New 8 generation: more cores, less consumption

The beginning of April was marked by the mass release of Intel products: the eighth generation of processors (Coffee Lake) and chipsets for them. Trends of the new season: 6-core mobile processors, new Thermal Velocity Boost (TVB) functionality, reduced power consumption in production processors and a plus in Optane-compatible models. We will not talk about the latter (we will manage with a picture), but for the rest we will go in more detail.
New desktop and mobile chipsets
In addition to the lonely formerly Z370 chipset, Intel has released a full range of models for all applications: workstations, home PCs, and budget options. The logic of building a ruler is the same as before: Z370 - advanced home, H370 - home / office, Q370 - corporate. The latter is different from all the support of vPro.

The main chip of the chipsets in 2018 was the support of the 802.11ac standard (2Tx2R), which provides data transfer rates up to 1.7 Gbit / s. Wi-Fi is implemented using CNVi technology, the meaning of which is to transfer all complex and expensive interface components (logic, memory) to the chipset, leaving only the radio module of the M.2 format “outside”. However, it should be noted that the available functionality does not mean that motherboard manufacturers will use it, because the implementation costs money (in this case, about $ 15). Keep this in mind, especially when choosing a budget option.
')
The second interesting feature is the introduction of USB 3.1 Gen 2 support into the chipset (speed up to 10 Gbit / s). The table shows the maximum possible number of ports, in reality there will be as many of them as the configuration of the HSIO lines will allow (for example, unspecified onboard 10G Ethernet ports also use this resource, and not only them).
The line of mobile chipsets also looks familiar: HM370 (home), QM370 (working), QMS380 (working budget). The functionality with minor nuances repeats desktop counterparts, the latter lacks USB 3.1 G2, vPro is present in corporate models.
Mobile processors: the six-core flagship and the long-awaited Xeon E
From now on, top-end wearable devices can have up to 6 cores and 12 threads - now we have a Core i9-8950HK, the first i9 in the mobile segment and the only one so far. The tablet shows a comparison of the new flagship with the previous one.
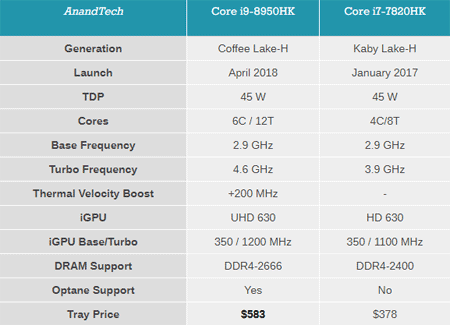
A few points are noteworthy. First, the flagship is still open for overclocking. Secondly, the maximum frequency is really maximum, even in comparison with desktop models. Thirdly, here we see support for Thermal Velocity Boost (TVB) technology.
TVB - the further development of technology Turbo Boost. If the processor temperature remains below a certain level (in this case, 53 ° C), one of its cores can increase its frequency more than the others by several hundred MHz (here 200), which allows more sharp, explosive loads to work more smoothly. However, again, whether a CPU is capable of TVB depends both on the quality of a specific processor instance and on the cooling efficiency of a given device model. In advance, without tests, it is problematic to say.
Next news: finally, Xeon E series processors are released, low-end "mobile server" models, announced before the launch of Xeon Scalable . While there are only 2 of them, Xeon E-2186M and Xeon E-2176M .
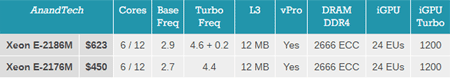
From the productive mobile processors Core i5 / i7 of the new generation Xeon E, they differ in increased cache, high maximum frequencies and ECC memory support. But their power consumption is no different - both there and there TDP 45 W, which is, of course, more honorable for the Xeon.
As for processors for ultra-and other beeches - the most honorable place in their row is now occupied by models with Radeon Vega graphics , however, their cost and TDP under 100 W may seem unnecessary to someone, and models with built-in Graphics Iris Plus latest generation Intel Core i3-8109U, i5-8259U, i5-8269U, i7-8559U .
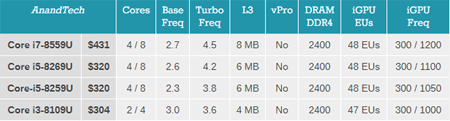
GT3e graphics use up to 128 MB eDRAM, has a maximum frequency of 1.2 GHz and 48 executive units (the previous generation graphics had a maximum of 24 executive units and did not use eDRAM). In this case, the heat dissipation of these processors is only 28 watts. These models will become the base for most notebook models in the middle segment.
Desktop processors: energy efficiency and diversity
The desktop line of Coffee Lake processors has nearly three dozen models and extends the entire length from Core i7 to Celeron. The table shows the most interesting models of the upper part of the line.
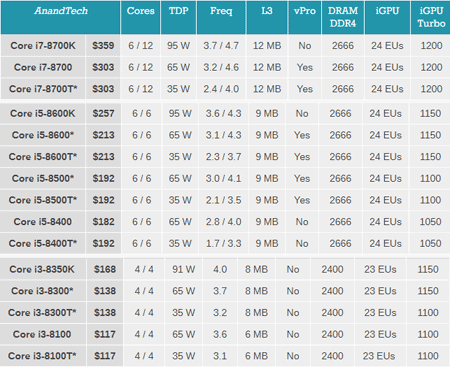
Each index is represented by two or three models: basic, with unlocked multiplier and low power consumption. The latter will undoubtedly attract attention: the Core i7 with a TDP of 35 W - sounds attractive. It is only necessary to keep in mind that the heat pack is calculated for the base frequency, and it is for processors with an index T very different from the maximum.
The younger models of the family, Intel Pentium Gold / Celeron , occupy a budget niche with all the attendant circumstances. In many cases, their performance is enough.
Most of the models shown here will be available in the very near future.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/371419/
All Articles