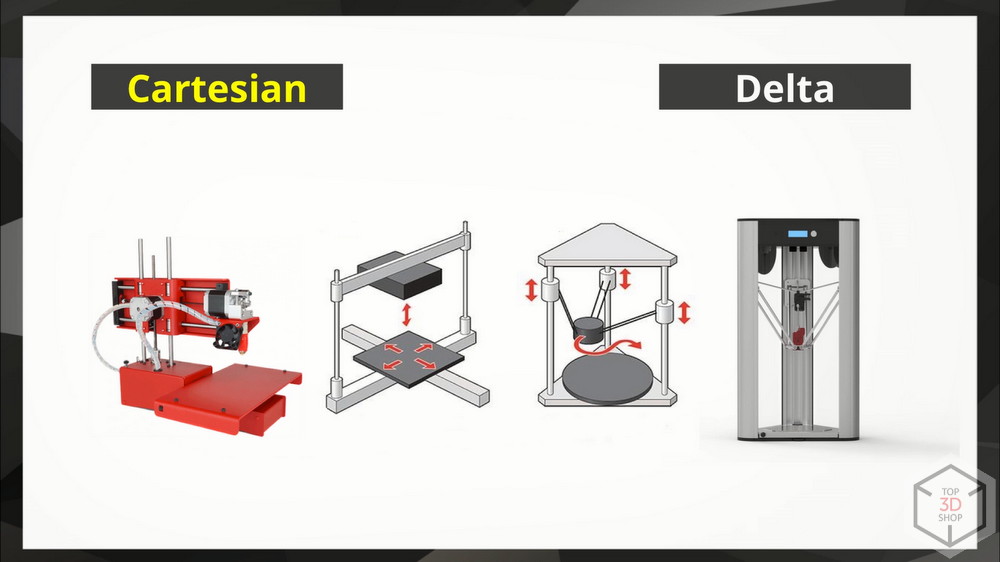
The most common - Cartesian, linear, where the movement of the extruder relative to the building platform occurs in three axes, for each of which is its own drive.
The second most popular system - Delta - the movement of the print head in it occurs along three parallel guides, the change of coordinates along the Z axis occurs due to the change in the angle between the drives. Workspace in printers with such a system, delta bots, is usually much more vertically. They, too, are open and closed.
Polar and Scara

The kinetic system of the Polar type is a fairly new system represented by the company of the same name. It differs from the Cartesian system in that the extruder, relative to the building platform, moves in the X and Y planes not linearly, but along a circle, like a sound-pickup needle moving along a plate.
Skara is a kinetic system that came from robotics, intended for manipulators with limited mobility but with increased accuracy and rigidity. In it, the extruder is located at the end of the manipulator moving due to the lever joints along the XY axes and a separate drive along the Z axis.
The advantages of such systems are speed, lower noise level. Disadvantages - more complex software, compared with the Cartesian.
Robotic Arms and 5-6 Axis
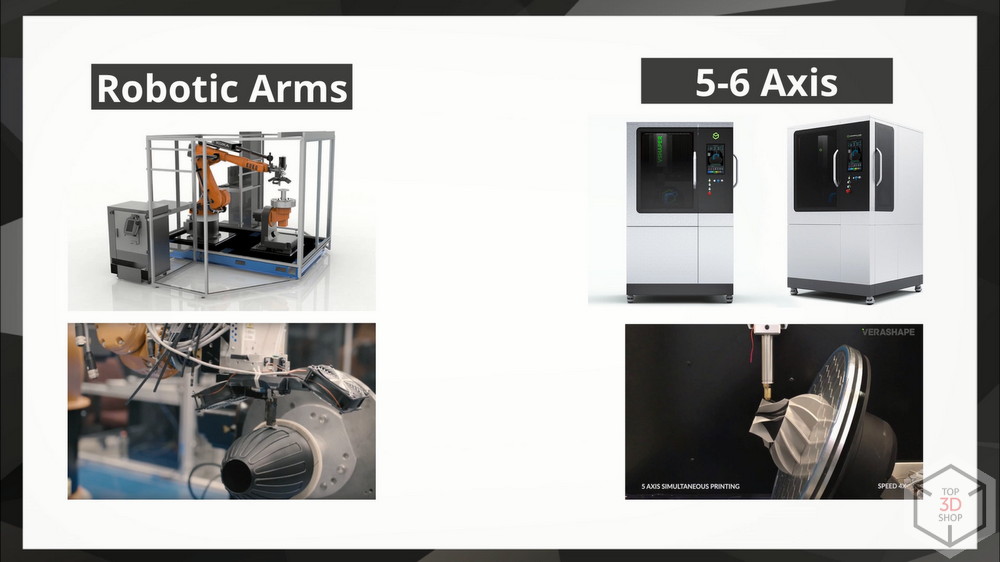
There are also 3D printing systems based on the use of full-fledged modern robotic manipulators. They are used in the automotive industry, the creation of large structures.
The five and six-axis systems are industrial machines with an increased number of degrees of freedom. Turntables allow you to change the angle at which the tool interacts with the workpiece. The tool here can be not only an extruder, but also a router, and a laser. The revolving tool changer system allows both 3D printing and processing with other tools.
Restrictions

Until recently, the materials and technologies by which extruders were made, did not allow to increase the printing temperature above 260-300 degrees Celsius. This limited the amount of materials used.
Most printers used a rather weak electronics, with low productivity and a small range of operating temperatures. This led to failures, the inability to resume printing when the process was interrupted.
The nozzles of ekutruderov, usually made of brass, because of wear did not allow for a long and stable work with composite materials.
The lack of thermostatic cameras in most printers did not allow printing with high shrinkage polymers.
Insufficient heating of the platforms and lack of vacuum tables caused problems with adhesion, holding the model on the platform during printing.
Basic polymers
Many new monopolymers and even more composites are now appearing on the market.

The two most common base polymers are PLA and ABS.
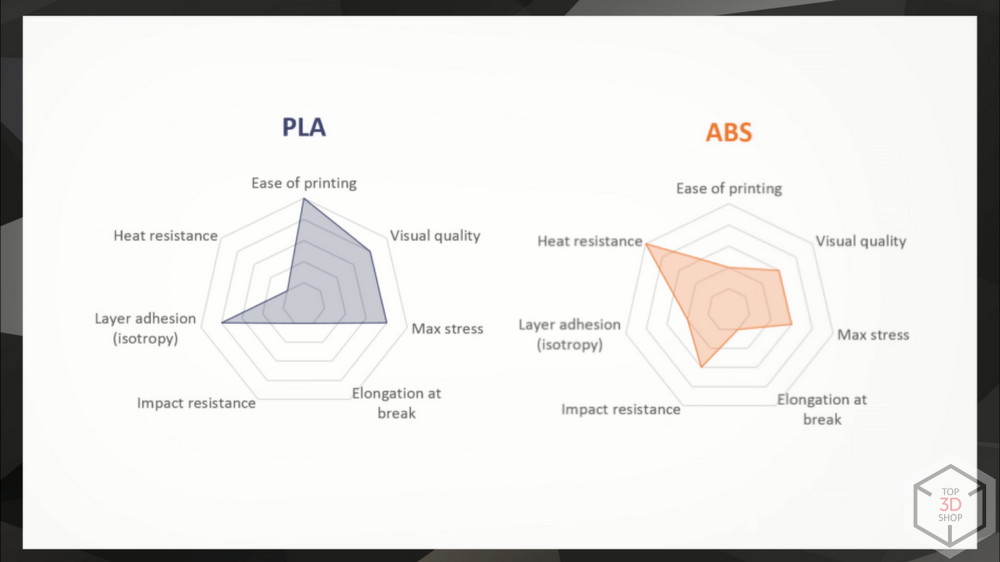
PLA
Polylactide, the easiest and most accessible material.
A lot of positive properties - no shrinkage, which allows printing without heating, a lot of colors, safe - made from bio-raw materials, does not give toxic fumes and the smell of synthetics when printing.
ABS
ABS - shockproof plastic from petroleum products. More toxic, gives significant shrinkage, which requires heating at least the platform, weak resistance to UV light. Mechanically durable and heat resistant, moisture resistant and dielectric. Very popular.
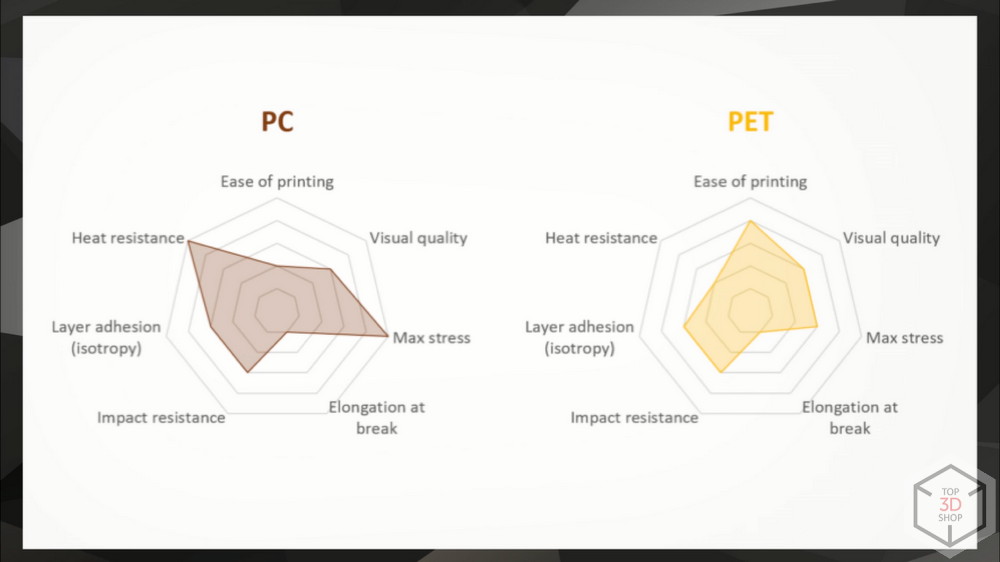

PC
Polycarbonate - widely used as a substitute for glass. Resistant to a wide range of temperatures, very durable, fireproof.
PET
Polyethylene terephthalate is used in the food industry, in particular - in plastic bottles. It has a number of interesting properties: transparent to ultraviolet, quite wear-resistant.

TPU
Thermoplastic polyurethane is a flexible and abrasion resistant material, the properties of which depend largely on the additives used in it.
Nylon
Nylon is one of the most common plastics in the industry. Can be used in moving parts, such as gears and bushings, due to the low coefficient of friction.
Support materials

Support materials are used when you need to create supports in the process of printing on printers with two or more extruders.
Hips
HIPS - high-strength polystyrene, has excellent adhesion to ABS, dissolves with limonene. ABS to limonene is absolutely stable.
PVA
Polyvinyl acetate is soluble in water. Perfectly proved himself as a material of support when working with PLA, with which it adheres perfectly. The only, probably, minus is quite expensive.
Superstructure materials

Peek
Polyetheretherketone is resistant to a wide range of temperatures, chemical and mechanical effects. Keeps strength characteristics with simultaneous exposure to all these factors. It is printed at a temperature above 400 degrees, parts from PEEK are capable of working for a short time up to 300 degrees, continuously for 260. Resistant to ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma radiation. Chemically resistant to oils, fats, alcohols, ethers and other solvents.
Exists in modifications with reinforcement with fiberglass, carbon fiber, ceramics. There is a modification sertiitsirovannaya for medical purposes.

PEI
Polyetherimide is a structural polymer with temperature stability up to 153 or 213 degrees Celsius, depending on the modification. It has the same chemical resistance as PEEK.

PPSU
Polyvinyl sulfone is the best thermoplastic for use in aggressive environments, alkalis, acids, gasoline. Resistant to 189 degrees. Mechanically durable. Used in the manufacture of automotive parts, medicine, aerospace, tool manufacturing. Withstands gamma sterilization and autoclaving.
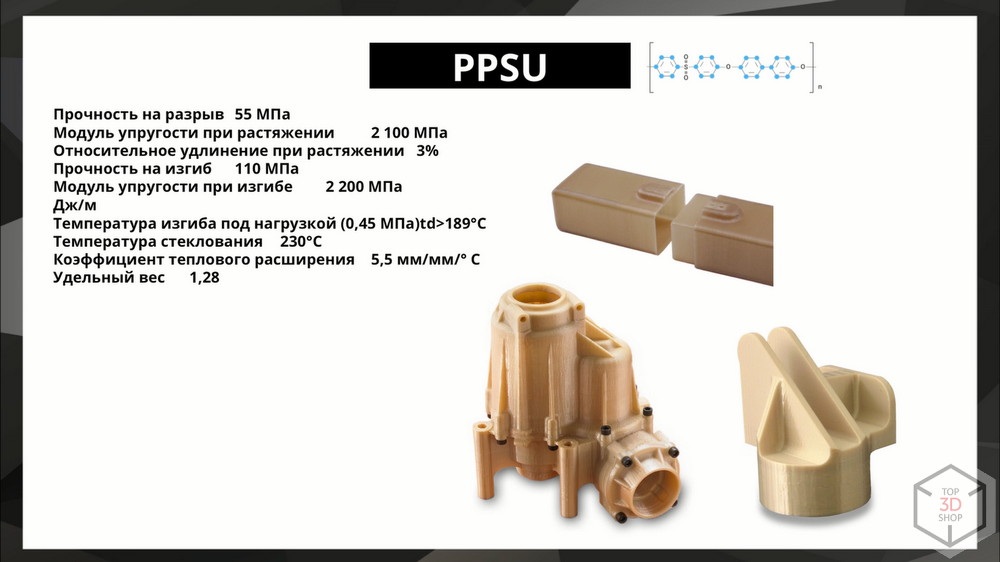
Construction materials
PVDF
Polyvinylidene fluoride is produced in Europe and in Russia. It has high mechanical properties and chemical resistance. Maintains temperatures to 140 degrees. It is quite flexible, has a low coefficient of friction.

POM
Polyformaldehyde, it is also polyacetal. Lowest friction coefficient. Ideal for sleeves and gears in specified temperature ranges. It works at temperatures from -50 to 100 degrees Celsius, short-term up to 140. Very high shrinkage, you can print only on printers with a thermally insulated camera and good heating.

Structural metal-filled composites
Structural metal-filled composites contain 80 percent or more of the metal. The number of variations in the composition of a fine powdered metal that can be added to such a composite varies widely and affects the properties of the material. Structural metal-filled composites, which give solid detail for practical use after baking, are mass-produced by Desktop Metal and the chemical concern BASF.

The BASF concern offers Ultrafuse 316LX on the basis of stainless steel. The shrinkage of the material on the XY axes is about 19%, on Z - 21%. This must be taken into account when preparing the model. Requires vacuum sintering.
Details turn out strong and full-featured, there is no problem of stratification.
In the coming years, we are waiting for the explosive growth of the range of such materials.
Printers
Stratasys Professional 3D Printers

Fortus 380 / 450mc and 900mc are professional FDM printers from Stratasys.
The 380th camera has a 350x300x350 mm, the 450th has a 406x350 mm and the 900th has a 900x600 mm. Stable work with basic and structural materials.
TOTAL Z - Anyform
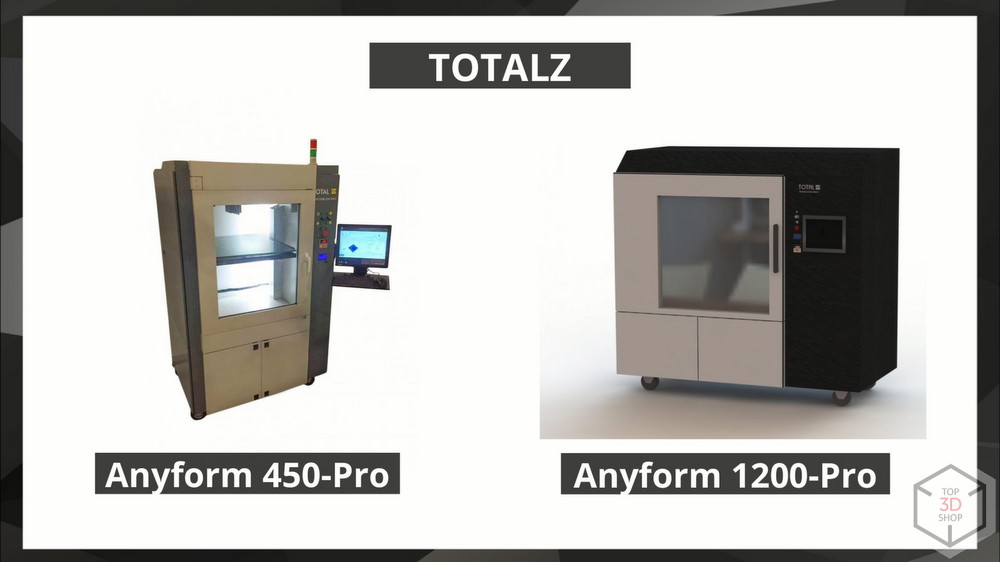
A current example of import substitution is the entirely Russian production of printers, following the example of Stratasys products. This is the only large-format printer in the Russian Federation for printing high-temperature plastics, equipped with a thermostatic chamber. The frame, housing, camera and some other elements of these devices are made from domestic components. In the 450 , 650 , 900, and 1200 model lines, the model's numeric index also indicates the size of the camera.
The temperature of the camera of these printers, depending on the options ordered, is increased to 200 degrees, the printing temperature is up to 500, which allows printing on them with all the available engineering plastics.
Available options: vacuum table, plastic preparation module, feed control and video control.
VERASHAPE

Poland still can not go to space, but it can already in FDM-technology, and very well. We saw live VSHAPER printers of the VERASHAPE series - excellent machines, high-quality and with good characteristics. We have already planned training and certification of our engineers from the manufacturer.
450 , PRO and 450 MED are high-temperature models. Medical modification is equipped with ultraviolet sterilization of each printed layer and HEPA-filter, which allows to use the device directly in hospitals.
In the near future, we are waiting for the release of 5Axis - a VERASHAPE five-axis 3D printer, the prototype of which we saw on Formnext in Frankfurt. There is already a revolving tool-changing system, and a milling head will also be installed. The turntable allows you to build a part of complex geometry without support, turning the part at any angle to the head. It will save time and material. One of the most promising developments.
3DGENCE

One of the biggest surprises is the 3DGENCE INDUSTRY F340 . The previous model of the company was a small budget printer of an open design, here we see a modern industrial design with a camera of more than 300 mm, modern control, heating. Print heads with different heating temperatures, for working with different materials, are located in quick-detachable modules and are easily replaced, the printer can be bought with any of the modules or all at once. The main advantage is a dvuhsopelnaya print head for high temperature, allowing you to print PEEK with support from another material. Support from the PEEK itself is very poorly removed from the models, so this is an important point.
The machine is assembled on modern industrial sites.
OMNI3D

Polish unit , with a cubic print area with an edge of 500 mm. A large unit, manufacturers of which also declared support for high-temperature materials.
MASS PORTAL

The line of cars from Latvia is large delta bots. A new line of “D” devices has been launched , and printers of the “XD” series are also being produced. Digital-controlled automatic material dryers have been released along with printers. In the top model there are two independent nozzles, for each of which you can set your own temperature for storage and operation.
The company also released the Dynasty system - a complete solution, which is completed on request by printers and dryers, has a special department for issuing ready-made prints and a box solution with an integrated manipulator that allows you to perform operations in automatic mode without opening the door.
A high degree of automation, a set of nozzles with an output diameter of 0.2 mm and high print quality make Dynasty a unique product among FDM solutions.
ROBOZE

The uniqueness of the Italian high-temperature printers ROBOZE lies in the fact that instead of the belts they use helical gear. This contributes to greater accuracy and reliability at elevated temperatures.
The recently introduced ROBOZE Argo 500 prints at 550 degrees Celsius and has a cubic chamber with an edge of 500 mm.
DYNAMICALTOOLS
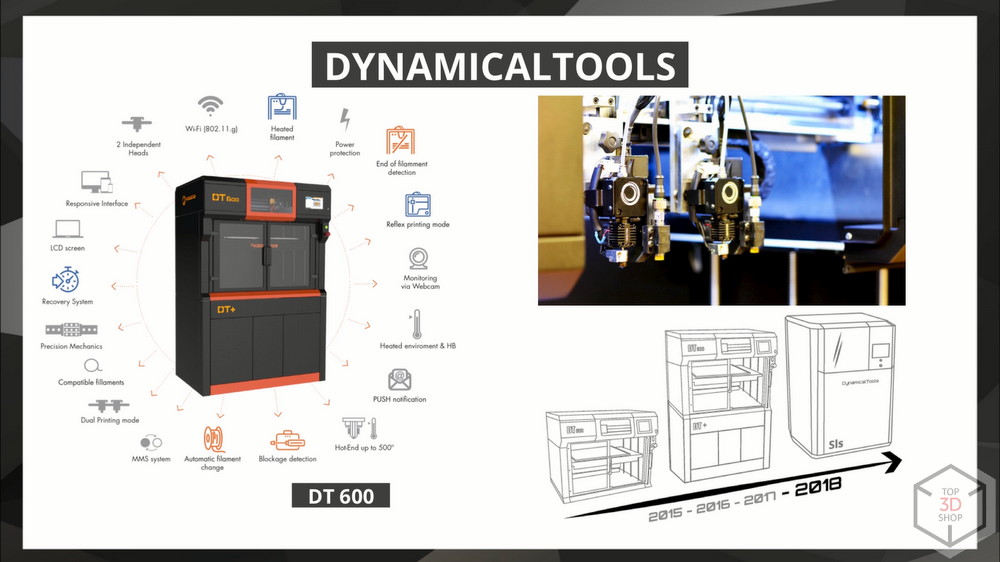
Spain. DT600 has two independent print heads, both high-temperature. You can print two independent parts at the same time. Wi-Fi, plastic control, print recovery and darkness of other functions. The company is actively developing, by the end of the year it is going to present a desktop SLS system.
APIUM

The German company Apium - the pioneer of high-temperature printing, it was they who released the first 3D printer that prints at temperatures above 400 degrees. Now the company supplies the P220 model, with a camera of 210x160x160 mm. The price is comparable to printers from other manufacturers with a print area of up to 500x500x500 mm, but this manufacturer is justified by extensive experience in the production of high temperature and heated cameras up to 300 degrees. Provides the highest quality printing refractory constructional thermoplastics at a temperature of 550 degrees Celsius, of all those listed. Minus is a relatively small print area.
Intamsys

Inhamsis - the leader in the production of high-temperature among Chinese companies.
Funmat HT has a camera of 260x260x260 mm. Funmat PRO HT - industrial model with a camera with an edge of more than 500 mm.
It is worth less than 500,000 rubles in Russia, at the level of desktop printers. Thermal insulation, heating the camera to 70 degrees, the nozzle 450 degrees.
CREATEBOT

Models of high-temperature F160 and F430 from Creatbot. F160 is a small device, F430 - 400x300x300 mm. Details with cases of application for these devices yet.
Comparison
In the comparative table you can see the difference in the characteristics and prices for the presented printers.

Practice
MASS PORTAL
MASS PORTAL prints watch parts in natural size, 1 to 1, with a 0.2 mm nozzle.

BOCAR

The Polish company BOCAR produces fire trucks using 3D-printers 3DGENCE. The printer is used to create prototypes of complex hydraulic systems in mobile fire extinguishing systems, saving up to 80% of time over 90% of finance at this stage of production.
Technical University of Kosice
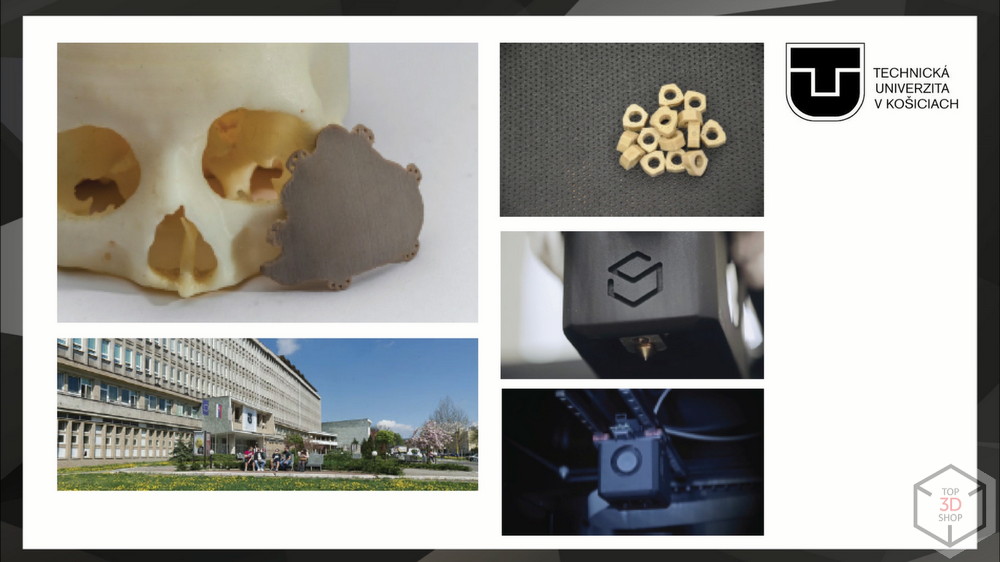

The Technical University of Kosice conducts neurosurgical and dental research. They needed a universal tool for creating textbooks and medical constructions from PEEK. The choice fell on the VShaper PRO MED, which completely satisfied the customer.
ARRINERA TECHNOLOGY SA

A company that develops supercars - they create mirrors for their cars by printing them on a 3D printer. The weight of rear-view mirrors has been reduced from 525 grams to 247. Printing a part takes 16 hours, in this case it is much faster than milling on a CNC machine. Used ABS with HIPS as support, printer - OMNI3D.
Qbig

Equipment developer. In the development of metal parts used HIPS, as a material for printing burnable models for casting. 12 parts were received in 11 hours: 7 hours to print the parts, 4 hours to create a ceramic mold around the burning out template, plus casting. The client is completely satisfied. Significantly reduced time and cost of manufacture. Printer - OMNI3D.
ROBOZE

The metal part is replaced with carbonated CFR PEEK. This is a carbon-filled polymer. The table shows the advantage in cost and time of technology, compared with direct metal printing and milling.
MEYRA
Manufacturer of wheelchairs. Printed pipe bending template for the production of PETG. Saving money - 86% compared to the metal form.

What to expect from technology

Manufacturers represent more and more conveyor and rack printing systems focused on mass production.
Racking systems are systems with several printers combined into a single work network, where incoming orders are processed automatically.
Conveyor system - a system where the function of the desktop is performed by a conveyor belt. They allow not only to print several products without human intervention, replacing the working area with the advancement of the tape, but also to print products of increased length.

Multi-axis systems with automatic replacement of print heads and other tools promise greater savings in material and time due to printing from different angles and carrying out other operations, several different in one cycle. Here the prospects are very broad.
Perspectives

Extruder printing has broad perspectives. In the construction field, 3D printing is just starting to spread.
Printing with biological materials in medicine is a very promising area. We cooperate with the Korean company RAKIT, which is a multifunctional system with the possibility of both classic FDM printing with special materials, and with a needle system for manipulating drugs.
There are projects for printing glass and ceramics. It is rather difficult to work with glass, but there are prospects and developments are underway.
In the food industry, chocolate and other food products are printed, there are already successful application cases: in the photo are prints from Chocola3D purchased from us, from our client, Chocolama. This area is actively developing. We are also following the developments of MIT - high-speed FDM printers that print at a speed of 10-20 times the speed of existing 3D printers.
Fast decision
If you have tasks for 3D printing , we are always happy to complete orders for any of the technologies presented.
You can buy equipment and materials for independent production from us - we will help with the choice, we will select the best set for the start. We will be glad to see you in our offices in Moscow and St. Petersburg.
Want more interesting news from the world of 3D technology?
Subscribe to us in the social. networks:




Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/371517/
All Articles