Russian scientists are developing a pacemaker without batteries

Source: Izvestia
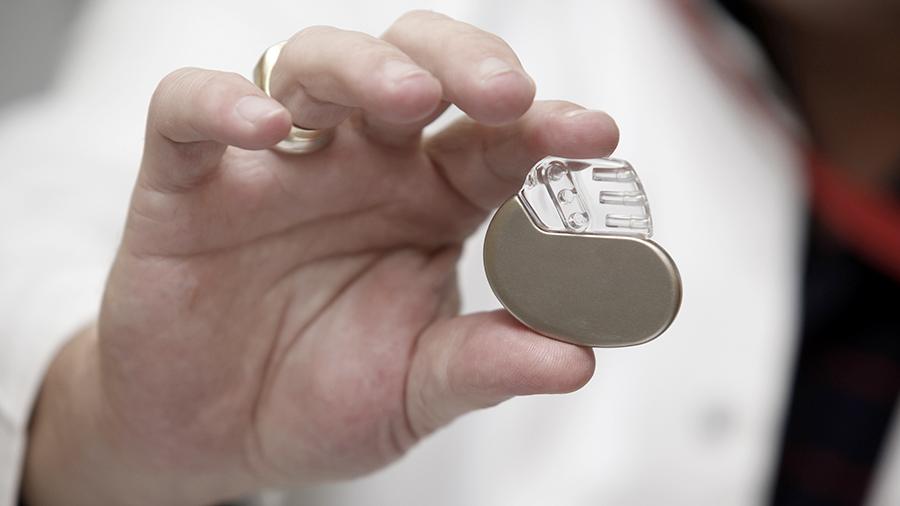
Specialists from the National Research Center "Kurchatov Institute" are developing a method for producing electricity from glucose, which is contained in human blood. This is necessary to create pacemakers that do not need batteries to work. Thus, patients with autonomous devices will not need to be periodically subjected to surgical intervention. The power of the glucose power station is very small - only 15-40 microwatts, but this is quite enough for a modern pacemaker, such devices consume very little energy.
“Electricity is generated through direct chemical conversion. A biofuel cell is introduced into the bloodstream. This is a system with two electrodes, on one of them or on both biocatalysts are located. In this case, the decomposition of organic compounds (in this case, glucose) occurs at the anode, as a result of which free electrons are formed. They move along the circuit to the cathode. And positively charged hydrogen atoms through a special membrane located between the electrodes (it is permeable practically only for them) are sent to the cathode, where they get the lost electrons. Then they react with oxygen to form ordinary water, ” said Pavel Gotovtsev, deputy head of the biotechnology and bioenergy department of the NBICS technology complex at Kurchatov Institute.
The technology is worked out in the laboratory on a model of some parts of the human circulatory system. A device is embedded in such a fragment, and then scientists test its work. The size of a miniature power plant is 5 cm, as mentioned above, the device delivers a power of 15-40 microwatts. According to experts, the person will not feel discomfort from the presence in his body of such a device.
')
They are made from biocompatible materials that do not give up rejection. The calculation of specialists is to ensure that the generator and the pacemaker remain in the human body until the end of life. In the future, if the current system shows itself well, other devices that need a constant power supply will be manufactured based on this technology.
Ahead of the stimulator and generator - tests on animals. Then, if everything goes well, the system will begin to undergo clinical trials, which will take about 10 years. According to other experts familiar with this project, it is very promising. “This is a super-interesting topic. The creation of such technology is the blue dream of all cardiac surgeons. This will avoid unnecessary surgery. However, until now all scientists faced one problem: a rather weak current is obtained. It is necessary either to increase its power, or to reduce the energy consumption of a pacemaker. Research in the whole world is now proceeding in these two directions, ”said the director of the Institute of Personalized Medicine and a professor at the Department of Preventive and Emergency Cardiology at the First Moscow State Medical University. THEM. Sechenov Philip Kopylov.
A number of scientists believe that these types of stimulants can be dangerous, since the level of glucose in a person’s blood changes, and if it is too low, the pacemaker may simply stop working. Therefore, the gadget must be equipped with a battery as a backup power source.
Pacemakers have another aspect - the possibility of hacking. So, many devices that have control using radio frequencies can be cracked. And the control module, which interacts with the stimulator itself, is not protected at all. Many manufacturers simply do not build any kind of friend or foe identification system. In theory , an attacker could use a similar system in order to affect the operation of the receiver located near the heart muscle of the victim.
The lack of protection in pacemakers has been criticized since 2013 , or even earlier. However, the manufacturers of these devices continue to release unprotected systems that can be used by a technically trained attacker at any time.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/371277/
All Articles